Background: Although Mcl-1 is normally subject to rapid turnover via a phosphodegron at Thr-163/Ser-159 and other pathways, sustained expression promotes viability/chemoresistance in cancer cells.
Results: Inhibition or knockdown of PP2A increases phosphorylation at Thr-163 and Ser-159 while decreasing Mcl-1 expression.
Conclusion: Dephosphorylation via PP2A maintains Mcl-1 expression.
Significance: Mcl-1 overexpression in chemoresistant cancer cells can be dramatically reduced by inhibiting its dephosphorylation.
Keywords: B-cell Lymphoma 2 (Bcl-2) Family, Cancer, Cell Death, Extracellular Signal-regulated Kinase (ERK), Protein Phosphatase 2 (PP2A), Mcl-1
Abstract
Abundant, sustained expression of prosurvival Mcl-1 is an important determinant of viability and drug resistance in cancer cells. The Mcl-1 protein contains PEST sequences (enriched in proline, glutamic acid, serine, and threonine) and is normally subject to rapid turnover via multiple different pathways. One of these pathways involves a phosphodegron in the PEST region, where Thr-163 phosphorylation primes for Ser-159 phosphorylation by glycogen synthase kinase-3. Turnover via this phosphodegron-targeted pathway is reduced in Mcl-1-overexpressing BL41-3 Burkitt lymphoma and other cancer cells; turnover is further slowed in the presence of phorbol ester-induced ERK activation, resulting in Mcl-1 stabilization and an exacerbation of chemoresistance. The present studies focused on Mcl-1 dephosphorylation, which was also found to profoundly influence turnover. Exposure of BL41-3 cells to an inhibitor of protein phosphatase 2A (PP2A), okadaic acid, resulted in a rapid increase in phosphorylation at Thr-163 and Ser-159, along with a precipitous decrease in Mcl-1 expression. The decline in Mcl-1 expression preceded the appearance of cell death markers and was not slowed in the presence of phorbol ester. Upon exposure to calyculin A, which also potently inhibits PP2A, versus tautomycin, which does not, only the former increased Thr-163/Ser-159 phosphorylation and decreased Mcl-1 expression. Mcl-1 co-immunoprecipitated with PP2A upon transfection into CHO cells, and PP2A/Aα knockdown recapitulated the increase in Mcl-1 phosphorylation and decrease in expression. In sum, inhibition of PP2A prevents Mcl-1 dephosphorylation and results in rapid loss of this prosurvival protein in chemoresistant cancer cells.
Introduction
Rapid up- and down-regulation of the Bcl-2 family member Mcl-1, via environmental signals, is an important determinant of viability in normal cells (1–3). However, Mcl-1 is expressed abundantly and/or in a sustained fashion in many different types of cancer (e.g. leukemias, lymphomas, and solid tumors) and renders tumor cells resistant to multiple chemotherapeutic agents (1, 2, 4–9). Approaches to inhibit or down-regulate Mcl-1 are therefore being pursued actively (2, 6, 10–16).
The Mcl-1 protein contains PEST instability sequences (17) and is subject to rapid turnover via multiple different pathways (18–21). One of these pathways is targeted by phosphorylation at Ser-159 in the PEST region. Ser-159 phosphorylation is induced by glycogen synthase kinase-3 in the presence of a priming phosphorylation at Thr-163 (22–25), where Thr-163 phosphorylation is induced by MAP kinases such as ERK (23, 26, 27). The glycogen synthase kinase-3/phosphodegron-targeted pathway causes Mcl-1 ubiquitination and degradation in non-transformed cells exposed to growth factor deprivation or radiation, thereby enhancing cell death (22, 23, 28). However, cancer cells frequently exhibit alterations affecting Mcl-1 degradation via the GSK/phosphodegron-targeted and related pathways (2, 29–32). This promotes abundant Mcl-1 expression and stabilization and is associated with chemoresistance and poor patient outcome (29–32).
BL41-3 Burkitt lymphoma cells exhibit characteristics seen in human cancer, in particular, amplification of endogenous Mcl-1 and resistance to multiple chemotherapeutic agents (4, 27, 33, 34). In addition, Mcl-1 degradation in these cells is not mediated via the glycogen synthase kinase-3-targeted pathway (33). Finally, ERK activation, which is also common in cancer, can be mimicked by application of the phorbol ester, 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate (TPA).2 TPA markedly stabilizes Mcl-1 and exacerbates resistance in BL41-3 cells concomitantly exposed to chemotherapeutic agents.
The present work focused on Mcl-1 dephosphorylation, which has not been studied extensively and might also be expected to influence expression. Previous studies had shown that phosphorylation is present only at very low basal levels in BL41-3 cells, and is increased in the presence of the phosphatase inhibitor OA (26, 27). A possible explanation for this was that Mcl-1 was subject to dephosphorylation, which was inhibited by OA. This possibility was examined here, using antibodies that specifically recognized phosphorylated Thr-163 and Ser-159. A rapid increase in phosphorylation at these sites was seen with OA, as well as with calyculin A, another agent that inhibits. Increased phosphorylation was accompanied by a precipitous decline in Mcl-1 expression, followed by cell death. Importantly, these events were maintained in cells concomitantly exposed to TPA plus OA. Mcl-1 was found to interact with PP2A in a transfectable CHO cell system, and shRNA-mediated knockdown of PP2A/Aα recapitulated the increase in Thr-163/Ser-159 phosphorylation and decrease in Mcl-1 expression. In sum, inhibition of PP2A maintains Mcl-1 phosphorylation at Thr-163/Ser-159 and dramatically reduces abundant/stabilized expression of this prosurvival protein in chemoresistant cancer cells.
EXPERIMENTAL PROCEDURES
Cell Lines, Treatments, and Transfection
BL41-3 cells (34) were maintained at 37 °C (5% CO2) in RPMI 1640 medium containing 10% FBS, l-glutamine, and penicillin-streptomycin. CHO 5A-HSmyc cells (35–37) were maintained identically except that α-minimal essential medium was used.
BL41-3 cells were resuspended in fresh medium 1 day before exposure to the phosphatase inhibitors okadaic acid, calyculin A, and tautomycin (EMD Millipore) (38–40). Because effects on a marker of PP2A inhibition (phospho-ERK (41, 42)) were not observed with fostriecin (1 nm to 1 μm, from EMD Millipore or Alexis Biochemicals; see REf. 43), this phosphatase inhibitor was not further pursued. U0126 was from EMD Millipore, and LiCl was from Sigma.
Constructs
The WT Mcl-1 and phosphomutant constructs (in pcDNA3.1) have been described (26, 33) as has the PP2A/Aα shRNA construct (in pcDNA3.1/H1-TO) (44). The control shRNA is identical to the latter except that PP2A/Aα shRNA is replaced by sequence not represented in the human genome (insert: GATCCCCTTCGAAGCTCGCTATCTGCTTCAAGAGAGCAGATAGCGAGCTTCGAATTTTTGGAAA, where the replacement sequence is underlined). The hemagglutinin (HA)-tagged PP2A/C construct (45) and the GST-Mcl-1 and GST constructs (21) have been described. The latter two were expressed in SRP Escherichia coli grown in LB medium at 30 °C as described (46, 47).
Antibodies and Western Analysis
Ser-159 phosphorylation was monitored using a polyclonal antibody (Cell Signaling Technology, catalog no. 4579), which was found to recognize phosphorylation at Ser-159 but not Thr-163; although the antibody was originally directed against both these sites, the signal was essentially completely lost in the presence of a T159A mutation (data not shown). Different lots of the antibody exhibited stronger versus weaker phospho-Ser-159 signal. A previously described phospho-Thr-163-directed antibody was used in initial experiments (33) as indicated in the figure legends. Other figures utilized an antibody being developed by Cell Signaling Technology (no. BL13917 (3131)), which became available when the supply of the initial antibody was exhausted and which found to yield improved detection of pThr-163 Mcl-1. Antibodies recognizing Mcl-1 (S-19) and HA (F-7) were purchased from Santa Cruz Biotechnology. Rabbit antibodies directed against GAPDH, PP2A A subunit, PP2A C subunit, phospho-p44/42 MAPK (ERK1/2) (Thr-202/Tyr-204), β-catenin, and poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP) were from Cell Signaling Technology.
Western blotting was performed as described (33). Blots were imaged using the ChemiDoc Molecular Imaging System (Bio-Rad), and band density was quantitated using ImageJ (NIH). SigmaStat (Systat Software, Inc.) and Prism (GraphPad Software, Inc.) were used for statistical analysis.
Co-immunoprecipitation and GST Pulldown
CHO cells were co-transfected with WT Mcl-1 and HA PP2A/C and, after 24–48 h, cells were washed in ice-cold PBS followed by lysis in CHAPS buffer (20 mm Tris, 150 mm NaCl, 5 mm EDTA, 1% CHAPS, 10 mm NaF, 20 mm Na3PO4, and 5 mm Na2HPO4) to which 1 mm DTT and protease inhibitor mixture (Sigma) were added just before use. After mixing for 15 s and centrifugation at 16,000 × g for 10 min, the supernatant was incubated (4 h at 4 °C with rotation) with an antibody directed against either Mcl-1 or HA, in the presence of protein A/G beads (Sigma). After centrifugation at 2039 × g for 2 min, the beads were either washed twice with ice-cold CHAPS buffer containing DTT and protease inhibitors or passed twice through a 1 m sucrose cushion via centrifugation. Following washes, the beads were suspended in Laemmli buffer and boiled, and Western blotting was carried out.
Mcl-1 GST protein immobilized on glutathione-agarose beads (Sigma) was tested for the ability to pulldown endogenous PP2A from BL41-3 or CHO cell lysates, where an approximately equivalent amount of GST served as a control. For this purpose, cells were washed 1× in PBS and resuspended in 20 mm Tris buffer containing 12.5% glycerol, 0.2% Nonidet P-40, 200 mm NaCl, 1 mm EDTA, and 1 mm EGTA (48), to which 1 mm DTT and protease inhibitor mixture were added as above. After lysis by vortexing 3× (1-min each), followed by centrifugation at 16,000 × g for 10 min, the supernatant was incubated with the beads for 4 h at 4 °C. The beads were then washed three times in ice-cold PBS, followed by resuspension in Laemmli buffer and boiling. Expression of the GST proteins was monitored by Coomassie Blue staining of SDS-PAGE gels, and PP2A was detected by Western blot analysis.
Cell Death Assays
Previously described methods were used to assess PARP cleavage and to examine cell morphology using stained cytospin slide preparations (33). Slides were examined independently by two board-certified pathologists in a blind fashion. The CellTox Green Cytotoxicity assay was performed as suggested by the manufacturer (Promega).
RESULTS
Okadaic Acid Results in a Rapid Increase in Mcl-1 Phosphorylation at Thr-163 and Ser-159, along with a Decrease in Expression in Mcl-1-amplified Lymphoma Cells
In previous studies, an increase 32P-radiolabeling of Mcl-1 had been observed in BL41-3 cells exposed to 1 μm OA (27), a concentration that preferentially inhibits PP2A in other intact cells (49). A range of concentrations was therefore tested with a 6 h-exposure: phosphorylation at Thr-163 and Ser-159 was increased, most prominently at 0.25 μm OA (Fig. 1A, lane 3). Mcl-1 expression was decreased at this and higher concentrations, which was perhaps not unexpected given that these sites lie in a phosphodegron (22–24, 29). Phospho-ERK was monitored in parallel, because ERK is a substrate of PP2A (41, 42). Accordingly, phospho-ERK, while essentially undetectable in untreated cells, was readily detectable in cells treated with OA (Fig. 1A, bottom panel, and see below). In sum, OA increased this marker of PP2A inhibition and also increased phosphorylation at Thr-163/Ser-159 while decreasing expression of Mcl-1. This initial observation set the stage for further exploring the possibility that the PP2A inhibitor OA prevents Mcl-1 dephosphorylation and causes a decline in its expression.
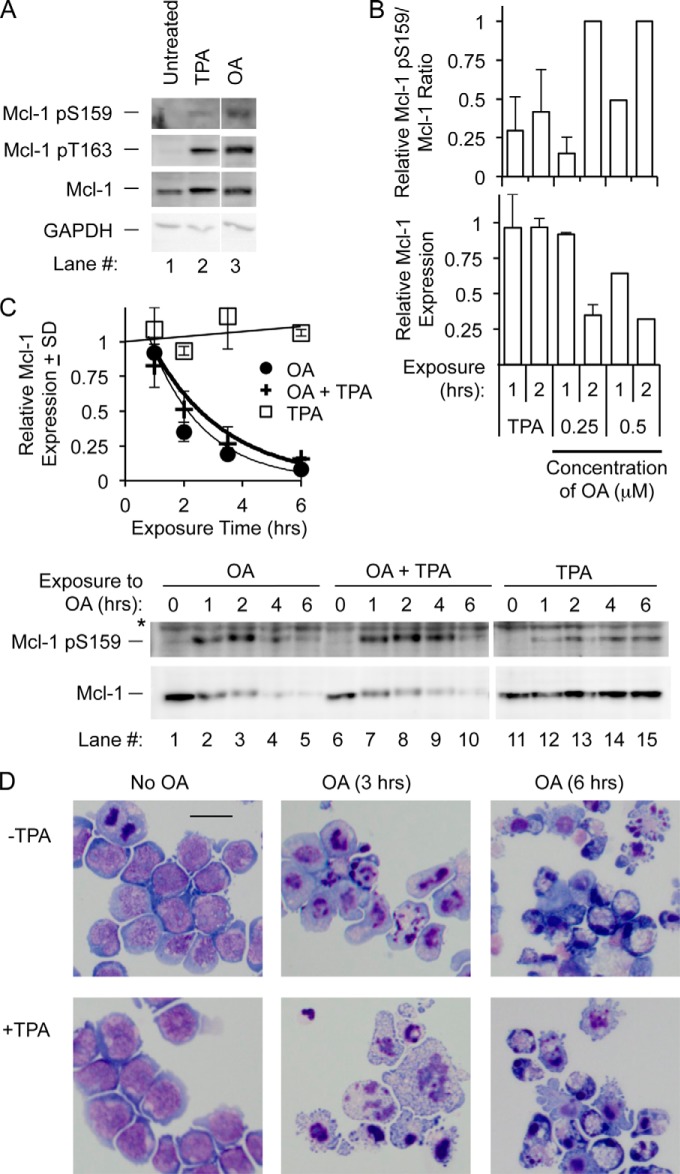
FIGURE 1.
Okadaic acid results in increased Mcl-1 phosphorylation at Thr-163 and Ser-159, along with a rapid decline in expression. A, BL41-3 cells were incubated with the indicated concentrations of OA for 6 h and assayed for Mcl-1 phosphorylation at Ser-159 and Thr-163 using a commercial antibody found to specifically recognize Ser-159-phosphorylated Mcl-1 (Mcl-1 pS159) and a previously described antibody directed against phospho-Thr-163 (33) (Mcl-1 pT163). Cells were also examined for Mcl-1 expression with a non-phosphospecific antibody and for phospho-ERK (pERK). The purpose of this initial experiment was to narrow in on OA concentrations to use in further experiments. With the higher OA concentrations examined here, Mcl-1 expression was extensively reduced (by ≥80% with 1–2 μm OA), and the phosphorylated species were below the level of detection with the phosphospecific antibodies available. B, BL41-3 cells were incubated with OA (0.5 μm) for the indicated times and assayed for Mcl-1 phosphorylation and expression and for pERK as described in A. C, the results of the experiment in B (Time Course Exp. 1), along with an additional independent experiment (Time Course Exp. 2), are shown graphically. Expression of Mcl-1 (lower graph) is shown relative to the initial (time 0) value. Expression of Mcl-1 pS159 (upper graph), which is very faint at time 0, is shown relative to the maximum value (e.g. the 3-h time point in B). After the initial increase in Mcl-1 pSer-159, this species declined with a half-life similar to that of total Mcl-1 (∼1–2.8 h). A similar time course is shown below in conjunction with assay of PARP cleavage. D, BL41-3 cells were incubated with OA (0.25 μm) for the indicated times and assayed for Mcl-1 phosphorylation and expression as in A except that a newly available phospho-Thr-163-specific antibody was used (see “Experimental Procedures”). The experiment shown is representative of three independent experiments. pERK expression, monitored in parallel in one of these, was prominent at 1–3 h. The reason for the irregularity in lane 4 is not known.
Time course studies showed that the effects of OA occurred rapidly, increased phosphorylation being seen within ∼1–3 h (Fig. 1B, lanes 2 and 3). Increased Ser-159 phosphorylation and decreased Mcl-1 expression became apparent together, as shown in the upper and lower graphs in Fig. 1C where different symbols represent independent experiments. After reaching a peak, the Ser-159 phosphorylated species declined in tandem with total Mcl-1 protein (Fig. 1B, lanes 3–5, and Fig. 1C). Thr-163 phosphorylation in initial experiments was apparent 1 h after the application of OA, which was before the peak in Ser-159 phosphorylation (Fig. 1B, lanes 2 and 3). The use of closely spaced time points confirmed that Thr-163 phosphorylation was prominent at 1 h and was transient (Fig. 1D). The timing of these events probably reflects the fact that Thr-163 phosphorylation primes for Ser-159 phosphorylation ((23) and comparable data in Mcl-1-transfected CHO cells, data not shown) and Ser-159 phosphorylation can target Mcl-1 for degradation (22, 24, 29). Overall, these findings were consistent with the premise that Mcl-1 undergoes dephosphorylation in untreated BL41-3 cells (resulting in barely detectable basal phosphorylation at the Thr-163/Ser-159 phosphodegron) and that dephosphorylation is prevented by the PP2A inhibitor OA.
Mcl-1 Phosphorylation Is Increased, and Expression Decreased, in the Presence of Calyculin A but Not Tautomycin
Given the striking effects observed with OA, two additional phosphatase inhibitors were tested: calyculin A (CA), which inhibits PP2A and PP1 non-selectively, and tautomycin, which has lower potency for inhibition of PP2A than for inhibition of PP1 (40, 50). In time course studies, CA had effects remarkably similar to those seen with OA, increasing the phospho-ERK marker and increasing Mcl-1 phosphorylation while decreasing its expression (Fig. 2A). The effects of various concentrations of OA or CA versus tautomycin were therefore examined, initially at a 1-h time point before extensive loss of Mcl-1. Although phosphorylation was potently increased with OA (≥0.25 μm) or CA (≥0.01 μm; Fig. 2B, lanes 1–10), only a minimal increase was seen with tautomycin at the highest concentration tested (1 μm) (Fig. 2B, lanes 11–15). Upon examination at a 3-h time point, Mcl-1 expression was markedly decreased with OA or CA even at the lowest concentrations tested (Fig. 2C, lanes 1–5, and see legend), whereas tautomycin had little effect except at the 1 μm concentration, which also increased phospho-ERK (Fig. 2C, lanes 6–10). The profile of these effects implicated PP2A inhibitors in increasing phosphorylation at Thr-163 and Ser-159 and decreasing expression of Mcl-1.
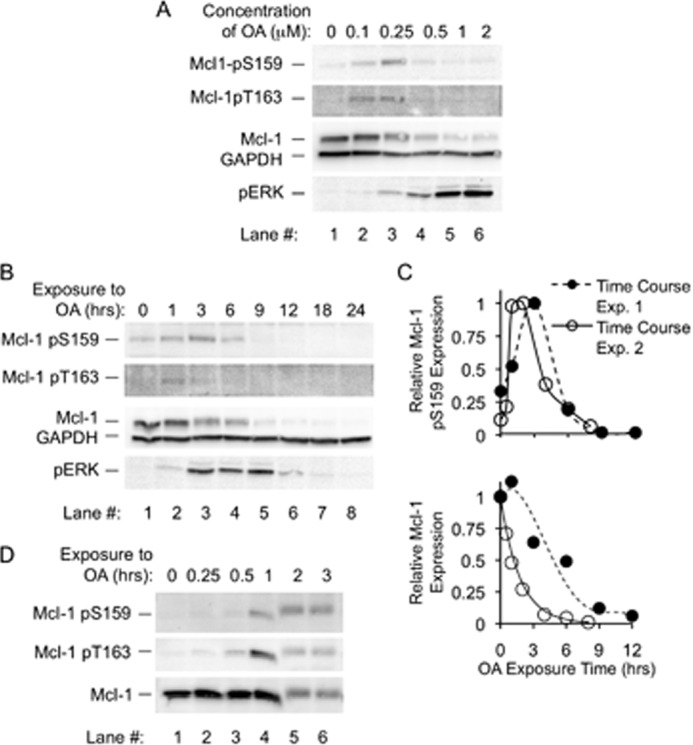
FIGURE 2.
Increased phosphorylation at Thr-163 and Ser-159 and decreased Mcl-1 expression occur in the presence of calyculin A but not tautomycin. A, BL41-3 cells were either left untreated or incubated with 0.25 μm OA (as a control) or 0.1 μm CA for the indicated times and then assayed for Mcl-1 phosphorylation and expression and for pERK. The experiment shown is representative of three independent experiments. Asterisks indicate nonspecific bands present in some blots. B, BL41-3 cells were incubated with the indicated concentrations of OA, CA, or tautomycin (TA) for 1 h and then assayed for Mcl-1 phosphorylation and expression and for pERK. White space between sample lanes on this and subsequent blots indicates that these lanes were non-adjacent on the original blot, where all samples were from the same experiment, and were processed and subjected to side-by-side autoradiography. The blot shown is representative of three independent experiments. C, BL41-3 cells were incubated with the indicated concentrations of OA or tautomycin for 3 h and then assayed as described in B. Expression of Mcl-1 and the phosphorylated species had declined to below detectable levels at this time point with CA (not shown). The blot shown is representative of two independent experiments.
Phosphorylation at Thr-163 and Ser-159 with Okadaic Acid or Calyculin A Is Maintained upon Inhibition of ERK Activation by U0126, whereas Ser-159 Phosphorylation Is Inhibited by LiCl
Interesting differences were noted above in the effects of phosphatase inhibitors on Mcl-1 versus ERK. Increased phosphorylation at Thr-163 and Ser-159 was prominent at OA concentrations that produced submaximal ERK activation (Fig. 1A). In addition, effects on Mcl-1 phosphorylation were underway before the major increase in phospho-ERK (Figs. 1B and 2A). Thus, although the increase in Mcl-1 phosphorylation appeared likely to relate to PP2A inhibition (Fig. 2), it did not seem to relate to the associated ERK activation. This was further examined using U0126, at a concentration found to inhibit ERK activation with OA as expected (33). LiCl was tested in parallel, at a concentration that increases expression of the glycogen synthase kinase-3 target, β-catenin (33).
In cells exposed to OA for 3 h, Ser-159 phosphorylation was not affected by U0126 but was inhibited by LiCl (Fig. 3A, lanes 5 and 6). This suggested the involvement of glycogen synthase kinase-3 but not ERK. In cells exposed to OA for 1 h, the Thr-163 phosphorylation prominent at this time (Fig. 1D) was not blocked in the presence of U0126 to inhibit ERK activation (Fig. 3, B and C). Similar results were seen in the case of CA, where phosphorylation was not prevented by U0126 but Ser-159 phosphorylation was inhibited by LiCl (Fig. 3D).
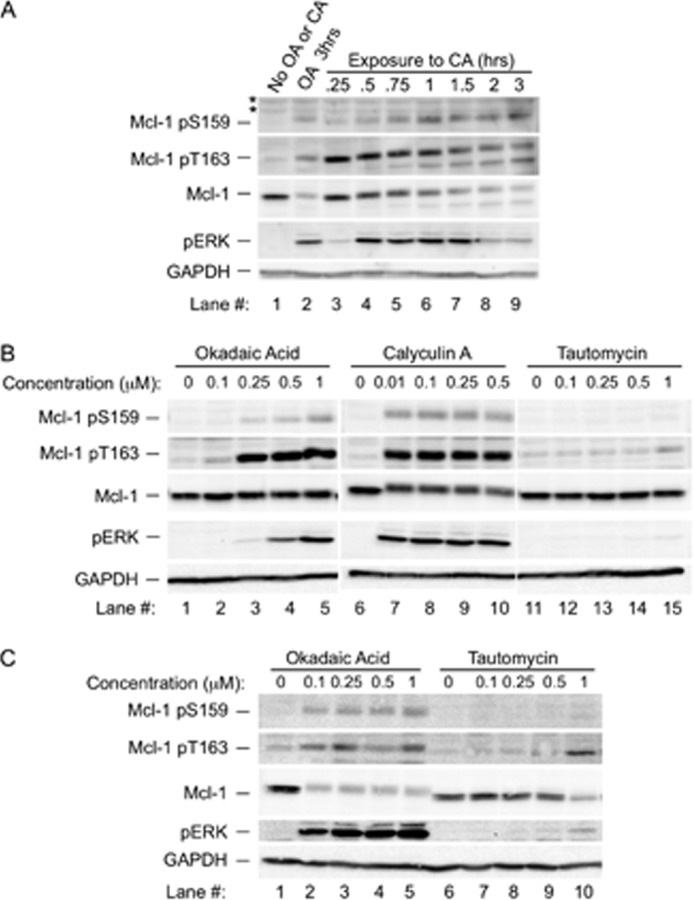
FIGURE 3.
Phosphorylation at Thr-163 and Ser-159 with okadaic acid or calyculin A is maintained in the presence of U0126, but phosphorylation at Ser-159 is inhibited by LiCl. A, BL41-3 cells were preincubated with U0126 (25 μm for 30 min) or LiCl (20 mm for 15 h) and then OA (0.25 μm) was added. After an additional 3 h, Mcl-1 phosphorylation and expression were assayed, where the antibody previously described for phospho-Thr-163 (33) was used. B, BL41-3 cells were preincubated with or without U0126 (25 μm for 30 min) prior to the addition of OA (0.25 μm). After 1 h, Thr-163 phosphorylation was assayed. C, BL41-3 cell preincubated with or without U0126 prior to the addition of OA (0.25 μm for 1 h, see B) were assayed for ERK phosphorylation. D, BL41-3 cells were preincubated with U0126 or LiCl as in A, 0.1 μm CA was added, and Western blotting was carried out after the indicated times. This experiment was carried out in parallel with that shown in Fig. 1D.
The U0126 insensitivity of Mcl-1 phosphorylation in the presence of OA or CA recalled earlier findings showing that the low basal Mcl-1 phosphorylation present in untreated cells is U0126-insensitive (26, 27). Taken together, these results suggest that Mcl-1 undergoes basal ERK-independent phosphorylation countered by dephosphorylation, where inhibition of the latter by OA or CA maintains basal Thr-163 phosphorylation and allows LiCl-inhibitable Ser-159 phosphorylation.
Protein Phosphatase 2A Interacts with Mcl-1
In view of the above results with pharmacological inhibitors affecting PP2A (Figs. 1 and 2), the transfectable CHO cell system was used to test for an interaction between Mcl-1 and this phosphatase. The active PP2A holoenzyme consists of a scaffolding subunit (the A subunit or PP2A/A), as well as a catalytic subunit (PP2A/C) and one of a variety of regulatory subunits (PP2A/B) (38, 51–53). In cells co-transfected with WT-Mcl-1 and HA-PP2A/C, HA-PP2A/C was co-immunoprecipitated upon immunoprecipitation of Mcl-1 (Fig. 4A). Similarly, Mcl-1 was co-immunoprecipitated with HA-PP2A/C (Fig. 4B). Co-immunoprecipitation of the endogenous PP2A/A subunit was detectable in the latter experiment although not the former (Fig. 4B, lowest blot). This is likely because the endogenous PP2A/A subunit is expressed at levels near the limit of detection (Fig. 4B, lane 4) and/or because PP2A generally interacts transiently with substrates. Further assessment using GST pulldown demonstrated a specific interaction between GST-Mcl-1 and endogenous PP2A/A and PP2A/C, as assessed using either BL41-3 or CHO cells (Fig. 4C). In brief, GST pulldown as well as immunoprecipitation demonstrated an association between Mcl-1 and PP2A.
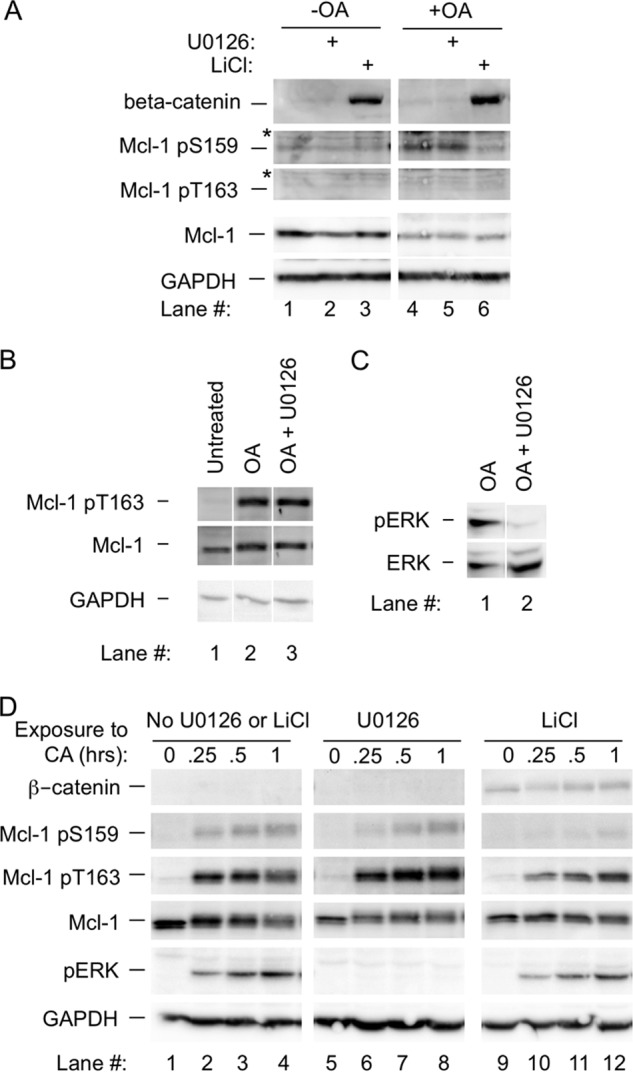
FIGURE 4.
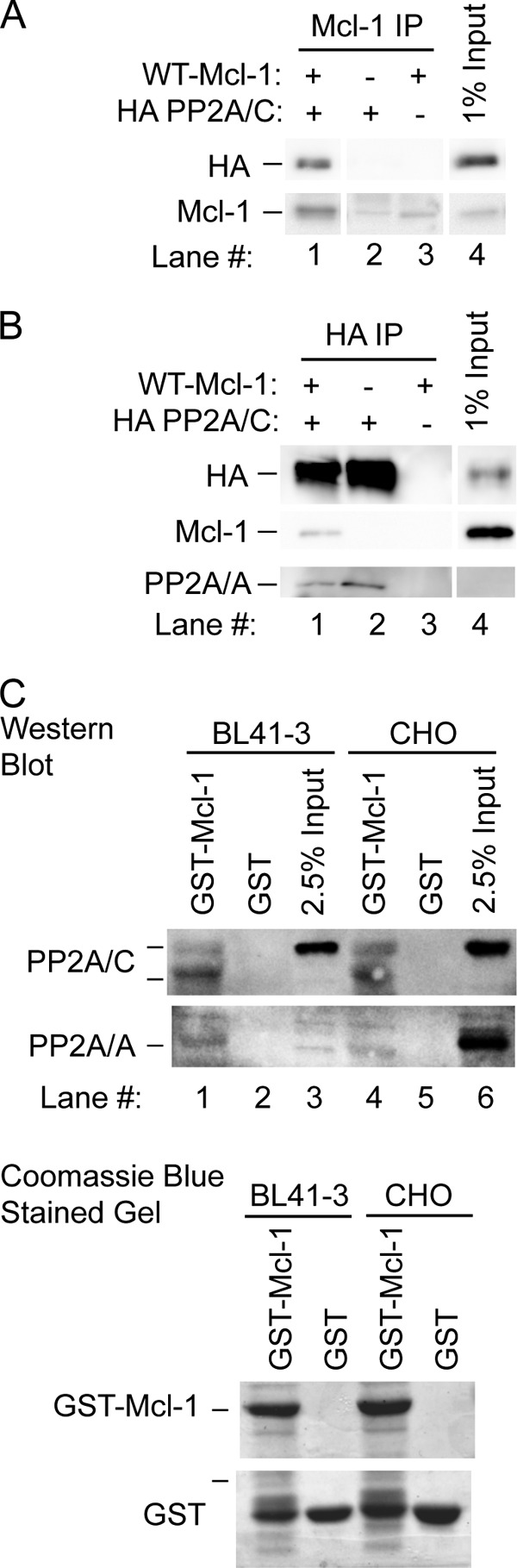
PP2A associates with Mcl-1 in co-immunoprecipitation as well as GST pulldown assays. A, CHO cells were co-transfected with WT Mcl-1 and/or HA PP2A/C (1:3 (w/w)), where empty vector was added with single constructs to equalize the total amount of DNA. After 24 h, immunoprecipitation (IP) was carried out for Mcl-1, followed by Western blotting as indicated. B, CHO cells were co-transfected as above with WT-Mcl-1 and/or HA-PP2A/C (3:1 (w/w)), and immunoprecipitation was carried out with anti-HA. C, GST-Mcl-1 and GST proteins were tested for the ability to pulldown PP2A/C and PP2A/A from BL41-3 and CHO cell lysates. Below the Western blot for these proteins is the Coomassie Blue-stained SDS-PAGE gel showing the GST proteins used for pulldown. The electrophoretic migration of PP2A/C reflects the fact that this protein undergoes disulfide bridge formation in the presence of DTT resulting in a higher molecular weight band (input samples in third and sixth lanes on the upper Western blot), which reverts to the unmodified form when the concentration of DTT is reduced (first and fourth lanes) (68). Multiple bands can also occur with PP2A due to oxidation-mediated modifications as described (68–70).
Knockdown of Protein Phosphatase 2A/Aα Increases Phosphorylation at Thr-163 and Ser-159 while Decreasing Mcl-1 Expression
The interaction observed above provided an additional impetus for carrying out knockdown experiments with an shRNA that effectively targets PP2A/Aα, the major isoform of the scaffolding subunit (Fig. 5A and legend) (44). The A subunit provides a structural base for the assembly of the PP2A holoenzyme (39), and its knockdown inhibits formation of the active complex and reduces the dephosphorylation of substrates (42, 44). Co-transfection with this shRNA and WT-Mcl-1 resulted in an increase in phosphorylation at Thr-163 and Ser-159 and a decrease in Mcl-1 expression (Fig. 5). Phospho-ERK is detectable basally in CHO cells unlike in BL41-3 cells and did not exhibit a significant further increase in the presence of the shRNA. This could relate to the fact that only a proportion of cells undergoes transfection and/or to a difference from BL41-3 cells in PP2A subunit composition (42, 54, 55). Whatever the case, knockdown experiments in transfected CHO cells reinforced observations with pharmacologic inhibitors of PP2A in endogenously expressing BL41-3 cells, demonstrating increased Mcl-1 phosphorylation and decreased expression.
FIGURE 5.
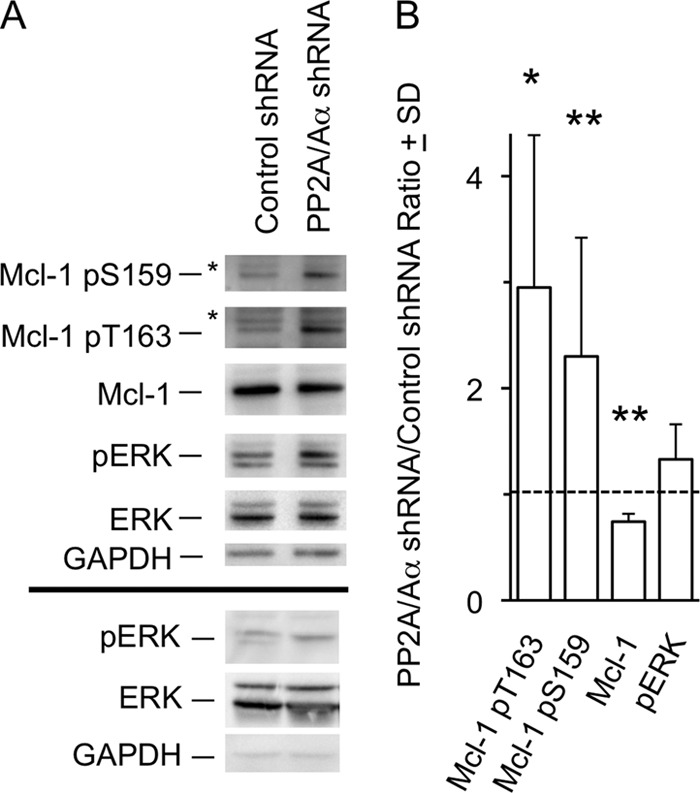
Knockdown of PP2A/Aα increases phosphorylation at Thr-163 and Ser-159 while decreasing Mcl-1 expression. A, CHO cells were co-transfected with WT Mcl-1 (0.25 μg/well) and either an shRNA directed against PP2A/Aα or a control shRNA (0.25 μg/well), where the former was found in preliminary tests to reduce endogenous PP2A/A expression by ∼45% as compared with the latter. Forty-eight hours after transfection, expression of Mcl-1, and the Thr-163-phosphorylated and Ser-159-phosphorylated forms, was assayed along with pERK. pERK expression in a second independent experiment is shown below the line in boldface type. B, a series of experiments such as that shown in A were quantitated (Chemidoc) and used to calculate the ratio of expression of the indicated species in the presence of PP2A/Aα shRNA versus control shRNA. Expression of Mcl-1 pSer-159 and total Mcl-1 was assayed in 6 independent experiments, with Mcl-1 pT163 and pERK being assayed in three experiments. Differences between PP2A/Aα and control shRNA are indicated with large asterisks (*, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01; paired Student's t test).
Increased Mcl-1 Phosphorylation and Decreased Expression with Okadaic Acid Appear before Markers of Cell Death
The decrease in Mcl-1 expression seen in BL41-3 cells exposed to OA could be an early event in cell death, as is often the case with Mcl-1 (56, 57) and was noted to occur before the loss of phospho-ERK (Fig. 1C). Indeed, changes in Mcl-1 phosphorylation and expression were found to precede the appearance of a variety of markers of cell death. Although increased phosphorylation and decreased Mcl-1 expression were seen 1 h after the application of OA, PARP cleavage did not come into evidence until ∼4 h (Fig. 6A). Similarly, morphological examination did not reveal a noticeable change at 1 h, the majority of cells appearing viable in the absence or presence of OA (Fig. 6B, upper panels). However, at 3 h, when Mcl-1 expression had declined extensively, cells exhibited premature chromatin condensation and cell death as is typical with phosphatase inhibitors (Fig. 6B, lower panels) (58). Loss of membrane integrity became apparent at ∼12 h (Fig. 6C). In sum, the effects of OA on Mcl-1 phosphorylation and expression were apparent within 1 h, whereas PARP cleavage and morphological death were not seen until ∼3–4 h, and membrane integrity was lost thereafter. In agreement with findings above suggesting that the effects of OA on Mcl-1 result from phosphatase inhibition, these effects preceded the appearance of markers of cell death rather than occurring as a result of this process.
FIGURE 6.
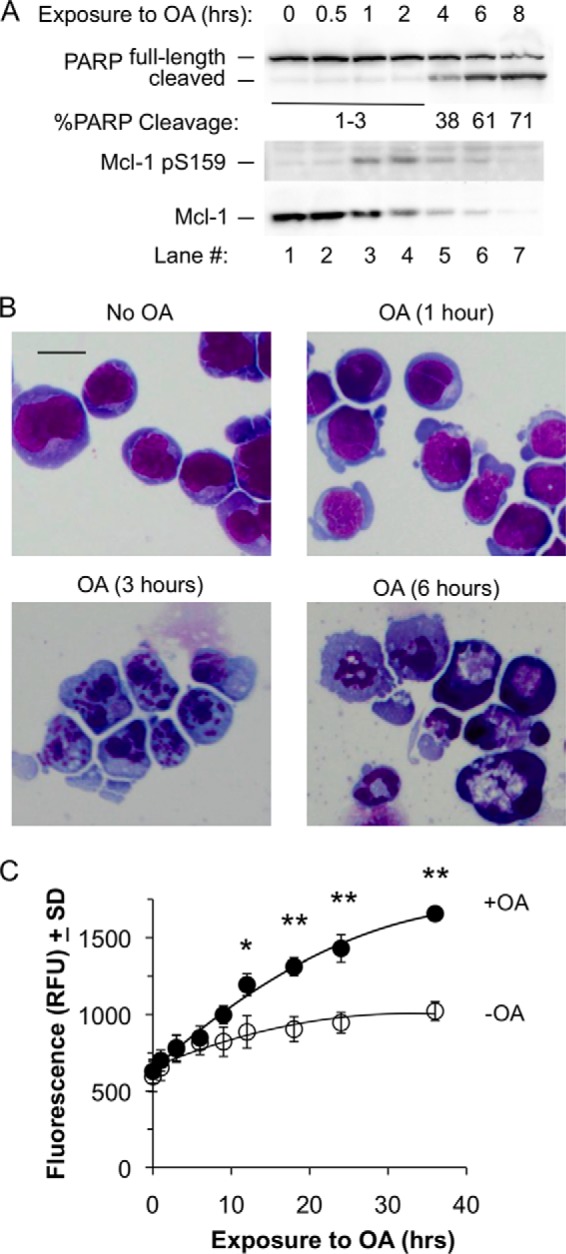
Increased Ser-159 phosphorylation and decreased Mcl-1 expression in the presence of okadaic acid precede the appearance of cell death. A, BL41-3 cells were incubated with 0.25 μm OA for the indicated times and were assayed for PARP cleavage, as well as for Ser-159 phosphorylation and Mcl-1 expression. The % PARP cleavage shown under the blot represents the mean of two experiments, where the coefficient of variation averaged 32%. Exposure to OA for 12 or 24 h resulted in little if any further increase in PARP cleavage, and PARP cleavage with 0.5 μm OA was similar to that seen with the 0.25 μm concentration (not shown). B, BL41-3 cells were incubated in the absence or presence of 0.25 μm OA for the indicated times and were examined morphologically. Cells exposed to OA for 1 h (upper right panel) could not be distinguished from untreated or vehicle-treated controls, where the vehicle (dimethyl sulfoxide) did not noticeably affect cell morphology. At later times, death was evident in the majority of the OA-treated cell population (>90%; lower panels). Photographs were taken at the same magnification (400×), where the scale bar on the top left panel represents 20 microns. C, BL41-3 cells incubated in the absence or presence of 0.25 μm OA were monitored for CellTox Green fluorescence as a measure of loss of membrane integrity. Two independent experiments were carried out, with four replicate wells being assayed in each experiment. The mean relative fluorescence (relative fluorescence units; RFU) of the four replicates for one of these experiments is shown. Large asterisks indicate time points exhibiting a difference between untreated and OA-treated cells in both experiments (*, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01; ANOVA, Holm-Sidak post hoc testing). Average fluorescence was slightly higher (∼10–20%) upon exposure to 0.5 μm as compared with 0.25 μm OA, where cells treated with 0.5 μm OA differed from untreated controls but did not differ significantly from cells exposed to 0.25 μm OA.
Okadaic Acid Results in a Rapid Decline in Mcl-1 Expression in the Presence as well as the Absence of TPA
The effects seen with OA provided an interesting counterpoint to previous observations with TPA, which does not cause a decline in Mcl-1 expression (26, 27, 33). In fact, TPA markedly slows the decline in Mcl-1 expression that occurs in the presence of chemotherapeutic agents (33). BL41-3 cells were therefore exposed to OA and TPA separately and together. Thr-163 phosphorylation at 1 h was similar with the two agents (Fig. 7A), the difference being that this increase was transient with OA (Fig. 1D) but is sustained with TPA (for > 6 h) (33). In addition, the Mcl-1 pS159/Mcl-1 ratio was increased to a greater extent with OA than with TPA (Fig. 7B), consistent with inhibition of Mcl-1 dephosphorylation by OA in conjunction with declining expression. Importantly, rapid Mcl-1 decay and ensuing death were maintained when OA was applied together with TPA (Fig. 7, B–D). This differed from the inhibition of Mcl-1 decay and reduced cell death seen when chemotherapeutic agents are applied with TPA (33).
FIGURE 7.
Robust Ser-159 phosphorylation, decreased Mcl-1 expression, and ensuing cell death occur with okadaic acid in the presence or absence of TPA. A, BL41-3 cells were incubated with OA (0.25 μm, same samples as in Fig. 3B) or TPA (5 nm) and assayed for Mcl-1 phosphorylation after 1 h. In the experiment shown and two additional experiments, the transient increase in the Thr-163 phosphorylated species seen at 1 h with OA was comparable to the increase with TPA. B, BL41-3 cells were incubated with OA or TPA for the indicated times and examined for expression of Ser-159-phosphorylated and total Mcl-1. The Mcl-1 pSer-159/total Mcl-1 ratio (upper graph) is shown relative to this value at 2 h. Mcl-1 expression (lower graph) is shown relative to the value at time 0. The values shown are from two experiments with 0.25 μm OA (mean ± S.D.; experiments independent from that in A) and one experiment with 0.5 μm OA. In these three experiments, the Mcl-1 pSer-159/total Mcl-1 ratio at 2 h was, on average, 3-fold higher with OA than with TPA (95% confidence interval, 1.4 to 4.7-fold), and Mcl-1 expression was decreased to about one-third of the time 0 value with OA (95% confidence interval, 0.28 to 0.38-fold the time 0 value) but was not decreased with TPA. C, the decline in Mcl-1 expression was monitored in BL41-3 cells incubated with OA and/or TPA. The graph represents two experiments with 0.25 μm OA (+ S.D., full decay curve for the experiments in B) and the blot below it is the experiment with 0.5 μm OA. The half-life of decline of Mcl-1 was estimated to be 1.3 h with 0.25 μm OA and 1.7 h with 0.25 μm OA plus TPA. These values were 1.4 h with 0.5 μm OA and 1.7 h with 0.5 μm OA plus TPA. D, BL41-3 cells were incubated with OA (0.25 μm) and/or TPA (5 nm) for 3 or 6 h as indicated. The scale bar represents 20 microns.
DISCUSSION
Mcl-1 is exquisitely controlled via up-regulation/stabilization and down-regulation/turnover, where expression level determines its effects on cell viability (1, 2, 8, 59). Turnover of the protein can occur rapidly and is regulated by phosphorylation as well as other post-translational modifications (2, 19, 26, 33, 60). As shown by the present studies, Mcl-1 dephosphorylation also plays a key role. Thus, pharmacologic inhibitors of PP2A such as OA resulted in increased phosphorylation at Thr-163/Ser-159 along with decreased Mcl-1 expression, and similar effects were seen in knockdown experiments. Increased Ser-159 phosphorylation in BL41-3 cells occurred in tandem with decreased expression, and these events preceded the appearance of a variety of cell death markers. The effects of OA were maintained upon concomitant application of TPA, providing a contrast to the slowed Mcl-1 decay and exacerbation of resistance seen when different types of chemotherapeutic agents are applied with TPA (33). In sum, inhibition of Mcl-1 dephosphorylation by inhibition of PP2A was capable of overriding abundant expression and stabilization of this prosurvival protein in chemoresistant cancer cells.
Although TPA activates ERK, which phosphorylates Thr-163 (26, 27), OA appeared to maintain the basal ERK-independent Thr-163 phosphorylation that occurs in BL41-3 cells. ERK activation with TPA is sustained and Thr-163 phosphorylation is as well, likely because ongoing phosphorylation can counter dephosphorylation. By instead inhibiting effects of the phosphatase PP2A on Mcl-1, OA is speculated to allow coupling to subsequent steps in the degradation process to occur before dephosphorylation. Because dephosphorylation is downstream of the stimulation of phosphorylation by TPA, the effect of OA is maintained upon combined application with TPA.
Many questions remain to be addressed regarding Mcl-1 dephosphorylation. The rapidity of the effects seen with OA or CA, the interaction of Mcl-1 with the core subunits of PP2A, and the fact that effects were seen upon PP2A knockdown as well as pharmacologic inhibition, are compatible with direct dephosphorylation of Mcl-1 by PP2A. At the same time, given the complexity of the interactions between PP2A and a variety of signaling pathways, other actions of PP2A could have a role (41, 42, 55, 61–63). Another point is that, because of the hierarchical relationship between phosphorylation at Thr-163 and Ser-159, effects at these two sites could not be separated completely. The effect of phosphatase inhibitors on Thr-163 phosphorylation could be seen in isolation from Ser-159 phosphorylation (i.e. in the presence of LiCl). Conversely, however, loss of Thr-163 phosphorylation itself prevents Ser-159 phosphorylation (i.e. an T163A as well as an S159A mutation result in loss of Ser-159 phosphorylation (23) and data not shown). Therefore, the effect of phosphatase inhibition on Ser-159 phosphorylation could not be examined in the absence of Thr-163 phosphorylation. A third point is that Mcl-1 is subject to phosphorylation at multiple additional sites (19, 60), which are likely also affected by phosphatases.
Another area for future investigation relates to the death that follows the decline in Mcl-1 in OA-treated BL41-3 cells. Additional actions of OA that contribute to this outcome are of interest as potential targets. It is also noted that some tumors exhibit alterations in various PP2A subunits (64–67), and it will be important to determine how this affects sensitivity to phosphatase inhibition. Overall, future studies of Mcl-1 dephosphorylation via PP2A may lead to approaches for reducing elevated/stabilized Mcl-1 expression in cancer cells, identifying PP2A profiles that render cells sensitive to this effect and promoting death even in the presence of extensive resistance to chemotherapeutic agents.
Acknowledgments
We thank Sierra Kent and Renee Risingsong for help in these studies.
This work was supported by National Institutes of Health Grant R01CA057359 (to R. W. C.).
- TPA
- 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate
- PP2A
- protein phosphatase 2A
- OA
- okadaic acid
- PARP
- poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase
- CA
- calyculin A.
REFERENCES
- 1. Craig R. W. (2002) MCL1 provides a window on the role of the BCL2 family in cell proliferation, differentiation and tumorigenesis. Leukemia 16, 444–454 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2. Ertel F., Nguyen M., Roulston A., Shore G. C. (2013) Programming cancer cells for high expression levels of Mcl1. EMBO Rep. 14, 328–336 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3. Marriott H. M., Bingle C. D., Read R. C., Braley K. E., Kroemer G., Hellewell P. G., Craig R. W., Whyte M. K., Dockrell D. H. (2005) Dynamic changes in Mcl-1 expression regulate macrophage viability or commitment to apoptosis during bacterial clearance. J. Clin. Invest. 115, 359–368 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4. Beroukhim R., Mermel C. H., Porter D., Wei G., Raychaudhuri S., Donovan J., Barretina J., Boehm J. S., Dobson J., Urashima M., Mc Henry K. T., Pinchback R. M., Ligon A. H., Cho Y. J., Haery L., Greulich H., Reich M., Winckler W., Lawrence M. S., Weir B. A., Tanaka K. E., Chiang D. Y., Bass A. J., Loo A., Hoffman C., Prensner J., Liefeld T., Gao Q., Yecies D., Signoretti S., Maher E., Kaye F. J., Sasaki H., Tepper J. E., Fletcher J. A., Tabernero J., Baselga J., Tsao M. S., Demichelis F., Rubin M. A., Janne P. A., Daly M. J., Nucera C., Levine R. L., Ebert B. L., Gabriel S., Rustgi A. K., Antonescu C. R., Ladanyi M., Letai A., Garraway L. A., Loda M., Beer D. G., True L. D., Okamoto A., Pomeroy S. L., Singer S., Golub T. R., Lander E. S., Getz G., Sellers W. R., Meyerson M. (2010) The landscape of somatic copy-number alteration across human cancers. Nature 463, 899–905 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5. Wei G., Margolin A. A., Haery L., Brown E., Cucolo L., Julian B., Shehata S., Kung A. L., Beroukhim R., Golub T. R. (2012) Chemical genomics identifies small-molecule MCL1 repressors and BCL-xL as a predictor of MCL1 dependency. Cancer Cell 21, 547–562 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6. Quinn B. A., Dash R., Azab B., Sarkar S., Das S. K., Kumar S., Oyesanya R. A., Dasgupta S., Dent P., Grant S., Rahmani M., Curiel D. T., Dmitriev I., Hedvat M., Wei J., Wu B., Stebbins J. L., Reed J. C., Pellecchia M., Sarkar D., Fisher P. B. (2011) Targeting Mcl-1 for the therapy of cancer. Expert. Opin. Investig. Drugs 20, 1397–1411 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7. Meric-Bernstam F., Frampton G. M., Ferrer-Lozano J., Yelensky R., Pérez-Fidalgo J. A., Wang Y., Palmer G. A., Ross J. S., Miller V. A., Su X., Eroles P., Barrera J. A., Burgues O., Lluch A. M., Zheng X., Sahin A., Stephens P. J., Mills G. B., Cronin M. T., Gonzalez-Angulo A. M. (2014) Concordance of genomic alterations between primary and recurrent breast cancer. Mol. Cancer Ther. 13, 1382–1389 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8. Okamoto T., Coultas L., Metcalf D., van Delft M. F., Glaser S. P., Takiguchi M., Strasser A., Bouillet P., Adams J. M., Huang D. C. (2014) Enhanced stability of Mcl1, a prosurvival Bcl2 relative, blunts stress-induced apoptosis, causes male sterility, and promotes tumorigenesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 111, 261–266 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9. Sio T. T., Mansfield A. S., Grotz T. E., Graham R. P., Molina J. R., Que F. G., Miller R. C. (2014) Concurrent MCL1 and JUN amplification in pseudomyxoma peritonei: a comprehensive genetic profiling and survival analysis. J. Hum. Genet. 59, 124–128 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10. Cohen N. A., Stewart M. L., Gavathiotis E., Tepper J. L., Bruekner S. R., Koss B., Opferman J. T., Walensky L. D. (2012) A competitive stapled peptide screen identifies a selective small molecule that overcomes MCL-1-dependent leukemia cell survival. Chem. Biol. 19, 1175–1186 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11. Thomas S., Quinn B. A., Das S. K., Dash R., Emdad L., Dasgupta S., Wang X. Y., Dent P., Reed J. C., Pellecchia M., Sarkar D., Fisher P. B. (2013) Targeting the Bcl-2 family for cancer therapy. Expert. Opin. Ther. Targets 17, 61–75 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12. Doi K., Li R., Sung S. S., Wu H., Liu Y., Manieri W., Krishnegowda G., Awwad A., Dewey A., Liu X., Amin S., Cheng C., Qin Y., Schonbrunn E., Daughdrill G., Loughran T. P., Jr., Sebti S., Wang H. G. (2012) Discovery of marinopyrrole A (maritoclax) as a selective Mcl-1 antagonist that overcomes ABT-737 resistance by binding to and targeting Mcl-1 for proteasomal degradation. J. Biol. Chem. 287, 10224–10235 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13. Kelly G. L., Grabow S., Glaser S. P., Fitzsimmons L., Aubrey B. J., Okamoto T., Valente L. J., Robati M., Tai L., Fairlie W. D., Lee E. F., Lindstrom M. S., Wiman K. G., Huang D. C., Bouillet P., Rowe M., Rickinson A. B., Herold M. J., Strasser A. (2014) Targeting of MCL-1 kills MYC-driven mouse and human lymphomas even when they bear mutations in p53. Genes Dev. 28, 58–70 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14. Moldoveanu T., Follis A. V., Kriwacki R. W., Green D. R. (2014) Many players in BCL-2 family affairs. Trends Biochem. Sci. 39, 101–111 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15. Cao X., Yap J. L., Newell-Rogers M. K., Peddaboina C., Jiang W., Papaconstantinou H. T., Jupitor D., Rai A., Jung K. Y., Tubin R. P., Yu W., Vanommeslaeghe K., Wilder P. T., MacKerell A. D., Jr., Fletcher S., Smythe R. W. (2013) The novel BH3 α-helix mimetic JY-1–106 induces apoptosis in a subset of cancer cells (lung cancer, colon cancer and mesothelioma) by disrupting Bcl-xL and Mcl-1 protein-protein interactions with Bak. Mol. Cancer 12, 42. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16. Peddaboina C., Jupiter D., Fletcher S., Yap J. L., Rai A., Tobin R. P., Jiang W., Rascoe P., Rogers M. K., Smythe W. R., Cao X. (2012) The downregulation of Mcl-1 via USP9X inhibition sensitizes solid tumors to Bcl-xl inhibition. BMC Cancer 12, 541. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17. Kozopas K. M., Yang T., Buchan H. L., Zhou P., Craig R. W. (1993) MCL1, a gene expressed in programmed myeloid cell differentiation, has sequence similarity to BCL-2. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 90, 3516–3520 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18. Zhong Q., Gao W., Du F., Wang X. (2005) Mule/ARF-BP1, a BH3-only E3 ubiquitin ligase catalyzes the polyubiquitination of Mcl-1 and regulates apoptosis. Cell 121, 1085–1095 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19. Harley M. E., Allan L. A., Sanderson H. S., Clarke P. R. (2010) Phosphorylation of Mcl-1 by CDK1-cyclin B1 initiates its Cdc20-dependent destruction during mitotic arrest. EMBO J. 29, 2407–2420 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20. Stewart D. P., Koss B., Bathina M., Perciavalle R. M., Bisanz K., Opferman J. T. (2010) Ubiquitin independent degradation of anti-apoptotic MCL-1. Mol. Cell Biol. 30, 3099–3110 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21. Yang T., Kozopas K. M., Craig R. W. (1995) The intracellular distribution and pattern of expression of Mcl-1 overlap with, but are not identical to, those of Bcl-2. J. Cell Biol. 128, 1173–1184 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22. Maurer U., Charvet C., Wagman A. S., Dejardin E., Green D. R. (2006) Glycogen synthase kinase-3 regulates mitochondrial outer membrane permeabilization and apoptosis by destabilization of MCL-1. Mol. Cell 21, 749–760 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23. Morel C., Carlson S. M., White F. M., Davis R. J. (2009) Mcl-1 integrates the opposing actions of signaling pathways that mediate survival and apoptosis. Mol. Cell Biol. 29, 3845–3852 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24. Ding Q., He X., Hsu J. M., Xia W., Chen C. T., Li L. Y., Lee D. F., Liu J. C., Zhong Q., Wang X., Hung M. C. (2007) Degradation of Mcl-1 by β-TrCP mediates glycogen synthase kinase 3-induced tumor suppression and chemosensitization. Mol. Cell Biol. 27, 4006–4017 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25. Ren H., Zhao L., Li Y., Yue P., Deng X., Owonikoko T. K., Chen M., Khuri F. R., Sun S. Y. (2013) The PI3 kinase inhibitor NVP-BKM120 induces GSK3/FBXW7-dependent Mcl-1 degradation, contributing to induction of apoptosis and enhancement of TRAIL-induced apoptosis. Cancer Lett. 338, 229–238 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26. Domina AM, Vrana JA, Gregory MA, Hann SR, Craig RW. (2004) MCL1 is phosphorylated in the PEST region and stabilized upon ERK activation in viable cells, and at additional sites with cytotoxic okadaic acid or taxol. Oncogene 23, 5301–5315 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27. Domina AM, Smith JH, Craig RW. (2000) Myeloid cell leukemia 1 is phosphorylated through two distinct pathways, one involving ERK activation and the other G2/M accumulation or protein phosphatase 1/2A inhibition. J. Biol. Chem. 275, 21688–21694 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28. Magiera M. M., Mora S., Mojsa B., Robbins I., Lassot I., Desagher S. (2013) Trim17-mediated ubiquitination and degradation of Mcl-1 initiate apoptosis in neurons. Cell Death Differ. 20, 281–292 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29. Ding Q., He X., Xia W., Hsu J. M., Chen C. T., Li L. Y., Lee D. F., Yang J. Y., Xie X., Liu J. C., Hung M. C. (2007) Myeloid cell leukemia-1 inversely correlates with glycogen synthase kinase-3β activity and associates with poor prognosis in human breast cancer. Cancer Res. 67, 4564–4571 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30. Inuzuka H., Shaik S., Onoyama I., Gao D., Tseng A., Maser R. S., Zhai B., Wan L., Gutierrez A., Lau A. W., Xiao Y., Christie A. L., Aster J., Settleman J., Gygi S. P., Kung A. L., Look T., Nakayama K. I., DePinho R. A., Wei W. (2011) SCF(FBW7) regulates cellular apoptosis by targeting MCL1 for ubiquitylation and destruction. Nature 471, 104–109 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31. Wertz I. E., Kusam S., Lam C., Okamoto T., Sandoval W., Anderson D. J., Helgason E., Ernst J. A., Eby M., Liu J., Belmont L. D., Kaminker J. S., O'Rourke K. M., Pujara K., Kohli P. B., Johnson A. R., Chiu M. L., Lill J. R., Jackson P. K., Fairbrother W. J., Seshagiri S., Ludlam M. J., Leong K. G., Dueber E. C., Maecker H., Huang D. C., Dixit V. M. (2011) Sensitivity to antitubulin chemotherapeutics is regulated by MCL1 and FBW7. Nature 471, 110–114 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32. Schwickart M., Huang X., Lill J. R., Liu J., Ferrando R., French D. M., Maecker H., O'Rourke K., Bazan F., Eastham-Anderson J., Yue P., Dornan D., Huang D. C., Dixit V. M. (2010) Deubiquitinase USP9X stabilizes MCL1 and promotes tumour cell survival. Nature 463, 103–107 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33. Nifoussi S. K., Vrana J. A., Domina A. M., De Biasio A., Gui J., Gregory M. A., Hann S. R., Craig R. W. (2012) Thr 163 phosphorylation causes Mcl-1 stabilization when degradation is independent of the adjacent GSK3-targeted phosphodegron, promoting drug resistance in cancer. PLoS One 7, e47060. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34. Vrana J. A., Bieszczad C. K., Cleaveland E. S., Ma Y., Park J. P., Mohandas T. K., Craig R. W. (2002) An MCL1-overexpressing Burkitt lymphoma subline exhibits enhanced survival upon exposure to serum-deprivation, topoisomerase inhibitors, or staurosporine, but remains sensitive to prolonged exposure to Ara-C. Cancer Res. 62, 892–900 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35. Reynolds J. E., Li J., Craig R. W., Eastman A. (1996) BCL-2 and MCL-1 expression in Chinese hamster ovary cells inhibits intracellular acidification and apoptosis induced by staurosporine. Exp. Cell Res. 225, 430–436 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36. Wurm F. M., Gwinn K. A., Kingston R. E. (1986) Inducible overproduction of the mouse c-myc protein in mammalian cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 83, 5414–5418 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37. Bissonnette R. P., Echeverri F., Mahboubi A., Green D. R. (1992) Apoptotic cell death induced by c-myc is inhibited by bcl-2. Nature 359, 552–554 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38. Janssens V., Goris J. (2001) Protein phosphatase 2A: a highly regulated family of serine/threonine phosphatases implicated in cell growth and signalling. Biochem. J. 353, 417–439 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39. Lechward K., Awotunde O. S., Swiatek W., Muszyńska G. (2001) Protein phosphatase 2A: variety of forms and diversity of functions. Acta Biochim. Pol. 48, 921–933 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40. Swingle M., Ni L., Honkanen R. E. (2007) Small-molecule inhibitors of ser/thr protein phosphatases: specificity, use and common forms of abuse. Methods Mol. Biol. 365, 23–38 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41. Letourneux C., Rocher G., Porteu F. (2006) B56-containing PP2A dephosphorylate ERK and their activity is controlled by the early gene IEX-1 and ERK. EMBO J. 25, 727–738 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42. Van Kanegan M. J., Adams D. G., Wadzinski B. E., Strack S. (2005) Distinct protein phosphatase 2A heterotrimers modulate growth factor signaling to extracellular signal-regulated kinases and Akt. J. Biol. Chem. 280, 36029–36036 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43. Lewy D. S., Gauss C. M., Soenen D. R., Boger D. L. (2002) Fostriecin: chemistry and biology. Curr. Med. Chem. 9, 2005–2032 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44. Strack S., Cribbs J. T., Gomez L. (2004) Critical role for protein phosphatase 2A heterotrimers in mammalian cell survival. J. Biol. Chem. 279, 47732–47739 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45. Bryant J. C., Westphal R. S., Wadzinski B. E. (1999) Methylated C-terminal leucine residue of PP2A catalytic subunit is important for binding of regulatory Bα subunit. Biochem. J. 339, 241–246 [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46. Frangioni J. V., Neel B. G. (1993) Solubilization and purification of enzymatically active glutathione S-transferase (pGEX) fusion proteins. Anal. Biochem. 210, 179–187 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47. Einarson M. B., Pugacheva E. N., Orlinick J. R. (2007) Preparation of GST fusion proteins. Cold Spring Harb. Protoc. 10.1101/pdb.prot4738 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48. Arnold H. K., Sears R. C. (2008) A tumor suppressor role for PP2A-B56α through negative regulation of c-Myc and other key oncoproteins. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 27, 147–158 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49. Favre B., Turowski P., Hemmings B. A. (1997) Differential inhibition and posttranslational modification of protein phosphatase 1 and 2A in MCF7 cells treated with calyculin-A, okadaic acid, and tautomycin. J. Biol. Chem. 272, 13856–13863 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50. Chatfield K., Eastman A. (2004) Inhibitors of protein phosphatases 1 and 2A differentially prevent intrinsic and extrinsic apoptosis pathways. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 323, 1313–1320 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51. Janssens V., Longin S., Goris J. (2008) PP2A holoenzyme assembly: in cauda venenum (the sting is in the tail). Trends Biochem. Sci. 33, 113–121 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52. McCright B., Rivers A. M., Audlin S., Virshup D. M. (1996) The B56 family of protein phosphatase 2A (PP2A) regulatory subunits encodes differentiation-induced phosphoproteins that target PP2A to both nucleus and cytoplasm. J. Biol. Chem. 271, 22081–22089 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53. Bononi A., Agnoletto C., De Marchi E., Marchi S., Patergnani S., Bonora M., Giorgi C., Missiroli S., Poletti F., Rimessi A., Pinton P. (2011) Protein kinases and phosphatases in the control of cell fate. Enzyme Res. 2011, 329098. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54. Junttila M. R., Li S. P., Westermarck J. (2008) Phosphatase-mediated crosstalk between MAPK signaling pathways in the regulation of cell survival. FASEB J. 22, 954–965 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55. Adams D. G., Coffee R. L., Jr., Zhang H., Pelech S., Strack S., Wadzinski B. E. (2005) Positive regulation of Raf1-MEK1/2-ERK1/2 signaling by protein serine/threonine phosphatase 2A holoenzymes. J. Biol. Chem. 280, 42644–42654 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56. Nijhawan D., Fang M., Traer E., Zhong Q., Gao W., Du F., Wang X. (2003) Elimination of Mcl-1 is required for the initiation of apoptosis following ultraviolet irradiation. Genes Dev. 17, 1475–1486 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57. Germain M., Nguyen A. P., Le Grand J. N., Arbour N., Vanderluit J. L., Park D. S., Opferman J. T., Slack R. S. (2011) MCL-1 is a stress sensor that regulates autophagy in a developmentally regulated manner. EMBO J. 30, 395–407 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58. Huang X., Kurose A., Tanaka T., Traganos F., Dai W., Darzynkiewicz Z. (2006) Sequential phosphorylation of Ser-10 on histone H3 and Ser-139 on histone H2AX and ATM activation during premature chromosome condensation: relationship to cell-cycle phase and apoptosis. Cytometry A 69, 222–229 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59. Rooswinkel R. W., van de Kooij B., de Vries E., Paauwe M., Braster R., Verheij M., Borst J. (2014) Anti-apoptotic potency of Bcl-2 proteins primarily relies on their stability, not binding selectivity. Blood 123, 2806–2815 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60. Kobayashi S., Lee S. H., Meng X. W., Mott J. L., Bronk S. F., Werneburg N. W., Craig R. W., Kaufmann S. H., Gores G. J. (2007) Serine 64 phosphorylation enhances the antiapoptotic function of Mcl-1. J. Biol. Chem. 282, 18407–18417 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61. Chiang C. W., Kanies C., Kim K. W., Fang W. B., Parkhurst C., Xie M., Henry T., Yang E. (2003) Protein phosphatase 2A dephosphorylation of phosphoserine 112 plays the gatekeeper role for BAD-mediated apoptosis. Mol. Cell. Biol. 23, 6350–6362 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62. Ruvolo P. P., Clark W., Mumby M., Gao F., May W. S. (2002) A functional role for the B56 α-subunit of protein phosphatase 2A in ceramide-mediated regulation of Bcl2 phosphorylation status and function. J. Biol. Chem. 277, 22847–22852 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63. Deng X., Gao F., May W. S. (2009) Protein phosphatase 2A inactivates Bcl2's antiapoptotic function by dephosphorylation and up-regulation of Bcl2-p53 binding. Blood 113, 422–428 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64. Chen W., Arroyo J. D., Timmons J. C., Possemato R., Hahn W. C. (2005) Cancer-associated PP2A Aα subunits induce functional haploinsufficiency and tumorigenicity. Cancer Res. 65, 8183–8192 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65. Chen W., Possemato R., Campbell K. T., Plattner C. A., Pallas D. C., Hahn W. C. (2004) Identification of specific PP2A complexes involved in human cell transformation. Cancer Cell 5, 127–136 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66. Seshacharyulu P., Pandey P., Datta K., Batra S. K. (2013) Phosphatase: PP2A structural importance, regulation and its aberrant expression in cancer. Cancer Lett. 335, 9–18 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67. Ruvolo P. P., Qui Y. H., Coombes K. R., Zhang N., Ruvolo V. R., Borthakur G., Konopleva M., Andreeff M., Kornblau S. M. (2011) Low expression of PP2A regulatory subunit B55α is associated with T308 phosphorylation of AKT and shorter complete remission duration in acute myeloid leukemia patients. Leukemia 25, 1711–1717 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68. Foley T. D., Petro L. A., Stredny C. M., Coppa T. M. (2007) Oxidative inhibition of protein phosphatase 2A activity: role of catalytic subunit disulfides. Neurochem. Res. 32, 1957–1964 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69. Foley T. D., Kintner M. E. (2005) Brain PP2A is modified by thiol-disulfide exchange and intermolecular disulfide formation. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 330, 1224–1229 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70. Foley T. D., Melideo S. L., Healey A. E., Lucas E. J., Koval J. A. (2011) Phenylarsine oxide binding reveals redox-active and potential regulatory vicinal thiols on the catalytic subunit of protein phosphatase 2A. Neurochem. Res. 36, 232–240 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]