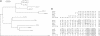Abstract
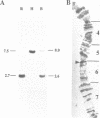
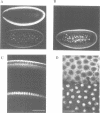
The sequence of a Drosophila melanogaster cDNA encoding a novel 35 kDa protein serine/threonine phosphatase, termed PPV, is presented. PPV is 40-41% identical to Drosophila PP1, 53% identical to Drosophila PP2A and 63% identical to Saccharomyces cerevisiae SIT4. Complementation studies demonstrated that PPV can functionally rescue a temperature sensitive mutant of SIT4, a protein phosphatase required for the G1 to S transition of the cell cycle. When placed under the SIT4 promoter, PPV cDNA is able to replace the SIT4 gene in S. cerevisiae. The amino-terminal domain of PPV fused to another phosphatase catalytic region (PP1) also rescues the temperature sensitive SIT4 mutant and the SIT4 deletion mutant, implicating this region in binding to regulatory subunits and/or altering specificity. In Drosophila, a substantial transient increase in both PPV mRNA and protein occurs in late syncytial and early cellular blastoderm embryos. At the latter stage PPV is localized to the cytoplasm of cells at the cortex. This increase in PPV correlates with introduction of the G2 phase of the cell cycle, elevated zygotic transcription and cellularization, indicating that PPV may play a role in one or more of these processes.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alessi D., MacDougall L. K., Sola M. M., Ikebe M., Cohen P. The control of protein phosphatase-1 by targetting subunits. The major myosin phosphatase in avian smooth muscle is a novel form of protein phosphatase-1. Eur J Biochem. 1992 Dec 15;210(3):1023–1035. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1992.tb17508.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson K. V., Lengyel J. A. Changing rates of histone mRNA synthesis and turnover in Drosophila embryos. Cell. 1980 Oct;21(3):717–727. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90435-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson K. V., Lengyel J. A. Rates of synthesis of major classes of RNA in Drosophila embryos. Dev Biol. 1979 May;70(1):217–231. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(79)90018-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arndt K. T., Styles C. A., Fink G. R. A suppressor of a HIS4 transcriptional defect encodes a protein with homology to the catalytic subunit of protein phosphatases. Cell. 1989 Feb 24;56(4):527–537. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90576-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berndt N., Campbell D. G., Caudwell F. B., Cohen P., da Cruz e Silva E. F., da Cruz e Silva O. B., Cohen P. T. Isolation and sequence analysis of a cDNA clone encoding a type-1 protein phosphatase catalytic subunit: homology with protein phosphatase 2A. FEBS Lett. 1987 Nov 2;223(2):340–346. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)80316-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brewis N. D., Street A. J., Prescott A. R., Cohen P. T. PPX, a novel protein serine/threonine phosphatase localized to centrosomes. EMBO J. 1993 Mar;12(3):987–996. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05739.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cavener D. R. Comparison of the consensus sequence flanking translational start sites in Drosophila and vertebrates. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Feb 25;15(4):1353–1361. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.4.1353. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen M. X., Chen Y. H., Cohen P. T. Polymerase chain reactions using Saccharomyces, Drosophila and human DNA predict a large family of protein serine/threonine phosphatases. FEBS Lett. 1992 Jul 13;306(1):54–58. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(92)80836-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen P. T., Brewis N. D., Hughes V., Mann D. J. Protein serine/threonine phosphatases; an expanding family. FEBS Lett. 1990 Aug 1;268(2):355–359. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)81285-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen P. T., Cohen P. Discovery of a protein phosphatase activity encoded in the genome of bacteriophage lambda. Probable identity with open reading frame 221. Biochem J. 1989 Jun 15;260(3):931–934. doi: 10.1042/bj2600931. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen P. Signal integration at the level of protein kinases, protein phosphatases and their substrates. Trends Biochem Sci. 1992 Oct;17(10):408–413. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(92)90010-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen P. The structure and regulation of protein phosphatases. Annu Rev Biochem. 1989;58:453–508. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.58.070189.002321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Da Cruz e Silva E. F., Hughes V., McDonald P., Stark M. J., Cohen P. T. Protein phosphatase 2Bw and protein phosphatase Z are Saccharomyces cerevisiae enzymes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 Jun 13;1089(2):269–272. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(91)90023-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalby B., Glover D. M. 3' non-translated sequences in Drosophila cyclin B transcripts direct posterior pole accumulation late in oogenesis and peri-nuclear association in syncytial embryos. Development. 1992 Aug;115(4):989–997. doi: 10.1242/dev.115.4.989. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dent P., Lavoinne A., Nakielny S., Caudwell F. B., Watt P., Cohen P. The molecular mechanism by which insulin stimulates glycogen synthesis in mammalian skeletal muscle. Nature. 1990 Nov 22;348(6299):302–308. doi: 10.1038/348302a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dent P., MacDougall L. K., MacKintosh C., Campbell D. G., Cohen P. A myofibrillar protein phosphatase from rabbit skeletal muscle contains the beta isoform of protein phosphatase-1 complexed to a regulatory subunit which greatly enhances the dephosphorylation of myosin. Eur J Biochem. 1992 Dec 15;210(3):1037–1044. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1992.tb17509.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dombrádi V., Axton J. M., Barker H. M., Cohen P. T. Protein phosphatase 1 activity in Drosophila mutants with abnormalities in mitosis and chromosome condensation. FEBS Lett. 1990 Nov 26;275(1-2):39–43. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)81434-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dombrádi V., Axton J. M., Brewis N. D., da Cruz e Silva E. F., Alphey L., Cohen P. T. Drosophila contains three genes that encode distinct isoforms of protein phosphatase 1. Eur J Biochem. 1990 Dec 27;194(3):739–745. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1990.tb19464.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dombrádi V., Axton J. M., Glover D. M., Cohen P. T. Cloning and chromosomal localization of Drosophila cDNA encoding the catalytic subunit of protein phosphatase 1 alpha. High conservation between mammalian and insect sequences. Eur J Biochem. 1989 Aug 15;183(3):603–610. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1989.tb21089.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dombrádi V., Axton J. M., Glover D. M., Cohen P. T. Molecular cloning and chromosomal localization of a novel Drosophila protein phosphatase. FEBS Lett. 1989 Apr 24;247(2):391–395. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)81377-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dombrádi V., Mann D. J., Saunders R. D., Cohen P. T. Cloning of the fourth functional gene for protein phosphatase 1 in Drosophila melanogaster from its chromosomal location. Eur J Biochem. 1993 Feb 15;212(1):177–183. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1993.tb17648.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doonan J. H., MacKintosh C., Osmani S., Cohen P., Bai G., Lee E. Y., Morris N. R. A cDNA encoding rabbit muscle protein phosphatase 1 alpha complements the Aspergillus cell cycle mutation, bimG11. J Biol Chem. 1991 Oct 5;266(28):18889–18894. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edgar B. A., O'Farrell P. H. The three postblastoderm cell cycles of Drosophila embryogenesis are regulated in G2 by string. Cell. 1990 Aug 10;62(3):469–480. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90012-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. "A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity". Addendum. Anal Biochem. 1984 Feb;137(1):266–267. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90381-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feng D. F., Doolittle R. F. Progressive alignment and phylogenetic tree construction of protein sequences. Methods Enzymol. 1990;183:375–387. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(90)83025-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernandez-Sarabia M. J., Sutton A., Zhong T., Arndt K. T. SIT4 protein phosphatase is required for the normal accumulation of SWI4, CLN1, CLN2, and HCS26 RNAs during late G1. Genes Dev. 1992 Dec;6(12A):2417–2428. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.12a.2417. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrigno P., Langan T. A., Cohen P. Protein phosphatase 2A1 is the major enzyme in vertebrate cell extracts that dephosphorylates several physiological substrates for cyclin-dependent protein kinases. Mol Biol Cell. 1993 Jul;4(7):669–677. doi: 10.1091/mbc.4.7.669. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilbert W., Marchionni M., McKnight G. On the antiquity of introns. Cell. 1986 Jul 18;46(2):151–153. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90730-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman C. S., Winston F. A ten-minute DNA preparation from yeast efficiently releases autonomous plasmids for transformation of Escherichia coli. Gene. 1987;57(2-3):267–272. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90131-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hubbard M. J., Cohen P. On target with a new mechanism for the regulation of protein phosphorylation. Trends Biochem Sci. 1993 May;18(5):172–177. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(93)90109-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes V., Müller A., Stark M. J., Cohen P. T. Both isoforms of protein phosphatase Z are essential for the maintenance of cell size and integrity in Saccharomyces cerevisiae in response to osmotic stress. Eur J Biochem. 1993 Aug 15;216(1):269–279. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1993.tb18142.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter T. Protein kinase classification. Methods Enzymol. 1991;200:3–37. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)00125-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito H., Fukuda Y., Murata K., Kimura A. Transformation of intact yeast cells treated with alkali cations. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jan;153(1):163–168. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.1.163-168.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalderon D., Rubin G. M. cGMP-dependent protein kinase genes in Drosophila. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jun 25;264(18):10738–10748. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinoshita N., Ohkura H., Yanagida M. Distinct, essential roles of type 1 and 2A protein phosphatases in the control of the fission yeast cell division cycle. Cell. 1990 Oct 19;63(2):405–415. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90173-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klämbt C., Jacobs J. R., Goodman C. S. The midline of the Drosophila central nervous system: a model for the genetic analysis of cell fate, cell migration, and growth cone guidance. Cell. 1991 Feb 22;64(4):801–815. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90509-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lahue E. E., Smith A. V., Orr-Weaver T. L. A novel cyclin gene from Drosophila complements CLN function in yeast. Genes Dev. 1991 Dec;5(12A):2166–2175. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.12a.2166. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehner C. F., O'Farrell P. H. Expression and function of Drosophila cyclin A during embryonic cell cycle progression. Cell. 1989 Mar 24;56(6):957–968. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90629-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehrach H., Diamond D., Wozney J. M., Boedtker H. RNA molecular weight determinations by gel electrophoresis under denaturing conditions, a critical reexamination. Biochemistry. 1977 Oct 18;16(21):4743–4751. doi: 10.1021/bi00640a033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Léopold P., O'Farrell P. H. An evolutionarily conserved cyclin homolog from Drosophila rescues yeast deficient in G1 cyclins. Cell. 1991 Sep 20;66(6):1207–1216. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90043-x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacDougall L. K., Campbell D. G., Hubbard M. J., Cohen P. Partial structure and hormonal regulation of rabbit liver inhibitor-1; distribution of inhibitor-1 and inhibitor-2 in rabbit and rat tissues. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 Feb 9;1010(2):218–226. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(89)90164-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsumoto T., Beach D. Interaction of the pim1/spi1 mitotic checkpoint with a protein phosphatase. Mol Biol Cell. 1993 Mar;4(3):337–345. doi: 10.1091/mbc.4.3.337. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meek D. W., Street A. J. Nuclear protein phosphorylation and growth control. Biochem J. 1992 Oct 1;287(Pt 1):1–15. doi: 10.1042/bj2870001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizusawa S., Nishimura S., Seela F. Improvement of the dideoxy chain termination method of DNA sequencing by use of deoxy-7-deazaguanosine triphosphate in place of dGTP. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Feb 11;14(3):1319–1324. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.3.1319. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mumby M. C., Walter G. Protein phosphatases and DNA tumor viruses: transformation through the back door? Cell Regul. 1991 Aug;2(8):589–598. doi: 10.1091/mbc.2.8.589. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orgad S., Brewis N. D., Alphey L., Axton J. M., Dudai Y., Cohen P. T. The structure of protein phosphatase 2A is as highly conserved as that of protein phosphatase 1. FEBS Lett. 1990 Nov 26;275(1-2):44–48. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)81435-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Posas F., Casamayor A., Morral N., Ariño J. Molecular cloning and analysis of a yeast protein phosphatase with an unusual amino-terminal region. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jun 15;267(17):11734–11740. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Posas F., Clotet J., Muns M. T., Corominas J., Casamayor A., Ariño J. The gene PPG encodes a novel yeast protein phosphatase involved in glycogen accumulation. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jan 15;268(2):1349–1354. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ronne H., Carlberg M., Hu G. Z., Nehlin J. O. Protein phosphatase 2A in Saccharomyces cerevisiae: effects on cell growth and bud morphogenesis. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Oct;11(10):4876–4884. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.10.4876. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose L. S., Wieschaus E. The Drosophila cellularization gene nullo produces a blastoderm-specific transcript whose levels respond to the nucleocytoplasmic ratio. Genes Dev. 1992 Jul;6(7):1255–1268. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.7.1255. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimanuki M., Kinoshita N., Ohkura H., Yoshida T., Toda T., Yanagida M. Isolation and characterization of the fission yeast protein phosphatase gene ppe1+ involved in cell shape control and mitosis. Mol Biol Cell. 1993 Mar;4(3):303–313. doi: 10.1091/mbc.4.3.303. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sneddon A. A., Cohen P. T., Stark M. J. Saccharomyces cerevisiae protein phosphatase 2A performs an essential cellular function and is encoded by two genes. EMBO J. 1990 Dec;9(13):4339–4346. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07883.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutton A., Immanuel D., Arndt K. T. The SIT4 protein phosphatase functions in late G1 for progression into S phase. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Apr;11(4):2133–2148. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.4.2133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutton A., Lin F., Arndt K. T. The SIT4 protein phosphatase is required in late G1 for progression into S phase. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1991;56:75–81. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1991.056.01.011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wickens M. How the messenger got its tail: addition of poly(A) in the nucleus. Trends Biochem Sci. 1990 Jul;15(7):277–281. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(90)90054-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanagida M., Kinoshita N., Stone E. M., Yamano H. Protein phosphatases and cell division cycle control. Ciba Found Symp. 1992;170:130–146. doi: 10.1002/9780470514320.ch9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- da Cruz e Silva O. B., Cohen P. T. A second catalytic subunit of type-2A protein phosphatase from rabbit skeletal muscle. FEBS Lett. 1987 Dec 21;226(1):176–178. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)80574-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]