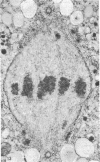
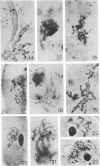
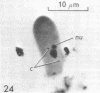
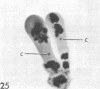
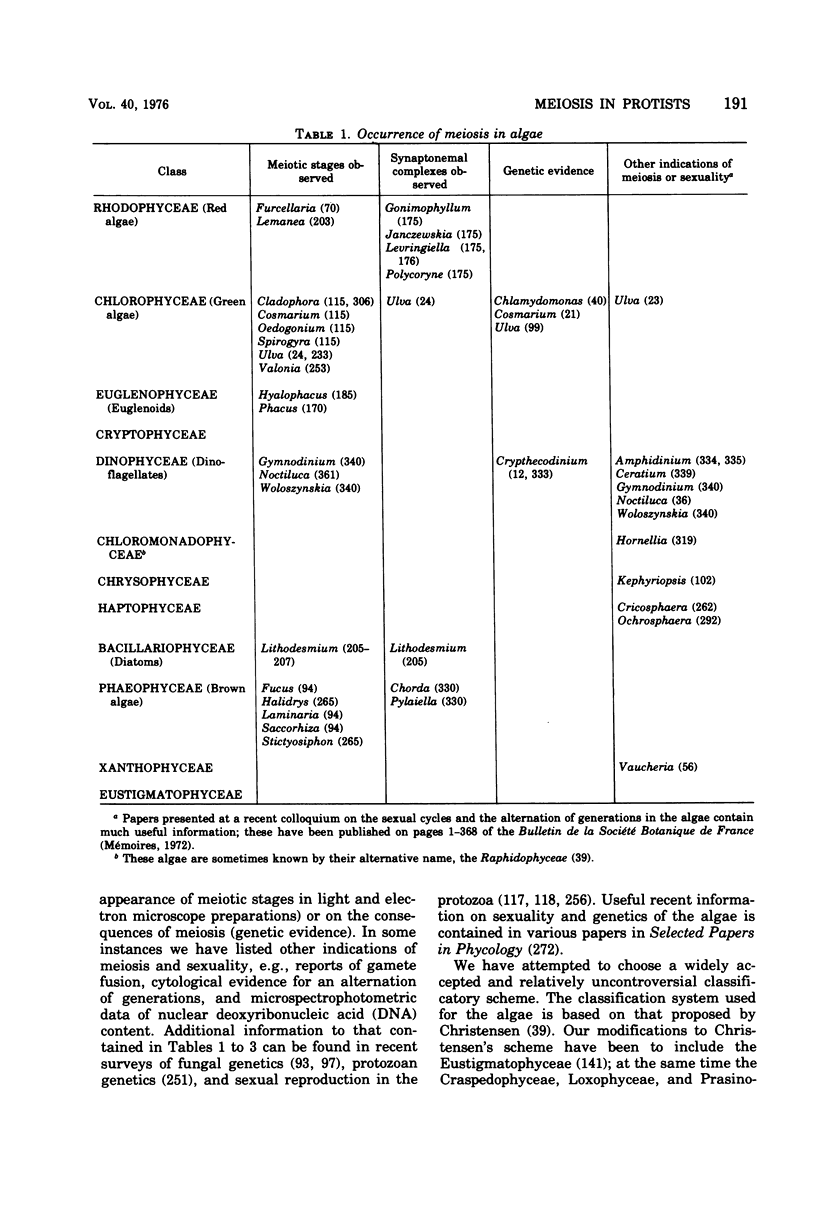
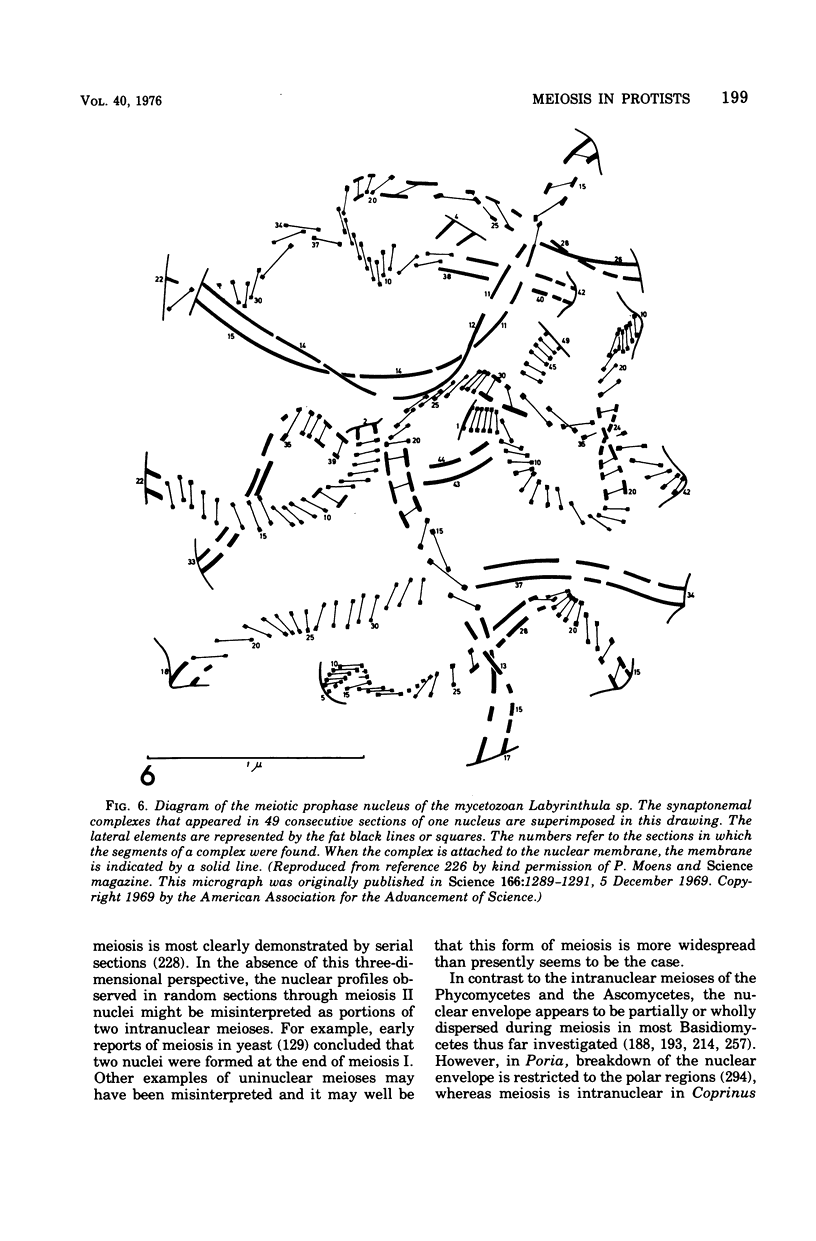
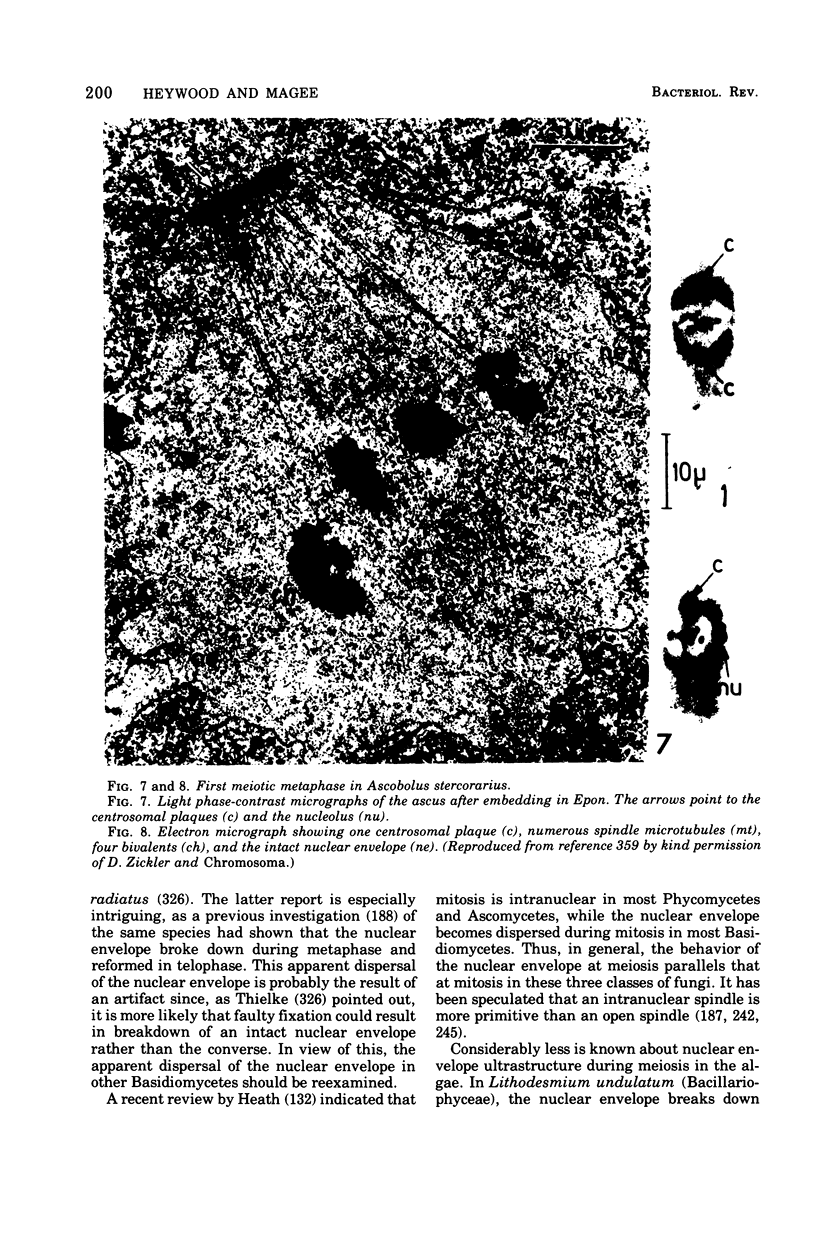
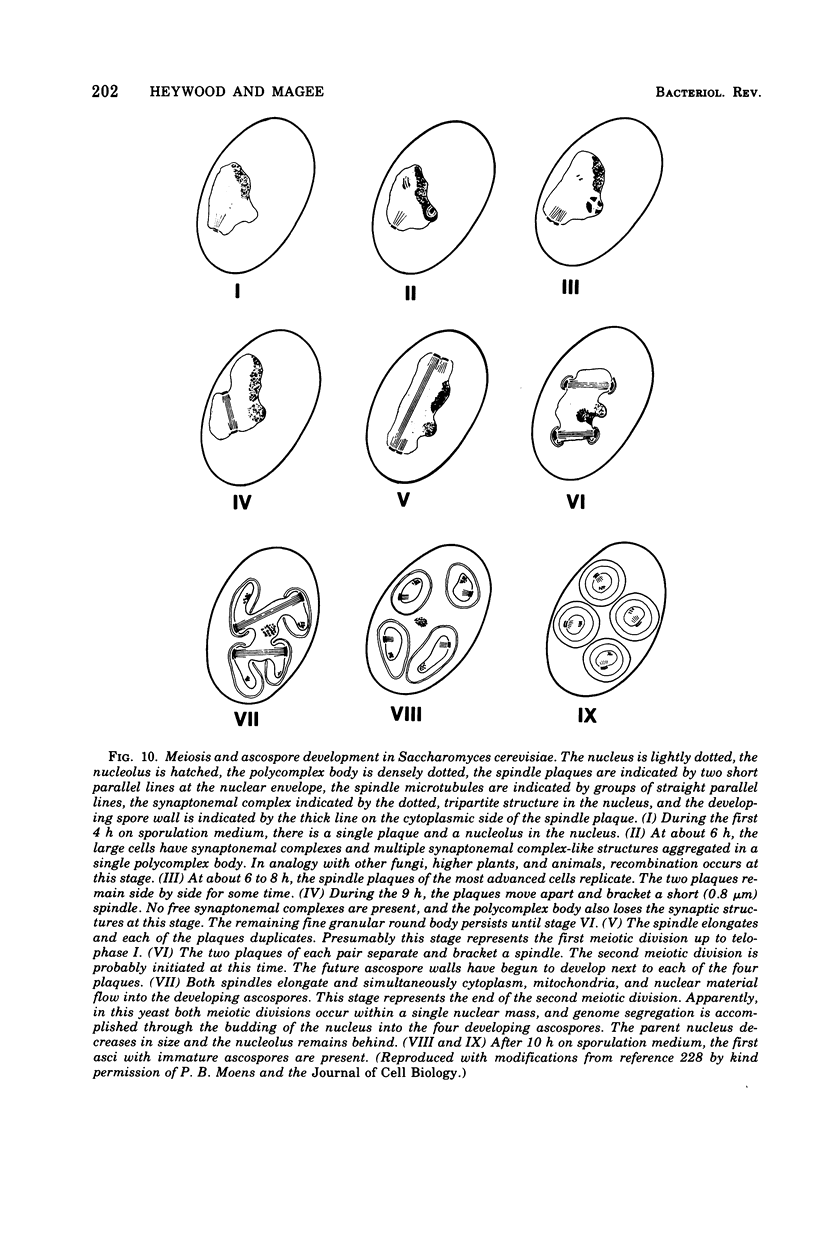
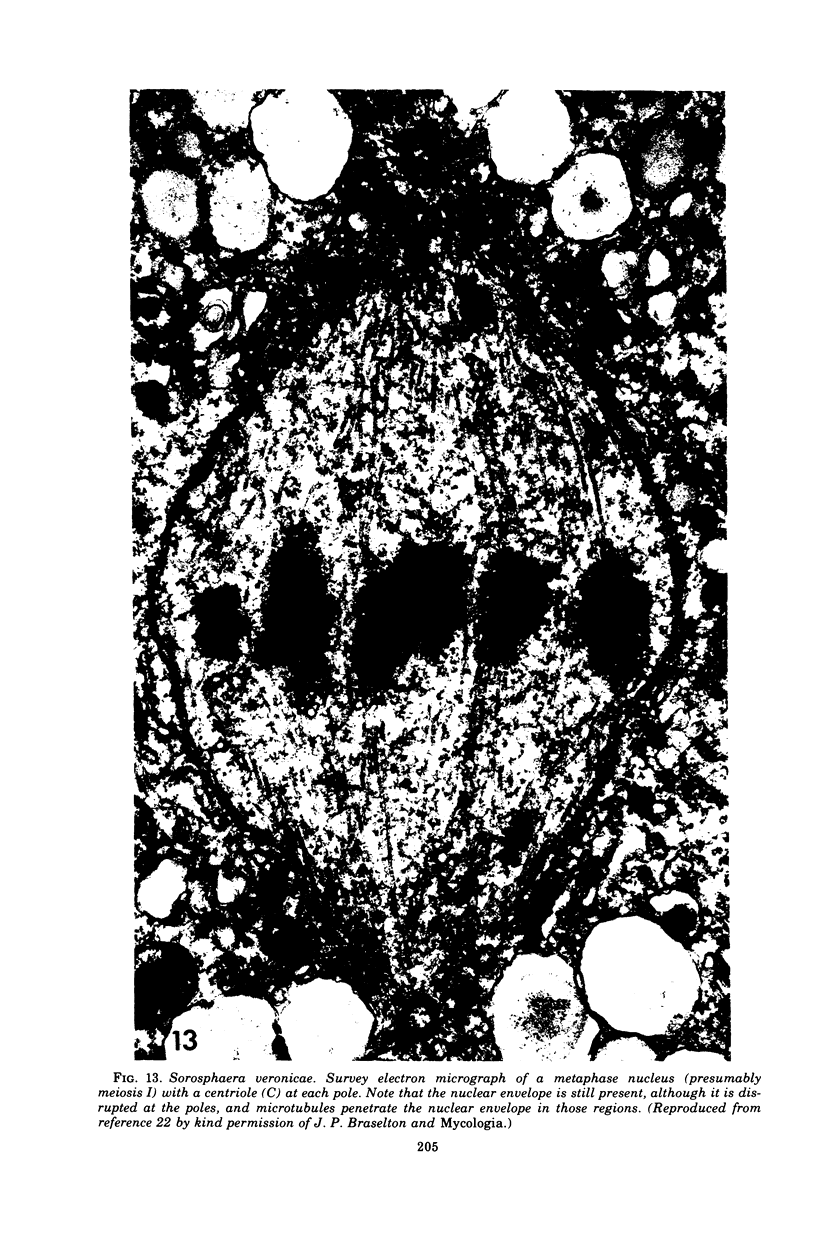
Full text
PDF










































Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aist J. R., Williams P. H. Ultrastructure and time course of mitosis in the fungus Fusarium oxysporum. J Cell Biol. 1972 Nov;55(2):368–389. doi: 10.1083/jcb.55.2.368. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aldrich H. C., Mims C. W. Synaptonemal complexes and meiosis in myxomycetes. Am J Bot. 1970 Sep;57(8):935–941. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aldrich H. C. The ultrastructure of meiosis in three species of Physarum. Mycologia. 1967 Jan-Feb;59(1):127–148. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bajer A. S. Interaction of microtubules and the mechanism of chromosome movement (zipper hypothesis). 1. General principle. Cytobios. 1973 Nov;8(31):139–160. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barry E. G. The diffuse diplotene stage of meiotic prophase in Neurospora. Chromosoma. 1969;26(2):119–129. doi: 10.1007/BF00326449. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bausum H. T. Genetic determination of high meiotic reversion frequencies in isoleucine-valine 1 homoallelic crosses in Neurospora. Can J Genet Cytol. 1972 Mar;14(1):1–11. doi: 10.1139/g72-001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beale G. H. Genetic studies on mitochondrially inherited mikamycin-resistance in Paramecium aurelia. Mol Gen Genet. 1973 Dec 31;127(3):241–248. doi: 10.1007/BF00333763. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beam C. A., Himes M. Evidence for sexual fusion and recombination in the dinoflagellate Crypthecodinium (Gyrodinium) cohnii. Nature. 1974 Aug 2;250(465):435–436. doi: 10.1038/250435a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berger J. D. Selective inhibition of DNA synthesis in macronuclear fragments in Paramecium aurelia exconjugants and its reversal during macronuclear regeneration. Chromosoma. 1973;44(1):33–48. doi: 10.1007/BF00372572. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bertrand H., Pittenger T. H. Isolation and classification of extranuclear mutants of Neurospora crassa. Genetics. 1972 Aug;71(4):521–533. doi: 10.1093/genetics/71.4.521. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beçak M. L., Beçak W. Origin of the synaptonemal complex. Experientia. 1972 Nov 15;28(11):1367–1369. doi: 10.1007/BF01965350. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Black S. H., Gorman C. The cytology of Hansenula. 3. Nuclear segregation and envelopment during ascosporogenesis in Hansenula wingei. Arch Mikrobiol. 1971;79(3):231–248. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bresch C., Müller G., Egel R. Genes involved in meiosis and sporulation of a yeast. Mol Gen Genet. 1968;102(4):301–306. doi: 10.1007/BF00433721. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brinkley B. R., Cartwright J., Jr Ultrastructural analysis of mitotic spindle elongation in mammalian cells in vitro. Direct microtubule counts. J Cell Biol. 1971 Aug;50(2):416–431. doi: 10.1083/jcb.50.2.416. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bråten T., Nordby O. Ultrastructure of meiosis and centriole behaviour in Ulva mutabilis Foyn. J Cell Sci. 1973 Jul;13(1):69–81. doi: 10.1242/jcs.13.1.69. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bråten T. The ultrastructure of fertilization and zygote formation in the green alga Ulva mutabilis Foyn. J Cell Sci. 1971 Nov;9(3):621–635. doi: 10.1242/jcs.9.3.621. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bunn C. L., Mitchell C. H., Lukins H. B., Linnane A. W. Biogenesis of mitochondria. 18. A new class of cytoplasmically determined antibiotic resistant mutants in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Nov;67(3):1233–1240. doi: 10.1073/pnas.67.3.1233. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Byers B., Goetsch L. Duplication of spindle plaques and integration of the yeast cell cycle. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1974;38:123–131. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1974.038.01.016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Byers B., Goetsch L. Electron microscopic observations on the meiotic karyotype of diploid and tetraploid Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Dec;72(12):5056–5060. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.12.5056. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Callen D. The effect of mating type on the polarity of mitochondrial gene transmission in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Gen Genet. 1974;128(4):321–329. doi: 10.1007/BF00268519. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Canning E. U., Anwar M. Studies on meiotic division in coccidial and malarial parasites. J Protozool. 1968 May;15(2):290–298. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1968.tb02125.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cavalier-Smith T. Basal body and flagellar development during the vegetative cell cycle and the sexual cycle of Chlamydomonas reinhardii. J Cell Sci. 1974 Dec;16(3):529–556. doi: 10.1242/jcs.16.3.529. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen A. W., Miller J. J. Proteolytic activity of intact yeast cells during sporulation. Can J Microbiol. 1968 Sep;14(9):957–963. doi: 10.1139/m68-159. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiang K. S., Kates J. R., Jones R. F., Sueoka N. On the formation of a homogeneous zygotic population in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Dev Biol. 1970 Aug;22(4):655–669. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(70)90174-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiu S. M., Hastings P. J. Pre-Meiotic DNA Synthesis and Recombination in CHLAMYDOMONAS REINHARDI. Genetics. 1973 Jan;73(1):29–43. doi: 10.1093/genetics/73.1.29. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chu-Der O. M., Chiang K. S. Interaction between mendelian and non-mendelian genes. Regulation of the transmission of non-mendelian genes by a mendelian gene in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Jan;71(1):153–157. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.1.153. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleveland L. R. Sex Produced in the Protozoa of Cryptocercus by Molting. Science. 1947 Jan 3;105(2714):16–17. doi: 10.1126/science.105.2714.16. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Comings D. E. The rationale for an ordered arrangement of chromatin in the interphase nucleus. Am J Hum Genet. 1968 Sep;20(5):440–460. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox B. S., Parry J. M. The isolation, genetics and survival characteristics of ultraviolet light-sensitive mutants in yeast. Mutat Res. 1968 Jul-Aug;6(1):37–55. doi: 10.1016/0027-5107(68)90101-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies D. R. The control of dark repair mechanisms in meiotic cells. Mol Gen Genet. 1967;100(2):140–149. doi: 10.1007/BF00333600. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies D. R. UV-sensitive mutants of Chlamydomonas reinhardi. Mutat Res. 1967 Nov-Dec;4(6):765–770. doi: 10.1016/0027-5107(67)90085-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis E. A., Epstein H. T. Some factors controlling step-wise variation of organelle number in Euglena gracilis. Exp Cell Res. 1971 Apr;65(2):273–280. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(71)90002-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dawes I. W., Hardie I. D. Selective killing of vegetative cells in sporulated yeast cultures by exposure to diethyl ether. Mol Gen Genet. 1974;131(4):281–289. doi: 10.1007/BF00264859. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Day A. W., Day L. L. Ultraviolet light sensitive mutants of Ustilago violacea. Can J Genet Cytol. 1970 Dec;12(4):891–904. doi: 10.1139/g70-113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Egel R., Egel-Mitani M. Premeiotic DNA synthesis in fission yeast. Exp Cell Res. 1974 Sep;88(1):127–134. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(74)90626-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Egel R. Genes involved in mating type expression of fission yeast. Mol Gen Genet. 1973 May 28;122(4):339–343. doi: 10.1007/BF00269434. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Egel R., Pentzos-Daponte A. Chromosome-like particles during meiosis in fission yeast. Arch Mikrobiol. 1974 Feb 13;95(4):319–323. doi: 10.1007/BF02451773. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellzey J. T. Ultrastructural observations of meiosis within antheridia of Achyla ambisexuals. Mycologia. 1974 Jan-Feb;66(1):32–47. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emerson R., Wilson C. M. The Significance of Meiosis in Allomyces. Science. 1949 Jul 22;110(2847):86–88. doi: 10.1126/science.110.2847.86. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engels F. M., Croes A. F. The synaptinemal complex in yeast. Chromosoma. 1968;25(1):104–106. doi: 10.1007/BF00338237. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esposito M. S., Esposito R. E., Arnaud M., Halvorson H. O. Acetate utilization and macromolecular synthesis during sporulation of yeast. J Bacteriol. 1969 Oct;100(1):180–186. doi: 10.1128/jb.100.1.180-186.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esposito M. S., Esposito R. E., Arnaud M., Halvorson H. O. Conditional mutants of meiosis in yeast. J Bacteriol. 1970 Oct;104(1):202–210. doi: 10.1128/jb.104.1.202-210.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esposito M. S., Esposito R. E. Genes controlling meiosis and spore formation in yeast. Genetics. 1974 Sep;78(1):215–225. doi: 10.1093/genetics/78.1.215. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esposito M. S., Esposito R. E. The genetic control of sporulation in Saccharomyces. I. The isolation of temperature-sensitive sporulation-deficient mutants. Genetics. 1969 Jan;61(1):79–89. doi: 10.1093/genetics/61.1.79. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esposito R. E., Esposito M. S. Genetic recombination and commitment to meiosis in Saccharomyces. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Aug;71(8):3172–3176. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.8.3172. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esposito R. E., Frink N., Bernstein P., Esposito M. S. The genetic control of sporulation in Saccharomyces. II. Dominance and complementation of mutants of meiosis and spore formation. Mol Gen Genet. 1972;114(3):241–248. doi: 10.1007/BF01788893. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FITZGERALD P. H. Genetic and epigenetic factors controlling female sterility in Neurospora crassa. Heredity (Edinb) 1963 Feb;18:47–62. doi: 10.1038/hdy.1963.4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fast D. Sporulation synchrony of Saccharomyces cerevisiae grown in various carbon sources. J Bacteriol. 1973 Nov;116(2):925–930. doi: 10.1128/jb.116.2.925-930.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fiil A., Moens P. B. The development, structure and function of modified synaptonemal complexes in mosquito oocytes. Chromosoma. 1973;41(1):37–62. doi: 10.1007/BF00284073. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fogel S., Roth R. Mutations affecting meiotic gene conversion in yeast. Mol Gen Genet. 1974 May 31;130(3):189–201. doi: 10.1007/BF00268799. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fortuin J. J. Another two genes controlling mitotic intragenic recombination and recovery from UV damage in Aspergillus nidulans. II. Recombination behaviour and x-ray-sensitivity of uvsD and uvsE mutants. Mutat Res. 1971 Mar;11(3):265–277. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedländer M., Wahrman J. The spindle as a basal body distributor. A study in the meiosis of the male silkworm moth, Bombyx mori. J Cell Sci. 1970 Jul;7(1):65–89. doi: 10.1242/jcs.7.1.65. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friis J., Roman H. The effect of the mating-type alleles on intragenic recombination in yeast. Genetics. 1968 May;59(1):33–36. doi: 10.1093/genetics/59.1.33. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GANESAN A. T., HOLTER H., ROBERTS C. Some observations on sporulation in Saccharomyces. C R Trav Lab Carlsberg Chim. 1958;31(1):1–6. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaillardin C. M., Charoy V., Heslot H. A study of copulation, sporulation and meiotic segregation in Candida lipolytica. Arch Mikrobiol. 1973;92(1):69–83. doi: 10.1007/BF00409513. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerlach W. L. Sporulation in mating type homozygotes of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Heredity (Edinb) 1974 Apr;32(2):241–249. doi: 10.1038/hdy.1974.28. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillies C. B. Reconstruction of the Neurospora crassa pachytene karyotype from serial sections of synaptonemal complexes. Chromosoma. 1972;36(2):119–130. doi: 10.1007/BF00285207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grewal N. S., Miller J. J. Formation of asci with two diploid spores by diploid cells of Saccharomyces. Can J Microbiol. 1972 Dec;18(12):1897–1905. doi: 10.1139/m72-295. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gull K., Newsam R. J. Meiosis in basidiomycetous Fungi. II. Fine structure of the synaptonemal complex. Protoplasma. 1975;83(3):259–268. doi: 10.1007/BF01282558. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gull K., Newsam R. J. Meiosis in basidiomycetous fungi I. Fine structure of spindle pole body organization. Protoplasma. 1975;83(3):247–257. doi: 10.1007/BF01282557. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guth E., Hashimoto T., Conti S. F. Morphogenesis of ascospores in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Bacteriol. 1972 Feb;109(2):869–880. doi: 10.1128/jb.109.2.869-880.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gutz H. "Twin meiosis" and other ambivalences in the life cycle of Schizosaccharomyces pombe. Science. 1967 Nov 10;158(3802):796–798. doi: 10.1126/science.158.3802.796. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HASHIMOTO T., GERHARDT P., CONTI S. F., NAYLOR H. B. Studies on the fine structure of microorganisms. V. Morphogenesis of nuclear and membrane structures during ascospore formation in yeast. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1960 Apr;7:305–310. doi: 10.1083/jcb.7.2.305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HONIGBERG B. M., BALAMUTH W., BOVEE E. C., CORLISS J. O., GOJDICS M., HALL R. P., KUDO R. R., LEVINE N. D., LOEBLICH A. R., Jr, WEISER J. A REVISED CLASSIFICATION OF THE PHYLUM PROTOZOA. J Protozool. 1964 Feb;11:7–20. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1964.tb01715.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOROWITZ N. H., FLING M., MACLEOD H., WATANABE Y. Structural and regulative genes controlling tyrosinase synthesis in Neurospora. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1961;26:233–238. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1961.026.01.028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haber J. E., Halvorson H. O. Cell cycle dependency of sporulation in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Bacteriol. 1972 Mar;109(3):1027–1033. doi: 10.1128/jb.109.3.1027-1033.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haber J. E., Halvorson H. O. Regulation of sporulation in yeast. Curr Top Dev Biol. 1972;7:61–83. doi: 10.1016/s0070-2153(08)60069-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halbach-Keup G., Ehrenberg M. Eingluss des Phasenstatus der Vorkulturzellen auf die Ascosporenbildung von Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Arch Mikrobiol. 1971;78(1):17–24. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartwell L. H. Genetic control of the cell division cycle in yeast. II. Genes controlling DNA replication and its initiation. J Mol Biol. 1971 Jul 14;59(1):183–194. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90420-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haskins E. F., Hinchee A. A., Cloney R. A. The occurrence of synaptonemal complexes in the slime mold Echinostelium minutum de Bary. J Cell Biol. 1971 Dec;51(3):898–903. doi: 10.1083/jcb.51.3.898. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heath I. B. Mitosis in the fungus Thraustotheca clavata. J Cell Biol. 1974 Jan;60(1):204–220. doi: 10.1083/jcb.60.1.204. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson S. A. The time and place of meiotic crossing-over. Annu Rev Genet. 1970;4:295–324. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.04.120170.001455. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henry S. A., Halvorson H. O. Lipid synthesis during sporulation of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Bacteriol. 1973 Jun;114(3):1158–1163. doi: 10.1128/jb.114.3.1158-1163.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hepler P. K., McIntosh J. R., Cleland S. Intermicrotubule bridges in mitotic spindle apparatus. J Cell Biol. 1970 May;45(2):438–444. doi: 10.1083/jcb.45.2.438. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hereford L. M., Hartwell L. H. Role of protein synthesis in the replication of yeast DNA. Nat New Biol. 1973 Aug 1;244(135):129–131. doi: 10.1038/newbio244129a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holliday R. Altered recombination frequencies in radiation sensitivie strains of Ustilago. Mutat Res. 1967 May-Jun;4(3):275–288. doi: 10.1016/0027-5107(67)90022-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holliday R. Radiation sensitive mutants of Ustilago maydis. Mutat Res. 1965 Dec;2(6):557–559. doi: 10.1016/0027-5107(65)90022-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopper A. K., Hall B. D. Mating type and sporulation in yeast. I. Mutations which alter mating-type control over sporulation. Genetics. 1975 May;80(1):41–59. doi: 10.1093/genetics/80.1.41. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopper A. K., Kirsch J., Hall B. D. Mating type and sporulation in yeast. II. Meiosis, recombination, and radiation sensitivity in an alpha-alpha diploid with altered sporulation control. Genetics. 1975 May;80(1):61–76. doi: 10.1093/genetics/80.1.61. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopper A. K., Magee P. T., Welch S. K., Friedman M., Hall B. D. Macromolecule synthesis and breakdown in relation to sporulation and meiosis in yeast. J Bacteriol. 1974 Aug;119(2):619–628. doi: 10.1128/jb.119.2.619-628.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howell N., Trembath M. K., Linnane A. W., Lukins H. B. Biogenesis of mitochondria. 30. An analysis of polarity of mitochondrial gene recombination and transmission. Mol Gen Genet. 1973 Mar 27;122(1):37–51. doi: 10.1007/BF00337972. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howland G. P., Ramus J. Analysis of blue-green and red algal ribosomal-RNAs by gel electrophoresis. Arch Mikrobiol. 1971;76(4):292–298. doi: 10.1007/BF00408526. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ichida A. A., Fuller M. S. Ultrastructure of mitosis in the aquatic fungus Catenaria anguillulae. Mycologia. 1968 Jan-Feb;60(1):141–155. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Illingworth R. F., Rose A. H., Beckett A. Changes in the lipid composition and fine structure of Saccharomyces cerevisiae during ascus formation. J Bacteriol. 1973 Jan;113(1):373–386. doi: 10.1128/jb.113.1.373-386.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
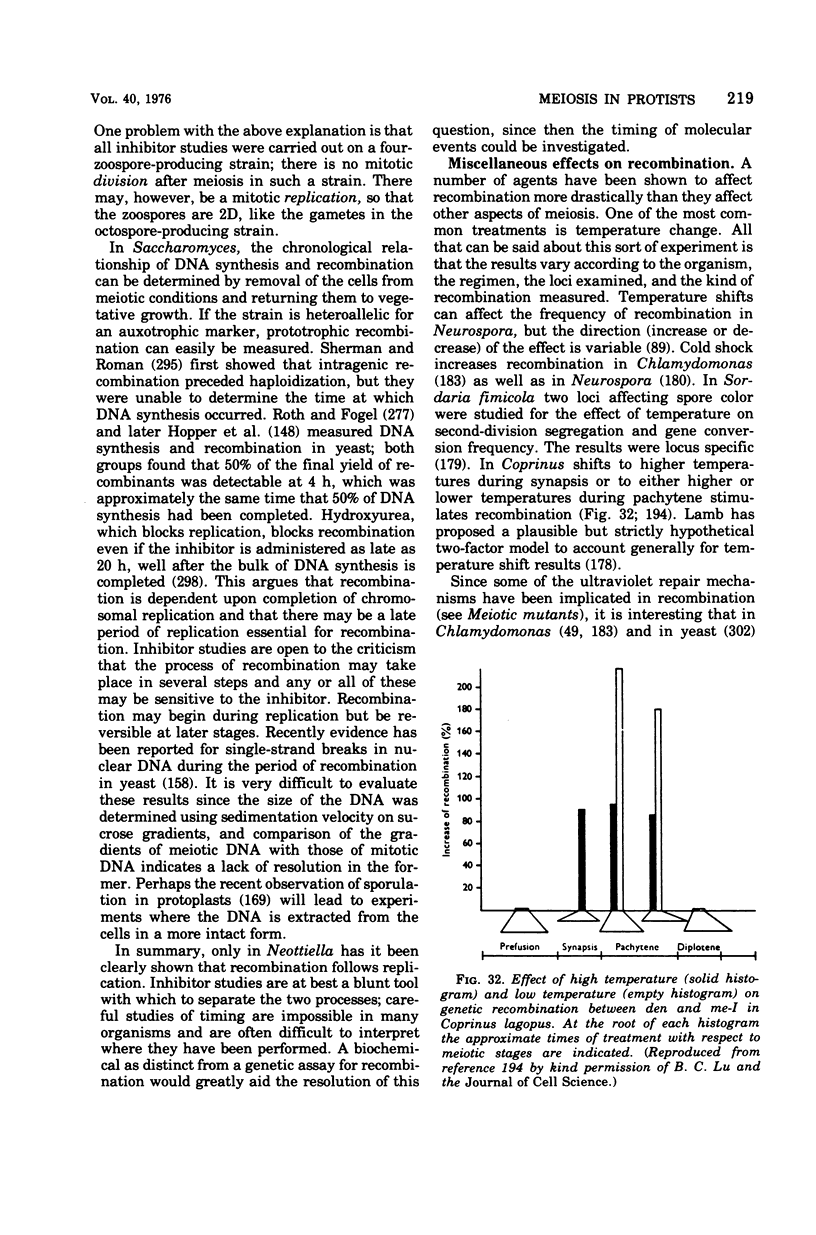
- Jacobson G. K., Pinon R., Esposito R. E., Esposito M. S. Single-strand scissions of chromosomal DNA during commitment to recombination at meiosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 May;72(5):1887–1891. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.5.1887. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jansen G. J. Abnormal frequencies of spontaneous mitotic recombination in uvsB and uvsC mutants of Aspergillus nidulans. Mutat Res. 1970 Jul;10(1):33–41. doi: 10.1016/0027-5107(70)90143-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenkins R. A. Fine structure of division in ciliate protozoa. I. Micronuclear mitosis in Blepharisma. J Cell Biol. 1967 Aug;34(2):463–481. doi: 10.1083/jcb.34.2.463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kadowaki K., Halvorson H. O. Appearance of a new species of ribonucleic acid during sporulation in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Bacteriol. 1971 Mar;105(3):826–830. doi: 10.1128/jb.105.3.826-830.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kadowaki K., Halvorson H. O. Isolation and properties of a new species of ribonucleic acid synthesized in sporulating cells of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Bacteriol. 1971 Mar;105(3):831–836. doi: 10.1128/jb.105.3.831-836.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kane S. M., Roth R. Carbohydrate metabolism during ascospore development in yeast. J Bacteriol. 1974 Apr;118(1):8–14. doi: 10.1128/jb.118.1.8-14.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kates J. R., Chiang K. S., Jones R. F. Studies on DNA replication during synchronized vegetative growth and gametic differentiation in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Exp Cell Res. 1968 Jan;49(1):121–135. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(68)90525-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein R. M., Cronquist A. A consideration of the evolutionary and taxonomic significance of some biochemical, micromorphology, and physiological characters in the thallophytes. Q Rev Biol. 1967 Jun;42(2):105–296. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koltin Y., Raper J. R. Dikaryosis: genetic determination in Schizophyllum. Science. 1968 Apr 5;160(3823):85–86. doi: 10.1126/science.160.3823.85. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kubai D. F., Ris H. Division in the dinoflagellate Gyrodinium cohnii (Schiller). A new type of nuclear reproduction. J Cell Biol. 1969 Feb;40(2):508–528. doi: 10.1083/jcb.40.2.508. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kubai D. F. Unorthodox mitosis in Trichonympha agilis: kinetochore differentiation and chromosome movement. J Cell Sci. 1973 Sep;13(2):511–552. doi: 10.1242/jcs.13.2.511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Küenzi M. T., Roth R. Timing of mitochondrial DNA synthesis during meiosis in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Exp Cell Res. 1974 Apr;85(2):377–382. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(74)90139-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Küenzi M. T., Tingle M. A., Halvorson H. O. Sporulation of Saccharomyces cerevisiae in the absence of a functional mitochondrial genome. J Bacteriol. 1974 Jan;117(1):80–88. doi: 10.1128/jb.117.1.80-88.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEEDALE G. F. The evidence for a meiotic process in the Euglenineae. Arch Mikrobiol. 1962;42:237–245. doi: 10.1007/BF00422042. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laane M. M. Nuclear behaviour during meiosis and ascus formation in Penicillium striatum. Hereditas. 1970;65(1):133–157. doi: 10.1111/j.1601-5223.1970.tb02311.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamb B. C. Evidence from Sordaria that recombination and conversion frequencies are partly determined before meiosis, and for a general model of the control of recombination frequencies. Genetics. 1969 Dec;63(4):807–820. doi: 10.1093/genetics/63.4.807. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamb B. C. Related and unrelated changes in conversion and recombination frequencies with temperature in Sordaria fimicola, and their relevance to hybrid-DNA models of recombination. Genetics. 1969 May;62(1):67–78. doi: 10.1093/genetics/62.1.67. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landner L. A possible causal relationship between iron deficiency, inhibition of DNA synthesis and reduction of meiotic recombination frequency in Neurospora crassa. Mol Gen Genet. 1972;119(2):103–117. doi: 10.1007/BF00269130. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landner L. Variation of recombination frequency in Neurospora crassa following temperature changes prior to and during meiosis and evidence for a premeiotic sensitive stage. Mol Gen Genet. 1970;109(3):219–232. doi: 10.1007/BF00267010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanier W. B., Tuveson R. W., Lennox J. E. A radiation-sensitive mutant of Aspergillus nidulans. Mutat Res. 1968 Jan-Feb;5(1):23–31. doi: 10.1016/0027-5107(68)90077-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawrence C. W. Influence of non-lethal doses of radiation on recombination in Chlamydomonas reinhardi. Nature. 1965 May 22;206(4986):789–791. doi: 10.1038/206789a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lovlie A., Bråten T. On mitosis in the multicellular alga Ulva mutabilis Føyn. J Cell Sci. 1970 Jan;6(1):109–129. doi: 10.1242/jcs.6.1.109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lu B. C. Genetic recombination in Coprinus. II. Its relations to the synaptinemal complexes. J Cell Sci. 1970 May;6(3):669–678. doi: 10.1242/jcs.6.3.669. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lu B. C. Meiosis in Coprinus lagopus: a comparative study with light and electron microscopy. J Cell Sci. 1967 Dec;2(4):529–536. doi: 10.1242/jcs.2.4.529. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lu B. C. Meiosis in Coprinus: VI. The control of the initiation of meiosis. Can J Genet Cytol. 1974 Mar;16(1):115–164. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lu B. C., Raju N. B. Meiosis in Coprinus. II. Chromosome pairing and the lampbrush diplotene stage of meiotic prophase. Chromosoma. 1970;29(3):305–316. doi: 10.1007/BF00325945. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lu B. C. The course of meiosis and centriole behaviour during the ascus development of the ascomycete Gelasinospora calospora. Chromosoma. 1967;22(2):210–226. doi: 10.1007/BF00326730. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lukins H. B., Tate J. R., Saunders G. W., Linnane A. W. The biogenesis of mitochondria 26. Mitochondrial recombination: the segregation of parental and recombinant mitochondrial genotypes during vegetative division of yeast. Mol Gen Genet. 1973 Jan 18;120(1):17–25. doi: 10.1007/BF00332981. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MCNELLY-INGLE C. A., FROST L. C. THE EFFECT OF TEMPERATURE ON THE PRODUCTION OF PERITHECIA BY NEUROSPORA CRASSA. J Gen Microbiol. 1965 Apr;39:33–42. doi: 10.1099/00221287-39-1-33. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MILLER J. J., HOFFMANN-OSTENHOF C. SPORE FORMATION AND GERMINATION IN SACCHAROMYCES. Z Allg Mikrobiol. 1964;4:273–294. doi: 10.1002/jobm.3630040404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MOSES M. J. Chromosomal structures in crayfish spermatocytes. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1956 Mar 25;2(2):215–218. doi: 10.1083/jcb.2.2.215. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macinnes M. A., Francis D. Meiosis in Dictyostelium mucoroides. Nature. 1974 Sep 27;251(5473):321–324. doi: 10.1038/251321a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magee P. T. Changes in DNA-dependent RNA polymerase in sporulating yeast. Mol Biol Rep. 1974 Feb;1(5):275–281. doi: 10.1007/BF00417583. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magee P. T., Hopper A. K. Protein synthesis in relation to sporulation and meiosis in yeast. J Bacteriol. 1974 Sep;119(3):952–960. doi: 10.1128/jb.119.3.952-960.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manton I., Kowallik K., von Stosch H. A. Observations on the fine structure and development of the spindle at mitosis and meiosis in a marine centric diatom (Lithodesmium undulatum). 3. The later stages of meiosis I in male gametogenesis. J Cell Sci. 1970 Jan;6(1):131–157. doi: 10.1242/jcs.6.1.131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manton I., Kowallik K., von Stosch H. A. Observations on the fine structure and development of the spindle at mitosis and meiosis in a marine centric diatom (Lithodesmium undulatum). II. The early meiotic stages in male gametogenesis. J Cell Sci. 1969 Jul;5(1):271–298. doi: 10.1242/jcs.5.1.271. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manton I., Kowallik K., von Stosch H. A. Observations on the fine structure and development of the spindle at mitosis and meiosis in a marine centric diatom (Lithodesmium undulatum). IV. The second meiotic division and conclusion. J Cell Sci. 1970 Sep;7(2):407–443. doi: 10.1242/jcs.7.2.407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Margulis L. On the evolutionary origin and possible mechanism of colchicine-sensitive mitotic movements. Biosystems. 1974 Jul;6(1):16–36. doi: 10.1016/0303-2647(74)90008-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLaughlin D. J. Centrosomes and microtubules during meiosis in the mushroom Boletus rubinellus. J Cell Biol. 1971 Sep;50(3):737–745. doi: 10.1083/jcb.50.3.737. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mills D. Effect of pH on adenine and amino acid uptake during sporulation in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Bacteriol. 1972 Oct;112(1):519–526. doi: 10.1128/jb.112.1.519-526.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mims C. W. Centrioles and Golgi apparatus in postmeiotic spores of the myxomycete stemonitis virginiensis. Mycologia. 1972 Mar-Apr;64(2):452–456. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moens P. B., Esposito R. E., Esposito M. S. Aberrant nuclear behavior at meiosis and anucleate spore formation by sporulation-deficient (SPO) mutants of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Exp Cell Res. 1974 Jan;83(1):166–174. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(74)90700-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moens P. B. Fine structure of ascospore development in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Can J Microbiol. 1971 Apr;17(4):507–510. doi: 10.1139/m71-084. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moens P. B. Modification of sporulation in yeast strains with two-spored asci (Saccharomyces, Ascomycetes). J Cell Sci. 1974 Dec;16(3):519–527. doi: 10.1242/jcs.16.3.519. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moens P. B., Perkins F. O. Chromosome number of a small protist: accurate determination. Science. 1969 Dec 5;166(3910):1289–1291. doi: 10.1126/science.166.3910.1289. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moens P. B., Rapport E. Spindles, spindle plaques, and meiosis in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae (Hansen). J Cell Biol. 1971 Aug;50(2):344–361. doi: 10.1083/jcb.50.2.344. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moens P. B., Rapport E. Synaptic structures in the nuclei of sporulating yeast, Saccharomyces cerevisiae (Hansen). J Cell Sci. 1971 Nov;9(3):665–677. doi: 10.1242/jcs.9.3.665. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mori S., Nakai S. Induction and repair of gene conversion in UV-sensitive mutants of yeast. Mol Gen Genet. 1972;117(3):187–196. doi: 10.1007/BF00271646. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moustacchi E. Cytoplasmic and nuclear genetic events induced by UV light in strains of Saccharomyces cerevisiae with different UV sensitivities. Mutat Res. 1969 Mar-Apr;7(2):171–185. doi: 10.1016/0027-5107(69)90029-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakai S., Matsumoto S. Two types of radiation-sensitive mutant in yeast. Mutat Res. 1967 Mar-Apr;4(2):129–136. doi: 10.1016/0027-5107(67)90064-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nordby O., Hoxmark R. C. Changes in cellular parameters during synchronous meiosis in Ulva mutabilis Foyn. Exp Cell Res. 1972 Dec;75(2):321–328. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(72)90436-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nordby O. Light microscopy of meiotic zoosporogenesis and mitotic gametogenesis in Ulva mutabilis Foyn. J Cell Sci. 1974 Jul;15(2):443–455. doi: 10.1242/jcs.15.2.443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novak D. R., Srb A. M. Genetic alterations of ascus development in Neurospora tetrasperma. Genetics. 1971 Feb;67(2):189–199. doi: 10.1093/genetics/67.2.189. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ORGEL L. E. The maintenance of the accuracy of protein synthesis and its relevance to ageing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1963 Apr;49:517–521. doi: 10.1073/pnas.49.4.517. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perkins F. O. Formation of centriole and centriole-like structures during meiosis and mitosis in Labyrinthula sp. (Rhizopodea, Labyrinthulida). An electron-microscope study. J Cell Sci. 1970 May;6(3):629–653. doi: 10.1242/jcs.6.3.629. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson J. B., Gray R. H., Ris H. Meiotic spindle plaques in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Cell Biol. 1972 Jun;53(3):837–841. doi: 10.1083/jcb.53.3.837. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pincheira G., Srb A. M. Cytology and genetics of two abnormal ascus mutants of Neurospora. Can J Genet Cytol. 1969 Jun;11(2):281–286. doi: 10.1139/g69-035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pincheira G., Srb A. M. Genetic variation in the orientation of nuclear spindles during the development of asci in Neurospora. Am J Bot. 1969 Sep;56(8):846–852. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piñon R., Salts Y., Simchen G. Nuclear and mitochondrial DNA synthesis during yeast sporulation. Exp Cell Res. 1974 Feb;83(2):231–238. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(74)90334-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radding C. M. Molecular mechanisms in genetic recombination. Annu Rev Genet. 1973;7:87–111. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.07.120173.000511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radu M., Steinlauf R., Koltin Y. Meiosis in Schizophyllum commune. Chromosomal behavior and the synaptinemal complex. Arch Microbiol. 1974 Jul 22;98(4):301–310. doi: 10.1007/BF00425291. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raju N. B., Lu B. C. Meiosis in Coprinus. IV. Morphology and behaviour of spindle pole bodies. J Cell Sci. 1973 Jan;12(1):131–141. doi: 10.1242/jcs.12.1.131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rapport E. Some fine structure features of meiosis in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Can J Genet Cytol. 1971 Mar;13(1):55–62. doi: 10.1139/g71-008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rasse-Messenguy F., Fink G. R. Temperature-sensitive nonsense suppressors in yeast. Genetics. 1973 Nov;75(3):459–464. doi: 10.1093/genetics/75.3.459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Resnick M. A. Genetic control of radiation sensitivity in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genetics. 1969 Jul;62(3):519–531. doi: 10.1093/genetics/62.3.519. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robb J. Ultrastructure of Ustilago hordei (Pers.) Lagerh. 3. Membrane complexes associated with meiotic nuclei. Can J Genet Cytol. 1974 Mar;16(1):183–191. doi: 10.1139/g74-018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodarte-Ramón U. S., Mortimer R. K. Radiation-induced recombination in Saccharomyces: isolation and genetic study of recombination-deficient mutants. Radiat Res. 1972 Jan;49(1):133–147. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodarte-Ramón U. S. Radiation-induced recombination in Saccharomyces: the genetic control of recombination in mitosis and meiosis. Radiat Res. 1972 Jan;49(1):148–154. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roman H, Phillips M M, Sands S M. Studies of Polyploid Saccharomyces. I. Tetraploid Segregation. Genetics. 1955 Jul;40(4):546–561. doi: 10.1093/genetics/40.4.546. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rooney L., Moens P. B. Nuclear divisions at meiosis in the ascomycetous yeast Wickerhamia fluorescens. Can J Microbiol. 1973 Nov;19(11):1383–1387. doi: 10.1139/m73-223. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosen H., Ebersold W. T. Recombination in relation to ultraviolet sensitivity in Chlamydomonas reinhardi. Genetics. 1972 Jun;71(2):247–253. doi: 10.1093/genetics/71.2.247. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossen J. M., Westergaard M. Studies on the mechanism of crossing over. II. Meiosis and the time of meiotic chromosome replication in the ascomycete Neottiella rutilans (Fr.) Dennis. C R Trav Lab Carlsberg. 1966;35(9):233–260. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth R. M., Dampier C. Dependence of ribonucleic acid synthesis on continuous protein synthesis in yeast. J Bacteriol. 1972 Feb;109(2):773–779. doi: 10.1128/jb.109.2.773-779.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth R. Carbohydrate accumulation during the sporulation of yeast. J Bacteriol. 1970 Jan;101(1):53–57. doi: 10.1128/jb.101.1.53-57.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth R. Chromosome replication during meiosis: identification of gene functions required for premeiotic DNA synthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Nov;70(11):3087–3091. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.11.3087. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth R., Fogel S. A system selective for yeast mutants deficient in meiotic recombination. Mol Gen Genet. 1971;112(4):295–305. doi: 10.1007/BF00334431. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth R., Halvorson H. O. Sporulation of yeast harvested during logarithmic growth. J Bacteriol. 1969 May;98(2):831–832. doi: 10.1128/jb.98.2.831-832.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth R., Lusnak K. DNA synthesis during yeast sporulation: genetic control of an early developmental event. Science. 1970 Apr 24;168(3930):493–494. doi: 10.1126/science.168.3930.493. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell P. J., Srb A. M. Dominance modifiers in neurospora crassa: phenocopy selection and influence of certain ascus mutants. Genetics. 1972 Jun;71(2):233–245. doi: 10.1093/genetics/71.2.233. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHERMAN F., ROMAN H. Evidence for two types of allelic recombination in yeast. Genetics. 1963 Feb;48:255–261. doi: 10.1093/genetics/48.2.255. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sager R., Lane D. Molecular basis of maternal inheritance. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Sep;69(9):2410–2413. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.9.2410. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sager R., Ramanis Z. Biparental inheritance of nonchromosomal genes induced by ultraviolet irradiation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Sep;58(3):931–937. doi: 10.1073/pnas.58.3.931. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sapra G. R., Ammermann D. An analysis of the development program in relation to RNA metabolism in the ciliate Stylonychia mytilus. Dev Biol. 1974 Jan;36(1):105–112. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(74)90194-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sapra G. R., Ammermann D. RNA synthesis and acquisition of actinomycin D insensitivity during conjugation in Stylonychia mytilus. Exp Cell Res. 1973 Mar 30;78(1):168–174. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(73)90051-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schroeder A. L. Ultraviolet-sensitive mutants of Neurospora. I. Genetic basis and effect on recombination. Mol Gen Genet. 1970;107(4):291–304. doi: 10.1007/BF00441192. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sen S. K. Synaptonemal complexes in haploid Petunia and Antirrhinum sp. Naturwissenschaften. 1970 Nov;57(11):550–550. doi: 10.1007/BF00625339. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shigenaka Y., Roth L. E., Pihlaja D. J. Microtubules in the heliozoan axopodium. 3. Degradation and reformation after dilute urea treatment. J Cell Sci. 1971 Jan;8(1):127–151. doi: 10.1242/jcs.8.1.127. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siersma P. W., Chiang K. S. Conservation and degradation of cytoplasmic and chloroplast ribosomes in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. J Mol Biol. 1971 May 28;58(1):167–185. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90239-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silva-Lopez E., Zamb T. J., Roth R. Role of premeiotic replication in gene conversion. Nature. 1975 Jan 17;253(5488):212–214. doi: 10.1038/253212a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simchen G. Are mitotic functions required in meiosis? Genetics. 1974 Apr;76(4):745–753. doi: 10.1093/genetics/76.4.745. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simchen G., Ball N., Nachshon I. Fine control of genetic recombination in yeast. Heredity (Edinb) 1971 Feb;26(1):137–140. doi: 10.1038/hdy.1971.12. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simchen G., Piñon R., Salts Y. Sporulation in Saccharomyces cerevisiae: premeiotic DNA synthesis, readiness and commitment. Exp Cell Res. 1972 Nov;75(1):207–218. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(72)90538-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simchen G., Salts Y., Piñon R. Sensitivity of meiotic yeast cells to ultraviolet light. Genetics. 1973 Apr;73(4):531–541. doi: 10.1093/genetics/73.4.531. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simchen G., Stamberg J. Genetic control of recombination in Schizophyllum commune: specific and independent regulation of adjacent and non-adjacent chromosomal regions. Heredity (Edinb) 1969 Aug;24(3):369–381. doi: 10.1038/hdy.1969.55. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simonet J. M. Mutations affecting meiosis in Podospora anserina. II. Effect of mei2 mutants on recombination. Mol Gen Genet. 1973 Jul 2;123(3):263–281. doi: 10.1007/BF00271244. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simonet J. M., Zickler D. Mutations affecting meiosis in Podospora anserina. I. Cytological studies. Chromosoma. 1972;37(3):327–351. doi: 10.1007/BF00319874. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. A. A mutant affecting meiosis in Neurospora. Genetics. 1975 May;80(1):125–133. doi: 10.1093/genetics/80.1.125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snow R. Recombination in ultraviolet-sensitive strains of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mutat Res. 1968 Nov-Dec;6(3):409–418. doi: 10.1016/0027-5107(68)90058-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sogin S. J., Haber J. E., Halvorson H. O. Relationship between sporulation-specific 20S ribonucleic acid and ribosomal ribonucleic acid processing in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Bacteriol. 1972 Nov;112(2):806–814. doi: 10.1128/jb.112.2.806-814.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stack S. M., Brown W. V. Somatic pairing, reduction and recombination: an evolutionary hypothesis of meiosis. Nature. 1969 Jun 28;222(5200):1275–1276. doi: 10.1038/2221275a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stadler D. R., Smith D. A. A new mutation in Neurospora for sensitivity to ultraviolet. Can J Genet Cytol. 1968 Dec;10(4):916–919. doi: 10.1139/g68-115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stadler D. R. The mechanism of intragenic recombination. Annu Rev Genet. 1973;7:113–127. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.07.120173.000553. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stern H., Hotta Y. Biochemical controls of meiosis. Annu Rev Genet. 1973;7:37–66. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.07.120173.000345. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevenson I., Lloyd F. P. Ultrastructure of nuclear division in Paramecium aurella. I. Mitosis in the micronucleus. Aust J Biol Sci. 1971 Oct;24(5):963–975. doi: 10.1071/bi9710963. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevenson I. Ultrastructure of nuclear division in Paramecium aurelia. 3. Meiosis in the micronucleus during conjugation. Aust J Biol Sci. 1972 Aug;25(4):775–799. doi: 10.1071/bi9720775. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stubblefield E. The structure of mammalian chromosomes. Int Rev Cytol. 1973;35:1–60. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)60351-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sueoka N., Chiang K. S., Kates J. R. Deoxyribonucleic acid replication in meiosis of Chlamydomonas reinhardi. I. Isotopic transfer experiments with a strain producing eight zoospores. J Mol Biol. 1967 Apr 14;25(1):47–66. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90278-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugai T., Hiwatashi K. Cytologic and autoradiographic studies of the micronucleus at meiotic prophase in Tetrahymena pyriformis. J Protozool. 1974 Oct;21(4):542–548. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1974.tb03695.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TAYLOR J. H., McMASTER R. D. Autoradiographic and microphotometric studies of desoxyribose nucleic acid during microgametogenesis in Lilium longiflorum. Chromosoma. 1954;6(6-7):489–521. doi: 10.1007/BF01259951. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi M., Hiwatashi K. Potassium: a factor necessary for the expression of mating reactivity in Paramecium caudatum. Exp Cell Res. 1974 Mar 30;85(1):23–30. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(74)90208-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tee T. S., Choke H. C. A gene controlling the early development of protoperithecium in Neurospora crassa. Mol Gen Genet. 1970;107(2):158–161. doi: 10.1007/BF00333631. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thielke C. Intranucleäre Spindeln und Reduktion des Kernvolumens bei der Meiose von Coprinus radiatus (Bolt) Fr. Arch Microbiol. 1974 Jul 16;98(3):225–237. doi: 10.1007/BF00425285. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tilney L. G., Goddard J. Nucleated sites for the assembly of cytoplasmic microtubules in the ectodermal cells of blastulae of Arbacia punctulata. J Cell Biol. 1970 Sep;46(3):564–575. doi: 10.1083/jcb.46.3.564. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tingle M. A., Küenzi M. T., Halvorson H. O. Germination of yeast spores lacking mitochondrial deoxyribonucleic acid. J Bacteriol. 1974 Jan;117(1):89–93. doi: 10.1128/jb.117.1.89-93.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toth R., Markey D. R. Synaptonemal complexes in brown algae. Nature. 1973 May 25;243(5404):236–237. doi: 10.1038/243236a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsuboi M., Yanagishima N. Effect of cyclic AMP, theophylline and caffeine on the glucose repression of sporulation in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Arch Mikrobiol. 1973 Oct 4;93(1):1–12. doi: 10.1007/BF00666076. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuttle R. C., Loeblich A. R., 3rd Genetic recombination in the dinoflagellate Crypthecodinium cohnii. Science. 1974 Sep 20;185(4156):1061–1062. doi: 10.1126/science.185.4156.1061. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vigfusson N. V., Cano R. J. Artificial induction of the sexual cycle of Neurospora crassa. Nature. 1974 May 24;249(455):383–385. doi: 10.1038/249383a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walliker D., Carter R., Morgan S. Genetic recombination in Plasmodium berghei. Parasitology. 1973 Apr;66(2):309–320. doi: 10.1017/s0031182000045248. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walliker D., Carter R., Morgan S. Genetic recombination in malaria parasites. Nature. 1971 Aug 20;232(5312):561–562. doi: 10.1038/232561a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wejksnora P. J., Haber J. E. Methionine-dependent synthesis of ribosomal ribonucleic acid during sporulation and vegetative growth of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Bacteriol. 1974 Dec;120(3):1344–1355. doi: 10.1128/jb.120.3.1344-1355.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Werner D. Der Entwicklungscyclus mit Sexualphase bei der marinen Diatomee Coscinodiscus asteromphalus. I. Kultur und Synchronisation von Entwicklungsstadien. Arch Mikrobiol. 1971;80(1):43–49. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Werner D. Der Entwicklungscyclus mit Sexualphase bei der marinen Diatomee coscinodiscus asteromophalus. 3. Differenzierung und Spermatogenese. Arch Mikrobiol. 1971;80(2):134–146. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westergaard M., von Wettstein D. Studies on the mechanism of crossing over. IV. The molecular organization of the synaptinemal complex in Neottiella (Cooke) saccardo (Ascomycetes). C R Trav Lab Carlsberg. 1970;37(11):239–268. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westergaard M., von Wettstein D. The nucleolar cycle in an ascomycete. C R Trav Lab Carlsberg. 1970;37(10):195–237. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westergaard M., von Wettstein D. The synaptinemal complex. Annu Rev Genet. 1972;6:71–110. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.06.120172.000443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wheals A. E. A homothallic strain of the myxomycete Physarum polycephalum. Genetics. 1970 Dec;66(4):623–633. doi: 10.1093/genetics/66.4.623. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoo B. Y., Calleja G. B., Johnson B. F. Ultrastructural changes of the fission yeast (Schizosaccharomyces pombe) during ascospore formation. Arch Mikrobiol. 1973 Apr 8;91(1):1–10. doi: 10.1007/BF00409533. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zickler D. Fine structure of chromosome pairing in ten Ascomycetes: meiotic and premeiotic (mitotic) synaptonemal complexes. Chromosoma. 1973;40(4):401–416. doi: 10.1007/BF00399431. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zickler D., Olson L. W. The synaptonemal complex and the spindle plaque during meiosis in yeast. Chromosoma. 1975;50(1):1–23. doi: 10.1007/BF00284959. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]