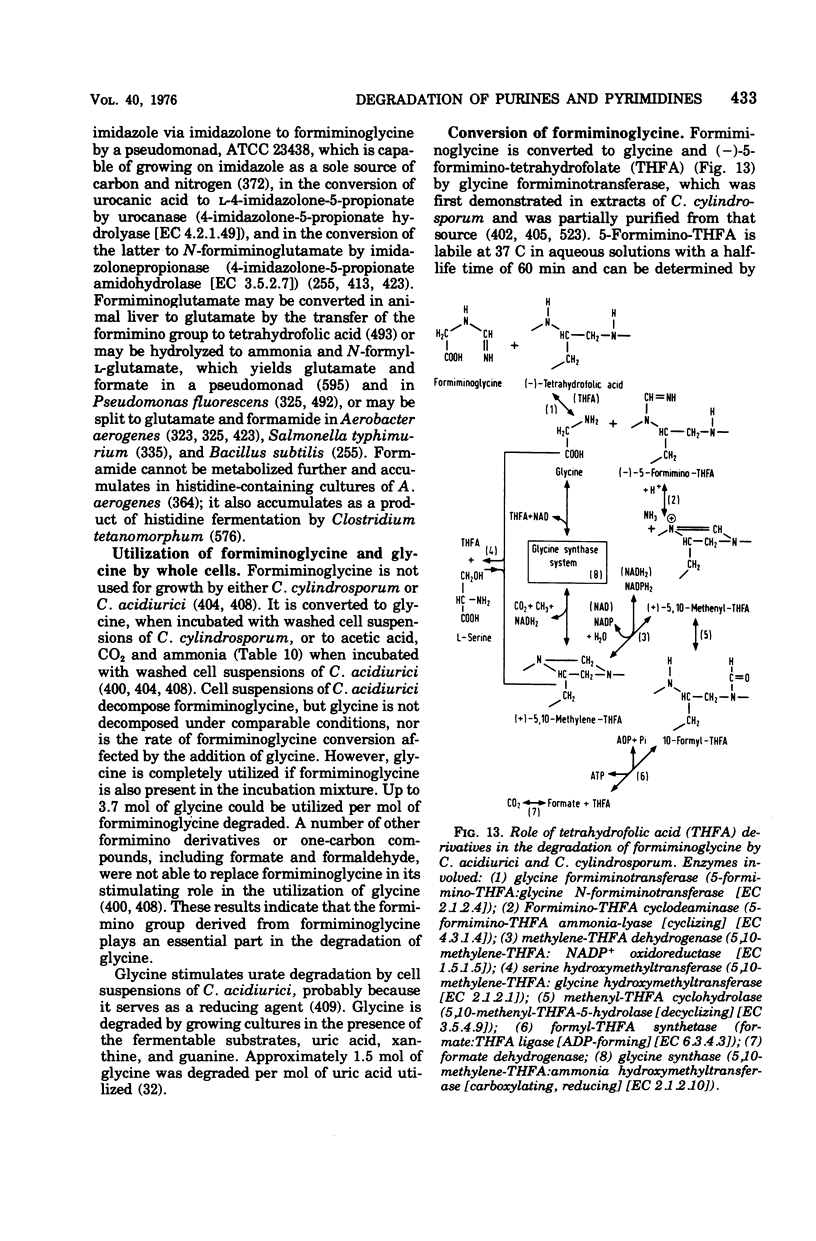
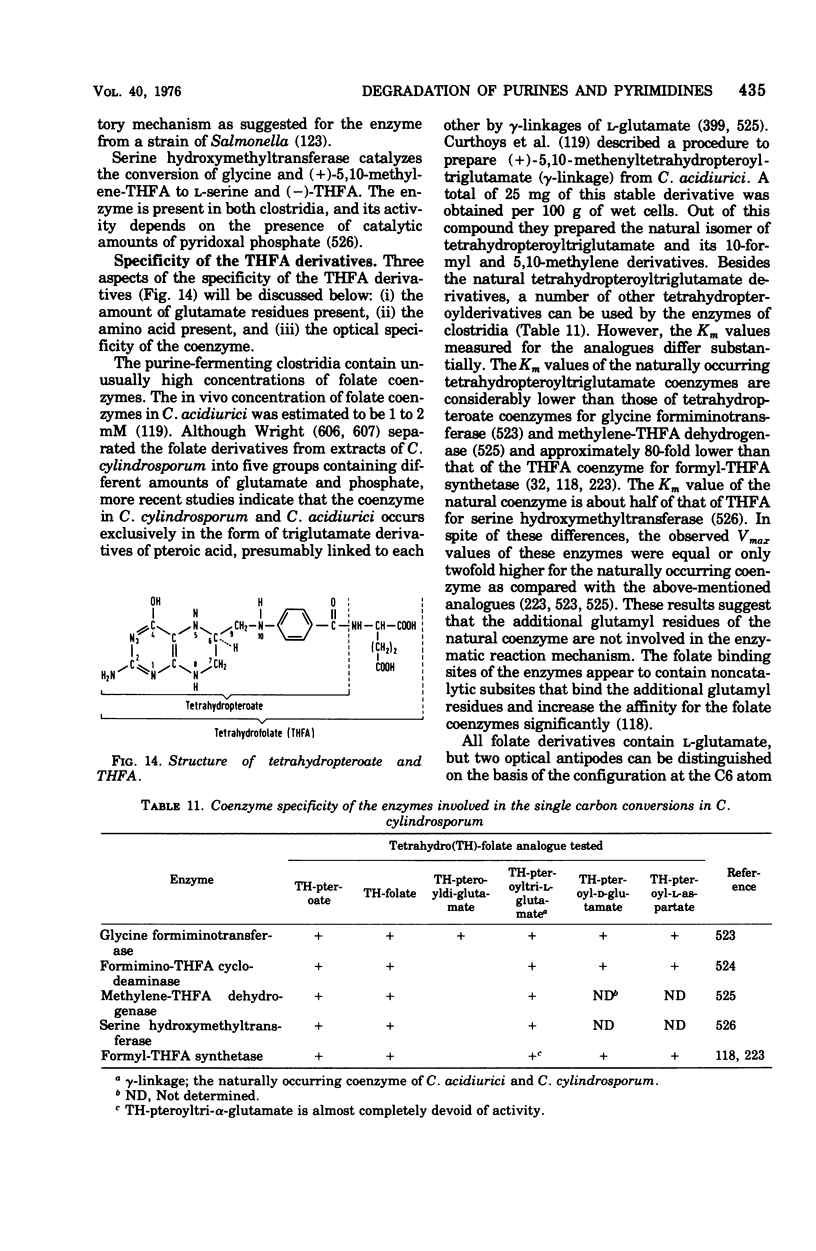
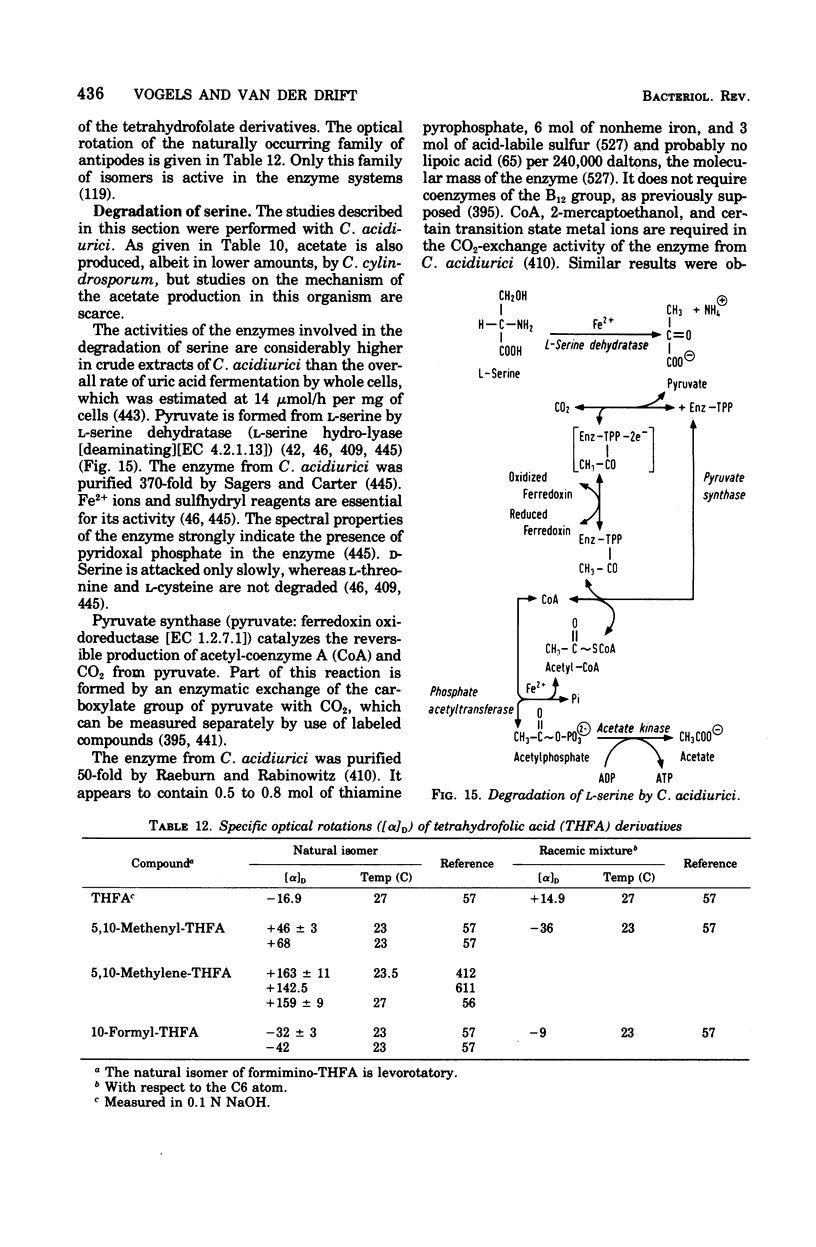
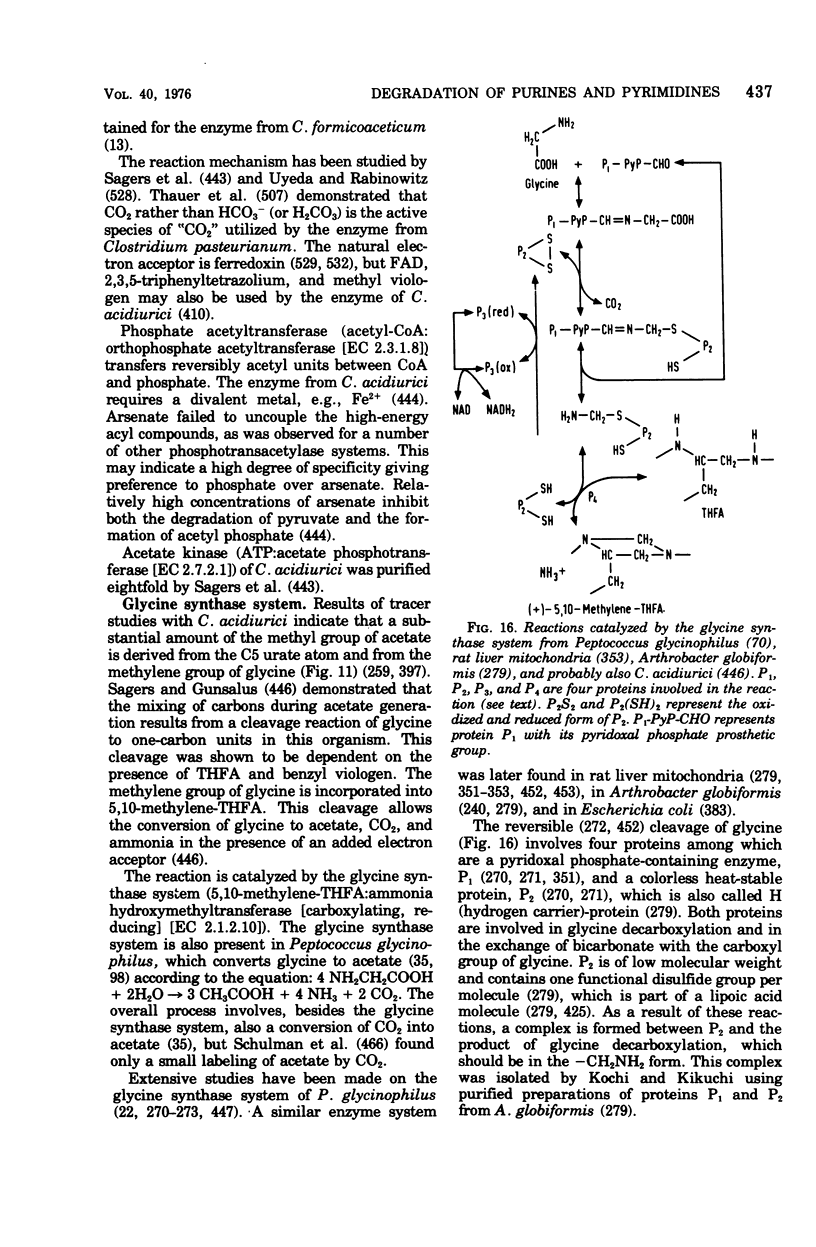
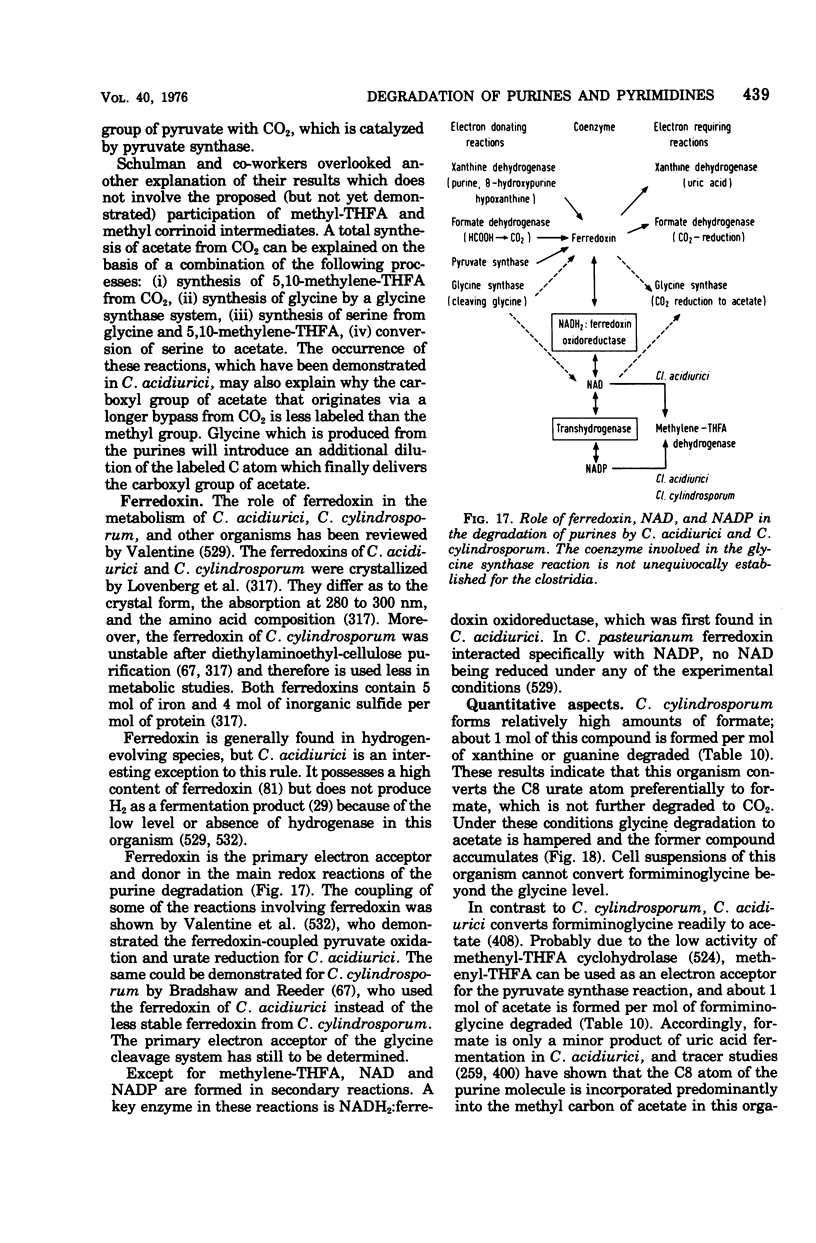
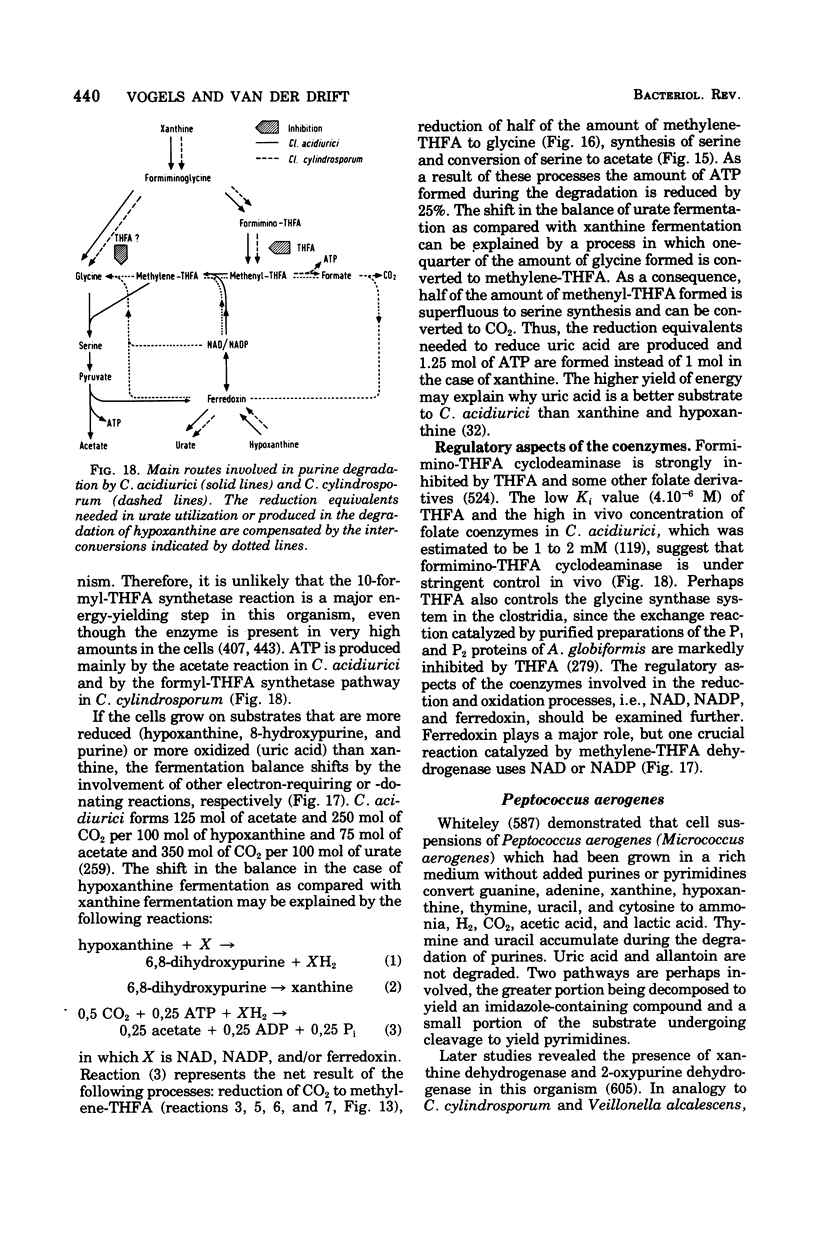
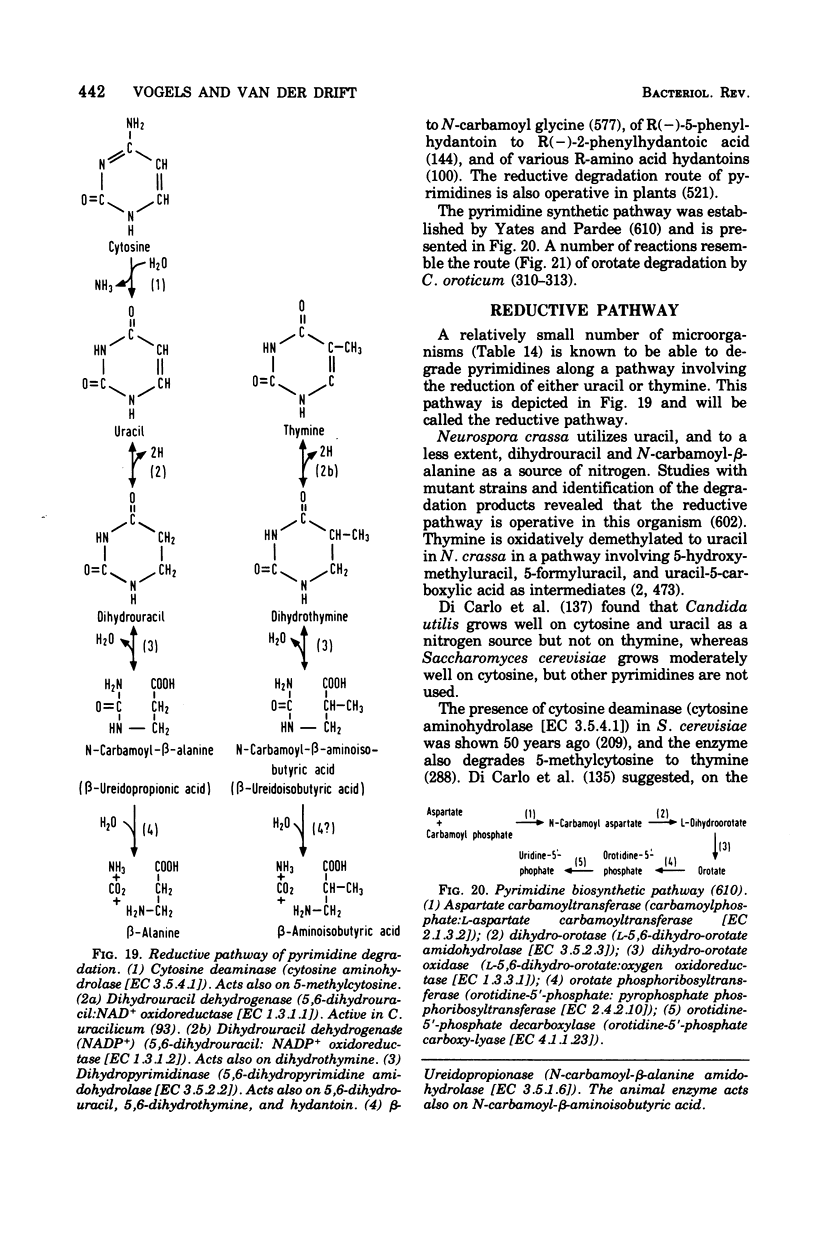
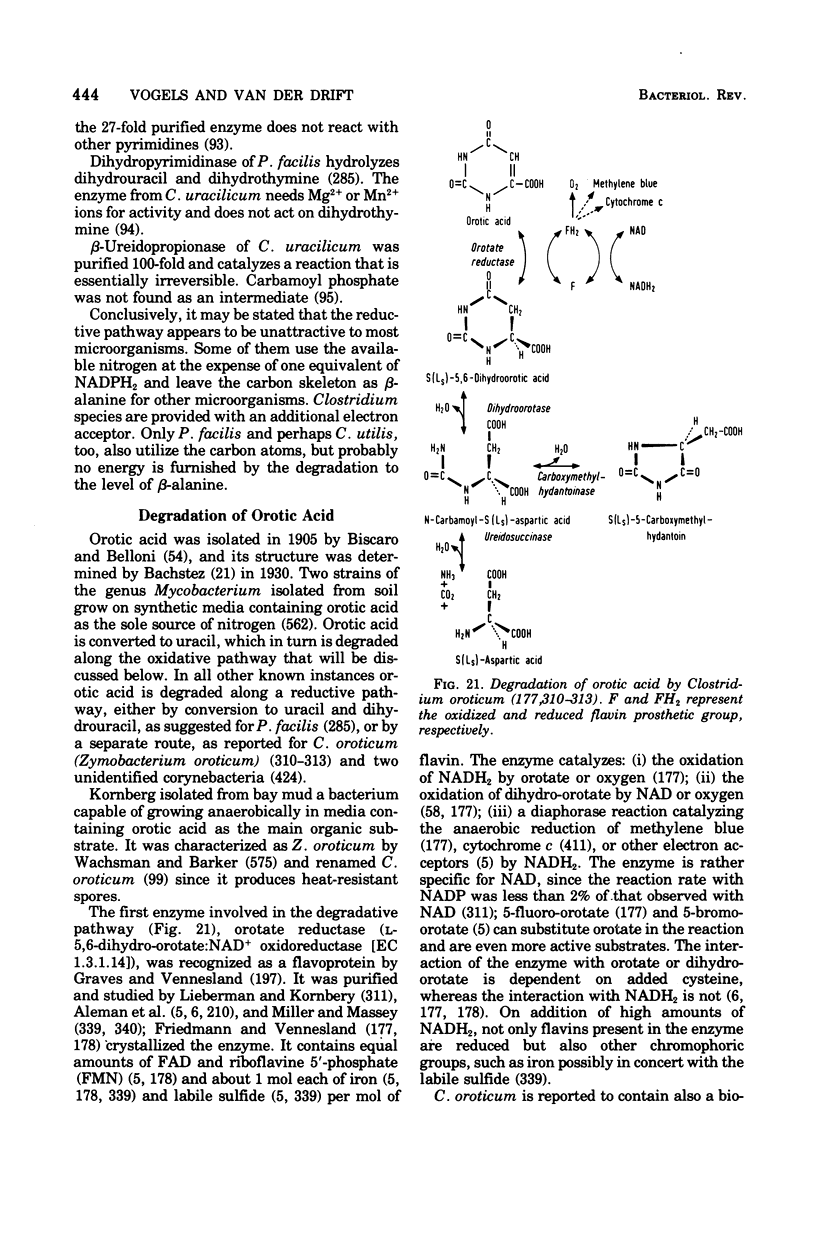
Full text
PDF















































Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AGARWALA S. C., MURTI C. R. K., SHRIVASTAVA D. L. Metabolism of purine and pyrimidine compounds by vibrios. Enzymologia. 1954 Mar 15;16(5):322–328. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- AMMANN E. C., LYNCH V. H. PURINE METABOLISM BY UNICELLULAR ALGAE. II. ADENINE, HYPOXANTHINE, AND XANTHINE DEGRADATION BY CHORELLA PYRENOIDOSA. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1964 Jul 22;87:370–379. doi: 10.1016/0926-6550(64)90110-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ANDREWS J. C., SELL I. T. The properties and interrelationship of oxaluric and parabanic acids. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1955 Jun;56(2):405–411. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(55)90261-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Abbondandolo A., Weyer A., Heslot H., Lambert M. Study of adenine aminohydrolase in the yeast, Schizosaccharomyces pombe. J Bacteriol. 1971 Dec;108(3):959–963. doi: 10.1128/jb.108.3.959-963.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Abbott M. T., Schandl E. K., Lee R. F., Parker T. S., Midgett R. J. Cofactor requirements of thymine 7-hydroxylase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1967 Mar 15;132(2):525–528. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(67)90177-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aleman V., Handler P. Dihydroorotate dehydrogenase. I. General properties. J Biol Chem. 1967 Sep 25;242(18):4087–4096. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allam A. M., Elzainy T. A. Degradation of xanthine by Penicillium chrysogenum. J Gen Microbiol. 1969 Jun;56(3):293–300. doi: 10.1099/00221287-56-3-293. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allam A. M., Elzainy T. A. Purine catabolism in Fusarium moniliforme. J Gen Microbiol. 1970 Oct;63(2):183–187. doi: 10.1099/00221287-63-2-183. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ammann E. C., Lynch V. H. Purine metabolism by unicellular algae. 3. The photochemical degradation of uric acid by chlorophyll. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 May 12;120(1):181–182. doi: 10.1016/0926-6585(66)90295-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ammann E. C., Reed L. L. Metabolism of nitrogen compounds by Hydrogenomonas eutropha. I. Utilization of uric acid, allantoin, hippuric acid, and creatinine. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1967 Jun 13;141(1):135–143. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(67)90252-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andreesen J. R., El Ghazzawi E., Gottschalk G. The effect of ferrous ions, tungstate and selenite on the level of formate dehydrogenase in Clostridium formicoaceticum and formate synthesis from CO2 during pyruvate fermentation. Arch Mikrobiol. 1974 Mar 4;96(2):103–118. doi: 10.1007/BF00590167. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Antheunisse J. Decomposition of nucleic acids and some of their degradation products by microorganisms. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1972;38(3):311–327. doi: 10.1007/BF02328101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arima K., Nose K. Studies on bacterial urate:oxygen oxidoreductase. I. Purification and properties of the enzyme. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Jan 8;151(1):54–62. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(68)90160-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arst H. N., Jr, MacDonald D. W., Cove D. J. Molybdate metabolism in Aspergillus nidulans. I. Mutations affecting nitrate reductase and-or xanthine dehydrogenase. Mol Gen Genet. 1970;108(2):129–145. doi: 10.1007/BF02430519. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BACHRACH U. The aerobic breakdown of uric acid by certain pseudomonads. J Gen Microbiol. 1957 Aug;17(1):1–11. doi: 10.1099/00221287-17-1-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BALIS M. E., LEVIN D. H., BROWN G. B., ELION G. B., VANDERWERFF H., HITCHINGS G. H. The incorporation of exogenous purines into pentose nucleic acid by Lactobacillus casei. J Biol Chem. 1952 May;196(2):729–747. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BARKULIS S. S., KRAKOW G. Conversion of glyoxylate to hydroxypyruvate by extracts of Escherichia coli. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1956 Sep;21(3):593–594. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(56)90208-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BAUM H. M., HUBSCHER G., MAHLER H. R. Enzymatic oxidation of urate. Science. 1956 Oct 19;124(3225):705–708. doi: 10.1126/science.124.3225.705. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BAUM H., HUBSCHER G., MAHLER H. R. Studies on uricase. II. The enzyme-substrate complex. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1956 Dec;22(3):514–527. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(56)90062-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BAUM H., HUBSCHER G., MAHLER H. R. Studies on uricase. III. The oxidation of uric acid by model copper complexes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1956 Dec;22(3):528–536. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(56)90063-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BECK J. V., SAGERS R. D., MORRIS L. R. Intermediary metabolism of Clostridium acidi-urici. I. Formation of pyruvate from glycine. J Bacteriol. 1957 Apr;73(4):465–469. doi: 10.1128/jb.73.4.465-469.1957. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BECK J. V., SAGERS R. D. Studies on the formation of formate, glycine, serine, pyruvate and acetate from purines by Clostridium acidi-urici. J Bacteriol. 1956 Aug;72(2):199–208. doi: 10.1128/jb.72.2.199-208.1956. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BENTLEY R., NEUBERGER A. The mechanism of the action of uricase. Biochem J. 1952 Dec;52(4):694–699. doi: 10.1042/bj0520694. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BENZIMAN M., SAGERS R. D., GUNSALUS I. C. L-serine specific dehydrase from Clostridium acidi-urici. J Bacteriol. 1960 Apr;79:474–479. doi: 10.1128/jb.79.4.474-479.1960. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BERGMANN F., DIKSTEIN S., HENIS Y. Studies on uric acid and related compounds. IV. The specificity of bacterial xanthine oxidases. J Biol Chem. 1957 Jan;224(1):67–77. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BERGMANN F., KWIETNY H., LEVIN G., ENGELBERG H. Studies on the enzymic oxidation of aminopurines. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1960 Jan 29;37:433–441. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(60)90499-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BERGMANN F., UNGAR-WARON H., KWIETNY-GOVRIN H., GOLDBERG H., LEON S. Some specific reactions of the purine-oxidizing system of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1962 Apr 2;55:512–522. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(62)90984-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BIRDSEY E. C., LYNCH V. H. Utilization of nitrogen compounds by unicellular algae. Science. 1962 Sep 7;137(3532):763–764. doi: 10.1126/science.137.3532.763. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BOJANOWSKI R., GAUDY E., VALENTINE R. C., WOLFE R. S. OXAMIC TRANSCARBAMYLASE OF STREPTOCOCCUS ALLANTOICUS. J Bacteriol. 1964 Jan;87:75–80. doi: 10.1128/jb.87.1.75-80.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRILL W. J., WOLIN E. A., WOLFE R. S. ANAEROBIC FORMATE OXIDATION: A FERREDOXIN-DEPENDENT REACTION. Science. 1964 Apr 17;144(3616):297–298. doi: 10.1126/science.144.3616.297. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BROOKE M. S., MAGASANIK B. The metabolism of purines in Aerobacter aerogenes: a study of purineless mutants. J Bacteriol. 1954 Dec;68(6):727–733. doi: 10.1128/jb.68.6.727-733.1954. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BUCHANAN B. B., LOVENBERG W., RABINOWITZ J. C. A comparison of clostridial ferredoxins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1963 Mar 15;49:345–353. doi: 10.1073/pnas.49.3.345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baginsky M. L., Huennekens F. M. Electron transport function of a heat-stable protein and a flavoprotein in the oxidative decarboxylation of glycine by Peptococcus glycinophilus. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1966 Jun 13;23(5):600–605. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(66)90441-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ban J., Vitale L., Kos E. Thymine and uracil catabolism in Escherichia coli. J Gen Microbiol. 1972 Nov;73(2):267–272. doi: 10.1099/00221287-73-2-267. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bare L. N., Wiseman R. F., Ruchman I. Uricolysis by Escherichia spp.. Appl Microbiol. 1966 May;14(3):474–474. doi: 10.1128/am.14.3.474-.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barker H. A., Beck J. V. Clostridium acidi-uridi and Clostridium cylindrosporum, Organisms Fermenting Uric Acid and Some Other Purines. J Bacteriol. 1942 Mar;43(3):291–304. doi: 10.1128/jb.43.3.291-304.1942. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barker H. A. Streptococcus allantoicus and the Fermentation of Allantoin. J Bacteriol. 1943 Sep;46(3):251–259. doi: 10.1128/jb.46.3.251-259.1943. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnes E. M., Impey C. S. The occurence and properties of uric acid decomposing anaerobic bacteria in the avian caecum. J Appl Bacteriol. 1974 Sep;37(3):393–409. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1974.tb00455.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Battelli M. G., Lorenzoni E., Stripe F. Milk xanthine oxidase type D (dehydrogenase) and type O (oxidase). Purification, interconversion and some properties. Biochem J. 1973 Feb;131(2):191–198. doi: 10.1042/bj1310191. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beck C. F., Ingraham J. L., Neuhard J., Thomassen E. Metabolism of pyrimidines and pyrimidine nucleosides by Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1972 Apr;110(1):219–228. doi: 10.1128/jb.110.1.219-228.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergmann F., Ungar-Waron H., Kwietny-Govrin H. Action of 8-azaguanine and 8-azaxanthine on Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Biochem J. 1964 May;91(2):270–276. doi: 10.1042/bj0910270. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J. The physiology of excretion in the cotton stainer, Dysdercus fasciatus signoret. 3. Nitrogen excretion and excretory metabolism. J Exp Biol. 1965 Dec;43(3):535–552. doi: 10.1242/jeb.43.3.535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blair R. Evaluation of dehydrated poultry waste as a feed ingredient for poultry. Fed Proc. 1974 Aug;33(8):1934–1936. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blattmann P., Rétey J. Stereospecificity of the dihydroorotate-dehydrogenase reaction. Eur J Biochem. 1972 Oct 17;30(1):130–137. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1972.tb02079.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bongaerts G. P., Vogels G. D. Uric acid degradation by Bacillus fastidiosus strains. J Bacteriol. 1976 Feb;125(2):689–697. doi: 10.1128/jb.125.2.689-697.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bordeleau L. M., Lachance R. A. Effets des purines et des pyrimidines sur la croissance de Corynebacterium sepedonicum (Spiek. & Kott.) Skapt. & Burkh. Can J Microbiol. 1968 Apr;14(4):475–478. doi: 10.1139/m68-075. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braná H. Degradation of 5' adenosine monophosphate in a cell-free system of Escherichia coli. Folia Microbiol (Praha) 1967;12(1):1–5. doi: 10.1007/BF02895083. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brodie J. D. Origin of photolabile methyl groups in methionine biosynthesis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1967 Feb 8;26(3):261–264. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(67)90115-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brogard J. M., Coumaros D., Franckhauser J., Stahl A., Stahl J. Enzymatic uricolysis: a study of the effect of a fungal urate-oxydase. Rev Eur Etud Clin Biol. 1972 Nov;17(9):890–895. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broughton W. J., Dilworth M. J., Passmore I. K. Base ratio determination using unpurified DNA. Anal Biochem. 1972 Mar;46(1):164–172. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(72)90408-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown G. W., Jr, James J., Henderson R. J., Thomas W. N., Robinson R. O., Thompson A. L., Brown E., Brown S. G. Uricolytic enzymes in liver of the Dipnoan Protopterus aethiopicus. Science. 1966 Sep 30;153(3744):1653–1654. doi: 10.1126/science.153.3744.1653. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bryant M. P. Nutritional features and ecology of predominant anaerobic bacteria of the intestinal tract. Am J Clin Nutr. 1974 Nov;27(11):1313–1319. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/27.11.1313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buttlaire D. H., Hersh R. T., Himes R. H. Hydrogen ion-induced reversible inactivation and dissociation of formyltetrahydrofolate synthetase. J Biol Chem. 1972 Apr 10;247(7):2059–2068. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buttlaire D. H., Reed G. H., Himes R. Electron paramagnetic resonance and water proton relaxation rate studies of formyltetrahydrofolate synthetase-manganous ion complexes. Evidence for involvement of substrates in the promotion of a catalytically competent active site. J Biol Chem. 1975 Jan 10;250(1):261–270. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CAMPBELL L. L., Jr Oxidative degradation of uric acid by cell extracts of a Pseudomonas. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1955 Sep;18(1):160–161. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(55)90035-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CAMPBELL L. L., Jr Reductive degradation of pyrimidines. I. The isolation and characterization of a uracil fermenting bacterium, Clostridium uracilicum nov. spec. J Bacteriol. 1957 Feb;73(2):220–224. doi: 10.1128/jb.73.2.220-224.1957. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CAMPBELL L. L., Jr Reductive degradation of pyrimidines. II. Mechanism of uracil degradation by Clostridium uracilicum. J Bacteriol. 1957 Feb;73(2):225–229. doi: 10.1128/jb.73.2.225-229.1957. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CAMPBELL L. L., Jr Reductive degradation of pyrimidines. III. Purification and properties of dihydrouracil dehydrogenase. J Biol Chem. 1957 Aug;227(2):693–700. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CAMPBELL L. L., Jr Reductive degradation of pyrimidines. IV. Purification and properties of dihydrouracil hydrase. J Biol Chem. 1958 Nov;233(5):1236–1240. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CAMPBELL L. L., Jr The mechanism of allantoin degradation by a Pseudomonas. J Bacteriol. 1954 Nov;68(5):598–603. doi: 10.1128/jb.68.5.598-603.1954. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CAMPBELL L. L. Reductive degradation of pyrimidines. 5. Enzymatic conversion of N-carbamyl-beta-alanine to beta-alanine, carbon dioxide, and ammonia. J Biol Chem. 1960 Aug;235:2375–2378. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CANELLAKIS E. S., COHEN P. P. The end-products and intermediates of uric acid oxidation by uricase. J Biol Chem. 1955 Mar;213(1):385–395. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CANELLAKIS E. S., TUTTLE A. L., COHEN P. P. A comparative study of the end-products of uric acid oxidation by peroxidases. J Biol Chem. 1955 Mar;213(1):397–404. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cecere F., Galli G., Morisi F. Substrate and steric specificity of hydropyrimidine hydrase. FEBS Lett. 1975 Sep 15;57(2):192–194. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(75)80714-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen C. C., Rettger L. F. A Correlation Study of the Colon-Aerogenes Group of Bacteria, with Special Reference to the Organisms Occurring in the Soil. J Bacteriol. 1920 May;5(3):253–298. doi: 10.1128/jb.5.3.253-298.1920. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Childs G. E. Hartmannella culbertsoni: enzymatic, ultrastructural, and cytochemical characteristics of peroxisomes in a density gradient. Exp Parasitol. 1973 Aug;34(1):44–55. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(73)90061-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choi K. S., Lee K. W., Hico S. C., Roush A. H. Assay, purification and properties of allantoicase from Candida utilis. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1968 Jul;126(1):261–268. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(68)90582-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choi K. S., Lee K. W., Roush A. H. The assay of yeast ureidoglycolatase. Anal Biochem. 1966 Dec;17(3):413–422. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(66)90177-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christen P., Peacock W. C., Christen A. E., Wacker W. E. Urate oxidase in primate phylogenesis. Eur J Biochem. 1970 Jan;12(1):3–5. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1970.tb00813.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coleman G. S., Laurie J. I. The metabolism of starch, glucose, amino acids, purines, pyrimidines and bacteria by three Epidinium spp. isolated from the rumen. J Gen Microbiol. 1974 Dec;85(2):244–256. doi: 10.1099/00221287-85-2-244. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper T. G., Lawther R. Induction of the allantoin degradative enzymes by allophanic acid, the last intermediate of the pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1973 May 1;52(1):137–142. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(73)90965-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper T. G., Sumrada R. Urea transport in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Bacteriol. 1975 Feb;121(2):571–576. doi: 10.1128/jb.121.2.571-576.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corte E. D., Stirpe F. The regulation of rat liver xanthine oxidase. Involvement of thiol groups in the conversion of the enzyme activity from dehydrogenase (type D) into oxidase (type O) and purification of the enzyme. Biochem J. 1972 Feb;126(3):739–745. doi: 10.1042/bj1260739. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coulter W. H., Costilow R. N. The role of barbituric acid in the nutrition of Bacillus popilliae. Can J Microbiol. 1970 Sep;16(9):801–807. doi: 10.1139/m70-135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curthoys N. P., D'Ari Straus L., Rabinowitz J. C. Formyltetrahydrofolate synthetase. Substrate binding to monomeric subunits. Biochemistry. 1972 Feb 1;11(3):345–349. doi: 10.1021/bi00753a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curthoys N. P., Rabinowitz J. C. Formyltetrahydrofolate synthetase. Binding of folate substrates and kinetics of the reverse reaction. J Biol Chem. 1972 Apr 10;247(7):1965–1971. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAGLEY S., TRUDGILL P. W., CALLELY A. G. Synthesis of cell constituents from glycine by a Pseudomonas. Biochem J. 1961 Dec;81:623–631. doi: 10.1042/bj0810623. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DI CARLO F. J., SCHULTZ A. S., KENT A. M. On the mechanism of pyrimidine metabolism by yeasts. J Biol Chem. 1952 Nov;199(1):333–343. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DI CARLO F. J., SCHULTZ A. S., KENT A. M. The mechanism of allantoin catabolism by yeast. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1953 Jun;44(2):468–474. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(53)90064-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DI FONZA M. Purine enzymes in mycobacteria. Am Rev Tuberc. 1952 Aug;66(2):240–243. doi: 10.1164/art.1952.66.2.240. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DOMNAS A. Amide metabolism in yeasts. II. The uptake of amide and amide like compounds by yeast. J Biochem. 1962 Sep;52:149–154. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalal F. R., Gots J. S. Inhibition of 5,10-methylenetetrahydrofolate dehydrogenase by purine nucleotides. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1966 Feb 3;22(3):340–345. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(66)90488-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darlington A. J., Scazzocchio C. Evidence for an alternative pathway of xanthine oxidation in Aspergillus nidulans. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Sep 24;166(2):569–571. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(68)90244-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darlington A. J., Scazzocchio C., Pateman J. A. Biochemical and genetical studies of purine breakdown in Aspergillus. Nature. 1965 May 8;206(984):599–600. doi: 10.1038/206599a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis R. H. Sources of urea in Neurospora. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Aug 14;215(2):412–414. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(70)90042-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Duve C., Baudhuin P. Peroxisomes (microbodies and related particles). Physiol Rev. 1966 Apr;46(2):323–357. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1966.46.2.323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Demain A. L., Hendlin D. Phosphohydrolases of a Bacillus subtilis mutant accumulating inosine and hypoxanthine. J Bacteriol. 1967 Jul;94(1):66–74. doi: 10.1128/jb.94.1.66-74.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Di CARLO F. J., SCHULTZ A. S., McMANUS D. K. The assimilation of nucleic acid derivatives and related compounds by yeasts. J Biol Chem. 1951 Mar;189(1):151–157. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Domagk G. F., Schlicke H. H. A colorimetric method using uricase and peroxidase for the determination of uric acid. Anal Biochem. 1968 Feb;22(2):219–224. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(68)90309-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donnellan J. F., Kilby B. A. Uric acid metabolism by symbiotic bacteria from the fat body of Periplaneta americana. Comp Biochem Physiol. 1967 Jul;22(1):235–252. doi: 10.1016/0010-406x(67)90184-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dudley K. H., Butler T. C., Bius D. L. The role of dihydropyrimidinase in the metabolism of some hydantoin and succinimide drugs. Drug Metab Dispos. 1974 Mar-Apr;2(2):103–112. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dumas R., Castel J., Jean R. Urate oxydase en pédiatrie. Pathol Biol (Paris) 1973 Apr;21(4):425–429. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EICHEL H. J. Purine-metabolizing enzymes of Tetrahymena pyriformis. J Biol Chem. 1956 May;220(1):209–220. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edmondson D., Massey V., Palmer G., Beacham L. M., 3rd, Elion G. B. The resolution of active and inactive xanthine oxidase by affinity chromatography. J Biol Chem. 1972 Mar 10;247(5):1597–1604. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edozien J. C., Udo U. U., Young V. R., Scrimshaw N. S. Effects of high levels of yeast feeding on uric acid metabolism of young man. Nature. 1970 Oct 10;228(5267):180–180. doi: 10.1038/228180a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FERGUSON W. S., TERRY R. A. Purines in grassland herbage. Nature. 1953 Aug 15;172(4372):346–347. doi: 10.1038/172346b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FINK R. M., FINK K., HENDERSON R. B. beta-amino acid formation by tissue slices incubated with pyrimidines. J Biol Chem. 1953 Mar;201(1):349–355. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRANKE W., HAHN G. E. Untersuchungen zum bakteriellen Purin-Abbau. II. Uber den Abbau von Amino-, Oxy - und Methyl-purinen durch Pseudomonas aeruginosa (B. pyocyaneum). Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1955 Jun 30;301(1-2):90–106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRANKE W., HAHN G. E. Untersuchungen zum bakteriellen Purinabbau. I. Uber den Harnsäureabbau durch Pseudomonas aeurginosa (Badt. pyocyaneum). Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1955;299(1):15–38. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRANKE W. Zum Stoffwechsel der Purine und Pyrimidine. Z Vitam Horm Fermentforsch. 1953;5(4):279–314. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRIDOVICH I. THE COMPETITIVE INHIBITION OF URICASE BY OXONATE AND BY RELATED DERIVATIVES OF S-TRIAZINES. J Biol Chem. 1965 Jun;240:2491–2494. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRIEDMANN H. C., VENNESLAND B. Crystalline dihydroorotic dehydrogenase. J Biol Chem. 1960 May;235:1526–1532. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRIEDMANN H. C., VENNESLAND B. Purification and properties of dihydro-orotic dehydrogenase. J Biol Chem. 1958 Dec;233(6):1398–1406. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRIEDMAN S., GOTS J. S. Deamination of isoguanine by Escherichia coli. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1951 Jun;32(1):227–229. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(51)90263-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forster R. P., Goldstein L. Urea synthesis in the lungfish: relative importance of purine and ornithine cycle pathways. Science. 1966 Sep 30;153(3744):1650–1652. doi: 10.1126/science.153.3744.1650. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franke W., Thiemann A., Remily C., Möchel L., Heye K. Zur Kenntnis ureidspaltender Enzyme. I. Soja-Allantoinase. Enzymologia. 1965 Nov 6;29(3):251–271. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOLDFINE H., STADTMAN E. R. Propionic acid metabolism. 5. The conversion of beta-alanine to propionic acid by cellfree extracts of Clostridium propioncum. J Biol Chem. 1960 Aug;235:2238–2245. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOLDSTEIN L., FORSTER R. P. THE ROLE OF URICOLYSIS IN THE PRODUCTION OF UREA BY FISHES AND OTHER AQUATIC VERTEBRATES. Comp Biochem Physiol. 1965 Apr;14:567–576. doi: 10.1016/0010-406x(65)90246-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOTTO A. M., KORNBERG H. L. The metabolism of C2 compounds in micro-organisms. 7. Preparation and properties of crystalline tartronic semialdehyde reductase. Biochem J. 1961 Nov;81:273–284. doi: 10.1042/bj0810273. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRAVES J. L., VENNESLAND B. The stereospecific hydrogen exchange in the dihydroorotic dehydrogenase reaction. J Biol Chem. 1957 May;226(1):307–316. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRAY C. T., BROOKE M. S., GERHART J. C. Metabolism of alloxanic acid in a soil microorganism. J Bacteriol. 1961 May;81:755–761. doi: 10.1128/jb.81.5.755-761.1961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREENE R. C., MITCHELL H. K. Uricase in Neurospora crassa. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1957 Aug;70(2):603–613. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(57)90148-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRIFFITHS M. Oxidations of uric acid catalyzed by copper and by the cytochrome oxidase system. J Biol Chem. 1952 May;197(1):399–407. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GUPTA N. K., VENNESLAND B. GLYOXYLATE CARBOLIGASE OF ESCHERICHIA COLI: A FLAVOPROTEIN. J Biol Chem. 1964 Nov;239:3787–3789. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gassner E. B. On the Pigment Absorbing at 750 mmu Occurring in Some Blue-Green Algae. Plant Physiol. 1962 Sep;37(5):637–639. doi: 10.1104/pp.37.5.637. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaudy E. T., Bojanowski R., Valentine R. C., Wolfe R. S. Ureidoglycolate synthetase of Streptococcus allantoicus. I. Measurement of glyoxylate and enzyme purification. J Bacteriol. 1965 Dec;90(6):1525–1530. doi: 10.1128/jb.90.6.1525-1530.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaudy E. T., Wolfe R. S. Ureidoglycolate synthetase of Streptococcus allantoicus. II. Properties of the enzyme and reaction equilibrium. J Bacteriol. 1965 Dec;90(6):1531–1536. doi: 10.1128/jb.90.6.1531-1536.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerhardt B. Zur Lokalisation von Enzymen der Microbodies in Polytomella caeca. Arch Mikrobiol. 1971;80(3):205–218. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gifford C. A. Accumulation of uric acid in the land crab, Cardisoma guanhumi. Am Zool. 1968 Aug;8(3):521–528. doi: 10.1093/icb/8.3.521. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodfellow M., Lind A., Mordarska H., Pattyn S., Tsukamura M. A co-operative numerical analysis of cultures considered to belong to the 'rhodochrous' taxon. J Gen Microbiol. 1974 Dec;85(2):291–302. doi: 10.1099/00221287-85-2-291. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gravenmade E. J., Vogels G. D., Van der Drift C. Hydrolysis, racemization and absolute configuration of ureidoglycolate, a substrate of allantoicase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Mar 18;198(3):569–582. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(70)90134-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grenson M. The utilization of exogenous pyrimidines and the recycling of uridine-5'-phosphate derivatives in Saccharomyces cerevisiae, as studied by means of mutants affected in pyrimidine uptake and metabolism. Eur J Biochem. 1969 Dec;11(2):249–260. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1969.tb00767.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grigg G. W. Effects of coumarin, pyronin Y, 6,9-dimethyl 2-methylthiopurine and caffeine on excision repair and recombination repair in Escherichia coli. J Gen Microbiol. 1972 Apr;70(2):221–230. doi: 10.1099/00221287-70-2-221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HANDLER P., RAJAGOPALAN K. V., ALEMAN V. STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION OF IRON-FLAVOPROTEINS. Fed Proc. 1964 Jan-Feb;23:30–38. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HARVEY A. M., CHRISTENSEN H. N. URIC ACID TRANSPORT SYSTEM: APPARENT ABSENCE IN ERYTHROCYTES OF THE DALMATIAN COACH HOUND. Science. 1964 Aug 21;145(3634):826–827. doi: 10.1126/science.145.3634.826. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
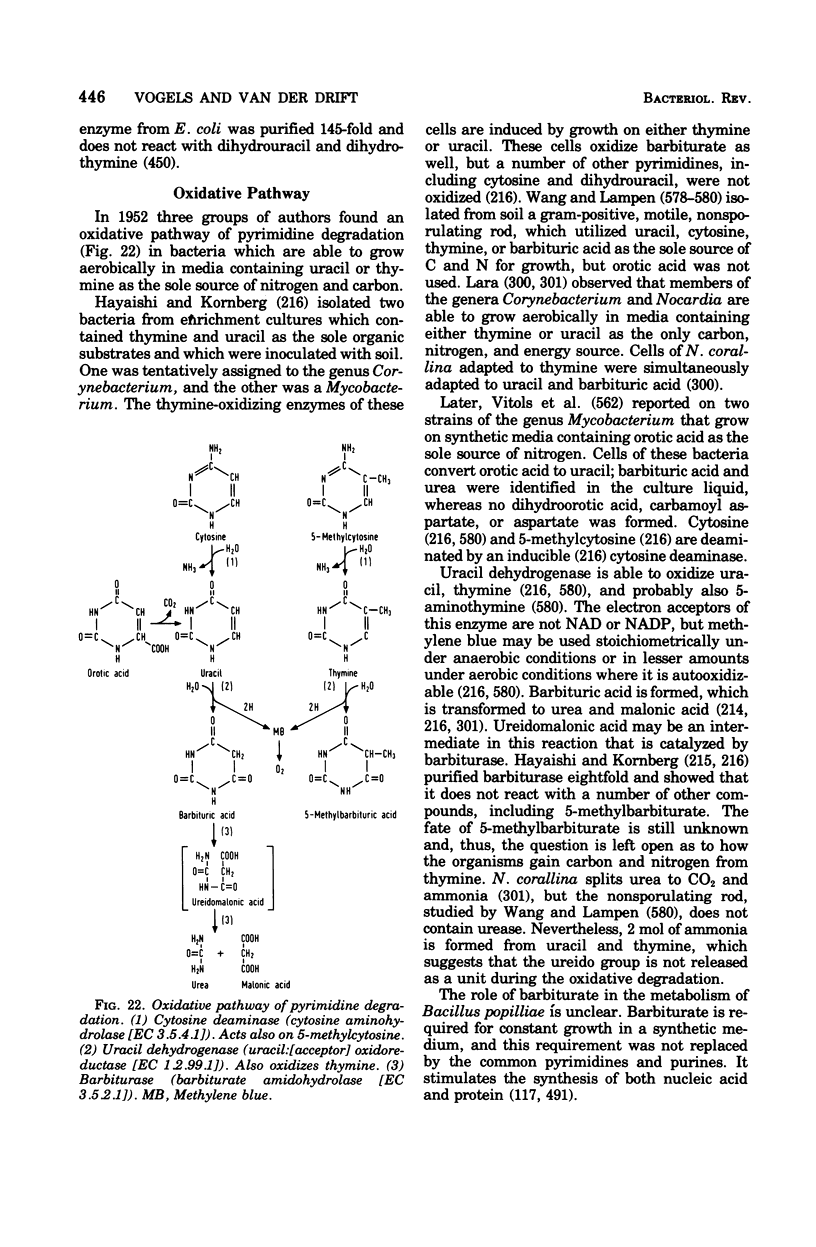
- HAYAISHI O., KORNBERG A. Metabolism of cytosine, thymine, uracil, and barbituric acid by bacterial enzymes. J Biol Chem. 1952 May;197(2):717–732. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAYAISHI O., NISHIZUKA Y., TATIBANA M., TAKESHITA M., KUNO S. Enzymatic studies on the metabolism of beta-alanine. J Biol Chem. 1961 Mar;236:781–790. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HEINRICH M. R., DEWEY V. C., KIDDER G. W. The origin of thymine and cytosine in Tetrahymena. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1957 Jul;25(1):199–200. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(57)90444-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HIMES R. H., RABINOWITZ J. C. Formyltetrahydrofolate synthetase. II. Characteristics of the enzyme and the enzymic reaction. J Biol Chem. 1962 Sep;237:2903–2914. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUBSCHER G., BAUM H., MAHLER H. R. Studies on uricase. IV. The nature and composition of some stable reaction products. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1957 Jan;23(1):43–53. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(57)90283-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartenstein R. C., Fridovich I. Adenine aminohydrolase. An investigation of specificity. J Biol Chem. 1967 Feb 25;242(4):740–746. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haury H. Enzymatische Bestimmung von Harnsäure als UV-Test. Med Klin. 1973 Sep 7;68(36):1161–1163. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayashi H., Suga T., Ninobe S. Studies on peroxisones. 3. Further studies on the intraparticulate localization of peroxisomal components in the liver of the rat. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Jan 24;297(1):110–119. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(73)90054-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill D. L., Chambers P. The purine and pyrimidine metabolism of Tetrahymena pyriformis. J Cell Physiol. 1967 Jun;69(3):321–329. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040690308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hilton M. G. The metabolism of pyrimidines by proteolytic clostridia. Arch Microbiol. 1975;102(2):145–149. doi: 10.1007/BF00428359. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hodson R. C., Williams S. K., 2nd, Davidson W. R., Jr Metabolic control of urea catabolism in Chlamydomonas reinhardi and Chlorella pyrenoidosa. J Bacteriol. 1975 Mar;121(3):1022–1035. doi: 10.1128/jb.121.3.1022-1035.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffmeyer J., Neuhard J. Metabolism of exogenous purine bases and nucleosides by Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1971 Apr;106(1):14–24. doi: 10.1128/jb.106.1.14-24.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holt S. C., Leadbetter E. R. Comparative ultrastructure of selected aerobic spore-forming bacteria: a freeze-etching study. Bacteriol Rev. 1969 Jun;33(2):346–378. doi: 10.1128/br.33.2.346-378.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horner C. K., Allison F. E. Utilization of Fixed Nitrogen by Azotobacter and Influence on Nitrogen Fixation. J Bacteriol. 1944 Jan;47(1):1–14. doi: 10.1128/jb.47.1.1-14.1944. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hosono R., Kuno S. Mechanism of inhibition of bacterial growth by adenine. J Biochem. 1974 Feb;75(2):215–220. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a130388. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howell L. G., Fridovich I. Adenine aminohydrolase. An investigation of mechanism. J Biol Chem. 1967 Nov 10;242(21):4930–4932. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imsenecki A. A., Popova L. S. Razlozhenie mochevoi kisloty aérobnymi bakteriiami, vydelennymi iz pochvy. Mikrobiologiia. 1971 Mar-Apr;40(2):269–274. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imsenecki A. A., Popova L. S. Vydelenie i kharakteristika mikroorganizmov, razlagaiushchikh mochevuiu kislotu. Mikrobiologiia. 1970 Sep-Oct;39(5):805–811. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingram L. O., Fisher W. D. Selective inhibition of deoxyribonucleic acid synthesis by 2-deoxyadenosine in the blue-green bacterium Agmenellum quadruplicatum. J Bacteriol. 1972 Oct;112(1):170–175. doi: 10.1128/jb.112.1.170-175.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James K. A., Tate W. P., Truscoe R. Effects of treatment with dithiothreitol on the extraction, activity and purification of ox-kidney urate oxidase. Enzymologia. 1969 Aug 29;37(2):131–152. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones M. E., Lipmann F. CHEMICAL AND ENZYMATIC SYNTHESIS OF CARBAMYL PHOSPHATE. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1960 Sep;46(9):1194–1205. doi: 10.1073/pnas.46.9.1194. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joyce B. K., Himes R. H. Formyltetrahydrofolate synthetase. A study of equilibrium reaction rates. J Biol Chem. 1966 Dec 10;241(23):5716–5724. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joyce B. K., Himes R. H. Formyltetrahydrofolate synthetase. Initial velocity and product inhibition studies. J Biol Chem. 1966 Dec 10;241(23):5725–5731. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Judewicz N. D., De Robertis E. M., Jr, Torres H. N. Control of uracil transport by cyclic AMP in E. coli. FEBS Lett. 1974 Sep 1;45(1):155–158. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(74)80834-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KONDO H., FRIEDMANN H. C., VENNESLAND B. Flavin changes accompanying adaptation of Zymobacterium oroticum to orotate. J Biol Chem. 1960 May;235:1533–1535. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KORNBERG H. L., GOTTO A. M. The metabolism of C2 compounds in micro-organisms. 6. Synthesis of cell constituents from glycollate by Pseudomonas sp. Biochem J. 1961 Jan;78:69–82. doi: 10.1042/bj0780069. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaltwasser H. Harnsäureabbau und Biosynthese der Enzyme Uricase, Glyoxylatcarboligase und Urease bei Hydrogenomonas H 16. I. Bildung von Glyoxylatcarbioligase und D-Glycerat-3-Dehydrogenase. Arch Mikrobiol. 1968;64(1):71–84. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaltwasser H. Harnsäureabbau und Biosynthese der Enzyme uricase, glyoxylatcarboligase und Urease bei Hydrogenomonas H 16. II. Einfluss von Harnsäure, Fructose und Stickstoffmangel. Arch Mikrobiol. 1969;65(3):288–302. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaltwasser H. Induktive Bildung partikelgebundener Uricase bei Hydrogenomonas H16 und anderen aeroben Bakterien. Arch Mikrobiol. 1968;60(2):160–171. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaltwasser H., Krämer J. Verwertung von Cytosin and Uracil durch Hydrogenomonas facilis und Hydrogenomonas H16. Arch Mikrobiol. 1968;60(2):172–181. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaltwasser H. Studies on the physiology of Bacillus fastidiosus. J Bacteriol. 1971 Sep;107(3):780–786. doi: 10.1128/jb.107.3.780-786.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaminskas E., Kimhi Y., Magasanik B. Urocanase and N-formimino-L-glutamate formiminohydrolase of Bacillus subtilis, two enzymes of the histidine degradation pathway. J Biol Chem. 1970 Jul 25;245(14):3536–3544. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kapp R., Stevens S. E., Jr, fox J. L. A survey of available nitrogen sources for growth of the blue-green alga, Agmenellum quadruplicatum. Arch Microbiol. 1975 Jun 22;104(2):135–138. doi: 10.1007/BF00447313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karibian D., Couchoud P. Dihydro-orotate oxidase of Escherichia coli K12: purification, properties, and relation to the cytoplasmic membrane. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Oct 17;364(2):218–232. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(74)90007-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karibian D. Dihydro-orotate dehydrogenase of Escherichia coli K12: effects of triton X-100 and phospholipids. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Apr 12;302(2):205–215. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(73)90149-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kearny J. J., Sagers R. D. Formate dehydrogenase from Clostridium acidiurici. J Bacteriol. 1972 Jan;109(1):152–161. doi: 10.1128/jb.109.1.152-161.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelln R. A., Warren R. A. Pyrimidine metabolism in Pseudomonas acidovorans. Can J Microbiol. 1974 Apr;20(4):427–433. doi: 10.1139/m74-067. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirschner L. B. Comparative physiology: invertebrate excretory organs. Annu Rev Physiol. 1967;29:169–196. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.29.030167.001125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kissel P., Lamarche M., Royer R. Modification of uricaemia and the excretion of uric acid nitrogen by an enzyme of fungal origin. Nature. 1968 Jan 6;217(5123):72–74. doi: 10.1038/217072a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein S. M., Sagers R. D. Glycine metabolism. 3. A flavin-linked dehydrogenase associated with the glycine cleavage system in Peptococcus glycinophilus. J Biol Chem. 1967 Jan 25;242(2):297–300. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein S. M., Sagers R. D. Glycine metabolism. I. Properties of the system catalyzing the exchange of bicarbonate with the carboxyl group of glycine in Peptococcus glycinophilus. J Biol Chem. 1966 Jan 10;241(1):197–205. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein S. M., Sagers R. D. Glycine metabolism. II. Kinetic and optical studies on the glycine decarboxylase system from Peptococcus glycinophilus. J Biol Chem. 1966 Jan 10;241(1):206–209. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein S. M., Sagers R. D. Glycine metabolism. IV. Effect of borohydride reduction on the pyridoxal phosphate-containing glycine decarboxylase from Peptococcus glycinophilus. J Biol Chem. 1967 Jan 25;242(2):301–305. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klemperer F., Scott C., Bagchi S. Uric acid oxidation by mycobacteria. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1967 May;95(5):833–837. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1967.95.5.833. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knutsen G. Degradation of uracil by synchronous cultures of Chlorella fusca. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 May 29;269(3):333–343. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(72)90119-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kochi H., Kikuchi G. Mechanism of the reversible glycine cleavage reaction in Arthrobacter globiformis. I. Purification and function of protein components required for the reaction. J Biochem. 1974 May;75(5):1113–1127. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a130483. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krenitsky T. A., Tuttle J. V., Cattau E. L., Jr, Wang P. A comparison of the distribution and electron acceptor specificities of xanthine oxidase and aldehyde oxidase. Comp Biochem Physiol B. 1974 Dec 15;49(4):687–703. doi: 10.1016/0305-0491(74)90256-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krämer J., Kaltwasser H., Schlegel H. G. Die Bedutung der Ureaserepression für die taxonomische Klassifizierung von Bakterine. Zentralbl Bakteriol Parasitenkd Infektionskr Hyg. 1967;121(4):414–423. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krämer J., Kaltwasser H. Verwertung von Pyrimidinderivaten durch Hydrogenomonas facilis. I. Intermediärprodukte und Enzyme des Cytosinabbaues. Arch Mikrobiol. 1969;68(3):227–235. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krämer J., Kaltwasser H. Verwertung von Pyrimidinderivaten durch Hydrogenomonas facilis. II. Abbau von Thymin und Uracil durch Wildstamm und Mutanten. Arch Mikrobiol. 1969;69(2):138–148. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurtzman R. H., Jr, Schwimmer S. Caffeine removal from growth media by microorganisms. Experientia. 1971 Apr 15;27(4):481–482. doi: 10.1007/BF02137327. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuster G., Shorter R. G., Dawson B., Hallenbeck G. A. Uric acid metabolism in dalmatians and other dogs. Role of the liver. Arch Intern Med. 1972 Mar;129(3):492–496. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LAHOU J. Metabolisme de la guanine-8-14C chez la levure. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1958 Feb;27(2):371–377. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(58)90344-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LARA F. J. S. On the decomposition of pyrimidines by bacteria. I. Studies by means of the technique of simultaneous adaptation. J Bacteriol. 1952 Aug;64(2):271–277. doi: 10.1128/jb.64.2.271-277.1952. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LARA F. J. S. On the decomposition of pyrimidines by bacteria. II. Studies with cell-free enzyme preparations. J Bacteriol. 1952 Aug;64(2):279–285. doi: 10.1128/jb.64.2.279-285.1952. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEBOY P. S., CLINE S. G., CONNER R. L. PHOSPHATE, PURINES AND PYRIMIDINES AS EXCRETORY PRODUCTS OF TETRAHYMENA. J Protozool. 1964 May;11:217–222. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1964.tb01743.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEE K. W., ROUSH A. H. ALLANTOINASE ASSAYS AND THEIR APPLICATION TO YEAST AND SOYBEAN ALLANTOINASES. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1964 Dec;108:460–467. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(64)90427-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LIEBERMAN I., KORNBERG A. Enzymatic synthesis and breakdown of a pyrimidine, orotic acid. I. Dihydroortic acid, ureidosuccinic acid, and 5-carboxymethylhydantoin. J Biol Chem. 1954 Apr;207(2):911–924. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LIEBERMAN I., KORNBERG A. Enzymatic synthesis and breakdown of a pyrimidine, orotic acid. III. Ureidosuccinase. J Biol Chem. 1955 Feb;212(2):909–920. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LIEBERMAN I., KORNBERG A. Enzymic synthesis and breakdown of a pyrimidine, orotic acid. I. Dihydro-orotic dehydrogenase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1953 Sep-Oct;12(1-2):223–234. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(53)90141-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOVENBERG W., BUCHANAN B. B., RABINOWITZ J. C. STUDIES ON THE CHEMICAL NATURE OF CLOSTRIDIAL FERREDOXIN. J Biol Chem. 1963 Dec;238:3899–3913. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LaRue T. A., Spencer J. F. The utilization of purines and pyrimidines by yeasts. Can J Microbiol. 1968 Jan;14(1):79–86. doi: 10.1139/m68-012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laboureur P., Langlois C. Propriétés d'une urate oxydase fongique à haute activité. C R Acad Sci Hebd Seances Acad Sci D. 1967 May 3;264(18):2244–2246. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laboureur P., Langlois C. Urate oxydase d'Aspergillus flavus. I. Obtention, purification, propriétés. Bull Soc Chim Biol (Paris) 1968;50(4):811–825. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laboureur P., Langlois C. Urate oxydase d'Aspergillus flavus. II. Métabolisme, inhibitions, spécificité. Bull Soc Chim Biol (Paris) 1968;50(4):827–841. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lacey J., Goodfellow M., Lacy J., Goodfellow M. A novel actinomycete from sugar-cane bagasse: Saccharopolyspora hirsuta gen. et. sp. nov. J Gen Microbiol. 1975 May;88(1):75–85. doi: 10.1099/00221287-88-1-75. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis J. B. Nitrogenous excretion in the tropical sea urchin Diadema antillarum Philippi. Biol Bull. 1967 Feb;132(1):34–37. doi: 10.2307/1539875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ljungdahl L. G. Total synthesis of acetate from CO2 by heterotrophic bacteria. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1969;23:515–538. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.23.100169.002503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lockwood G. F., Garrison R. G. The possibel role of uric acid in the ecology of Histoplasma capsulatum. Mycopathol Mycol Appl. 1968 Oct 14;35(3):377–388. doi: 10.1007/BF02050753. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lui N. S., Roels O. A. Nitrogen metabolism of aquatic organisms. I. The assimilation and formation of urea in Ochromonas malhamensis. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1970 Aug;139(2):269–277. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(70)90478-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lui N. S., Roels O. A., Trout M. E., Anderson O. R. Subcellular distribution of enzymes in Ochromonas malhamensis. J Protozool. 1968 Aug;15(3):536–542. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1968.tb02171.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lund P., Magasanik B. N-formimino-L-glutamate formiminohydrolase of Aerobacter aerogenes. J Biol Chem. 1965 Nov;240(11):4316–4319. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAGASANIK B., BOWSER H. R. The degradation of histidine by Aerobacter aerogenes. J Biol Chem. 1955 Apr;213(2):571–580. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAHLER H. R., HUBSCHER G., BAUM R. Studies on uricase. I. Preparation, purification, and properties of a cuproprotein. J Biol Chem. 1955 Oct;216(2):625–641. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARUYAMA Y., ALEXANDER M. Localization of enzymes in the mycelium and microconidia of Fusarium oxysporum. J Bacteriol. 1962 Aug;84:307–312. doi: 10.1128/jb.84.2.307-312.1962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MILLER J. D., FOGG G. E. Studies on the growth of Xanthophyceae in pure culture. II. The relations of Monodus subterraneus to organic substances. Arch Mikrobiol. 1958;30(1):1–16. doi: 10.1007/BF00509222. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MILLER R. W., MASSEY V. DIHYDROOROTIC DEHYDROGENASE. I. SOME PROPERTIES OF THE ENZYME. J Biol Chem. 1965 Mar;240:1453–1465. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MILLER R. W., MASSEY V. DIHYDROOROTIC DEHYDROGENASE. II. OXIDATION AND REDUCTION OF CYTOCHROME C. J Biol Chem. 1965 Mar;240:1466–1472. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MOYED H. S. INHIBITION OF THE BIOSYNTHESIS OF THE PYRIMIDINE PORTION OF THIAMINE BY ADENOSINE. J Bacteriol. 1964 Oct;88:1024–1029. doi: 10.1128/jb.88.4.1024-1029.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacKenzie R. E., Rabinowitz J. C. Cation-dependent reassociation of subunits of N10-formyltetrahydrofolate synthetase from Clostridium acidi-urici and Clostridium cylindrosporum. J Biol Chem. 1971 Jun 10;246(11):3731–3736. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magill J. M., Magill C. W. Purine base transport in Neurospora crassa. J Bacteriol. 1975 Oct;124(1):149–154. doi: 10.1128/jb.124.1.149-154.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahler J. L. A new bacterial uricase for uric acid determination. Anal Biochem. 1970 Nov;38(1):65–84. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(70)90156-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masover G. K., Benson J. R., Hayflick L. Growth of T-strain mycoplasmas in medium without added urea: effect of trace amounts of urea and of a urease inhibitor. J Bacteriol. 1974 Feb;117(2):765–774. doi: 10.1128/jb.117.2.765-774.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McIllmurray M. B., Lascelles J. Anaerobiosis and the activity of enzymes of pyrimidine biosynthesis in Staphylococcus aureus. J Gen Microbiol. 1970 Dec;64(3):269–277. doi: 10.1099/00221287-64-3-269. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mead G. C. Anaerobic utilization of uric acid by some group D streptococci. J Gen Microbiol. 1974 Jun;82(2):421–423. doi: 10.1099/00221287-82-2-421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meiss H. K., Brill W. J., Magasanik B. Genetic control of histidine degradation in Salmonella typhimurium, strain LT-2. J Biol Chem. 1969 Oct 10;244(19):5382–5391. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller R. W., Kerr C. T. Particulate dihydroorotate oxidase system from a pseudomonad. Linkage with the respiratory chain. Can J Biochem. 1967 Sep;45(9):1283–1294. doi: 10.1139/o67-150. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minnich J. E. Excretion of urate salts by reptiles. Comp Biochem Physiol A Comp Physiol. 1972 Mar;41(3):535–549. doi: 10.1016/0300-9629(72)90011-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell N. B., Levine M. Nitrogen Availability as an Aid in the Differentiation of Bacteria in the Coli-Aerogenes Group. J Bacteriol. 1938 Dec;36(6):587–598. doi: 10.1128/jb.36.6.587-598.1938. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitidieri E., Affonso O. R. Molybdenum requirement for bacterial xanthine dehydrogenase activity. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1965 Aug 24;105(2):371–373. doi: 10.1016/s0926-6593(65)80161-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Molnár J., Prágai B. Possible role of adenosine deaminase in suboptimal growth of the bacillus anthracis adenine auxotroph mutant. Acta Microbiol Acad Sci Hung. 1973;20(4):255–265. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore M. R., O'Brien W. E., Ljungdahl L. G. Purification and characterization of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide-dependent methylenetetrahydrofolate dehydrogenase from Clostridium formicoaceticum. J Biol Chem. 1974 Aug 25;249(16):5250–5253. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosteller R. D., Goldstein R. V. Unusual sensitivity of Escherichia coli to adenine or adenine plus histidine. J Bacteriol. 1975 Aug;123(2):750–751. doi: 10.1128/jb.123.2.750-751.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Motokawa Y., Kikuchi G. Glycine metabolism by rat liver mitochondria. II. Methylene tetrahydrofolate as the direct on carbon donor in the reaction of glycine synthesis. J Biochem. 1969 Jan;65(1):71–75. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Motokawa Y., Kikuchi G. Glycine metabolism by rat liver mitochondria. IV. Isolation and characterization of hydrogen carrier protein, an essential factor for glycine metabolism. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1969 Dec;135(1):402–409. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(69)90556-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Motokawa Y., Kikuchi G. Glycine metabolism by rat liver mitochondria. Reconstruction of the reversible glycine cleavage system with partially purified protein components. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1974 Oct;164(2):624–633. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(74)90074-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller M., Hogg J. F., De Duve C. Distribution of tricarboxylic acid cycle enzymes and glyoxylate cycle enzymes between mitochondria and peroxisomes in Tetrahymena pyriformis. J Biol Chem. 1968 Oct 25;243(20):5385–5395. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller M., Moller K. M. Studies on some enzymes of purine metabolism in the amoebae Chaos chaos and Amoeba proteus. C R Trav Lab Carlsberg. 1969;36(24):463–497. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller M., Moller K. M. Urate oxidase and its association with peroxisomes in Acanthamoeba sp. Eur J Biochem. 1969 Jun;9(3):424–430. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1969.tb00626.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NEIDHARDT F. C., MAGASANIK B. Reversal of the glucose inhibition of histidase biosynthesis in Aerobacter aerogenes. J Bacteriol. 1957 Feb;73(2):253–259. doi: 10.1128/jb.73.2.253-259.1957. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NEIDHARDT F. C. Properties of a bacterial mutant lacking amino acid control of RNA synthesis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1963 Mar 26;68:365–379. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(63)90158-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NOVOA W. B., WINER A. D., GLAID A. J., SCHWERT G. W. Lactic dehydrogenase. V. Inhibition by oxamate and by oxalate. J Biol Chem. 1959 May;234(5):1143–1148. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakajima Y., Bourne G. H. Histochemical studies on urate oxidase in several mammals with special reference to uricolytic ability of primates. Histochemie. 1970;22(1):20–24. doi: 10.1007/BF00310545. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nirmala J., Sivarama Sastry K. The effect of thiourea on ureide metabolism in Neurospora crassa. Biochem J. 1973 Nov;136(3):749–755. doi: 10.1042/bj1360749. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nose K., Arima K. Studies on bacterial urate:oxygen oxidoreductase. II. Observations concerning the properties and components of the active site. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Jan 8;151(1):63–69. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(68)90161-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Donovan G. A., Neuhard J. Pyrimidine metabolism in microorganisms. Bacteriol Rev. 1970 Sep;34(3):278–343. doi: 10.1128/br.34.3.278-343.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oien H. G., Wright L. D. Metabolism of imidazole by a pseudomonad. J Bacteriol. 1971 Mar;105(3):1229–1231. doi: 10.1128/jb.105.3.1229-1231.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olson J. S., Ballou D. P., Palmer G., Massey V. The mechanism of action of xanthine oxidase. J Biol Chem. 1974 Jul 25;249(14):4363–4382. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olson J. S., Ballow D. P., Palmer G., Massey V. The reaction of xanthine oxidase with molecular oxygen. J Biol Chem. 1974 Jul 25;249(14):4350–4362. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Omura H., Osajima Y., Tsukamoto T. Some properties of urea dehydrogenase in tissues of higher plants. Enzymologia. 1966 Sep 30;31(3):129–154. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PARDEE A. B., YATES R. A. Pyrimidine biosynthesis in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1956 Aug;221(2):743–756. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PIZER L. I. GLYCINE SYNTHESIS AND METABOLISM IN ESCHERICHIA COLI. J Bacteriol. 1965 Apr;89:1145–1150. doi: 10.1128/jb.89.4.1145-1150.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- POTTS W. T. AMMONIA EXCRETION IN OCTOPUS DOFLEINI. Comp Biochem Physiol. 1965 Feb;14:339–355. doi: 10.1016/0010-406x(65)90209-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PRICER W. E., Jr, RABINOWITZ J. C. Purine fermentation by Clostridium cylindrosporum. V. Formiminoglycine. J Biol Chem. 1956 Oct;222(2):537–554. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piret M. C., Crokaert R., Christophe J. Le catabolisme réductif de l'uracile chez Torulopsis utilis. Arch Int Physiol Biochim. 1964 Mar;72(2):256–266. doi: 10.3109/13813456409058971. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pitts O. M., Priest D. G. A steady-state kinetic investigation of the uricase reaction mechanism. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1974 Jul;163(1):359–366. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(74)90487-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pitts O. M., Priest D. G., Fish W. W. Uricase. Subunit composition and resistance to denaturants. Biochemistry. 1974 Feb 26;13(5):888–892. doi: 10.1021/bi00702a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pitts O. M., Priest D. G. Uricase reaction intermediate. Mechanism of borate and hydroxide ion catalysis. Biochemistry. 1973 Mar 27;12(7):1358–1363. doi: 10.1021/bi00731a016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polak A., Grenson M. Evidence for a common transport system for cytosine, adenine and hypoxanthine in Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Candida albicans. Eur J Biochem. 1973 Jan 15;32(2):276–282. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1973.tb02608.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polkinghorne M., Hynes M. J. Effect of L-histidine on the catabolism of nitrogenous compounds in Aspergillus nidulans. J Gen Microbiol. 1975 Mar;87(1):185–187. doi: 10.1099/00221287-87-1-185. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pradhan T. K., Sander E. G. Noncompetitive inhibition by substituted sulfonamides of dihydroorotase from Zymobacterium oroticum. Life Sci. 1973 Dec 16;13(12):1747–1752. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(73)90121-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Putrament A., Baranowska H., Biliński T., Prazmo W. On the specificity of caffeine effects. Inhibition by caffeine of RNA and protein synthesis in yeast and Escherichia coli. Mol Gen Genet. 1972;118(4):373–379. doi: 10.1007/BF00333572. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RABINOWITZ J. C., BARKER H. A. Purine fermentation by Clostridium cylindrosporum. I. Tracer experiments on the fermentation of guanine. J Biol Chem. 1956 Jan;218(1):147–160. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RABINOWITZ J. C., BARKER H. A. Purine fermentation by Clostridium cylindrosporum. II. Purine transformations. J Biol Chem. 1956 Jan;218(1):161–173. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RABINOWITZ J. C., HIMES R. H. Folic acid coenzymes. Fed Proc. 1960 Dec;19:963–970. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RABINOWITZ J. C., PRICER W. E., Jr An enzymatic method for the determination of formic acid. J Biol Chem. 1957 Nov;229(1):321–328. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RABINOWITZ J. C., PRICER W. E., Jr Formyltetrahydrofolate synthetase. I. Isolation and crystallization of the enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1962 Sep;237:2898–2902. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RABINOWITZ J. C., PRICER W. E., Jr METABOLISM OF FORMIMINOGLYCINE. DEGRADATION BY WHOLE CELLS. J Biol Chem. 1965 Apr;240:1696–1700. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RABINOWITZ J. C., PRICER W. E., Jr Purine fermentation by Clostridium cylindrosporum. IV. 4-Ureido-5-imidazolecarboxylic acid. J Biol Chem. 1956 Jan;218(1):189–199. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RABINOWITZ J. C. Purine fermentation by Clostridium cylindrosporum. III. 4-Amino-5-imidazolecarboxylic acid and 4-aminoimidazole. J Biol Chem. 1956 Jan;218(1):175–187. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RAEBURN S., RABINOWITZ J. C. PYRUVATE SYNTHESIS BY A PARTIALLY PURIFIED ENZYME FROM CLOSTRIDIUM ACIDI-URICI. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1965 Feb 3;18:303–307. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(65)90703-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RAJAGOPALAN K. V., ALEMAN V., HANDLER P., HEINEN W., PALMER G., BEINERT H. Electron paramagnetic resonance studies of iron reduction and semiquinone formation in metalloflavoproteins. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1962 Jul 3;8:220–226. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(62)90267-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RAMASASTRI B. V., BLAKLEY R. L. OPTICAL ROTATIONS OF THE DIASTEREOISOMERS OF DL,L-METHYLENETETRAHYDROFOLATE. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1963 Aug 20;12:478–482. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(63)90319-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RAO D. R., GREENBERG D. M. Studies on the enzymic decomposition of urocanic acid. IV. Purification and properties of 4(5)-imidazolone-5(4)-propionic acid hydrolase. J Biol Chem. 1961 Jun;236:1758–1763. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REVEL H. R. B., MAGASANIK B. The enzymatic degradation of urocanic acid. J Biol Chem. 1958 Oct;233(4):930–935. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REYNOLDS E. S., LIEBERMAN I., KORNBERG A. The metabolism of orotic acid in aerobic bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1955 Mar;69(3):250–255. doi: 10.1128/jb.69.3.250-255.1955. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROGOSA M., BISHOP F. S. THE GENUS VEILLONELLA . II. NUTRITIONAL STUDIES. J Bacteriol. 1964 Mar;87:574–580. doi: 10.1128/jb.87.3.574-580.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROUSH A. H., DOMNAS A. J. Induced biosynthesis of uricase in yeast. Science. 1956 Jul 20;124(3212):125–126. doi: 10.1126/science.124.3212.125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROUSH A. H., QUESTIAUX L. M., DOMNAS A. J. The active transport and metabolism of purines in the yeast, Candida utilis. J Cell Comp Physiol. 1959 Dec;54:275–286. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1030540310. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROUSH A. H., SAEED M. Adenine metabolism in Saccharomyces cerevisiae adenase from bakers' yeast. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1960 Jan;2:43–47. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(60)90262-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROUSH A. H. Yeast adenase. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1954 Jun;50(2):510–512. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(54)90070-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RUBAN E. L. Azotnyl obmen u Nitrosomonas europaea. Mikrobiologiia. 1958 Sep-Oct;27(5):536–541. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radin N. S., Barker H. A. Enzymatic Reactions in Purine Decomposition by Preparations of Clostridium Acidi-Urici. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1953 Dec;39(12):1196–1204. doi: 10.1073/pnas.39.12.1196. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reichert U., Schmidt R., Foret M. A possible mechanism of energy coupling in purine transport of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. FEBS Lett. 1975 Mar 15;52(1):100–102. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(75)80647-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reichert U., Winter M. Uptake and accumulation of purine bases by stationary yeast cells pretreated with glucose. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Jul 12;356(1):108–116. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(74)90298-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reinert W. R., Marzluf G. A. Genetic and metabolic control of the purine catabolic enzymes of Neurospora crasse. Mol Gen Genet. 1975 Aug 5;139(1):39–55. doi: 10.1007/BF00267994. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reinert W. R., Marzluf G. A. Regulation of the purine catabolic enzymes in Neurospora crassa. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1975 Feb;166(2):565–574. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(75)90421-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Remy C. N., Love S. H. Induction of adenosine deaminase in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1968 Jul;96(1):76–85. doi: 10.1128/jb.96.1.76-85.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson J. R., Klein S. M., Sagers R. D. Glycine metabolism. Lipoic acid as the prosthetic group in the electron transfer protein P2 from Peptococcus glycinophilus. J Biol Chem. 1973 Aug 10;248(15):5319–5323. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roon R. J., Hampshire J., Levenberg B. Urea amidolyase. The involvement of biotin in urea cleavage. J Biol Chem. 1972 Dec 10;247(23):7539–7545. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roon R. J., Levenberg B. An adenosine triphosphate-dependent, avidin-sensitive enzymatic cleavage of urea in yeast and green algae. J Biol Chem. 1968 Oct 10;243(19):5213–5215. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roon R. J., Levenberg B. CO2 fixation and the involvement of allophanate in the biotin-enzyme-catalyzed cleavage of urea. J Biol Chem. 1970 Sep 10;245(17):4593–4595. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roon R. J., Levenberg B. Urea amidolyase. I. Properties of the enzyme from Candida utilis. J Biol Chem. 1972 Jul 10;247(13):4107–4113. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rouf M. A., Lomprey R. F., Jr Degradation of uric acid by certain aerobic bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1968 Sep;96(3):617–622. doi: 10.1128/jb.96.3.617-622.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Röhrscheidt E., Tárnok Z., Tárnok I. Purin- und pyrimidinabbauende Enzyme in Mycobakterien und Nocardien. Zentralbl Bakteriol Orig. 1970;215(4):550–554. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SAGERS R. D., BECK J. V. Exchange of radioactive bicarbonate with the carboxyl group of pyruvate by Clostridium acidiurici. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1955 Jan;54(1):249–250. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(55)90030-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SAGERS R. D., BENZIMAN M., GUNSALUS I. C. Acetate formation in Clostridium acidi-urici: acetokinase. J Bacteriol. 1961 Aug;82:233–238. doi: 10.1002/path.1700820136. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SAGERS R. D., BENZIMAN M., KLEIN S. M. FAILURE OF ARSENATE TO UNCOUPLE THE PHOSPHOTRANSACETYLASE SYSTEM IN CLOSTRIDIUM ACIDIURICI. J Bacteriol. 1963 Nov;86:978–984. doi: 10.1128/jb.86.5.978-984.1963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SAGERS R. D., GUNSALUS I. C. Intermediatry metabolism of Diplococcus glycinophilus. I. Glycine cleavage and one-carbon interconversions. J Bacteriol. 1961 Apr;81:541–549. doi: 10.1128/jb.81.4.541-549.1961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SEAMAN G. R. Metabolism of purines by extracts of Tetrahymena. J Protozool. 1963 Feb;10:87–91. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1963.tb01639.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SYLVESTER C. J., COSTILOW R. N. NUTRITIONAL REQUIREMENTS OF BACILLUS POPILLIAE. J Bacteriol. 1964 Jan;87:114–119. doi: 10.1128/jb.87.1.114-119.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salanitro J. P., Blake I. G., Muirhead P. A. Studies on the cecal microflora of commercial broiler chickens. Appl Microbiol. 1974 Sep;28(3):439–447. doi: 10.1128/am.28.3.439-447.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sander E. G., Heeb M. J. Purification and properties of dihydroorotase from Escherichia coli B. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Feb 10;227(2):442–452. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(71)90075-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sander E. G., Wright L. D., McCormick D. B. Evidence for function of a metal ion in the activity of dihydroorotase from Zymobacterium oroticum. J Biol Chem. 1965 Sep;240(9):3628–3630. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato T., Kochi H., Motokawa Y., Kawasaki H., Kikuchi G. Glycin metabolism by rat liver mitochondria. I. Synthesis of two molecules of glycine from one molecule each of serine, bicarbonate and ammonia. J Biochem. 1969 Jan;65(1):63–70. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato T., Kochi H., Sato N., Kikuchi G. Glycine metabolism by rat liver mitochondria. 3. The glycine cleavage and the exchange of carboxyl carbon of glycine with bicarbonate. J Biochem. 1969 Jan;65(1):77–83. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scazzocchio C., Darlington A. J. The induction and repression of the enzymes of purine breakdown in Aspergillus nidulans. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Sep 24;166(2):557–568. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(68)90243-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scazzocchio C., Holl F. B., Foguelman A. I. The genetic control of molybdoflavoproteins in Aspergillus nidulans. Allopurinol-resistant mutants constitutive for xanthine-dehydrogenase. Eur J Biochem. 1973 Jul 16;36(2):428–445. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1973.tb02928.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schefferle H. E. The decomposition of uric acid in built up poultry litter. J Appl Bacteriol. 1965 Dec;28(3):412–420. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1965.tb02171.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schein A. H., Kunin A. S. Urate oxidation by cupric ion (Cu(++)). FEBS Lett. 1969 Mar;2(5):339–341. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(69)80059-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlee D., Reinbothe H., Fritsche W. Der Einfluss von Eisen auf den Purinstoffwechsel und die Riboflavinbildung von Candida guiliermondii (Cast.) Lang. et G. Z Allg Mikrobiol. 1968;8(2):127–138. doi: 10.1002/jobm.3630080206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schulman M., Ghambeer R. K., Ljungdahl L. G., Wood H. G. Total synthesis of acetate from CO2. VII. Evidence with Clostridium thermoaceticum that the carboxyl of acetate is derived from the carboxyl of pyruvate by transcarboxylation and not by fixation of CO2. J Biol Chem. 1973 Sep 25;248(18):6255–6261. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schulman M., Parker D., Ljungdahl L. G., Wood H. G. Total synthesis of acetate from CO 2 . V. Determination by mass analysis of the different types of acetate formed from 13 CO 2 by heterotrophic bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1972 Feb;109(2):633–644. doi: 10.1128/jb.109.2.633-644.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwimmer S., Kurtzman R. H., Jr, Heftmann E. Caffeine metabolism by Penicillium roqueforti. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1971 Nov;147(1):109–113. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(71)90315-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott J. M., Rabinowitz J. C. The association-dissociation of formyltetrahydrofolate synthetase and its relation to monovalent cation activation of catalytic activity. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1967 Nov 17;29(3):418–423. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(67)90473-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Semler B. L., Hodson R. C., Williams SK I. I., Howell S. H. The induction of allophanate lyase during the vegetative cell cycle in light-synchronized cultures of Chlamydomonas reinhardi. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Jul 14;399(1):71–78. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(75)90212-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaffer P. M., Hsu C. A., Abbott M. T. Metabolism of pyrimidine deoxyribonucleosides in Neurospora crassa. J Bacteriol. 1975 Feb;121(2):648–655. doi: 10.1128/jb.121.2.648-655.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shavlovskii G. M., Ksheminskaia G. P., Kuznetsova R. A. Mutanty Candida guilliermondii s blokirovannym katabolizmom purinov i flavinogennaia sktivnost' étikh mutantov. Mikrobiologiia. 1971 Nov-Dec;40(6):1070–1076. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sin I. L. Purification and properties of xanthine dehydrogenase from Pseudomonas acidovorans. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Nov 20;410(1):12–20. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(75)90203-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith A. E., Yamada E. W. Dihydrouracil dehydrogenase of rat liver. Separation of hydrogenase and dehydrogenase activities. J Biol Chem. 1971 Jun 10;246(11):3610–3617. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith R. F. Nitrogen requirements and uricolytic activity of cutaneous bacteria. Appl Microbiol. 1970 Apr;19(4):643–648. doi: 10.1128/am.19.4.643-648.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith S. T., Rajagopalan K. V., Handler P. Purification and properties of xanthine dehydroganase from Micrococcus lactilyticus. J Biol Chem. 1967 Sep 25;242(18):4108–4117. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stabenau H., Beevers H. Isolation and Characterization of Microbodies from the Alga Chlorogonium elongatum. Plant Physiol. 1974 Jun;53(6):866–869. doi: 10.1104/pp.53.6.866. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart D. J. The urease activity of fluorescent pseudomonads. J Gen Microbiol. 1965 Nov;41(2):169–174. doi: 10.1099/00221287-41-2-169. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TABOR H., MEHLER A. H. Isolation of N-formyl-L-glutamic acid as an intermediate in the enzymatic degradation of L-histidine. J Biol Chem. 1954 Oct;210(2):559–568. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TABOR H., WYNGARDEN L. The enzymatic formation of formiminotetrahydrofolic acid, 5,10-methenyltetrahydrofolic acid, and 10-formyltetrahydrofolic acid in the metabolism of formiminoglutamic acid. J Biol Chem. 1959 Jul;234(7):1830–1846. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TAHA E. E., STORCK-KRIEG L., FRANKE W. Purinoxydierende Fermente aus Schimmelpilzen. IV. Uber die Xanthindehydrase der Schimmelpilze. Arch Mikrobiol. 1955;23(1):67–78. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TAYLOR W. H., NOVELLI G. D. ENZYMES OF THE PYRIMIDINE PATHWAY IN ESCHERICHIA COLI. I. SYNTHESIS BY CELLS AND SPHEROPLASTS. J Bacteriol. 1964 Jul;88:99–104. doi: 10.1128/jb.88.1.99-104.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TAYLOR W. H., TAYLOR M. L. ENZYMES OF THE PYRIMIDINE PATHWAY IN ESCHERICHIA COLI. II. INTRACELLULAR LOCALIZATION AND PROPERTIES OF DIHYDROOROTIC DEHYDROGENASE. J Bacteriol. 1964 Jul;88:105–110. doi: 10.1128/jb.88.1.105-110.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TIGIER H., GRISOLIA S. INDUCTION OF CARBAMYL-P SPECIFIC OXAMATE TRANSCARBAMYLASE BY PARABANIC ACID IN A STREPTOCOCCUS. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1965 Apr 9;19:209–214. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(65)90506-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tacquet A., Tison F., Roos P., Devulder B. Activité amidasique des mycobactéries. Technique qualitative nouvelle d'étude en milieu de culture solide. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1967 Mar;112(3):378–383. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor M. L., Taylor W. H., Eames D. F., Taylor C. D. Biosynthetic dihydroorotate dehydrogenase from Lactobacillus bulgaricus. J Bacteriol. 1971 Mar;105(3):1015–1027. doi: 10.1128/jb.105.3.1015-1027.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor W. H., Taylor M. L., Eames D. F. Two functionally different dihydroorotic dehydrogenases in bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1966 Jun;91(6):2251–2256. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.6.2251-2256.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thauer R. K. CO 2 reduction to formate in Clostridium acidi-urici. J Bacteriol. 1973 Apr;114(1):443–444. doi: 10.1128/jb.114.1.443-444.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thauer R. K. CO(2)-reduction to formate by NADPH. The initial step in the total synthesis of acetate from CO(2) in Clostridium thermoaceticum. FEBS Lett. 1972 Oct 15;27(1):111–115. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(72)80421-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thauer R. K., Fuchs G., Jungermann K. Reduced ferredoxin: CO2 oxidoreductase from Clostridium pasteurianum: its role in formate metabolism. J Bacteriol. 1974 May;118(2):758–760. doi: 10.1128/jb.118.2.758-760.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thauer R. K., Fuchs G., Schnitker U., Jungermann K. CO2 reductase from Clostridium pasteurianum: molybdenum dependence of synthesis and inactivation by cyanide. FEBS Lett. 1973 Dec 15;38(1):45–48. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(73)80509-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thauer R. K., Käufer B., Fuchs G. The active species of 'CO2' utilized by reduced ferredoxin:CO2 oxidoreductase from Clostridium pasteurianum. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Jun 16;55(1):111–117. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb02143.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thauer R. K., Käufer B., Scherer P. The active species of "CO2" utilized in ferredoxin-linked carboxylation reactions. Arch Microbiol. 1975 Aug 28;104(3):237–240. doi: 10.1007/BF00447330. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson J. F., Muenster A. M. Separation of the Chlorella ATP:Urea amido-lyase into two components. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1971 Jun 4;43(5):1049–1055. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(71)90568-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tintemann H., Reinbothe H. Harnstoffassimilation in der Hefe Candida guilliermondii durch ATP: Urea-amidolyase. Acta Biol Med Ger. 1973;30(3):317–322. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Townsend D., Lata G. F. Purification of urate oxidase; a sex dependent enzyme from rat liver. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1969 Dec;135(1):166–172. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(69)90527-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trijbels F., Vogels G. D. Allantoate and ureidoglycolate degradation by Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1967 Jan 11;132(1):115–126. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(67)90197-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trijbels F., Vogels G. D. Allantoicase and ureidoglycolase in Pseudomonas and Penicillium species. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 May 5;118(2):387–395. doi: 10.1016/s0926-6593(66)80047-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trijbels F., Vogels G. D. Catabolism of allantoate and ureidoglycolate in Rana esculenta. Comp Biochem Physiol. 1969 Jul 15;30(2):359–365. doi: 10.1016/0010-406x(69)90817-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trijbels F., Vogels G. D. Degradation of allantoin by Pseudomonas acidovorans. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 Feb 14;113(2):292–301. doi: 10.1016/s0926-6593(66)80068-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Truscoe R., Williams V. Effect of inhibitors on activity of ox-kidney urate oxidase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1965 Aug 24;105(2):292–300. doi: 10.1016/s0926-6593(65)80153-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Truszkowski R. Uricase and its action: Bacterial nature of the action of uricolytic extracts and dialysates. Biochem J. 1930;24(5):1340–1348. doi: 10.1042/bj0241340. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai C. S., Axelrod B. Catabolism of Pyrimidines in Rape Seedlings. Plant Physiol. 1965 Jan;40(1):39–44. doi: 10.1104/pp.40.1.39. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- UDAKA S., VENNESLAND B. Properties of triphosphopyridine nucleotide-linked dihydroorotic dehydrogenase. J Biol Chem. 1962 Jun;237:2018–2024. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- UYEDA K., RABINOWITZ J. C. METABOLISM OF FORMIMINOGLYCINE. GLYCINE FORMIMINOTRANSFERASE. J Biol Chem. 1965 Apr;240:1701–1710. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uyeda K., Rabinowitz J. C. Enzymes of clostridial purine fermentation. Methylenetetrahydrofolate dehydrogenase. J Biol Chem. 1967 Oct 10;242(19):4378–4385. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uyeda K., Rabinowitz J. C. Enzymes of the clostridial purine fermentation. Serine hydroxymethyltransferase. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1968 Feb;123(2):271–278. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(68)90134-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uyeda K., Rabinowitz J. C. Metabolism of formiminoglycine. Formiminotetrahydrofolate cyclodeaminase. J Biol Chem. 1967 Jan 10;242(1):24–31. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uyeda K., Rabinowitz J. C. Pyruvate-ferredoxin oxidoreductase. IV. Studies on the reaction mechanism. J Biol Chem. 1971 May 25;246(10):3120–3125. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VALENTINE R. C. BACTERIAL FERREDOXIN. Bacteriol Rev. 1964 Dec;28:497–517. doi: 10.1128/br.28.4.497-517.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VALENTINE R. C., BOJANOWSKI R., GAUDY E., WOLFE R. S. Mechanism of the allantoin fermentation. J Biol Chem. 1962 Jul;237:2271–2277. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VALENTINE R. C., BRILL W. J., SAGERS R. D. FERREDOXIN LINKED DPN REDUCTION BY PYRUVATE IN EXTRACTS OF CLOSTRIDIUM ACIDI-URICI. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1963 Aug 1;12:315–319. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(63)90303-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VALENTINE R. C., DRUCKER H., WOLFE R. S. GLYOXYLATE FERMENTATION BY STREPTOCOCCUS ALLANTOICUS. J Bacteriol. 1964 Feb;87:241–246. doi: 10.1128/jb.87.2.241-246.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VALENTINE R. C., JACKSON R. L., WOLFE R. S. Role of ferredoxin in hydrogen metabolism of Micrococcus lactilyticus. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1962 Jun 4;7:453–456. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(62)90334-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VALENTINE R. C., WOLFE R. S. Glyoxylurea. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1961 Jul 26;5:305–308. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(61)90168-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VALENTINE R. C., WOLFE R. S. Phosphate-dependent degradation of urea. Nature. 1961 Aug 26;191:925–926. doi: 10.1038/191925b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VALENTINE R. C., WOLFE R. S. Phosphorolysis of carbamyl oxamic acid. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1960 Dec 4;45:389–391. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(60)91467-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VALENTINE R. C., WOLFE R. S. ROLE OF FERREDOXIN IN THE METABOLISM OF MOLECULAR HYDROGEN. J Bacteriol. 1963 May;85:1114–1120. doi: 10.1128/jb.85.5.1114-1120.1963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VANBAALEN C., MARLER J. E. CHARACTERISTICS OF MARINE BLUE-GREEN ALGAE WITH URIC ACID AS NITROGEN SOURCE. J Gen Microbiol. 1963 Sep;32:457–463. doi: 10.1099/00221287-32-3-457. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VILLELA G. G., AFFONSO O. R., MITIDIERI E. Xanthine oxidase in Lactobacillus casei. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1955 Dec;59(2):532–533. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(55)90521-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VILLELA G. G. DEHYDROGENASES OF PURINE METABOLISM IN TETRAHYMENA PYRIFORMIS. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1965 Mar;118:834–838. doi: 10.3181/00379727-118-29985. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VOGELS G. D. Intermediates in anaerobic allantoin degradation by bacteria. Biochem Z. 1961;334:457–461. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Baalen C. The Photooxidation of Uric Acid by Anacystis nidulans. Plant Physiol. 1965 Mar;40(2):368–371. doi: 10.1104/pp.40.2.368. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van der Drift C., Vogels G. D. Stereospecificity of allantoin degradation in Streptococcus allantoicus. Experientia. 1969 May 15;25(5):477–477. doi: 10.1007/BF01900764. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van der Drift L., Vogels G. D., Van der Drift C. Allantoin racemase: a new enzyme from Pseudomonas species. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 May 23;391(1):240–248. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(75)90170-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varel V. H., Bryant M. P., Holdeman L. V., Moore W. E. Isolation of ureolytic Peptostreptococcus productus from feces using defined medium; failure of common urease tests. Appl Microbiol. 1974 Oct;28(4):594–599. doi: 10.1128/am.28.4.594-599.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varel V. H., Bryant M. P. Nutritional features of Bacteroides fragilis subsp. fragilis. Appl Microbiol. 1974 Aug;28(2):251–257. doi: 10.1128/am.28.2.251-257.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vitol M. Ia, Shaposhinkov V. N., Shvachkin Iu P. Novyi put'katabolizma orotovoi kisloty u mikroorganizmov. Dokl Akad Nauk SSSR. 1967 Jun 11;174(5):1202–1204. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogels G. D. Reversible activation of allantoate amidohydrolase by acid-pretreatment and other properties of the enzyme. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 Feb 14;113(2):277–291. doi: 10.1016/s0926-6593(66)80067-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogels G. D. Specificity of binding subsites of allantoicase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969 Jul 8;185(1):186–197. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(69)90294-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogels G. D. Stereospecificity in the allantoin metabolism. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1969;35(2):236–238. doi: 10.1007/BF02219137. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogels G. D., Van der Drift C. Differential analyses of glyoxylate derivatives. Anal Biochem. 1970 Jan;33(1):143–157. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(70)90448-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vízdalová M., Janovská E., Zhestjanikov V. D. Effect of dark-repair inhibitors on the survival of Escherichia coli B under different post-irradiation conditions. Int J Radiat Biol Relat Stud Phys Chem Med. 1971;20(1):49–59. doi: 10.1080/09553007114550861. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WACHSMAN J. T., BARKER H. A. Characterization of an orotic acid fermenting bacterium, zymobacterium oroticum, nov. gen., nov. spec. J Bacteriol. 1954 Oct;68(4):400–404. doi: 10.1128/jb.68.4.400-404.1954. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WACHSMAN J. T., BARKER H. A. The accumulation of formamide during the fermentation of histidine by Clostridium tetanomorphum. J Bacteriol. 1955 Jan;69(1):83–88. doi: 10.1128/jb.69.1.83-88.1955. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WALLACH D. P., GRISOLIA S. The purification and properties of hydropyrimidine hydrase. J Biol Chem. 1957 May;226(1):277–288. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WANG T. P., LAMPEN J. O. Metabolism of pyrimidines by a soil bacterium. J Biol Chem. 1952 Feb;194(2):775–783. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WANG T. P., LAMPEN J. O. Uracil oxidase and the isolation of barbituric acid from uracil oxidation. J Biol Chem. 1952 Feb;194(2):785–791. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WHITELEY H. R., DOUGLAS H. C. The fermentation of purines by Micrococcus lactilyticus. J Bacteriol. 1951 May;61(5):605–616. doi: 10.1128/jb.61.5.605-616.1951. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WHITELEY H. R., OSBORN M. J., HUENNEKENS F. M. Purification and properties of the formate-activating enzyme from Micrococcus aerogenes. J Biol Chem. 1959 Jun;234(6):1538–1543. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WHITELEY H. R. The fermentation of purines by Micrococcus aerogenes. J Bacteriol. 1952 Feb;63(2):163–175. doi: 10.1128/jb.63.2.163-175.1952. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WHITELEY H. R., WOOLFOLK C. A. Ferredoxin-dependent reactions in Micrococcus lactilyticus. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1962 Dec 19;9:517–522. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(62)90118-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WOOD R. C., STEERS E. Study of the purine metabolism of Staphylococcus aureus. J Bacteriol. 1959 Jun;77(6):760–765. doi: 10.1128/jb.77.6.760-765.1959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WOODWARD V. W., MUNKRES K. D., SUYAMA Y. Uracil metabolism in Neurospora crassa. Experientia. 1957 Dec 15;13(12):484–486. doi: 10.1007/BF02159410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WRIGHT B. E. The rôle of polyglutamyl pteridine coenzymes in serine metabolism. II. A comparison of various pteridine derivatives. J Biol Chem. 1956 Apr;219(2):873–883. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waslien C. I., Calloway D. H., Margen S. Uric acid production of men fed graded amounts of egg protein and yeast nucleic acid. Am J Clin Nutr. 1968 Sep;21(9):892–897. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/21.9.892. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welch W. H., Buttlaire D. H., Hersh R. T., Himes R. H. The subunit structure of formyltetrahydrofolate synthetase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Jun 29;236(3):599–611. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(71)90245-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitney P. A., Cooper T. G., Magasanik B. The induction of urea carboxylase and allophanate hydrolase in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Biol Chem. 1973 Sep 10;248(17):6203–6209. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitney P. A., Cooper T. G. Urea carboxylase and allophanate hydrolase. Two components of adenosine triphosphate:urea amido-lyase in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Biol Chem. 1972 Mar 10;247(5):1349–1353. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitney P. A., Cooper T. G. Urea carboxylase and allophanate hydrolase: two components of a multienzyme complex in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 Oct 6;49(1):45–51. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(72)90007-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wickner R. B., Tabor H. N-Formimino-L-glutamate iminohydrolase from histidine-adapted Pseudomonas. Purification and properties. J Biol Chem. 1972 Mar 10;247(5):1605–1609. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woolfolk C. A. Metabolism of N-methylpurines by a Pseudomonas putida strain isolated by enrichment on caffeine as the sole source of carbon and nitrogen. J Bacteriol. 1975 Sep;123(3):1088–1106. doi: 10.1128/jb.123.3.1088-1106.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woolfolk C. A., Woolfolk B. S., Whiteley H. R. 2-oxypurine dehydrogenase from Micrococcus aerogenes. I. Isolation, specificity, and some chemical and physical properties. J Biol Chem. 1970 Jun;245(12):3167–3178. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu C. H., Eisenbraun E. J., Gaudy E. T. Enzymatic degradation of ureidoglycine by Pseudomonas acidovorans. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1970 Jun 5;39(5):976–982. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(70)90420-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yeh Y. C., Greenberg D. M. Purification and properties of N5, N10-Methylenetetra-hydrofolate dehydrogenase of calf thymus. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1965 Aug 24;105(2):279–291. doi: 10.1016/s0926-6593(65)80152-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young E. G., Hawkins W. W. The Decomposition of Allantoin by Intestinal Bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1944 Apr;47(4):351–353. doi: 10.1128/jb.47.4.351-353.1944. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Repentigny J., Mathieu L. G., Turgeon S., Sonea S. Effects of exogenous purines on growth rates and other properties of Staphyloccus aureus strains including a pyrimidineless mutant of the Wood 46 strain. Can J Microbiol. 1968 Jan;14(1):39–44. doi: 10.1139/m68-007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Hartingsveldt J., Stouthamer A. H. Mapping and characerization of mutants of Pseudomonas aeruginosa affected in nitrate respiration in aerobic or anaerobic growth. J Gen Microbiol. 1973 Jan;74(1):97–106. doi: 10.1099/00221287-74-1-97. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Drift C., Ketelaars H. C. Carnosinase: its presence in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1974;40(3):377–384. doi: 10.1007/BF00399349. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Drift C., Vogels G. D. Activation and inactivation of allantoate amindohydrolase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1967 May 16;139(1):162–168. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(67)90122-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Drift C., Vogels G. D. Allantoate amidohydrolase. I. pH- and anion-dependent activation. Enzymologia. 1969;36(4):269–277. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Drift C., Vogels G. D. Allantoate amidohydrolase. II. Inactivation and instability. Enzymologia. 1969;36(4):278–286. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Drift C., Vogels G. D. Effect of metal and hydrogen ions on the activity and stability of allantoicase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Feb 11;198(2):339–352. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(70)90067-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Drift C., de Windt F. E., Vogels G. D. Allantoate hydrolysis by allantoate amidohydrolase. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1970 Jan;136(1):273–279. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(70)90351-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Drift C., van Helvoort P. E., Vogels G. D. S-ureidoglycolate dehydrogenase: purification and properties. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1971 Aug;145(2):465–469. doi: 10.1016/s0003-9861(71)80006-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



