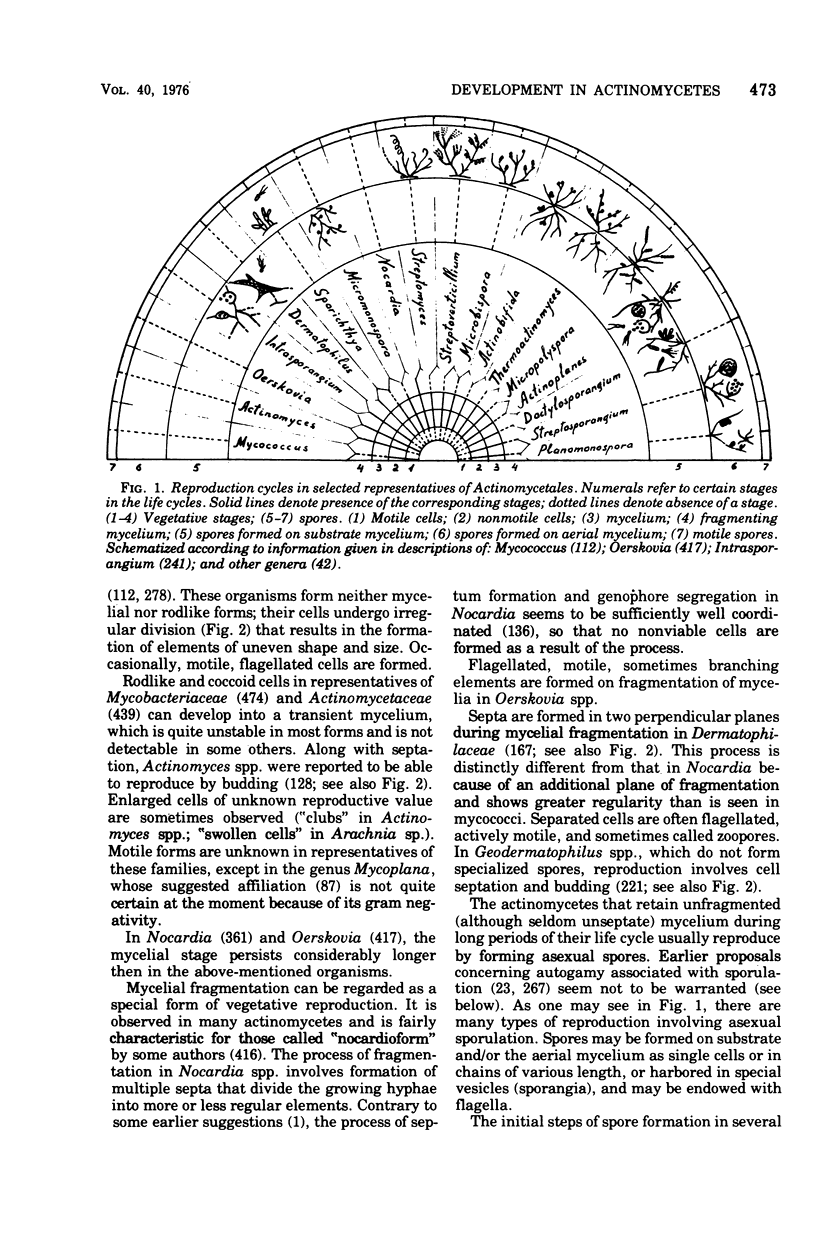
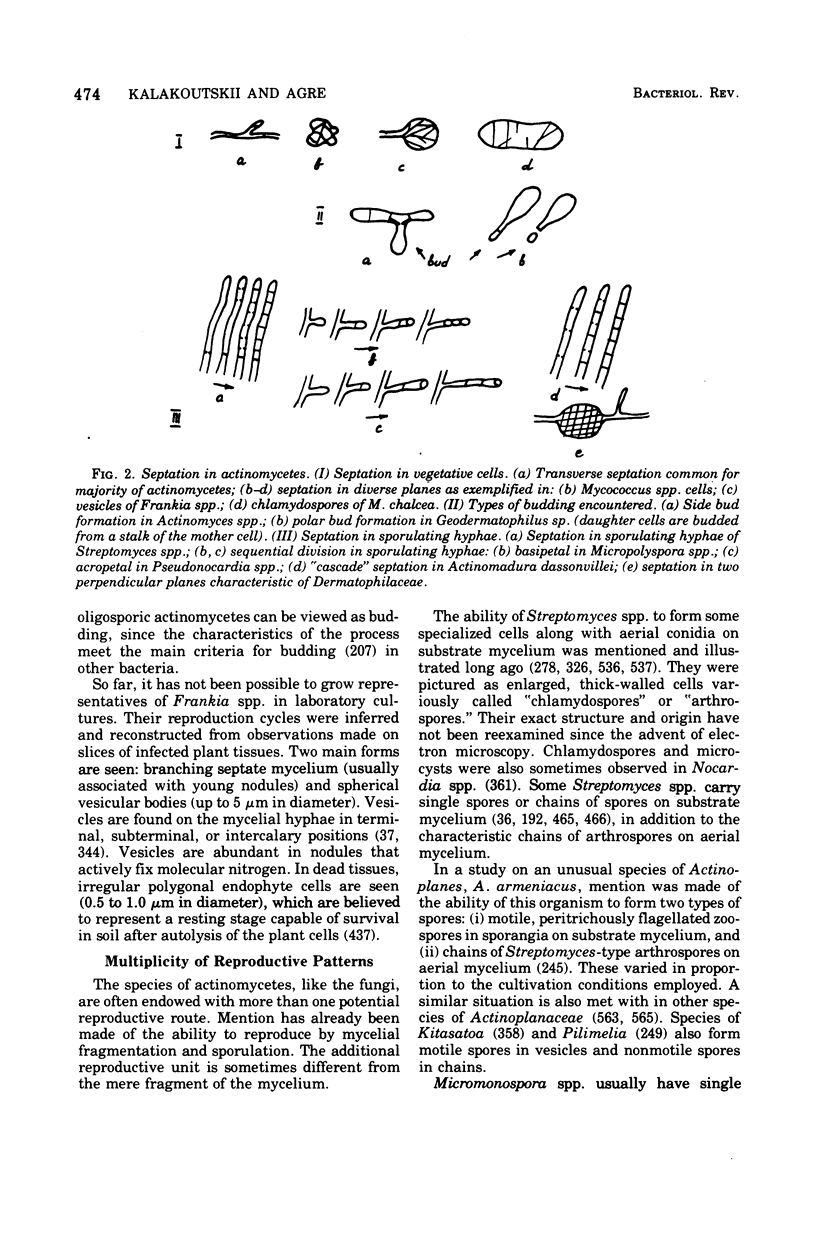
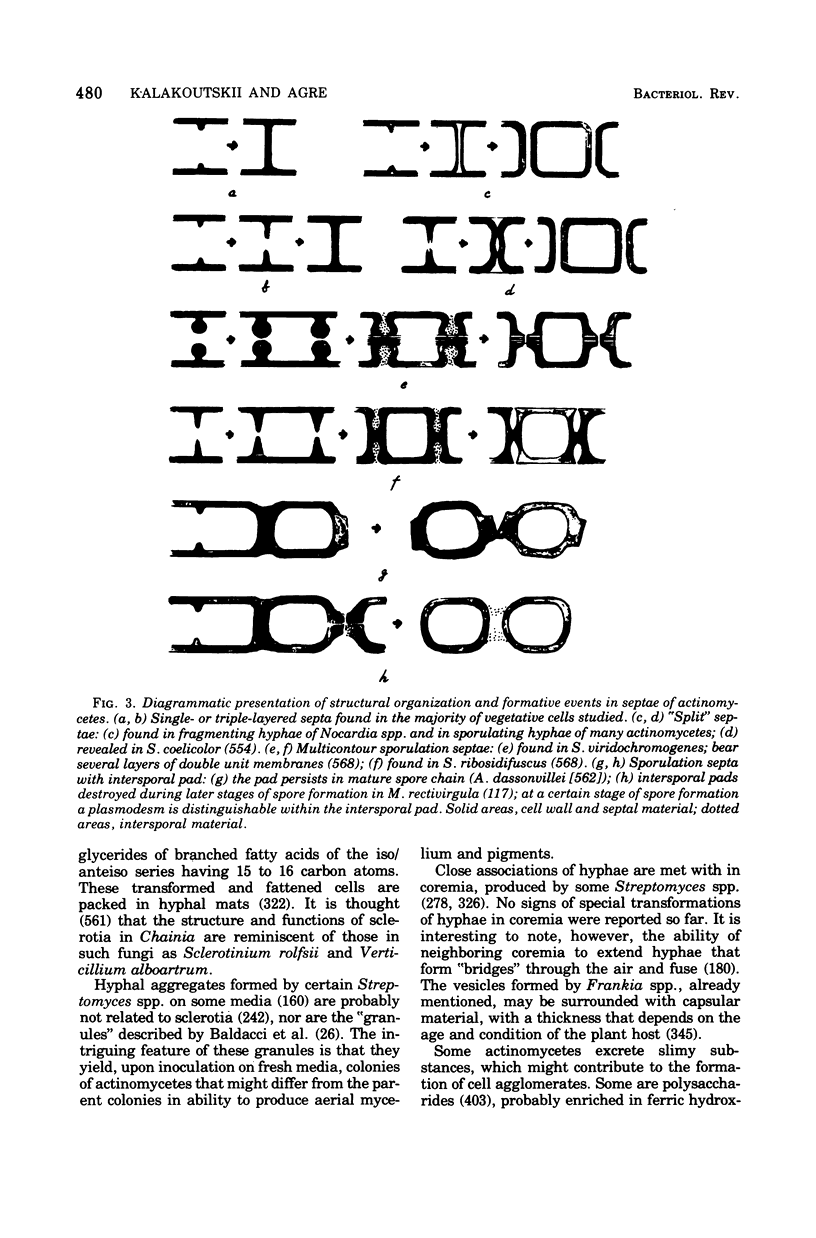
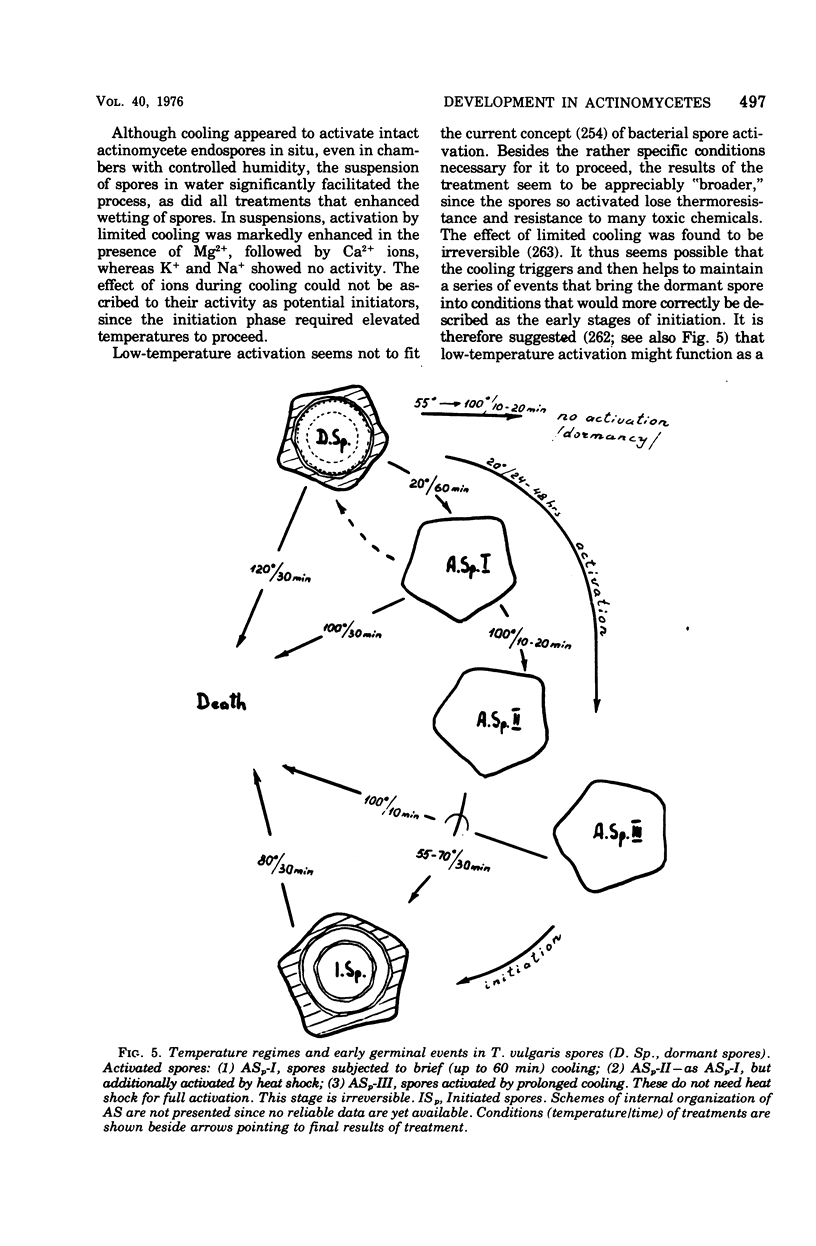
Full text
PDF


















































Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AGRE N. S. [Electron-microscopic studies on Micromonospora vulgaris spores]. Mon Bull Minist Health Public Health Lab Serv. 1962 Mar-Apr;31:275–276. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ARAI T., KURODA S. Fine structure of spiny spores of Streptomyces. J Bacteriol. 1962 Apr;83:924–924. doi: 10.1128/jb.83.4.924-924.1962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adams J. N. Studies on the fragmentation of Nocardia erythropolis in liquid medium. Can J Microbiol. 1966 Jun;12(3):433–441. doi: 10.1139/m66-064. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Agre N. S., Aristovskaia T. V., Parinkina O. M. Akinomitsety v mikrobnykh peizazhakh podzolistykh pochv. Mikrobiologiia. 1973 Mar-Apr;42(2):332–335. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Agre N. S., Dorokhova L. A. Znachenie tonkogo stroeniia reproduktivnykh struktur dlia sistematiki aktinomitsetov. Zh Obshch Biol. 1972 Mar-Apr;33(2):176–186. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Agre N. S., Kirillova I. P., Kalakoutskii L. V. Spore germination in thermophilic actinomycetes. I. Preliminary observations with Thermoactinomyces vulgaris and Actinobifida dichotomica. Zentralbl Bakteriol Parasitenkd Infektionskr Hyg. 1972;127(6):525–538. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Agre N. S., Sokolov A. A., Soina V. S. Elektronno-mikroskopicheskoe izuchenie sporoobrazovaniia Micropolyspora viridinigra i Micropolyspora rubrobrunea. Mikrobiologiia. 1972 Sep-Oct;41(5):854–858. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Agre N. S., Sokolov A. A., Soina V. S. Strukturnye defekty pri sporoobrazovanii u aktinomitsetov. Izv Akad Nauk SSSR Biol. 1973 Nov-Dec;6:814–818. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aronson A. I., Fitz-James P. C. Reconstitution of bacterial spore coat layers in vitro. J Bacteriol. 1971 Oct;108(1):571–578. doi: 10.1128/jb.108.1.571-578.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aslanian R. R., Agre N. S., Tartakovskii A. S. Ustoichivost' aktinomitsetov k deistviiu nekotorykh khimicheskikh reagentov. Mikrobiologiia. 1972 Jul-Aug;41(4):746–747. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Attwell R. W., Cross T. Germination of actinomycete spores. Soc Appl Bacteriol Symp Ser. 1973 Jan;2:197–207. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BALDACCI E., SPALLA C., GREIN A. The classification of the Actinomyces species Streptomyces. Arch Mikrobiol. 1954;20(4):347–357. doi: 10.1007/BF00690879. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BARABAS G., SZABO G. COMPARISON OF CELL WALL COMPOSITION OF STREPTOMYCES GRISEUS STRAINS. Arch Mikrobiol. 1965 Jan 22;50:156–163. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BECKER B., LECHEVALIER M. P., LECHEVALIER H. A. CHEMICAL COMPOSITION OF CELL-WALL PREPARATIONS FROM STRAINS OF VARIOUS FORM-GENERA OF AEROBIC ACTINOMYCETES. Appl Microbiol. 1965 Mar;13:236–243. doi: 10.1128/am.13.2.236-243.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BECKING J. H., DE BOER W. E., HOUWINK A. L. ELECTRON MICROSCOPY OF THE ENDOPHYTE OF ALNUS GLUTINOSA. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1964;30:343–376. doi: 10.1007/BF02046749. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BEKHTEREVA M. N., KOLESNIKOVA I. G. [Morphological characteristics of actinomycetes Act. Iavendulae and Act. aureofaciens after a prolonged cultivation of flowing media]. Mikrobiologiia. 1961 May-Jun;30:402–408. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BENEDICT R. G., LINDENFELSER L. A., STODOLA F. H., TRAUFLER D. H. Studies on Streptomyces griseocarneus and the production of hydroxystreptomycin. J Bacteriol. 1951 Oct;62(4):487–497. doi: 10.1128/jb.62.4.487-497.1951. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRADLEY S. G., LEDERBERG J. Heterokaryosis in Streptomyces. J Bacteriol. 1956 Aug;72(2):219–225. doi: 10.1128/jb.72.2.219-225.1956. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BURKHOLDER P. R., SUN S. H., EHRLICH J., ANDERSON L. Criteria of speciation in the genus Streptomyces. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1954 Oct 29;60(1):102–123. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1954.tb40001.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balassa G. The genetic control of spore formation in bacilli. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1971;56:99–192. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-65241-7_4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baldy R. W., Sommer N. F., Buckley P. M. Recovery of viability and radiation resistance by heat-injured conidia of Penicillium expansum Lk. ex Thom. J Bacteriol. 1970 May;102(2):514–520. doi: 10.1128/jb.102.2.514-520.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barabás G., Szabó G., Müller F., Hevessy Z. Streptomycin-like compound enzymically released from a streptomycin-non-producing Streptomyces griseus strain. Acta Microbiol Acad Sci Hung. 1968;15(2):97–102. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bayne-Jones S. CLUB-FORMATION BY ACTINOMYCES HOMINIS IN GLUCOSE BROTH, WITH A NOTE ON B. ACTINOMYCETUM-COMITANS. J Bacteriol. 1925 Nov;10(6):569–577. doi: 10.1128/jb.10.6.569-577.1925. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beaman B. L., Shankel D. M. Ultrastructure of Nocardia cell growth and development on defined and complex agar media. J Bacteriol. 1969 Sep;99(3):876–884. doi: 10.1128/jb.99.3.876-884.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boltianskaia E. V., Agre N. S., Sokolov A. A., Kalakutskii L. V. Kol'tsa v koloniiakh Thermoactinomyces vulgaris v sviazi s izmeneniiami temperatury i otnositel'noi vlazhnosti. Mikrobiologiia. 1972 Jul-Aug;41(4):675–679. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bott K. F., Davidoff-Abelson R. Altered sporulation and respiratory patterns in mutants of Bacillus subtilis induced by acridine orange. J Bacteriol. 1966 Jul;92(1):229–240. doi: 10.1128/jb.92.1.229-240.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradley S. G., Ritzi D. Composition and ultrastructure of Streptomyces venezuelae. J Bacteriol. 1968 Jun;95(6):2358–2364. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.6.2358-2364.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brevet J. Direct assay for sigma factor activity and demonstration of the loss of this activity during sporulation in Bacillus subtilis. Mol Gen Genet. 1974 Feb 6;128(3):223–221. doi: 10.1007/BF00267111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown O. R., Reda S. Enzyme and permeability changes during morphogenesis of Nocardia corallina. J Gen Microbiol. 1967 May;47(2):199–205. doi: 10.1099/00221287-47-2-199. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brownell G. H., Walsh R. S. Colony mutants of compatible nocardiae displaying variations in recombining capacity. Genetics. 1972 Mar;70(3):341–351. doi: 10.1093/genetics/70.3.341. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHALOUPKA J. Obrazovanie i vydelenie proteazy Streptomyces griseus. Mikrobiologiia. 1958 Jul-Aug;27(4):422–428. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CORTI G. A new method of staining spores of Streptomycetaceae. J Bacteriol. 1954 Sep;68(3):389–390. doi: 10.1128/jb.68.3.389-390.1954. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CRAVERI R., LUGLI A. M., SGARZI B., GIOLITTI G. Distribution of antibiotic-producing streptomycetes in Italian soils. Antibiot Chemother. 1960 May;10:306–311. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CUMMINS C. S., HARRIS H. Studies on the cell-wall composition and taxonomy of Actinomycetales and related groups. J Gen Microbiol. 1958 Feb;18(1):173–189. doi: 10.1099/00221287-18-1-173. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cella R., Vining L. C. Rsistance to streptomycin in a producing strain of Streptomyces griseus. Can J Microbiol. 1975 Apr;21(4):463–472. doi: 10.1139/m75-065. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chater K. F. Construction and phenotypes of double sporulation deficient mutants in Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2). J Gen Microbiol. 1975 Apr;87(2):312–325. doi: 10.1099/00221287-87-2-312. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chater K. F. Rifampicin-resistant mutants of Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2). J Gen Microbiol. 1974 Jan;80(1):277–290. doi: 10.1099/00221287-80-1-277. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cherny N. E., Tikhonenko A. S. Comparative structural characterization of material extractable from aerial sheath of Streptomyces roseoflavus var. roseofungini. Arch Microbiol. 1974;101(1):71–82. doi: 10.1007/BF00455926. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cherny N. E., Tikhonenko A. S., Kuroda S., Kalakoutskii L. V. Purification and preliminary characterization of extracellular tubular structures from a culture of a 'fructose' mutant of Streptomyces roseoflavus var. roseofungini. Microbios. 1974 Apr;10(37):7–14. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clutterbuck A. J. A mutational analysis of conidial development in Aspergillus nidulans. Genetics. 1969 Oct;63(2):317–327. doi: 10.1093/genetics/63.2.317. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen B. L. The neutral and alkaline proteases of Aspergillus nidulans. J Gen Microbiol. 1973 Aug;77(2):521–528. doi: 10.1099/00221287-77-2-521. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collett M. S., Jones G. H. Morphological changes accompanying actinomycin production in Streptomyces antibioticus. J Ultrastruct Res. 1974 Mar;46(3):452–465. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(74)90067-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cross T. Symposium on bacterial spores: 8. The diversity of bacterial spores. J Appl Bacteriol. 1970 Mar;33(1):95–102. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1970.tb05236.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cross T. Thermophilic actinomycetes. J Appl Bacteriol. 1968 Mar;31(1):36–53. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1968.tb00339.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cross T., Walker P. D., Gould G. W. Thermophilic actinomycetes producing resistant endospores. Nature. 1968 Oct 26;220(5165):352–354. doi: 10.1038/220352a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DEMIANOVSKAIA N. S., BELOZERSKII A. N. Dezoksiribonukleinovaia kislota Actinomyces globisporus streptomicini Kras. v protsesse ego razvitiia. Biokhimiia. 1954 Nov-Dec;19(6):688–692. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DOLEZILOVA L., VANEK Z., KRALIK O. An electron-microscopic study of spores of morphological variants of Streptomyces erythreus strains. Nature. 1959 Dec 12;184(Suppl 24):1888–1889. doi: 10.1038/1841888b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DONDERO N. C., SCOTTI T. Excretion by streptomycetes of factors causing formation of aerial hyphae by old cultures. J Bacteriol. 1957 Apr;73(4):584–585. doi: 10.1128/jb.73.4.584-585.1957. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DULANEY E. L. Induced mutation and strain selection in some industrially important microorganisms. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1954 Oct 29;60(1):155–167. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1954.tb40005.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daneo-Moore L., Higgins M. L. Morphokinetic reaction of Streptococcus faecalis (ATCC 9790) cells to the specific inhibition of macromolecular synthesis: nucleoid condensation on the inhibition of protein synthesis. J Bacteriol. 1972 Mar;109(3):1210–1220. doi: 10.1128/jb.109.3.1210-1220.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davey C. B., Miller R. J., Nelson L. A. Temperature-dependent anomalies in the growth of microorganims. J Bacteriol. 1966 May;91(5):1827–1830. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.5.1827-1830.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dawes I. W., Kay D., Mandelstam J. Determining effect of growth medium on the shape and position of daughter chromosomes and on sporulation in Bacillus subtilis. Nature. 1971 Apr 30;230(5296):567–569. doi: 10.1038/230567a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dawes I. W., Mandelstam J. Sporulation of Bacillus subtilis in continuous culture. J Bacteriol. 1970 Sep;103(3):529–535. doi: 10.1128/jb.103.3.529-535.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeJong P. J., McCoy E. Qualitative analyses of vegetative cell walls and spore walls of some representative species of Streptomyces. Can J Microbiol. 1966 Oct;12(5):985–994. doi: 10.1139/m66-133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dean D. H., Douthit H. A. Buoyant density heterogeneity in spores of Bacillus subtilis: biochemical and physiological basis. J Bacteriol. 1974 Feb;117(2):601–610. doi: 10.1128/jb.117.2.601-610.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Demain A. L. How do antibiotic-producing microorganisms avoid suicide? Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1974 May 10;235(0):601–612. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1974.tb43294.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Demain A. L., Inamine E. Biochemistry and regulation of streptomycin and mannosidostreptomycinase (alpha-D-mannosidase) formation. Bacteriol Rev. 1970 Mar;34(1):1–19. doi: 10.1128/br.34.1.1-19.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Demain A. L. Mutation and the production of secondary metabolites. Adv Appl Microbiol. 1973;16:177–202. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2164(08)70027-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dietz A., Mathews J. Classification of Streptomyces spore surfaces into five groups. Appl Microbiol. 1971 Mar;21(3):527–533. doi: 10.1128/am.21.3.527-533.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dipersio J. R., Deal S. J. Identification of intracellular polysaccharide granules in thin sections of Nocardia asteroides. J Gen Microbiol. 1974 Aug;83(2):349–358. doi: 10.1099/00221287-83-2-349. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dmitrieva S. V., Anisova L. N., Ivkina N. S. Izuchenie vzaimodeistviia mutantov actinomyces streptomycini. Antibiotiki. 1973 May;18(5):387–391. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dmitrieva S. V., Ostrikova N. A., Kosheleva G. I. Ispol'sovanie metoda differentsial'nogo tsentrifugirovaniia pri izuchenii geteromorfnosti glubinnoi kul'tury Actinomyces streptomicini 773. Antibiotiki. 1970 May;15(5):397–401. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dmitrieva S. V., Rodionova E. G. Tsitologicheskii analiz razvitiia produtsenta streptomitina v glubinnoi kul'ture v sviazi s ego estestvennoi izmenchivost'iu. Antibiotiki. 1971 Jun;16(6):529–534. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doi R. H., Brown L. R., Rodgers G., Hsu Y. Bacillus subtilis mutant altered in spore morphology and in RNA polymerase activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Jun;66(2):404–410. doi: 10.1073/pnas.66.2.404. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorokhova L. A., Agre N. A., Kalakutskii L. V., Krasil'nikov N. A. Elektronnomikroskopicheskoe izuchenie sporoobrazovaniia u Micromonospora vulgaris. Mikrobiologiia. 1970 Jul-Aug;39(4):680–684. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorokhova L. A., Agre N. S., Kalakutskii L. V., Krasil'nikov N. A. Izuchenie morfologii dvykh kul'tur, otnosiashchikhsia k rodu Micropolyspora. Mikrobiologiia. 1970 Jan-Feb;39(1):95–100. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorokhova L. A., Agre N. S., Krasil'nikov N. A. Ul'trastruktura gif i spor Actinomyces megasporus. Mikrobiologiia. 1971 May-Jun;40(3):517–521. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Draper P., Rees R. J. The nature of the electron-transparent zone that surrounds Mycobacterium lepraemurium inside host cells. J Gen Microbiol. 1973 Jul;77(1):79–87. doi: 10.1099/00221287-77-1-79. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drucker D. B., Whittaker D. K. Examination of certain bacterial colonies by scanning electron microscopy. Microbios. 1971 Sep;4(14):109–113. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duda J. J., Slack J. M. Ultrastructural studies on the genus Actinomyces. J Gen Microbiol. 1972 Jun;71(1):63–68. doi: 10.1099/00221287-71-1-63. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ENSIGN J. C., WOLFE R. S. NUTRITIONAL CONTROL OF MORPHOGENESIS IN ARTHROBACTER CRYSTALLOPIETES. J Bacteriol. 1964 Apr;87:924–932. doi: 10.1128/jb.87.4.924-932.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ERIKSON D. Factors promoting cell division in a soft mycelial type of Nocardia: Nocardia turbata n. sp. J Gen Microbiol. 1954 Oct;11(2):198–208. doi: 10.1099/00221287-11-2-198. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ERIKSON D. Loss of aerial mycelium and other changes in Streptomycete development due to physical variations of cultural conditions. J Gen Microbiol. 1955 Aug;13(1):136–148. doi: 10.1099/00221287-13-1-136. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ERIKSON D. Temperature/growth relationships of a thermophilic actinomycete, Micromonospora vulgaris. J Gen Microbiol. 1952 May;6(3-4):286–294. doi: 10.1099/00221287-6-3-4-286. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ERIKSON D. Thermoduric properties of Nocardia sebivorans and other pathogenic aerobic actinomycetes. J Gen Microbiol. 1955 Aug;13(1):127–135. doi: 10.1099/00221287-13-1-127. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ERIKSON D., WEBLEY D. M. The respiration of a thermophilic Actinomycete, Micromonospora vulgaris. J Gen Microbiol. 1953 Jun;8(3):455–463. doi: 10.1099/00221287-8-3-455. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Egorov N. S., Al'-Nuri M. A. Sravnitel'noe izuchenie soderzhaniia fosfornykh soedinenii kislotorastvorimoi fraktsii 2 shtammov (35 i 144) Act. spheroides v sviaiz s biosintezom antibiotika i mekhanizmom ego deistviia. Antibiotiki. 1968 Dec;13(12):1059–1063. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellar D. J., Lundgren D. G., Slepecky R. A. Fine structure of Bacillus megaterium during synchronous growth. J Bacteriol. 1967 Oct;94(4):1189–1205. doi: 10.1128/jb.94.4.1189-1205.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falkowski J. Elektronenmikroskopische Beobachtungen an den Kernstrukturen unfixierter Sporen eines Stammes von Streptomyces scabies (THAXTER) WAKSMAN et HENRIC. Z Allg Mikrobiol. 1971;11(4):353–355. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feofilova E. P., Lebedeva N. E., Taptykova S. D., Kirillova N. F. Izuchenie dykhaniia okrashennogo i bestsvetnogo variantov Actinomyces longispororuber. Mikrobiologiia. 1966 Jul-Aug;35(4):651–659. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fergus C. L. Resistance of spores of some thermlophilic actinomycetes to high temperature. Mycopathol Mycol Appl. 1967 Aug 14;32(3):205–208. doi: 10.1007/BF02049798. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foster J. W., McDaniel L. E., Woodruff H. B., Stokes J. L. Microbiological Aspects of Penicillin: V. Conidiospore Formation in Submerged Cultures of Penicillium Notatum. J Bacteriol. 1945 Sep;50(3):365–368. doi: 10.1128/jb.50.3.365-368.1945. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Francisco D. E., Silvey J. K. The effect of carbon monoxide inhibition on the growth of an aquatic streptomycete. Can J Microbiol. 1971 Mar;17(3):347–351. doi: 10.1139/m71-058. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freese E. Sporulation of bacilli, a model of cellular differentiation. Curr Top Dev Biol. 1972;7:85–124. doi: 10.1016/s0070-2153(08)60070-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GIOLITTI G. Some observations on the cytochemistry of Streptomyces. J Gen Microbiol. 1960 Aug;23:83–86. doi: 10.1099/00221287-23-1-83. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GLAUERT A. M., HOPWOOD D. A. The fine structure of Streptomyces coelicolor. I. The cytoplasmic membrane system. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1960 Jun;7:479–488. doi: 10.1083/jcb.7.3.479. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GLAUERT A. M., HOPWOOD D. A. The fine structure of Streptomyces violaceoruber (S. coelicolor). III. The walls of the mycelium and spores. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1961 Aug;10:505–516. doi: 10.1083/jcb.10.4.505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOODMAN J. J., MATRISHIN M., BACKUS E. J. The effect of anhydrochlortetracycline on the growth of actinomycetes. J Bacteriol. 1955 Jan;69(1):70–72. doi: 10.1128/jb.69.1.70-72.1955. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GORDON R. E., MIHM J. M. A comparative study of some strains received as nocardiae. J Bacteriol. 1957 Jan;73(1):15–27. doi: 10.1128/jb.73.1.15-27.1957. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GORDON R. E., SMITH M. M. Proposed group of characters for the separation of Streptomyces and Nocardia. J Bacteriol. 1955 Feb;69(2):147–150. doi: 10.1128/jb.69.2.147-150.1955. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREGORY K. F., HUANG J. C. TYROSINASE INHERITANCE IN STREPTOMYCES SCABIES. II. INDUCTION OF TYROSINASE DEFICIENCY BY ACRIDINE DYES. J Bacteriol. 1964 Jun;87:1287–1294. doi: 10.1128/jb.87.6.1287-1294.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GUBERNIEV M. A., TORBOCHKINA L. I., KATS L. N. [On polyphosphates in Act, aureofaciens]. Antibiotiki. 1959 Nov-Dec;4:24–30. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gledhill W. E., Casida L. E. Predominant Catalase-negative Soil Bacteria. III. Agromyces, gen. n., Microorganisms Intermediary to Actinomyces and Nocardia. Appl Microbiol. 1969 Sep;18(3):340–349. doi: 10.1128/am.18.3.340-349.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goren M. B. Mycobacterial lipids: selected topics. Bacteriol Rev. 1972 Mar;36(1):33–64. doi: 10.1128/br.36.1.33-64.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gould G. W., Stubbs J. M., King W. L. Structure and composition of resistant layers in bacterial spore coats. J Gen Microbiol. 1970 Mar;60(3):347–355. doi: 10.1099/00221287-60-3-347. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grove S. N., Bracker C. E. Protoplasmic organization of hyphal tips among fungi: vesicles and Spitzenkörper. J Bacteriol. 1970 Nov;104(2):989–1009. doi: 10.1128/jb.104.2.989-1009.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HENSSEN A. Beiträge zur Morphologie und Systematik der thermophilen Actinomyceten. Arch Mikrobiol. 1957;26(4):373–414. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HESSELTINE C. W., BENEDICT R. G., PRIDHAM T. G. Useful criteria for species differentiation in the genus Streptomyces. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1954 Oct 29;60(1):136–151. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1954.tb40003.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HICKEY R. J., TRESNER H. D. A cobalt-containing medium for sporulation of Streptomyces species. J Bacteriol. 1952 Dec;64(6):891–892. doi: 10.1128/jb.64.6.891-892.1952. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOPWOOD D. A., GLAUERT A. M. Electron microscope observations on the surface structures of Streptomyces violaceoruber. J Gen Microbiol. 1961 Oct;26:325–330. doi: 10.1099/00221287-26-2-325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton-Miller J. M. Chemistry and biology of the polyene macrolide antibiotics. Bacteriol Rev. 1973 Jun;37(2):166–196. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton-Miller J. M. Non-emergence of polyene-resistant yeasts: an hypothesis. Microbios. 1974 Jun-Jul;10A SUPPL(41):91–95. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton W. A., Stubbs J. M. Comparison of the germination and outgrowth of spores of Bacillus cereus and Bacillus polymyxa. J Gen Microbiol. 1967 Apr;47(1):121–129. doi: 10.1099/00221287-47-1-121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heinzen R. J., Ensign J. C. Effect of growth substrates on morphology of Nocardia corallina. Arch Microbiol. 1975 May 5;103(3):209–217. doi: 10.1007/BF00436352. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henssen A., Schnepf E. Zur Kenntnis thermophiler Actinomyceten. Arch Mikrobiol. 1967 Jun 21;57(3):214–231. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henssen A. Streptomyces fragmentosporus, ein neuer thermophiler Actinomycet. Arch Mikrobiol. 1969;67(1):21–27. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hess W. M., Sassen M. M., Remsen C. C. Surface characteristics of Penicillum conidia. Mycologia. 1968 Mar-Apr;60(2):290–303. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hey-Ferguson A., Mitchell M., Elbein A. D. Trehalose metabolism in germinating spores of Streptomyces hygroscopicus. J Bacteriol. 1973 Nov;116(2):1084–1085. doi: 10.1128/jb.116.2.1084-1085.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgins M. L., Pooley H. M., Shockman G. D. Site of initiation of cellular autolysis in Streptococcus faecalis as seen by electron microscopy. J Bacteriol. 1970 Aug;103(2):504–512. doi: 10.1128/jb.103.2.504-512.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgins M. L. Release of sporangiospores by a strain of Actinoplanes. J Bacteriol. 1967 Sep;94(3):495–498. doi: 10.1128/jb.94.3.495-498.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgins M. L., Shockman G. D. Model for cell wall growth of Streptococcus faecalis. J Bacteriol. 1970 Feb;101(2):643–648. doi: 10.1128/jb.101.2.643-648.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgins M. L., Silvey J. K. Slide culture observations of two freshwater actinomycetes. Trans Am Microsc Soc. 1966 Jul;85(3):390–398. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirsch P. Budding bacteria. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1974;28(0):391–444. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.28.100174.002135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hitchins A. D., Slepecky R. A. Bacterial sporulation as a modified procaryotic cell division. Nature. 1969 Aug 23;223(5208):804–807. doi: 10.1038/223804a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hodgson B. Possible roles for antibiotics and other biologically active peptides at specific stages during sporulation of Bacillaceae. J Theor Biol. 1971 Jan;30(1):111–119. doi: 10.1016/0022-5193(71)90040-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holt S. C., Leadbetter E. R. Comparative ultrastructure of selected aerobic spore-forming bacteria: a freeze-etching study. Bacteriol Rev. 1969 Jun;33(2):346–378. doi: 10.1128/br.33.2.346-378.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopwood D. A., Chater K. F., Dowding J. E., Vivian A. Advances in Streptomyces coelicolor genetics. Bacteriol Rev. 1973 Sep;37(3):371–405. doi: 10.1128/br.37.3.371-405.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopwood D. A. Genetics of the Actinomycetales. Soc Appl Bacteriol Symp Ser. 1973 Jan;2:131–153. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopwood D. A., Wildermuth H., Palmer H. M. Mutants of Streptomyces coelicolor defective in sporulation. J Gen Microbiol. 1970 Jun;61(3):397–408. doi: 10.1099/00221287-61-3-397. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hranueli D., Piggot P. J., Mandelstam J. Statistical estimate of the total number of operons specific for Bacillus subtilis sporulation. J Bacteriol. 1974 Sep;119(3):684–690. doi: 10.1128/jb.119.3.684-690.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hussein A., Krasil'nikov N. A. Slizistye aktinomitsety pochv Egipta. Mikrobiologiia. 1969 Sep-Oct;38(5):878–882. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishiguro E. E., Wolfe R. S. Control of morphogenesis in Geodermatophilus: ultrastructural studies. J Bacteriol. 1970 Oct;104(1):566–580. doi: 10.1128/jb.104.1.566-580.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishiguro E. E., Wolfe R. S. Induction of morphogenesis in Geodermatophilus by inorganic cations and by organic nitrogenous cations. J Bacteriol. 1974 Jan;117(1):189–195. doi: 10.1128/jb.117.1.189-195.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ivanitskaia L. P. Morfologicheskie osobennosti produtsenta protivoopukjolevogo antibiotika sibiromitsina Streptosporangium sibiricum Gause et al., 1969, v glubinnykh kul'turakh. Antibiotiki. 1971 Mar;16(3):233–236. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JAGNOW G. Beiträge zur Okologie der Streptomyceten. Arch Mikrobiol. 1957;26(2):175–191. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JANSSEN F. W., LUND A. J., ANDERSON L. E. Colorimetric assay for dipicolinic acid in bacterial spores. Science. 1958 Jan 3;127(3288):26–27. doi: 10.1126/science.127.3288.26. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JONES K. L. Variation in Streptomyces. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1954 Oct 29;60(1):124–135. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1954.tb40002.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JORDAN H. V., HOWELL A. NUTRITIONAL CONTROL OF CELLULAR MORPHOLOGY IN AN AEROBIC ACTINOMYCETE FROM THE HAMSTER. J Gen Microbiol. 1965 Jan;38:125–130. doi: 10.1099/00221287-38-1-125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jagger J., Stafford R. S., Mackin R. J., Jr Killing and photoreactivation of Streptomyces griseus conidia by vacuum-ultraviolet and far-ultraviolet radiation (1500 to 2700 A). Radiat Res. 1967 Sep;32(1):64–92. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jayaraman K., Kannan R. The role of polypeptide antibiotics on the bacterial differentiation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 Sep 5;48(5):1235–1239. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(72)90843-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones K. L. Further Notes on Variation in Certain Saprophytic Actinomycetes. J Bacteriol. 1946 Feb;51(2):211–216. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KOSMACHEV A. E. [Thermomonophilic Micromonospora and its production of the antibiotic T-12 in conditions of surface and deep fermentation at 50-60 degrees]. Mikrobiologiia. 1962 Jan-Feb;31:66–71. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KRASIL'NIKOV N. A. O nekletochnykh formakh u mikroorganizmov. Usp Sovrem Biol. 1954 Jan-Feb;37(1):22–32. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KUDRINA E. S., PREOBRAZHENSKAIA T. P., SVESHNIKOVA M. A., MAKSIMOVA Ts. SRAVNITEL'NAIA OTSENKA RAZLICHNYKH PITATEL'NYKH SRED DLIA VYIAVLENIIA MORFOLOGICHESKIKH I KUL'TURAL'NYKH PRIZNAKOV AKTINOMITSETOV. Mikrobiologiia. 1964 Sep-Oct;33:873–879. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalakoutskii L. V., Agre N. S. Endospores of actinomycetes: dormancy and germination. Soc Appl Bacteriol Symp Ser. 1973 Jan;2:179–195. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalakutskii L. V., Agre N. S., Aslanian R. R. Termoustoichivost' spor aktinomitsetov v sviazi s soderzhaniem v nikh dipikolinovoi kisloty, kal'tsiia i magniia. Dokl Akad Nauk SSSR. 1969 Feb 11;184(5):1214–1216. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalakutskii L. V., Bobkova E. A., Krasil'nikov N. A. Vkliuchenie P32 v neprorastaiushchie konidii aktinomitseta Actinomyces streptomycini Krass. Dokl Akad Nauk SSSR. 1966 Sep 21;170(3):705–707. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalakutskii L. V., Kuimova T. F. O deistvii faga na konidii Actinomyces streptomycini B-6. Dokl Akad Nauk SSSR. 1967 Mar 11;173(2):443–444. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalakutskii L. V., Mukhin L. M., Lapteva E. A., Taptykova S. D., Skvortsova I. I. Kharakteristika protsessov, soprovozhdaiushchikh prorastanie konidii Actinomyces streptomycini B-6. Izv Akad Nauk SSSR Biol. 1970 Jul-Aug;4:593–599. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kannan L. V., Rehacek Z. Formation of poly-beta-hydroxybutyrate by Actinomycetes. Indian J Biochem. 1970 Jun;7(2):126–129. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanne R., Klein-Vogler U., Zähner H. Stoffwechselprodukte von Mikroorganismen. 122. Uber Beziehungen zwischen Makroterolidbildung und Kaliumtransport bei Streptomyces griseus. Arch Mikrobiol. 1973 Nov 2;93(3):205–218. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz E. Biosynthesis of polypeptide antibiotics. Pure Appl Chem. 1971;28(4):551–570. doi: 10.1351/pac197128040551. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelner A. Effect of Visible Light on the Recovery of Streptomyces Griseus Conidia from Ultra-violet Irradiation Injury. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1949 Feb;35(2):73–79. doi: 10.1073/pnas.35.2.73. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khokhlov A. S., Anisova L. N., Tovarova I. I., Kleiner E. M., Kovalenko I. V., Krasilnikova O. I., Kornitskaya E. Y., Pliner S. A. Effect of A-factor on the growth of asporogenous mutants of Streptomyces griseus, not producing this factor. Z Allg Mikrobiol. 1973;13(8):647–655. doi: 10.1002/jobm.3630130803. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konev Iu E., Tsyganov V. A., Minbaev R., Morozov V. M. Novyi rod aktinomitsetov Microechinospora ge. nov. Mikrobiologiia. 1967 Mar-Apr;36(2):309–317. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornberg A., Spudich J. A., Nelson D. L., Deutscher M. P. Origin of proteins in sporulation. Annu Rev Biochem. 1968;37:51–78. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.37.070168.000411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krulwich T. A., Ensign J. C. Alteration of glucose metabolism of Arthrobacter crystallopoietes by compounds which induce sphere to rod morphogenesis. J Bacteriol. 1969 Feb;97(2):526–534. doi: 10.1128/jb.97.2.526-534.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krulwich T. A., Ensign J. C., Tipper D. J., Strominger J. L. Sphere-rod morphogenesis in Arthrobacter crystallopoietes. I. Cell wall composition and polysaccharides of the peptidoglycan. J Bacteriol. 1967 Sep;94(3):734–740. doi: 10.1128/jb.94.3.734-740.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krulwich T. A., Ensign J. C., Tipper D. J., Strominger J. L. Sphere-rod morphogenesis in Arthrobacter crystallopoietes. II. Peptides of the cell wall peptidoglycan. J Bacteriol. 1967 Sep;94(3):741–750. doi: 10.1128/jb.94.3.741-750.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kudo K., Kikuchi M., Ishida N. Biogenesis of an antitumor antibiotic protein, neocarzinostatin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1972 Apr;1(4):289–295. doi: 10.1128/aac.1.4.289. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurylowicz W., Kurzatkowski W., Woźnicka W., Paszkiewicz A., Williams S. T. Ultrastructure of selected strains of actinomycetes during biosynthesis of antibiotics. Postepy Hig Med Dosw. 1974 Jul-Aug;28(4):419–426. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurylowicz W., Malinowski K. Ultrastructure of the mycelium of Streptomyces aureofaciens in the course of biosynthesis of tetracycline. Postepy Hig Med Dosw. 1972 Jul-Aug;26(4):563–569. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kutzner H. J. Variabilität bei Streptomyzete. Eine Ubersicht. Zentralbl Bakteriol Parasitenkd Infektionskr Hyg. 1967;121(4):394–413. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuznetsov V. D. Gomologicheskie riady nasledstvennoi izmenchivosti aktinomitsetov. Antibiotiki. 1973 Jul;18(7):579–586. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuznetsov V. D., Rodionova E. G. Izuchenie sostava diaminopimelinovykh kislot kletochnykhstenok aktinomitsetov--produtsentov antibiotikov i ikh proaktinomitsetopodobnykh variantov. Antibiotiki. 1974 Feb;19(2):131–135. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kvasnikov E. I., Pisarchuk E. N., Stepaniuk V. V., Nesterenko O. A. Osobennosti biologii Arthrobacter simplex (Jensen) Lochhead. Izv Akad Nauk SSSR Biol. 1974 Jul-Aug;4(0):587–590. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LECHEVALIER H. A., SOLOTOROVSKY M., McDURMONT C. I. A new genus of the Actinomycetales: Micropolyspora gen. nov. J Gen Microbiol. 1961 Sep;26:11–18. doi: 10.1099/00221287-26-1-11. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LECHEVALIER H., HOLBERT P. E. ELECTRON MICROSCOPIC OBSERVATION OF THE SPORANGIAL STRUCTURE OF A STRAIN OF ACTINOPLANES. J Bacteriol. 1965 Jan;89:217–222. doi: 10.1128/jb.89.1.217-222.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LION M. B., KIRBY-SMITH J. S., RANDOLPH M. L. Electronspin resonance signals from lyophilized bacterial cells exposed to oxygen. Nature. 1961 Oct 7;192:34–36. doi: 10.1038/192034a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lacey J. Thermoactinomyces sacchari sp. nov., a thermophilic actinomycete causing bagassosis. J Gen Microbiol. 1971 Jun;66(3):327–338. doi: 10.1099/00221287-66-3-327. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamanna C. The Taxonomy of the Genus Bacillus: I. Modes of Spore Germination. J Bacteriol. 1940 Sep;40(3):347–361. doi: 10.1128/jb.40.3.347-361.1940. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lapteva E. A., Kuznetsov V. D., Kalakutskii L. V. Zhiznesposobnost' spor Actinomyces spp. pri khranenii v usloviiakh razlichnoi otnositel'noi vlazhnosti. Mikrobiologiia. 1972 Sep-Oct;41(5):845–848. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leach C. K., Ashworth J. M. Characterization of DNA from the cellular slime mould Dictyostelium discoideum after growth of the amoebae in different media. J Mol Biol. 1972 Jul 14;68(1):35–48. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90260-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lechevalier H. A., Lechevalier M. P., Holbert P. E. Electron microscopic observation of the sporangial structure of strains of Actinoplanaceae. J Bacteriol. 1966 Oct;92(4):1228–1235. doi: 10.1128/jb.92.4.1228-1235.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lechevalier H., Lechevalier M. P. Ultramicroscopic structure of Intrasporangium calvum (Actinomycetales). J Bacteriol. 1969 Oct;100(1):522–525. doi: 10.1128/jb.100.1.522-525.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levitov M. M., Navol'neva I. N., Meshkov A. N. Vliianie kharaktera azotistogo pitaniia na biosintez proteazy aktinomitsetom 771. Mikrobiologiia. 1974 Jan-Feb;43(1):76–82. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lingg A. J., McMahon K. J., Consigli R. A. Heat-induced increase in the number of viable cells in lyophilized preparations of Bacillus popilliae. Appl Microbiol. 1975 Feb;29(2):303–304. doi: 10.1128/am.29.2.303-304.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowry R. J., Sussman A. S. Intra-hyphal hyphae in "clock" mutants of Neurospora. Mycologia. 1966 Jul-Aug;58(4):541–548. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ludvík J., Mikulík K., Vanek Z. Fine structure of Streptomyces aureofaciens producing tetracycline. Folia Microbiol (Praha) 1971;16(6):479–480. doi: 10.1007/BF02872723. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luedemann G. Micromonospora taxonomy. Adv Appl Microbiol. 1969;11:101–133. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2164(08)70608-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MACH B., TATUM E. L. ENVIRONMENTAL CONTROL OF AMINO ACID SUBSTITUTIONS IN THE BIOSYNTHESIS OF THE ANTIBIOTIC POLYPEPTIDE TYROCIDINE. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1964 Oct;52:876–884. doi: 10.1073/pnas.52.4.876. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MACH F. [Electron microscopic research on the origin of "spiral" Streptomyces spores]. Experientia. 1960 Apr 15;16:142–144. doi: 10.1007/BF02157720. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARSHALL K. C., ALEXANDER M. Growth characteristics of fungi and actinomycetes. J Bacteriol. 1960 Sep;80:412–416. doi: 10.1128/jb.80.3.412-416.1960. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARTON M., SZABO I. Occurrence and ecology of Actinomyces levoris in Hungarian soils. Acta Microbiol Acad Sci Hung. 1962;9:39–44. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mach F., Agre N. S. Die Feinstruktur der Sporen von Actinobifida chromogena. Acta Biol Med Ger. 1968;21(4):575–576. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malik V. S. Chloramphenicol. Adv Appl Microbiol. 1972;15:297–336. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2164(08)70095-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marchenko I. V., Egorova S. A., Blinov N. O., Krassilnikov N. A. The role of iron in the formation of green pigments by actinomycetes. Z Allg Mikrobiol. 1968;8(5):437–439. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marchenko I. V., Egorova S. A., Blinov N. O. Proviridomitsin-predshestvennik zelenykh pigmentov Aktinomitsetov. Dokl Akad Nauk SSSR. 1968 Aug;180(4):978–980. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall R., Redfield B., Katz E., Weissbach H. Changes in phenoxazinone synthetase activity during the growth cycle of Streptomyces antibioticus. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1968 Feb;123(2):317–323. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(68)90141-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martinelli S. D., Clutterbuck A. J. A quantitative survey of conidiation mutants in Aspergillus nidulans. J Gen Microbiol. 1971 Dec;69(2):261–268. doi: 10.1099/00221287-69-2-261. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matseliukh B. P., Andreiuk E. I. Elektronnomikroskopicheskoe issledovanie stroniniia voloskov na obolochke spor Actinomyces olivaceus VKX-50. Dokl Akad Nauk SSSR. 1968 Aug 11;181(5):1263–1265. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsumae A., Ohtani M., Takeshima H., Hata T. A new genus of the Actinomycetales: Kitasatoa gen. nov. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1968 Oct;21(10):616–625. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.21.616. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGinnis M. R., Padhye A. A., Ajello L. Storage of stock cultures of filamentous fungi, yeasts, and some aerobic actinomycetes in sterile distilled water. Appl Microbiol. 1974 Aug;28(2):218–222. doi: 10.1128/am.28.2.218-222.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mikulík K., Karnetová J., Quyen N., Blumauerová M., Komersová I., Vanek Z. Interaction of tetracycline with protein synthesizing system of Streptomyces aureofaciens. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1971 Dec;24(12):801–809. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.24.801. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mikulíl K., Dinh Quyen N., Blumauerová M., Vanek Z. Binding of aureovocin to ribosomes of Streptomyces aureofaciens B-96. FEBS Lett. 1969 Oct 21;5(2):131–134. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(69)80313-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mukvich N. S., Matseliuk B. P. Syntez DNK v dynamitsi prorostannia spor Actinomyces olivaceus V K. Mikrobiol Zh. 1973 May-Jun;35(3):293–298. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray C. D., Pun P., Strauss N. Template specificity changes of DNA-dependent RNA polymerase in B. subtilis during sporulation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1974 Sep 9;60(1):295–303. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(74)90204-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murrell W. G., Scott W. J. The heat resistance of bacterial spores at various water activities. J Gen Microbiol. 1966 Jun;43(3):411–425. doi: 10.1099/00221287-43-3-411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muñoz E., Marquet A., Larraga V., Coyette J. Isolation, partial characterization of the cytoplasmic membrane fraction of Streptomyces albus G and DD-carboxypeptidase localization. Arch Mikrobiol. 1972;81(3):273–288. doi: 10.1007/BF00412246. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NEEDHAM A. E. The quadratic relation in differential growth. Nature. 1957 Dec 7;180(4597):1293–1293. doi: 10.1038/1801293a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NEWCOMBE H. B. Radiation-induced instabilities in Streptomyces. J Gen Microbiol. 1953 Aug;9(1):30–36. doi: 10.1099/00221287-9-1-30. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nikitina E. T., Kalakoutskii L. V. Actinomycete variants with impaired differentiation: production in high yield, recognition and phenotypic characterization in seven species. J Appl Bacteriol. 1973 Dec;36(4):599–618. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1973.tb04146.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nikitina E. T., Kalakoutskii L. V. Induction of nocardioform growth in actinomycetes on media with D-fructose. Z Allg Mikrobiol. 1971;11(7):601–606. doi: 10.1002/jobm.3630110705. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nikitina E. T., Kazakova G. G., Kalakutskii L. V. Induktsiia osobogo tipa razvitiia u Actinomyces roseoflavus var. roseofungini na srede s fruktozoi. Dokl Akad Nauk SSSR. 1971 Jan 11;196(2):448–450. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novikova N. L., Kapitonova O. N., Lomovskaia N. D. Termoinduktsiia profaga v prorastaiushchikh sporakh Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2) (0C31ct-1. Mikrobiologiia. 1973 Jul-Aug;42(4):713–718. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OGINSKY E. L., SMITH P. H., UMBREIT W. W. The action of streptomycin on the respiration of Streptomyces griseus. J Bacteriol. 1951 May;61(5):639–642. doi: 10.1128/jb.61.5.639-642.1951. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okorokov L. A., Kholodenko V. P., Kulaev I. S. Polimernyi ortofosfat zheleza u aktinomitsetov. Izv Akad Nauk SSSR Biol. 1973 Sep-Oct;5:748–751. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orrego C., Kerjan P., Manca de Nadra M. C., Szulmajster J. Ribonucleic acid polymerase in a thermosensitive sporulation mutant (ts-4) of Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1973 Nov;116(2):636–647. doi: 10.1128/jb.116.2.636-647.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PENAU H., HAGEMANN G., VELU H., PEYRE M. Modalités du cycle évolutif de Streptomyces griseus en culture profonde. Rev Immunol Ther Antimicrob. 1954;18(4):265–281. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PENAU H., PEYRE M., VELU H. Sur un mode de multiplication des Streptomyces. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1954 Apr;86(4):527–528. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PFENNIG N. Untersuchungen über extracelluläre Schleimsubstanzen von Streptomyces spec. Arch Mikrobiol. 1958;29(1):90–100. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PINE L., OVERMAN J. R. DETERMINATION OF THE STRUCTURE AND COMPOSITION OF THE 'SULPHUR GRANULES' OF ACTINOMYCES BOVIS. J Gen Microbiol. 1963 Aug;32:209–223. doi: 10.1099/00221287-32-2-209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PRIDHAM T. G., ANDERSON P., FOLEY C., LINDENFELSER L. A., HESSELTINE C. W., BENEDICT R. G. A selection of media for maintenance and taxonomic study of Streptomyces. Antibiot Annu. 1956:947–953. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pavlasová E., Stejskalová E. Transport of histone into Escherichia coli. Folia Microbiol (Praha) 1972;17(6):471–478. doi: 10.1007/BF02872732. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perlman D., Sebek O. K. Microbial transformations of antibiotics. Pure Appl Chem. 1971;28(4):637–648. doi: 10.1351/pac197128040637. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pirt S. J. A theory of the mode of growth of fungi in the form of pellets in submerged culture. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1966 Dec 13;166(1004):369–373. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1966.0105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polacheck Y., Rosengerger R. F. Autolytic enzymes in hyphae of Aspergillus nidulans: their action on old and newly formed walls. J Bacteriol. 1975 Jan;121(1):332–337. doi: 10.1128/jb.121.1.332-337.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollock M. R. The changing concept of organism in microbiology. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 1969;19(2):271–305. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pozharitskaia L. M., Vanin A. F., Kalakutskii L. V. Paramagnitnye tsentry intaktnykh i prorastaiushchikh spor Actinomyces streptomycini B-6. Dokl Akad Nauk SSSR. 1972 Feb 21;202(6):1429–1431. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prauser H., Lechevalier M. P., Lechevalier H. Description of Oerskovia gen. n. to harbor Orskov's motile nocardia. Appl Microbiol. 1970 Mar;19(3):534–534. doi: 10.1128/am.19.3.534-534.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preobrazhenskaia T. P., Altukhova L. B., Dorozhinskii V. B., Ivanova L. V. Infrakrasnye spektry spor aktinomitsetov. Mikrobiologiia. 1966 Jan-Feb;35(1):96–99. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RAMIREZ C., MILLER J. J. Accumulation of free proline during yeast sporogenesis. Nature. 1963 Feb 16;197:723–723. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RANCOURT M. W., LECHEVALIER H. A. ELECTRON MICROSCOPIC STUDY OF THE FORMATION OF SPINY CONIDIA IN SPECIES OF STREPTOMYCES. Can J Microbiol. 1964 Jun;10:311–316. doi: 10.1139/m64-042. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RANCOURT M., LECHEVALIER H. A. Electron microscopic observation of the sporangial structure of an actinomycete, Microellobosporia flavea. J Gen Microbiol. 1963 Jun;31:495–498. doi: 10.1099/00221287-31-3-495. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RAUTENSHTEIN Ia I., SOKOLOVA A. I. Sravintel'noe izuchenie aktivnosti katalazy i nekotorykh drugikh biokhimicheskikh pokazatelei u fagoustoichivykh i fagochuvstvitel'nykh form aktinomitsetov. Mikrobiologiia. 1956 Jul-Aug;25(4):466–470. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REUSSER F. STABILITY AND DEGENERATION OF MICROBIAL CULTURES ON REPEATED TRANSFER. Adv Appl Microbiol. 1963;5:189–215. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2164(08)70011-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RIZZO A. A., SCOTT D. B., BLADEN H. A. Calcification of oral bacteria. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1963 May 31;109:14–22. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1963.tb13458.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROBERTS D. S. SYNERGISTIC EFFECTS OF SALTS AND CARBON DIOXIDE ON DERMATOPHILUS DERMATONOMUS. J Gen Microbiol. 1964 Dec;37:403–410. doi: 10.1099/00221287-37-3-403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rehácek Z., Ramankutty M., Kaslík J. Composition of the rigid-layer of Streptomyces antibioticus producing peptide antibiotics. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1968 Jun;21(6):393–398. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.21.393. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richard J. L., Ritchie A. E., Pier A. C. Electron microscopic anatomy of motile-phase and germinating cells of Dermatophilus congolensis. J Gen Microbiol. 1967 Oct;49(1):23–29. doi: 10.1099/00221287-49-1-23. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SABO I., MARTON M., PARTAI G. K SISTEMATIKE I 'EKOLOGII GRUPPY ACTINOMYCES GRISEUS. Antibiotiki. 1964 Feb;9:105–109. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SAITO H., IKEDA Y. Evidences for the bipartite or diploid nuclei in conidia of Streptomyces griseoflavus. Experientia. 1957 Dec 15;13(12):473–474. doi: 10.1007/BF02159403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHNEIDAU J. D., Jr, SHAFFER M. F. Studies on Nocardia and other actinomycetales. I. Cultural studies. Am Rev Tuberc. 1957 Nov;76(5):770–788. doi: 10.1164/artpd.1957.76.5.770. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHAMINA Z. B. NABLIUDENIIA ZA IADERNYMI 'ELEMENTAMI V PROTSESSE SPOROOBRAZOVANIIA U AKTINOMITSETOV. Mikrobiologiia. 1964 Sep-Oct;33:831–835. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SILVESTRI L. G. L'importanza fondamentale del pH nella sporificazione dello Streptomyces aureofaciens. Rend Ist Sup Sanit. 1955;18(12):1312–1321. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SKINNER F. A. A method for distinguishing between viable spores and mycelial fragments of actinomycetes in soils. J Gen Microbiol. 1951 Feb;5(1):159–166. doi: 10.1099/00221287-5-1-159. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SNEATH P. H. Longevity of micro-organisms. Nature. 1962 Aug 18;195:643–646. doi: 10.1038/195643a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SOHLER A., ROMANO A. H., NICKERSON W. J. Biochemistry of the Actinomycetales. III. Cell wall composition and the action of lysozyme upon cells and cell walls of the Actinomycetales. J Bacteriol. 1958 Mar;75(3):283–290. doi: 10.1128/jb.75.3.283-290.1958. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STUART D. C., Jr Fine structure of the nucleoid and internal membrane systems of Streptomyces. J Bacteriol. 1959 Aug;78:272–281. doi: 10.1128/jb.78.2.272-281.1959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sadoff H. L. Comparative aspects of morphogenesis in three prokaryotic genera. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1973;27:133–153. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.27.100173.001025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sadoff H. L. The antibiotics of Bacillus species: their possible roles in sporulation. Prog Ind Microbiol. 1972;11:1–27. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarkar N., Paulus H. Function of peptide antibiotics in sporulation. Nat New Biol. 1972 Oct 25;239(95):228–230. doi: 10.1038/newbio239228a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarngadharan M. G., Pogell B. M., Kariya M. Occurrence of new metabolites containing N 6 ,N 6 -dimethyladenine in spores of Streptomyces alboniger. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Apr 12;262(4):405–409. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(72)90483-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaeffer P., Millet J., Aubert J. P. Catabolic repression of bacterial sporulation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1965 Sep;54(3):704–711. doi: 10.1073/pnas.54.3.704. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaeffer P. Sporulation and the production of antibiotics, exoenzymes, and exotonins. Bacteriol Rev. 1969 Mar;33(1):48–71. doi: 10.1128/br.33.1.48-71.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaffner C. P., Gordon H. W. The hypocholesterolemic activity of orally administered polyene macrolides. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Sep;61(1):36–41. doi: 10.1073/pnas.61.1.36. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scribner H. E., 3rd, Tang T., Bradley S. G. Production of a sporulation pigment by Streptomyces venezuelae. Appl Microbiol. 1973 Jun;25(6):873–879. doi: 10.1128/am.25.6.873-879.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharples G. P., Williams S. T., Bradshaw R. M. Spore formation in the Actinoplanaceae (Actinomycetales). Arch Microbiol. 1974;101(1):9–20. doi: 10.1007/BF00455921. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharples G. P., Williams S. T. Fine structure of the globose bodies of dactylosporangium thailandense (actinomycetales). J Gen Microbiol. 1974 Sep;84(1):219–222. doi: 10.1099/00221287-84-1-219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shively J. M. Inclusion bodies of prokaryotes. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1974;28(0):167–187. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.28.100174.001123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simúth J., Zelinka J. Nucleic acid degradation products of Streptomyces aureofaciens. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1970 May;23(5):242–249. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.23.242. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinberg W. Properties and developmental roles of the lysyl- and tryptophanyl-transfer ribonucleic acid synthetases of Bacillus subtilis: common genetic origin of the corresponding spore and vegetative enzymes. J Bacteriol. 1974 Apr;118(1):70–82. doi: 10.1128/jb.118.1.70-82.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sudo S. Z., Dworkin M. Comparative biology of prokaryotic resting cells. Adv Microb Physiol. 1973;9:153–224. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2911(08)60378-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suput J., Lechevalier M. P., Lechevalier H. A. Chemical composition of variants of aerobic actinomycetes. Appl Microbiol. 1967 Nov;15(6):1356–1361. doi: 10.1128/am.15.6.1356-1361.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szabó G., Békési I., Vitális S. Mode of action of Factor C, a substance of regulatory function in cyto-differentiation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1967 Aug 22;145(1):159–165. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(67)90665-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szabó G., Vályi-Nagy T., Vitális S. An endogenous factor regulating the life cycle of Streptomyces griseus. Acta Biol Acad Sci Hung. 1967;18(3):237–243. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szeszák F., Szabó G. Alteration of RNA synthesis in vitro with an endogenous regulating factor of cytodifferentiation of Streptomyces griseus. Acta Biol Acad Sci Hung. 1973;24(1):11–17. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szeszák F., Szabó G. Antibiotic production of hyphal fractions of Streptomyces griseus. II. Streptomycin production of different fractions obtained by density gradient centrifugation. Appl Microbiol. 1967 Sep;15(5):1010–1013. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- THIRUMALACHAR M. J. Chainia, a new genus of the Actinomycetales. Nature. 1955 Nov 12;176(4489):934–935. doi: 10.1038/176934b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TRESNER H. D., DANGA F., PORTER J. N. Long-term maintenance of Streptomyces in deep freeze. Appl Microbiol. 1960 Nov;8:339–341. doi: 10.1128/am.8.6.339-341.1960. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taptykova S. D., Kalakutskii L. V. Obratimoe sniatie svetom ingibiruiushchego deistviia polienovogo antibiotika na aktinomitset-produtsent. Dokl Akad Nauk SSSR. 1975 Jan 21;220(3):715–718. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teraoka H., Tanaka K. Properties of ribosomes from Streptomyces erythreus and Streptomyces griseus. J Bacteriol. 1974 Oct;120(1):316–321. doi: 10.1128/jb.120.1.316-321.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tewfik E. M., Bradley S. G. Characterization of deoxyribonucleic acids from streptomycetes and nocardiae. J Bacteriol. 1967 Dec;94(6):1994–2000. doi: 10.1128/jb.94.6.1994-2000.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thiemann J. E., Pagani H., Beretta G. A new genus of the Actinomycetales: Microtetraspora gen. nov. J Gen Microbiol. 1968 Feb;50(2):295–303. doi: 10.1099/00221287-50-2-295. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tikhonenko A. S., Rudaia S. M., Solov'eva N. K., Singal E. M. Neobychnye strukturnye élementy v liziruiushchikhsia kletkakh aktinomitseta. Antibiotiki. 1972 Sep;17(9):781–786. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tjian R., Losick R. An immunological assay for the sigma subunit of RNA polymerase in extracts of vegetative and sporulating Bacillus subtilis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Jul;71(7):2872–2876. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.7.2872. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toropova E. G., Egorov N. S., Bil'trikova A. A. Fiziologicheskaia rol' antibiotikov v zhinznedeiatel'nosti organizmov, obrazuiushchikh ikh. Antibiotiki. 1970 Jul;15(7):658–668. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toropova E. G., Egorov N. S., Ivanova I. V. Izuchenie aktivnosti suktsinatdegidrogenazy u produtsenta novobiotsina--Actinomyces spheroides. Antibiotiki. 1973 Apr;18(4):309–313. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toropova E. G., Nugumanov B. S., Egorov N. S. Izuchenie aktivnosti nekotorykh fermentov i deistviia na nikh nistatina uaktivnogo shtamma i neaktivnogog mutanta Actinomyces noursei. Antibiotiki. 1974 Mar;19(3):223–226. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torstensson N. T. Protease inhibitors from Streptomyces violascens. 3. Purification and some properties of the inhibitors. Arch Mikrobiol. 1973 Apr 8;91(1):11–18. doi: 10.1007/BF00409534. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trinci A. P., Righelato R. C. Changes in constituents and ultrastructure of hyphal compartments during autolysis of glucose-starved Penicillium chrysogenum. J Gen Microbiol. 1970 Feb;60(2):239–249. doi: 10.1099/00221287-60-2-239. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trinci A. P. The hyphal growth unit of wild type and spreading colonial mutants of Neurospora crassa. Arch Mikrobiol. 1973 May 24;91(2):127–136. doi: 10.1007/BF00424756. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsyganov V. A., Pronina M. I. Izmenchivost' Act. Hygroscopicus pod vozdeistviem obrazuemogo im gigromitsina b. Antibiotiki. 1969 Oct;14(10):903–907. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uesaka I. Breaking up of vegetative mycelium of Nocardia and Streptomyces cultures on agar film. Jpn J Microbiol. 1969 Mar;13(1):65–77. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1969.tb00436.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Umezawa H., Aoyagi T., Morishima H., Kunimoto S., Matsuzaki M. Chymostatin, a new chymotrypsin inhibitor produced by actinomycetes. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1970 Aug;23(8):425–427. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.23.425. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Umezawa H., Aoyagi T., Morishima H., Matsuzaki M., Hamada M. Pepstatin, a new pepsin inhibitor produced by Actinomycetes. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1970 May;23(5):259–262. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.23.259. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Umezawa H. Biosynthesis of oncostatic antibiotics: artificial bleomycins. Postepy Hig Med Dosw. 1972 Jul-Aug;26(4):431–443. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VERNON T. R. Spore formation in the genus Streptomyces. Nature. 1955 Nov 12;176(4489):935–936. doi: 10.1038/176935a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VITALIS S., SZABO G., VALYI NAGY T. COMPARISON OF THE MORPHOLOGY OF STREPTOMYCIN-PRODUCING AND NONPRODUCING STRAINS OF STREPTOMYCES GRISEUS. Acta Biol Acad Sci Hung. 1963;14:1–15. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valu G., Szabó G. Comparison of deoxyribonucleic acids from Streptomyces griseus strains. Acta Biol Acad Sci Hung. 1970;21(4):375–379. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valu G., Szabó G. Isolation and characterization of ribosomes from Streptomyces griseus spores. Acta Biol Acad Sci Hung. 1973;24(3):171–174. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vanek Z., Cudlín J., Blumauerová M., Hostálek Z. How many genes are required for the synthesis of chlortetracycline? Folia Microbiol (Praha) 1971;16(3):225–240. doi: 10.1007/BF02884211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vanek Z., Hostálek Z., Blumauerová M., Mikulík K., Podojil M., Behal V., Jechová V. The biosynthesis of tetracycline. Pure Appl Chem. 1973;34(3):463–486. doi: 10.1351/pac197334030463. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vinogradova K. A., Duda V. I., Monosov E. Z., Vasil'eva L. S. Lokalizatsiia antibiotika geliomitsina v koloniiakh i mitselii Actinomyces variabilis i Actinomyces olivocinereus. Dokl Akad Nauk SSSR. 1974 May 1;216(1):205–208. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vitális S., Szabó G. Cytomorphological effect of factor C in submerged cultures on the hyphae of Streptomyces griseus strain no. 52-1. Acta Biol Acad Sci Hung. 1969;20(1):85–92. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEBB R. B., CLARK J. B. Cytogenetic study of Nocardia corallina. J Bacteriol. 1957 Jul;74(1):31–42. doi: 10.1002/path.1700740106. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEBLEY D. M. A defined medium for the growth of the thermophilic actinomycete Micromonospora vulgaris. J Gen Microbiol. 1958 Oct;19(2):402–406. doi: 10.1099/00221287-19-2-402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEBLEY D. M. The effect of deficiency of iron, zinc and manganese on the growth and morphology of Nocardia opaca. J Gen Microbiol. 1960 Aug;23:87–92. doi: 10.1099/00221287-23-1-87. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEBLEY D. M. The effect of oxygen on the growth and metabolism of the aerobic thermophilic actinomycete Micromonospora vulgaris. J Gen Microbiol. 1954 Aug;11(1):114–122. doi: 10.1099/00221287-11-1-114. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WINDLE J. J., SACKS L. E. Electron paramagnetic resonance of managanese(II) and copper(II) in spores. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1963 Mar 19;66:173–179. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(63)91183-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waksman S. A., Schatz A. Strain Specificity and Production of Antibiotic Substances: VI. Strain Variation and Production of Streptothricin by Actinomyces Lavendulae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1945 Jul;31(7):208–214. doi: 10.1073/pnas.31.7.208. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walbaum S., Biguet J., Tran-Van-Ky P. Structure antigénique de Thermopolyspora polyspora. Répercussions pratiques sur le diagnostic du "poumon du fermier". Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1969 Nov;117(5):673–693. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinberg E. D. Secondary metabolism: raison d'être. Perspect Biol Med. 1971;14(4):565–577. doi: 10.1353/pbm.1971.0033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wildermuth H. Development and organization of the aerial mycelium in Streptomyces coelicolor. J Gen Microbiol. 1970 Jan;60(1):43–50. doi: 10.1099/00221287-60-1-43. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wildermuth H., Hopwood D. A. Septation during sporulation in Streptomyces coelicolor. J Gen Microbiol. 1970 Jan;60(1):51–59. doi: 10.1099/00221287-60-1-51. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wildermuth H. Morphological surface characteristics of Streptomyces glaucescens and S. acrimycini, two streptomycetes with "hairy" spores. Arch Mikrobiol. 1972;81(4):321–332. doi: 10.1007/BF00412638. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wildermuth H. Surface structure of streptomycete spores as revealed by negative staining and freeze-etching. J Bacteriol. 1970 Jan;101(1):318–322. doi: 10.1128/jb.101.1.318-322.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wildermuth H. The surface structure of spores and aerial hyphae in Streptomyces viridochromogenes. Arch Mikrobiol. 1972;81(4):309–320. doi: 10.1007/BF00412637. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wildermuth H., Wehrli E., Horne R. W. The surface structure of spores and aerial mycelium in Streptomyces coelicolor. J Ultrastruct Res. 1971 Apr;35(1):168–180. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(71)80149-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams S. T., Bradshaw R. M., Costerton J. W., Forge A. Fine structure of the spore sheath of some Streptomyces species. J Gen Microbiol. 1972 Sep;72(2):249–258. doi: 10.1099/00221287-72-2-249. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams S. T. Further investigations of actinomycetes by scanning electron microscopy. J Gen Microbiol. 1970 Jul;62(1):67–73. doi: 10.1099/00221287-62-1-67. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams S. T., Sharples G. P., Bradshaw R. M. Spore formation in Actinomadura dassonvillei (Brocq-Rousseu) Lechevalier and Lechevalier. J Gen Microbiol. 1974 Oct;84(2):415–419. doi: 10.1099/00221287-84-2-415. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams S. T., Sharples G. P., Bradshaw R. M. The fine structure of the Actinomycetales. Soc Appl Bacteriol Symp Ser. 1973 Jan;2:113–130. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willoughby L. G. A conidial actinoplanes isolate from Blelham Tarn. J Gen Microbiol. 1966 Jul;44(1):69–72. doi: 10.1099/00221287-44-1-69. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zelinka J. Regulatory aspects of chlortetracycline fermentation. Biologia (Bratisl) 1968;23(3):169–174. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



