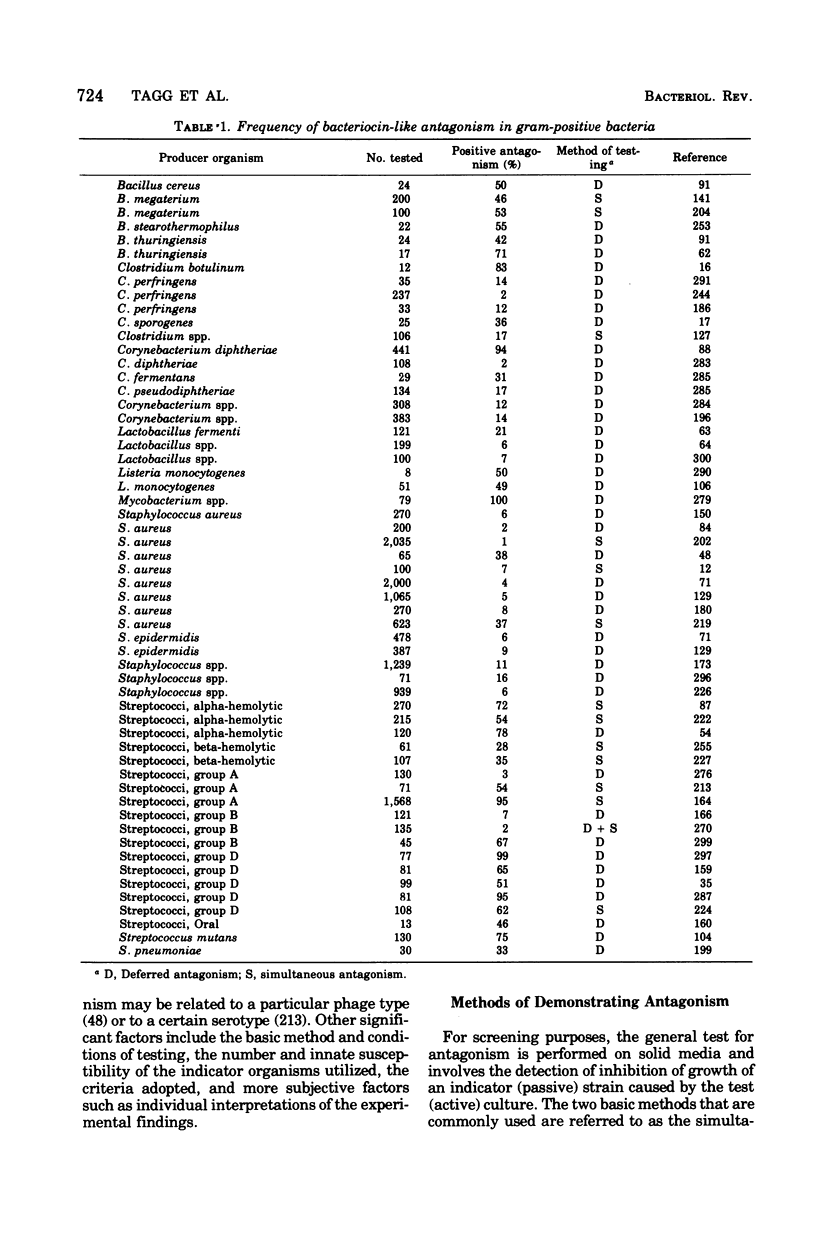
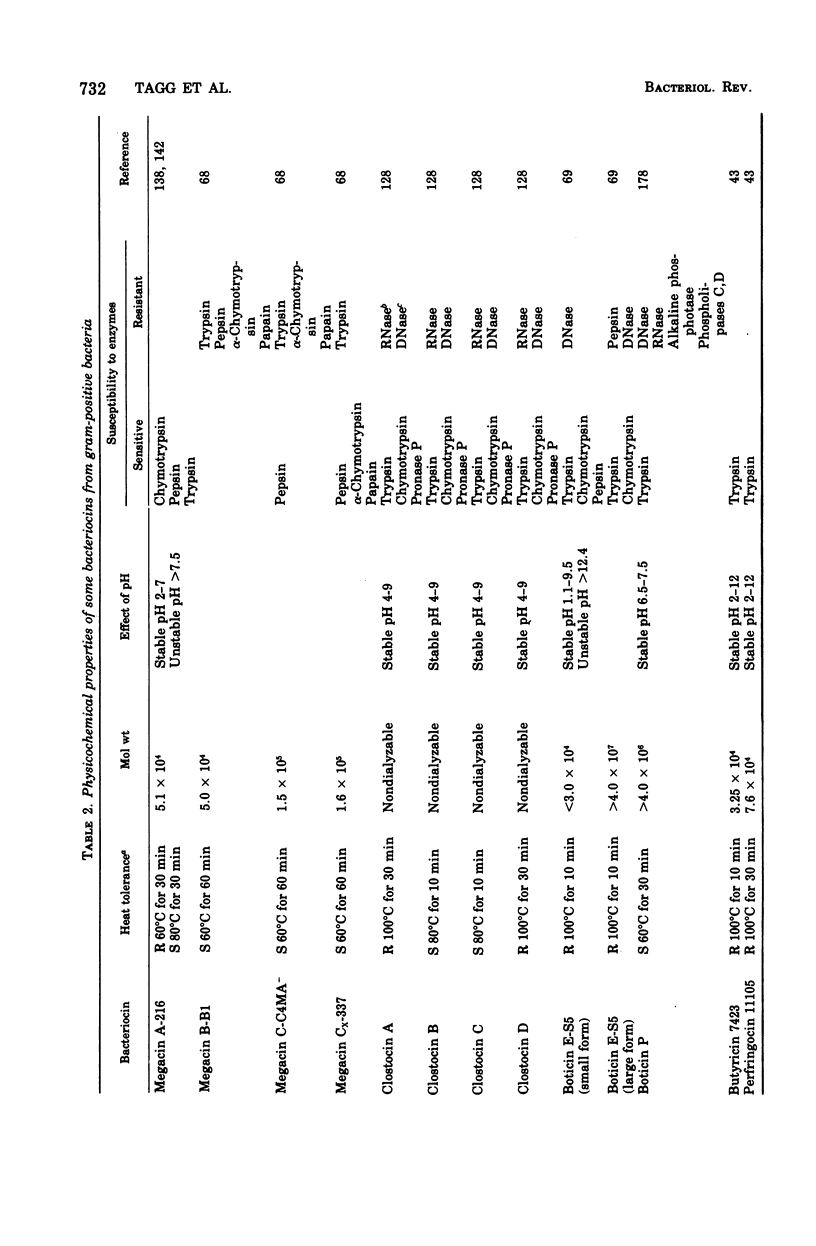
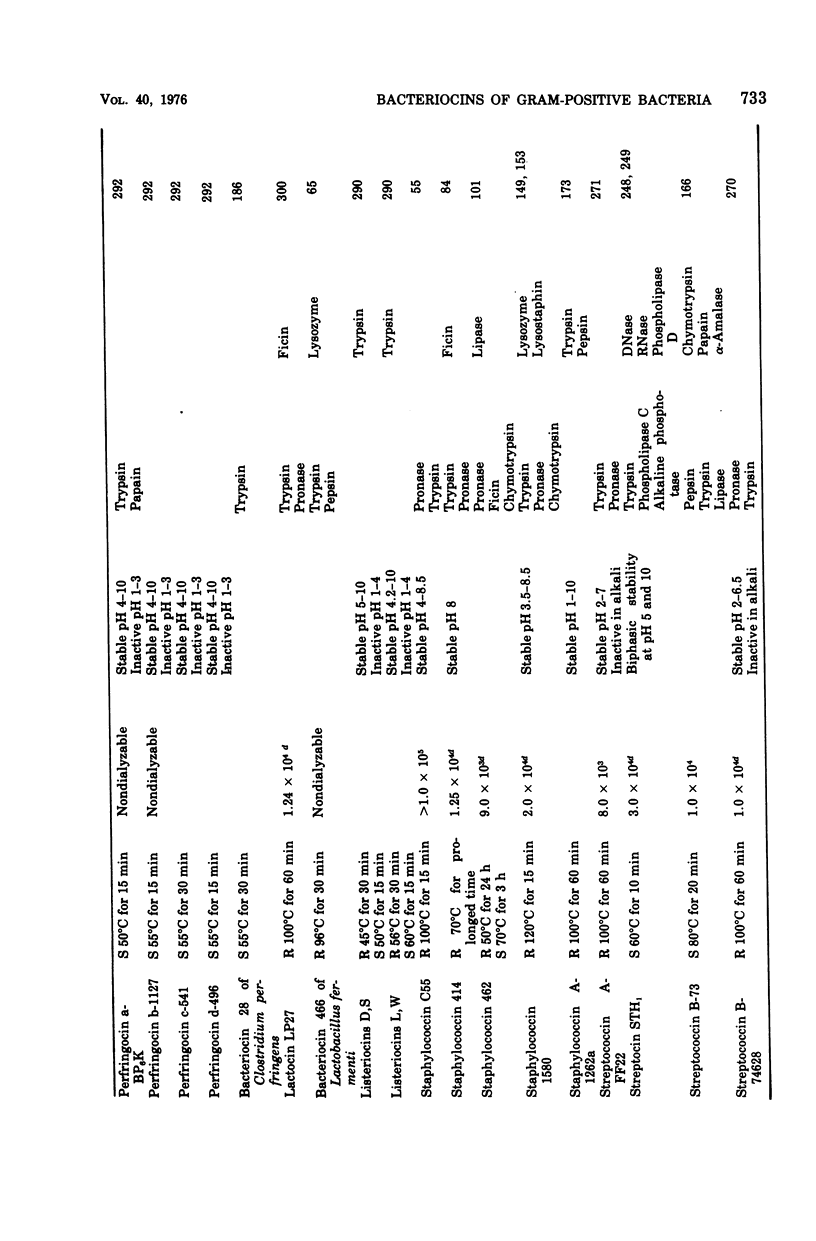
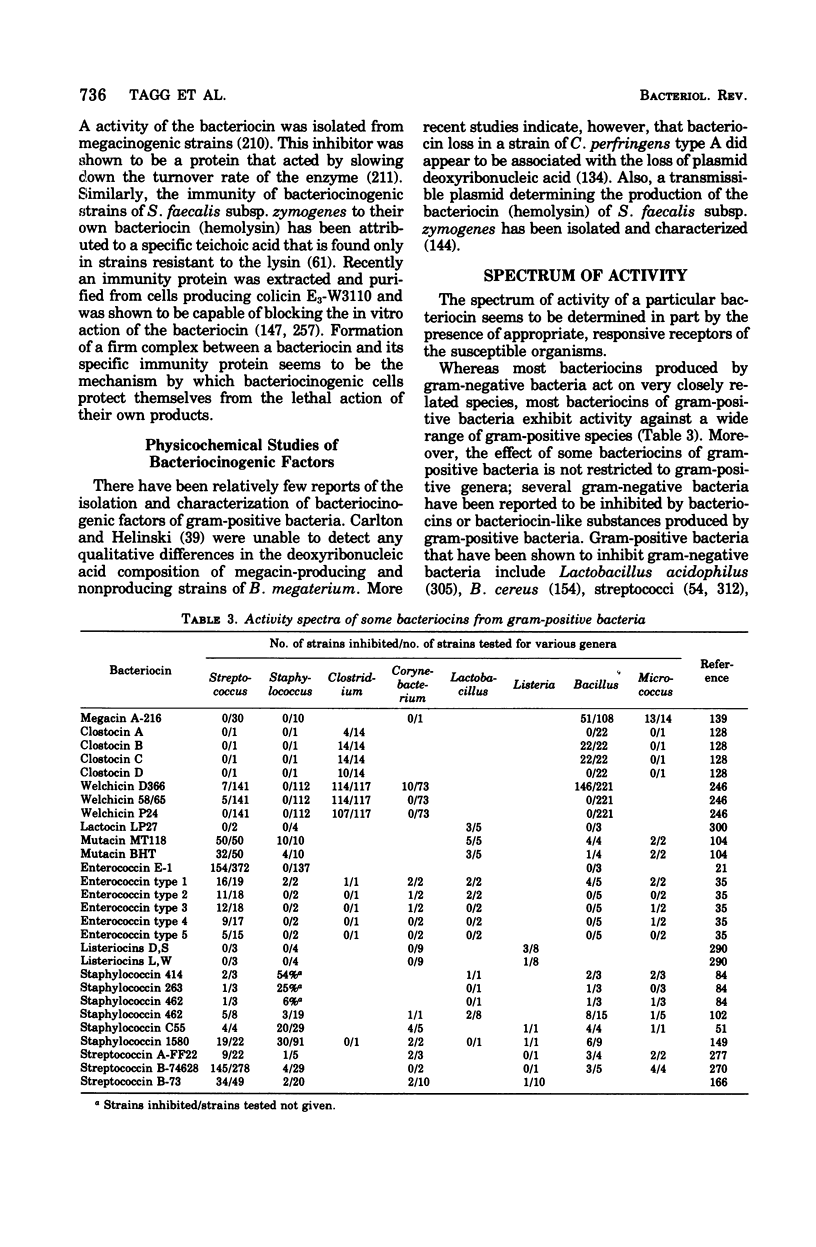
Full text
PDF





























Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ABBOTT J. D., SHANNON R. A method for typing Shigella sonnei, using colicine production as a marker. J Clin Pathol. 1958 Jan;11(1):71–77. doi: 10.1136/jcp.11.1.71. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ABRAHAM E. P., HEATLEY N. G., BROOKES P., FULLER A. T., WALKER J. Probable identity of an antibiotic produced by a spore-bearing bacillus of the B. pumilus group with micrococcin. Nature. 1956 Jul 7;178(4523):44–45. doi: 10.1038/178044a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ALFOLDI L. La production induite de mégacine en milieu synthétique. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1958 Apr;94(4):474–484. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ARBER W. Transduction of chromosomal genes and episomes in Escherichia coli. Virology. 1960 May;11:273–288. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(60)90066-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adámek L., Trnka L., Mion P., Gutová M. Hemmstoffe vom Bakteriocin-Typus bei schnell wachsenden saphrophytischen Stämmen der Mycobakterien. Beitr Klin Erforsch Tuberk Lungenkr. 1968;138(1):51–55. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aly R., Maibach H. I., Shinefield H. R., Mandel A. D. Protection of chicken embryos by viridans streptococci against the lethal effect of Staphylococcus aureus. Infect Immun. 1974 Mar;9(3):559–563. doi: 10.1128/iai.9.3.559-563.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aly R., Maibach H. I., Shinefield H. R., Mandel A., Strauss W. G. Bacterial interference among strains of Staphylococcus aureus in man. J Infect Dis. 1974 Jun;129(6):720–724. doi: 10.1093/infdis/129.6.720. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anastasio K. L., Soucheck J. A., Sugiyama H. Boticinogeny and actions of the bacteriocin. J Bacteriol. 1971 Jul;107(1):143–149. doi: 10.1128/jb.107.1.143-149.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anthony B. F., Giuliano D. M., Oh W. Nursery outbreak of staphylococcal scalded skin syndrome. Rapid identification of the epidemic bacterial strain. Am J Dis Child. 1972 Jul;124(1):41–44. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1972.02110130043006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BARROW G. I. Microbial antagonism by Staphylococcus aureus. J Gen Microbiol. 1963 Jun;31:471–481. doi: 10.1099/00221287-31-3-471. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BARROW G. I. THE NATURE OF INHIBITORY ACTIVITY BY STAPHYLOCOCCUS AUREUS TYPE 71. J Gen Microbiol. 1963 Aug;32:255–261. doi: 10.1099/00221287-32-2-255. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BETZ J. V., ANDERSON K. E. ISOLATION AND CHARACTERIZATION OF BACTERIOPHAGES ACTIVE ON CLOSTRIDIUM SPOROGENES. J Bacteriol. 1964 Feb;87:408–415. doi: 10.1128/jb.87.2.408-415.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BODANSZKY M., PERLMAN D. ARE PEPTIDE ANTIBIOTICS SMALL PROTEINS? Nature. 1964 Nov 28;204:840–844. doi: 10.1038/204840a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRANDIS H., BRANDIS U. AUFTRETEN UND VERHALTEN SPONTANER MUTANTEN VON ENTEROKOKKENSTAEMMEN MIT RESISTENZ GEGEN ENTEROCIN. Pathol Microbiol (Basel) 1963;26:688–695. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRAUDE A. I., SIEMIENSKI J. S. THE INFLUENCE OF BACTERIOCINS ON RESISTANCE TO INFECTION BY GRAM-NEGATIVE BACTERIA. I. THE EFFECT OF COLICIN ON BACTERICIDAL POWER OF BLOOD. J Clin Invest. 1965 May;44:849–859. doi: 10.1172/JCI105197. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BROCK T. D., DAVIE J. M. PROBABLE IDENTITY OF A GROUP D HEMOLYSIN WITH A BACTERIOCINE. J Bacteriol. 1963 Oct;86:708–712. doi: 10.1128/jb.86.4.708-712.1963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BROCK T. D., PEACHER B., PIERSON D. SURVEY OF THE BACTERIOCINES OF ENTEROCOCCI. J Bacteriol. 1963 Oct;86:702–707. doi: 10.1128/jb.86.4.702-707.1963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bailey F. J., Hurst A. Preparation of a highly active form of nisin from Streptococcus lactis. Can J Microbiol. 1971 Jan;17(1):61–67. doi: 10.1139/m71-010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Basinger S. F., Jackson R. W. Bacteriocin (hemolysin) of Streptococcus zymogenes. J Bacteriol. 1968 Dec;96(6):1895–1902. doi: 10.1128/jb.96.6.1895-1902.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bayer M. E. Areas of adhesion between wall and membrane of Escherichia coli. J Gen Microbiol. 1968 Oct;53(3):395–404. doi: 10.1099/00221287-53-3-395. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boon T. Inactivation of ribosomes in vitro by colicin E 3 . Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Oct;68(10):2421–2425. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.10.2421. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bottone E., Allerhand J., Pisano M. A. Characteristics of a bacteriocin derived from Streptococcus faecalis var. zymogenes antagonistic to Diplococcus peumoniae. Appl Microbiol. 1971 Aug;22(2):200–204. doi: 10.1128/am.22.2.200-204.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bottone E., Allerhand J., Pisano M. A. Effects of a bacteriocin produced by Streptococcus faecalis var. zymogenes (E1) on susceptible microorganisms. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1974;40(3):385–392. doi: 10.1007/BF00399350. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowman C. M., Sidikaro J., Nomura M. Specific inactivation of ribosomes by colicin E3 in vitro and mechanism of immunity in colicinogenic cells. Nat New Biol. 1971 Dec 1;234(48):133–137. doi: 10.1038/newbio234133a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradley D. E. The isolation and morphology of some new bacteriophages specific for Bacillus and Acetobacter species. J Gen Microbiol. 1965 Nov;41(2):233–241. doi: 10.1099/00221287-41-2-233. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradley D. E. Ultrastructure of bacteriophage and bacteriocins. Bacteriol Rev. 1967 Dec;31(4):230–314. doi: 10.1128/br.31.4.230-314.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braun V., Schaller K., Wabl M. R. Isolation, characterization, and action of colicin M. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1974 May;5(5):520–533. doi: 10.1128/aac.5.5.520. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braun V., Schaller K., Wolff H. A common receptor protein for phage T5 and colicin M in the outer membrane of Escherichia coli B. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Sep 27;323(1):87–97. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(73)90433-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braun V., Wolff H. Characterization of the receptor protein for phage T5 and colicin M in the outer membrane of E. coli B. FEBS Lett. 1973 Aug 1;34(1):77–80. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(73)80707-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brubaker R. R., Beesley E. D., Surgalla M. J. Pasteurella pestis: Role of Pesticin I and Iron in Experimental Plague. Science. 1965 Jul 23;149(3682):422–424. doi: 10.1126/science.149.3682.422. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buxton R. S. Genetic analysis of Escherichia coli K12 mutants resistant to bacteriophage BF23 and the E-group colicins. Mol Gen Genet. 1971;113(2):154–156. doi: 10.1007/BF00333188. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHEESEMAN G. C., BERRIDGE N. J. Observations on the molecular weight and chemical composition of nisin A. Biochem J. 1959 Jan;71(1):185–194. doi: 10.1042/bj0710185. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlton B. C., Helinski D. R. Heterogeneous circular DNA elements in vegetative cultures of Bacillus megaterium. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Oct;64(2):592–599. doi: 10.1073/pnas.64.2.592. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang Y. Y., Hager L. P. Inhibition of colicin e2 activity by bacterial lipopolysaccharide. J Bacteriol. 1970 Dec;104(3):1106–1109. doi: 10.1128/jb.104.3.1106-1109.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Changeux J. P., Thiéry J. On the mode of action of colicins: a model of regulation at the membrane level. J Theor Biol. 1967 Nov;17(2):315–318. doi: 10.1016/0022-5193(67)90175-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke D. J., Robson R. M., Morris J. G. Purification of two Clostridium bacteriocins by procedures appropriate to hydrophobic proteins. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1975 Mar;7(3):256–264. doi: 10.1128/aac.7.3.256. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clawson C. C., Dajani A. S. Effect of Bactericidal Substance from Staphylococcus aureus on Group A Streptococci II. Structural Alterations. Infect Immun. 1970 May;1(5):491–498. doi: 10.1128/iai.1.5.491-498.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cramer W. A., Phillips S. K., Keenan T. W. On the role of membrane phase in the transmission mechanism of colicin E1. Biochemistry. 1973 Mar 13;12(6):1177–1181. doi: 10.1021/bi00730a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crowe C. C., Sanders W. E., Jr, Longley S. Bacterial interference. II. Role of the normal throat flora in prevention of colonization by group A Streptococcus. J Infect Dis. 1973 Oct;128(4):527–532. doi: 10.1093/infdis/128.4.527. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cundliffe E., Dixon P. D. Inhibition of ribosomal A site functions by sporangiomycin and micrococcin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1975 Jul;8(1):1–4. doi: 10.1128/aac.8.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DE KLERK H. C., COETZEE J. N. Antibiosis among lactobacilli. Nature. 1961 Oct 28;192:340–341. doi: 10.1038/192340a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dajani A. S., Gray E. D., Wannamaker L. W. Bactericidal substance from Staphylococcus aureus. Biological properties. J Exp Med. 1970 May 1;131(5):1004–1015. doi: 10.1084/jem.131.5.1004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dajani A. S., Gray E. D., Wannamaker L. W. Effect of Bactericidal Substance from Staphylococcus aureus on Group A Streptococci I. Biochemical Alterations. Infect Immun. 1970 May;1(5):485–490. doi: 10.1128/iai.1.5.485-490.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dajani A. S. Neutralization of phage type 71 staphylococcal bacteriocin by immune and nonimmune sera. J Infect Dis. 1973 Oct;128(4):494–499. doi: 10.1093/infdis/128.4.494. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dajani A. S., Taube Z. Plasmid-mediated production of staphylococcin in bacteriophage type 71 Staphylococcus aureus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1974 Jun;5(6):594–598. doi: 10.1128/aac.5.6.594. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dajani A. S., Tom M. C., Law D. J. Viridins, bacteriocins of alpha-hemolytic streptococci: isolation, characterization, and partial purification. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1976 Jan;9(1):81–88. doi: 10.1128/aac.9.1.81. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dajani A. S., Wannamaker L. W. Bacteriocin of phage type 71 S. aureus. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1974 Jul 31;236(0):389–394. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1974.tb41505.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dajani A. S., Wannamaker L. W. Demonstration of a bactericidal substance against beta-hemolytic streptococci in supernatant fluids of staphylococcal cultures. J Bacteriol. 1969 Mar;97(3):985–991. doi: 10.1128/jb.97.3.985-991.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dajani A. S., Wannamaker L. W. Experimental infection of the skin in the hamster simulating human impetigo. III. Interaction between staphylococci and group A streptococci. J Exp Med. 1971 Sep 1;134(3 Pt 1):588–599. doi: 10.1084/jem.134.3.588. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dajani A. S., Wannamaker L. W. Kinetic studies on the interaction of bacteriophage type 71 staphylococcal bacteriocin with susceptible bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1973 May;114(2):738–742. doi: 10.1128/jb.114.2.738-742.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dandeu J. P. Chemical and immunological study of colicins e(1), k, a, and q. Infect Immun. 1971 Jan;3(1):1–9. doi: 10.1128/iai.3.1.1-9.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dastidar S. G., Mitra S., Sarkar S. N., Chakrabarty A. N. Transformation with bacteriocin factors in staphylococci. J Gen Microbiol. 1974 Oct;84(2):245–252. doi: 10.1099/00221287-84-2-245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davie J. M., Brock T. D. Effect of teichoic acid on resistance to the membrane-lytic agent of Streptococcus zymogenes. J Bacteriol. 1966 Dec;92(6):1623–1631. doi: 10.1128/jb.92.6.1623-1631.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Di Masi D. R., White J. C., Schnaitman C. A., Bradbeer C. Transport of vitamin B12 in Escherichia coli: common receptor sites for vitamin B12 and the E colicins on the outer membrane of the cell envelope. J Bacteriol. 1973 Aug;115(2):506–513. doi: 10.1128/jb.115.2.506-513.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dillon H. C., Jr Impetigo contagiosa: suppurative and non-suppurative complications. I. Clinical, bacteriologic, and epidemiologic characteristics of impetigo. Am J Dis Child. 1968 May;115(5):530–541. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1968.02100010532002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donoghue H. D. Properties and comparative starch-gel electrophoresis of megacins from several Bacillus megaterium strains. J Gen Microbiol. 1972 Oct;72(3):473–483. doi: 10.1099/00221287-72-3-473. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellison J. S., Kautter J. A. Purification and some properties of two boticins. J Bacteriol. 1970 Oct;104(1):19–26. doi: 10.1128/jb.104.1.19-26.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellison J. S., Mattern C. F., Daniel W. A. Structural changes in Clostridium botulinum type E after treatment with boticin S5 1 . J Bacteriol. 1971 Oct;108(1):526–534. doi: 10.1128/jb.108.1.526-534.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FREDERICQ P. COLICINES ET AUTRES BACTERIOCINES. Ergeb Mikrobiol Immunitatsforsch Exp Ther. 1963;37:114–161. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FREDERICQ P. Colicins. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1957;11:7–22. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.11.100157.000255. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FREDERICQ P., THIBAUT J. Actions antibiotiques réciproques chez Corynebacterium diphtheriae. C R Seances Soc Biol Fil. 1956;150(7):1512–1514. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FULLER A. T. A new antibiotic of bacterial origin. Nature. 1955 Apr 23;175(4460):722–722. doi: 10.1038/175722a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fink H., Ortel S. Untersuchungen über Staphylococcine. I. Isolierung staphylococcinbildender Stämme, Herkunft, Lysisbild und Antibiotikaresistenz. Zentralbl Bakteriol Orig. 1969;211(1):39–47. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foulds J. D., Shemin D. Concomitant synthesis of bacteriocin and bacteriocin inactivator from Serratia marcescens. J Bacteriol. 1969 Sep;99(3):661–666. doi: 10.1128/jb.99.3.661-666.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foulds J. Purification and partial characterization of a bacteriocin from Serratia marcescens. J Bacteriol. 1972 Jun;110(3):1001–1009. doi: 10.1128/jb.110.3.1001-1009.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox E. N. M proteins of group A streptococci. Bacteriol Rev. 1974 Mar;38(1):57–86. doi: 10.1128/br.38.1.57-86.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOEBEL W. F., BARRY G. T., JESAITIS M. A., MILLER E. M. Colicine K. Nature. 1955 Oct 8;176(4484):700–701. doi: 10.1038/176700a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOWANS J. L., SMITH N., FLOREY H. W. Some properties of nisin. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1952 Sep;7(3):438–449. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1952.tb00711.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garro A. J., Marmur J. Defective bacteriophages. J Cell Physiol. 1970 Dec;76(3):253–263. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040760305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerasimov A. V. Bakteriotsinogeniia u zeleniashchikh Streptokokkov. Zh Mikrobiol Epidemiol Immunobiol. 1968 Dec;45(12):28–32. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibson L. F., Colman G. Diphthericin types, bacteriophage types and serotypes of Corynebacterium diphtheriae strains isolated in Australia. J Hyg (Lond) 1973 Dec;71(4):679–689. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400022944. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goze A. Thuricines et céréines moléculaires. C R Seances Soc Biol Fil. 1972;166(1):200–204. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granato P. A., Jackson R. W. Bicomponent nature of lysin from Streptococcus zymogenes. J Bacteriol. 1969 Nov;100(2):865–868. doi: 10.1128/jb.100.2.865-868.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guterman S. K., Luria S. E. Escherichia coli: strains that excrete an inhibitor of colicin B. Science. 1969 Jun 20;164(3886):1414–1414. doi: 10.1126/science.164.3886.1414. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guze L. B., Hubert E. G., Kalmanson G. M. Pyelonephritis. X. Microbial interference in streptococcal infections in the rat kidney. J Lab Clin Med. 1969 Aug;74(2):274–287. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HALBERT S. P., SONN C., SWICK L. Mixed bacterial infections in relation to antibiotic activities. I. Clostridium septicum-Micrococcus infections. J Immunol. 1954 Sep;73(3):169–179. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HALBERT S. P., SWICK L. S. Antibiotic-producing bacteria of the ocular flora. Am J Ophthalmol. 1952 May;35(5 2):73–81. doi: 10.1016/0002-9394(52)90259-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HALBERT S. P., SWICK L. S. In vivo antibiotic production by Escherichia coli. J Immunol. 1950 Dec;65(6):675–686. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HALBERT S. P., SWICK L., SONN C. Characteristics of antibiotic-producing strains of the ocular bacterial flora. J Immunol. 1953 Apr;70(4):400–410. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAMON Y., PERON Y. QUELQUES REMARQUES SUR LES BACT'ERIOCINES PRODUITES PAR LES MICROBES GRAM-POSITIFS. C R Hebd Seances Acad Sci. 1963 Jul 29;257:1191–1193. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAMON Y., PERON Y. [Study of bacteriocinogenic power in the Listeria genus]. C R Hebd Seances Acad Sci. 1961 Oct 23;253:1883–1885. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAMON Y., PERON Y. [Study of the bacteriocinogenic potency in the genus Listeria. II. Individuality and classification of the bacteriocins in question]. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1963 Jan;104:55–65. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HEATLEY N. G., DOERY H. M. The preparation and some properties of purified micrococcin. Biochem J. 1951 Dec;50(2):247–253. doi: 10.1042/bj0500247. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HEATLEY N. G., KELLY B. K., SMITH N. The assay of micrococcin, an almost insoluble antibiotic. J Gen Microbiol. 1952 Feb;6(1-2):30–40. doi: 10.1099/00221287-6-1-2-30. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOFFMANN E. M., STREITFELD M. M. THE ANTIBIOTIC ACTIVITY ASSOCIATED WITH PREPARATIONS OF DELTA HEMOLYSIN OF STAPHYLOCOCCUS AUREUS. Can J Microbiol. 1965 Apr;11:203–211. doi: 10.1139/m65-026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOLLAND I. B. A BACTERIOCIN SPECIFICALLY AFFECTING DNA SYNTHESIS IN BACILLUS MEGATERIUM. J Mol Biol. 1965 Jun;12:429–438. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(65)80265-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOLLAND I. B. Further observations on the properties of megacin, a bacteriocine formed by Bacillus megaterium. J Gen Microbiol. 1962 Dec;29:603–614. doi: 10.1099/00221287-29-4-603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOLLAND I. B., ROBERTS C. F. SOME PROPERTIES OF A NEW BACTERIOCIN FORMED BY BACILLUS MEGATERIUM. J Gen Microbiol. 1964 May;35:271–285. doi: 10.1099/00221287-35-2-271. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOLLAND I. B. The purification and properties of megacin, a bacteriocin from Bacillus megaterium. Biochem J. 1961 Mar;78:641–648. doi: 10.1042/bj0780641. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hale E. M., Hinsdill R. D. Biological activity of staphylococcin 162: bacteriocin from Staphylococcus aureus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1975 Jan;7(1):74–81. doi: 10.1128/aac.7.1.74. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hale E. M., Hinsdill R. D. Characterization of a bacteriocin from Staphylococcus aureus strain 462. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1973 Dec;4(6):634–640. doi: 10.1128/aac.4.6.634. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hallander H. O. Characterization and partial purification of staphylococcal delta-lysin. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand. 1968;72(4):586–600. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1968.tb00471.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamada S., Ooshima T. Inhibitory spectrum of a bacteriocinlike substance (mutacin) produced by some strains of Streptococcus mutans. J Dent Res. 1975 Jan-Feb;54(1):140–145. doi: 10.1177/00220345750540010801. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamon Y., Peron Y. Sur les propriétés détergentes des molécules de bactériocines. C R Acad Sci Hebd Seances Acad Sci D. 1973 Oct 8;277(14):1401–1404. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamon Y., Péron Y. Sur la frequence des bacteries productrices de phages letaux. Distinction entre ces phages et les bacteriocines. Zentralbl Bakteriol Orig. 1968 May;206(4):439–444. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamon Y., Péron Y. Sur la nature des bactériocines produites par Listeria monocytogenes. C R Acad Sci Hebd Seances Acad Sci D. 1966 Jul 11;263(2):198–200. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardy K. G. Colicinogeny and related phenomena. Bacteriol Rev. 1975 Dec;39(4):464–515. doi: 10.1128/br.39.4.464-515.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harwick H. J., Montgomerie J. Z., Kalamanson G. M., Hubert E. G., Potter C. S., Guze L. B. Differential action of a streptococcal bacteriocin on mycoplasmas and microbial L-forms. Infect Immun. 1971 Sep;4(3):194–198. doi: 10.1128/iai.4.3.194-198.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawiger J. Purification and properties of lysozyme produced by Staphylococcus aureus. J Bacteriol. 1968 Feb;95(2):376–384. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.2.376-384.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herschman H. R., Helinski D. R. Purification and characterization of colicin E2 and colicin E3. J Biol Chem. 1967 Nov 25;242(22):5360–5368. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmberg K., Hallander H. O. Interference between gram-positive microorganisms in dental plaque. J Dent Res. 1972 Mar-Apr;51(2):588–595. doi: 10.1177/00220345720510025801. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmberg K., Hallander H. O. Production of bactericidal concentrations of hydrogen peroxide by Streptococcus sanguis. Arch Oral Biol. 1973 Mar;18(3):423–434. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(73)90167-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu C. Y., Wiseman G. M. Purification of epidermidins, new antibiotics from staphylococci. Can J Microbiol. 1971 Sep;17(9):1223–1226. doi: 10.1139/m71-195. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu C., Wiseman G. M. Antibacterial substances from staphylococci. Can J Microbiol. 1967 Aug;13(8):947–955. doi: 10.1139/m67-127. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurst A. Function of nisin and nisin-like basic proteins in the growth cycle of streptococcus lactis. Nature. 1967 Jun 17;214(5094):1232–1234. doi: 10.1038/2141232a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- IVANOVICS G., ALFOLDI L. A new antibacterial principle: megacine. Nature. 1954 Sep 4;174(4427):465–465. doi: 10.1038/174465a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- IVANOVICS G., ALFOLDI L., ABRAHAM E. Das antibaterielle Spektrum des Megacins. Zentralbl Bakteriol Orig. 1955 Jul;163(4):274–280. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- IVANOVICS G., ALFOLDI L., NAGY E. Mode of action of megacin. J Gen Microbiol. 1959 Aug;21:51–60. doi: 10.1099/00221287-21-1-51. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- IVANOVICS G., NAGY E., ALFOLDI L. Megacinogeny: inducible synthesis of a new immunospecific substance. Acta Microbiol Acad Sci Hung. 1959;6:161–169. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- IVANOVICS G., NAGY E. Hereditary aberrancy in growth of some Bacillus megaterium strains. J Gen Microbiol. 1958 Oct;19(2):407–418. doi: 10.1099/00221287-19-2-407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imaeda T., Rieber M. Mitomycin C-induced phage-like particles in a mutant of Mycobacterium tuberculosis BCG. J Bacteriol. 1968 Aug;96(2):557–559. doi: 10.1128/jb.96.2.557-559.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inoue K., Iida H. Bacteriophages of Clostridium botulinum. J Virol. 1968 May;2(5):537–540. doi: 10.1128/jvi.2.5.537-540.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ionesco H., Bouanchaud D. H. Production de bactériocine liée à présence d'un plasmide chez Clostridium perfringens type. C R Acad Sci Hebd Seances Acad Sci D. 1973 May 14;276(20):2855–2857. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ivanovics G. BACTERIOCINS AND BACTERIOCIN-LIKE SUBSTANCES. Bacteriol Rev. 1962 Jun;26(2 Pt 1):108–118. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JACOB F., LWOFF A., SIMINOVITCH A., WOLLMAN E. Définition de quelques termes relatifs a la lysogénie. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1953 Jan;84(1):222–224. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JACOB F., WOLLMAN E. L. Les épisomes, éléments génétiques ajoutés. C R Hebd Seances Acad Sci. 1958 Jul 7;247(1):154–156. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson R. W. Bacteriolysis and inhibition of gram-positive bacteria by components of Streptococcus zymogenes lysin. J Bacteriol. 1971 Jan;105(1):156–159. doi: 10.1128/jb.105.1.156-159.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacob A. E., Douglas G. J., Hobbs S. J. Self-transferable plasmids determining the hemolysin and bacteriocin of Streptococcus faecalis var. zymogenes. J Bacteriol. 1975 Mar;121(3):863–872. doi: 10.1128/jb.121.3.863-872.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jakes K., Zinder N. D., Boon T. Purification and properties of colicin E3 immunity protein. J Biol Chem. 1974 Jan 25;249(2):438–444. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jetten A. M., Vogels G. D. Characteristics of the killing effect of a Staphylococcus epidermidis bacteriocin. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1974;40(1):177–183. doi: 10.1007/BF00394565. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jetten A. M., Vogels G. D. Characterization and extrachromosomal control of bacteriocin production in Staphylococcus aureus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1973 Jul;4(1):49–57. doi: 10.1128/aac.4.1.49. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jetten A. M., Vogels G. D. Effects of colicin A and staphylococcin 1580 on amino acid uptake into membrane vesicles of Escherichia coli and staphylococcus aureus. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Jul 18;311(4):483–495. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(73)90124-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jetten A. M., Vogels G. D. Mode of action of a Staphylococcus epidermidis bacteriocin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1972 Dec;2(6):456–463. doi: 10.1128/aac.2.6.456. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jetten A. M., Vogels G. D. Nature and properties of a Staphylococcus epidermidis bacteriocin. J Bacteriol. 1972 Oct;112(1):243–250. doi: 10.1128/jb.112.1.243-250.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson C. W., West H. D., Jones H. L., Long C. J. BIOCERIN: AN ANTIBIOTIC PRODUCED BY BACILLUS CEREUS. J Bacteriol. 1949 Jan;57(1):63–65. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KJEMS E. Studies on streptococcal bacteriophages. I. Technique of isolating phage-producing strains. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand. 1955;36(5):433–440. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalmanson G. M., Hubert E. G., Guze L. B. Effect of bacteriocin from Streptococcus faecalis on microbial L-forms. J Infect Dis. 1970 Mar;121(3):311–315. doi: 10.1093/infdis/121.3.311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kautter D. A., Harmon S. M., Lynt R. K., Jr, Lilly T., Jr Antagonistic effect on Clostridium botulinum type E by organisms resembling it. Appl Microbiol. 1966 Jul;14(4):616–622. doi: 10.1128/am.14.4.616-622.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelstrup J., Gibbons R. J. Bacteriocins from human and rodent streptococci. Arch Oral Biol. 1969 Mar;14(3):251–258. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(69)90227-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelstrup J., Gibbons R. J. Inactivation of bacteriocins in the intestinal canal and oral cavity. J Bacteriol. 1969 Sep;99(3):888–890. doi: 10.1128/jb.99.3.888-890.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelstrup J., Richmond S., West C., Gibbons R. J. Fingerprinting human oral streptococci by bacteriocin production and sensitivity. Arch Oral Biol. 1970 Dec;15(12):1109–1116. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(70)90001-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozar W., Rajchert-Trzpil M., Dobrzański W. T. The effect of proflavin, ethidium bromide and an elevated temperature on the appearance of nisin-negative clones in nisin-producing strains of Streptococcus lactis. J Gen Microbiol. 1974 Aug;83(2):295–302. doi: 10.1099/00221287-83-2-295. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krylova M. D. Izuchenie bakteriotsinov difteriïnykh bakteriï tipa mitis. Zh Mikrobiol Epidemiol Immunobiol. 1969 Mar;46(3):11–15. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krylova M. D. Koritsin-test i primenenie ego sovmesto s fagotipovaniem dlia geneticheskogo markirovaniia netoksigennykh difteriinykh korinebakterii tipa mitis. Zh Mikrobiol Epidemiol Immunobiol. 1972 Nov;49(11):27–33. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krämer J., Brandis H. Charakterisierung eines Streptococcus agalactiae-Bacteriocins. Zentralbl Bakteriol Orig A. 1972 Mar;219(3):290–301. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krämer J., Brandis H. Mode of action of two streptococcus faecium bacteriocins. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1975 Feb;7(2):117–120. doi: 10.1128/aac.7.2.117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krämer J., Schallehn G. Enterocinwirkung aug Clostridium perfringens und Clostridium septicum. Zentralbl Bakteriol Orig A. 1974 Feb;226(1):105–113. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuttner A. G. Production of bacteriocines by group A streptococci with special reference to the nephritogenic types. J Exp Med. 1966 Sep 1;124(3):279–291. doi: 10.1084/jem.124.3.279. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kékessy D. A., Piguet J. D. Bactériocinogénie et typisation de Streptococcus faecalis. Pathol Microbiol (Basel) 1971;37(2):113–121. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kékessy D. A., Piguet J. D. New method for detecting bacteriocin production. Appl Microbiol. 1970 Aug;20(2):282–283. doi: 10.1128/am.20.2.282-283.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LURIA S. E. ON THE MECHANISMS OF ACTION OF COLICINS. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1964 Nov;107:SUPPL–SUPPL:73. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lachowicz T., Brodzicki S. Stimulation of staphylococcin A: production and some properties. Contrib Microbiol Immunol. 1973;1:450–456. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lachowicz T., Kwiatkowski B. A structural analysis of staphylococcin A in the electron microscope. Folia Histochem Cytochem (Krakow) 1972;10(3):257–264. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lachowicz T., Walczak Z. Purification and properties of staphylococcin A. Arch Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz) 1968;16(6):855–863. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lau A. H., Hawirko R. Z., Chow C. T. Purification and properties of boticin P produced by Clostridium botulinum. Can J Microbiol. 1974 Mar;20(3):385–390. doi: 10.1139/m74-059. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LeBien T. W., Bromel M. C. Antibacterial properties of a peroxidogenic strain of Streptococcus mitior (mitis). Can J Microbiol. 1975 Jan;21(1):101–103. doi: 10.1139/m75-015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leonova G. V. Bakteriotsiny stafilokokkov i ikh svoistva. Zh Mikrobiol Epidemiol Immunobiol. 1968 Mar;45(3):108–111. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levisohn R., Konisky J., Nomura M. Interaction of colicins with bacterial cells. IV. Immunity breakdown studied with colicins Ia and Ib. J Bacteriol. 1968 Sep;96(3):811–821. doi: 10.1128/jb.96.3.811-821.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luria S. E. Phage, colicins, and macroregulatory phenomena. Science. 1970 Jun 5;168(3936):1166–1170. doi: 10.1126/science.168.3936.1166. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARJAI E., IVANOVICS G. THE EFFECT OF DIFFERENT ANTICANCER AGENTS ON INDUCIBLE SYSTEMS OF BACILLUS MEGATERIUM. Acta Microbiol Acad Sci Hung. 1964;11:193–198. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahony D. E. Bacteriocin susceptibility of Clostridium perfringens: a provisional typing schema. Appl Microbiol. 1974 Aug;28(2):172–176. doi: 10.1128/am.28.2.172-176.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahony D. E., Butler M. E. Bacteriocins of Clostridium perfringens. 1. Isolation and preliminary studies. Can J Microbiol. 1971 Jan;17(1):1–6. doi: 10.1139/m71-001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malke H., Starke R., Jacob H. E., Köhler W. Bacteriocine-like activity of group-A streptococci due to the production of peroxide. J Med Microbiol. 1974 Aug;7(3):367–374. doi: 10.1099/00222615-7-3-367. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marotel-Schirmann J., Barbu E. Protection par des sérums antibactériens des bactéries ayant fixé à leur surface des molécules de colicine. C R Acad Sci Hebd Seances Acad Sci D. 1972 Nov 27;275(22):2563–2566. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathieu L. G., Legault-Hetu D. Decreased sensitivity to polymyxin B in colicin K tolerant cells of Escherichia coli K-12 in the presence of colicin K. Can J Microbiol. 1973 Mar;19(3):345–351. doi: 10.1139/m73-057. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGeachie J. An in vitro comparison of colicines K and V and some therapeutic antibiotics. Zentralbl Bakteriol Orig. 1970;215(2):245–251. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meitert E. Sur les bactériocines de Corynebacterium diphtheriae. I. Etude comparatives de plusieurs techniques pour la recherche des bactériocines chez C. diphtheriae et d'autres corynebactéries. Arch Roum Pathol Exp Microbiol. 1969 Dec;28(4):1082–1086. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meitert E. Sur les bactériocines de Corynebacterium diphtheriae. II. Etude des bactériocines produites par C. diphtheriae, C. ulcerans, C. atypique, C. hoffmani et C. xerose. Arch Roum Pathol Exp Microbiol. 1969 Dec;28(4):1086–1097. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyhack B., Meyhack I., Apirion D. Colicin E3: a unique endoribonuclease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Jan;70(1):156–160. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.1.156. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mindich L. Bacteriocins of Diplococcus pneumoniae. I. Antagonistic relationships and genetic transformations. J Bacteriol. 1966 Oct;92(4):1090–1098. doi: 10.1128/jb.92.4.1090-1098.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitsui E., Mizuno D. Stabilization of colicin E2 by bovine serum albumin. J Bacteriol. 1969 Nov;100(2):1136–1137. doi: 10.1128/jb.100.2.1136-1137.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montgomerie J. Z., Kalmanson G. M., Harwick H. J., Guze L. B. Relation between bacteriocin production and virulence of Streptococcus faecalis var. liquefaciens. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1973 Dec;144(3):868–870. doi: 10.3181/00379727-144-37700. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore E. E. Aureocin. J Med Microbiol. 1970 Feb;3(1):183–184. doi: 10.1099/00222615-3-1-183. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray F. J., Tetrault P. A., Kaufmann O. W., Koffler H., Peterson D. H., Colingsworth D. R. CIRCULIN AN ANTIBIOTIC FROM AN ORGANISM RESEMBLING BACILLUS CIRCULANS. J Bacteriol. 1949 Mar;57(3):305–312. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NORRIS J. R. A bacteriolytic principle associated with cultures of Bacillus cereus. J Gen Microbiol. 1957 Feb;16(1):1–8. doi: 10.1099/00221287-16-1-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nomura M. Colicins and related bacteriocins. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1967;21:257–284. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.21.100167.001353. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novick R. P. Extrachromosomal inheritance in bacteria. Bacteriol Rev. 1969 Jun;33(2):210–263. doi: 10.1128/br.33.2.210-263.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ochi T., Yanagase Y., Higashi Y., Inoue K., Amano T. A specific inhibitor of megacin A from Bacillus megaterium producing megacin A. Biken J. 1970 Jun;13(2):63–76. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ochi T., Yano K., Amano T. An improved method for purification of megacin A inhibitor. Biken J. 1971 Dec;14(4):423–424. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okamoto K., Mudd J. A., Mangan J., Huang W. M., Subbaiah T. V., Marmur J. Properties of the defective phage of Bacillus subtilis. J Mol Biol. 1968 Jun 28;34(3):413–428. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90169-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Overturf G. D., Mortimer E. A., Jr Studies of the relationship between the production of bacteriocines by group A streptococci and acute glomerulonephritis. J Exp Med. 1970 Oct 1;132(4):694–701. doi: 10.1084/jem.132.4.694. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oxford A. E. Diplococcin, an anti-bacterial protein elaborated by certain milk streptococci. Biochem J. 1944;38(2):178–182. doi: 10.1042/bj0380178. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ozaki M., Amano T. Immunity to magacin A in protoplasts of megacinogenic Bacillus megaterium. Biken J. 1967 Mar;10(1):23–24. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PARKER M. T., SIMMONS L. E. The inhibition of Corynebacterium diphtheriae and other gram-positive organisms by Staphylococcus aureus. J Gen Microbiol. 1959 Oct;21:457–476. doi: 10.1099/00221287-21-2-457. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PARKER M. T. Some cultural characteristics of Staphylococcus aureus strains from superficial skin infections. J Hyg (Lond) 1958 Jun;56(2):238–253. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400037712. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PARKER M. T., TOMLINSON A. J., WILLIAMS R. E. Impetigo contagiosa; the association of certain types of Staphylococcus aureus and of Streptococcus pyogenes with superficial skin infections. J Hyg (Lond) 1955 Dec;53(4):458–473. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400000966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piatkowski K., Szropińska D. Studies on bacteriocinogeny of Streptococcus strains. I. Bacteriocinogeny of strains of the Streptococcus viridans group. Arch Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz) 1971;19(2):137–145. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plate C. A., Luria S. E. Stages in colicin K action, as revealed by the action of trypsin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Aug;69(8):2030–2034. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.8.2030. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pleceas P., Bogdan C., Vereanu A. Enterocine-typing of group D streptococci. Zentralbl Bakteriol Orig A. 1972 Jul;221(2):173–181. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pleceaş P. Bactériocines des streptocoques groupe D. I Leur incidence. Arch Roum Pathol Exp Microbiol. 1970 Mar-Jun;29(1):229–232. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Popovici M., Nestoresco N., Alexenco E., Vianu I. Recherches sur les bactériocines chez les germes du genre Staphylococcus. Arch Roum Pathol Exp Microbiol. 1968 Mar;27(1):125–134. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prakash K., Ravindran P. C., Sharma K. B. Production of streptocines by beta haemolytic streptococci isolated from human sources. Indian J Med Res. 1973 Sep;61(9):1261–1264. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pulverer G., Sieg J. F. Bacteriocinotypie bei Staphylococcus aureus. Zentralbl Bakteriol Orig A. 1972 Dec;222(4):446–458. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RALSTON D. J., BAER B. S., LIEBERMAN M., KRUEGER A. P. Virolysin: a virus-induced lysin from staphylococcal phage lysates. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1955 Aug;89(4):502–507. doi: 10.3181/00379727-89-21859. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REEVES P. THE BACTERIOCINS. Bacteriol Rev. 1965 Mar;29:24–45. doi: 10.1128/br.29.1.24-45.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROELANTS P., NAUDTS F. PROPERTIES OF A BACTERIOCIN-LIKE SUBSTANCE PRODUCED BY STREPTOMYCES VIRGINIAE. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1964;30:45–53. doi: 10.1007/BF02046699. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROSEBURY T., GALE D., TAYLOR D. F. An approach to the study of interactive phenomena among microorganisms indigenous to man. J Bacteriol. 1954 Feb;67(2):135–152. doi: 10.1128/jb.67.2.135-152.1954. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ranhand J. M. Autolytic activity and its association with the development of competence in group H streptococci. J Bacteriol. 1973 Aug;115(2):607–614. doi: 10.1128/jb.115.2.607-614.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ranhand J. M., Cole R. M. Lysis of streptococci by an extracellular lysin produced by competent group H streptococcus strain CHALLIS. J Gen Microbiol. 1972 Jun;71(1):199–202. doi: 10.1099/00221287-71-1-199. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ringrose P. S. Interaction between colicin E2 and DNA in vitro. FEBS Lett. 1972 Jun 15;23(2):241–243. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(72)80351-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers A. H. Bacteriocin production and susceptibility among strains of Streptococcus mutans grown in the presence of sucrose. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1974 Nov;6(5):547–550. doi: 10.1128/aac.6.5.547. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers A. H. Effect of the medium on bacteriocin production among strains of Streptococcus mutans. Appl Microbiol. 1972 Aug;24(2):294–295. doi: 10.1128/am.24.2.294-295.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogul M., Carr S. R. Variable ammonia production among smooth and rough strains of Pseudomonas pseudomallei: resemblance to bacteriocin production. J Bacteriol. 1972 Oct;112(1):372–380. doi: 10.1128/jb.112.1.372-380.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SABINE D. B. AN ANTIBIOTIC-LIKE EFFECT OF LACTOBACILLUS ACIDOPHILUS. Nature. 1963 Aug 24;199:811–811. doi: 10.1038/199811a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHINDLER C. A., SCHUHARDT V. T. PURIFICATION AND PROPERTIES OF LYSOSTAPHIN--A LYTIC AGENT FOR STAPHYLOCOCCUS AUREUS. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1965 Feb 15;97:242–250. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(65)90088-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SEAMAN E., TARMY E., MARMUR J. INDUCIBLE PHAGES OF BACILLUS SUBTILIS. Biochemistry. 1964 May;3:607–613. doi: 10.1021/bi00893a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SMITH H. W. The bacteriophages of Clostridium perfringens. J Gen Microbiol. 1959 Dec;21:622–630. doi: 10.1099/00221287-21-3-622. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SWORD C. P., PICKETT M. J. The isolation and characterization of bacteriophages from Listeria monocytogenes. J Gen Microbiol. 1961 Jun;25:241–248. doi: 10.1099/00221287-25-2-241. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sabet S. F., Schnaitman C. A. Localization and solubilization of colicin receptors. J Bacteriol. 1971 Oct;108(1):422–430. doi: 10.1128/jb.108.1.422-430.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sabet S. F., Schnaitman C. A. Purification and properties of the colicin E3 receptor of Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1973 Mar 10;248(5):1797–1806. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanders E. Bacterial interference. I. Its occurrence among the respiratory tract flora and characterization of inhibition of group A streptococci by viridans streptococci. J Infect Dis. 1969 Dec;120(6):698–707. doi: 10.1093/infdis/120.6.698. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasarman A., Antohi M. Une nouvelle classe de welchicines. Rev Can Biol. 1971 Sep;30(3):183–189. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlegel R., Slade H. D. Alteration of macromolecular synthesis and membrane permeability by a Streptococcus sanguis bacteriocin. J Gen Microbiol. 1974 Mar;81(1):275–277. doi: 10.1099/00221287-81-1-275. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlegel R., Slade H. D. Bacteriocin production by transformable group H streptococci. J Bacteriol. 1972 Nov;112(2):824–829. doi: 10.1128/jb.112.2.824-829.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlegel R., Slade H. D. Properties of a Streptococcus sanguis (group H) bacteriocin and its separation from the competence factor of transformation. J Bacteriol. 1973 Aug;115(2):655–661. doi: 10.1128/jb.115.2.655-661.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sebald M., Ionesco H. Inhibition de l'initiation de la germination des spores de Clostridium perfringens type A par la bactériocine de Clostridium perfringens souche BP6K-N5. C R Acad Sci Hebd Seances Acad Sci D. 1974 Oct 21;279(17):1503–1506. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shafia F. Thermocins of Bacillus stearothermophilus. J Bacteriol. 1966 Aug;92(2):524–525. doi: 10.1128/jb.92.2.524-525.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shannon R., Hedges A. J. A colorimetric bioassay method for colicins. J Appl Bacteriol. 1970 Sep;33(3):555–565. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1970.tb02234.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinefield H. R., Ribble J. C., Boris M. Bacterial interference between strains of Staphylococcus aureus, 1960 to 1970. Am J Dis Child. 1971 Feb;121(2):148–152. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1971.02100130102013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sidikaro J., Nomura M. E3 immunity substance. A protein from e3-colicinogenic cells that accounts for their immunity to colicin E3. J Biol Chem. 1974 Jan 25;249(2):445–453. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smarda J., Ebringer L., Mach J. The effect of colicin E2 on the flagellate Euglena gracilis. J Gen Microbiol. 1975 Feb;86(2):363–366. doi: 10.1099/00221287-86-2-363. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smarda J., Havelková M. The effect of colicin G on the spheroplasts of Proteus mirabilis. Folia Microbiol (Praha) 1970;15(2):122–124. doi: 10.1007/BF02880094. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smarda J., Lanek B. Possibility of use of colicin-refractory mutants in the study of localization of colicin receptors. Folia Microbiol (Praha) 1971;16(6):481–484. doi: 10.1007/BF02872724. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smarda J. Novel approaches to the mode of action of colicins. Folia Microbiol (Praha) 1975;20(3):264–271. doi: 10.1007/BF02876789. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith H. W. A search for transmissible pathogenic characters in invasive strains of Escherichia coli: the discovery of a plasmid-controlled toxin and a plasmid-controlled lethal character closely associated, or identical, with colicine V. J Gen Microbiol. 1974 Jul;83(0):95–111. doi: 10.1099/00221287-83-1-95. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sonstein S. A., Hammel J. M., Bondi A. Staphylococcal bacteriophage-associated lysin: a lytic agent active against Staphylococcus aureus. J Bacteriol. 1971 Aug;107(2):499–504. doi: 10.1128/jb.107.2.499-504.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stamatin N. Blocage de la germination des spores et effet dáutoantibiose exercés par un métabolite synthétisé par Bacillus Laterosporus. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1969 Jan;116(1):19–26. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Săsărman A., Antohi M. Données préliminares sur le transfert de la capacité welchicinogène de Clostridium perfringens à Bacillus anthracis. Arch Roum Pathol Exp Microbiol. 1969 Jun-Sep;28(2):743–745. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TERRASSE G., SOHIER R. Recherches sur l'activité antibiotique et probiotique de diverses corynébactéries non pathogènes- à l'égard de Corynebacterium diphtheriae. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1954 Dec;87(6):727–731. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tagg J. R., Dajani A. S., Wannamaker L. W. Bacteriocin of a group B streptococcus: partial purification and characterization. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1975 Jun;7(6):764–772. doi: 10.1128/aac.7.6.764. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tagg J. R., Dajani A. S., Wannamaker L. W., Gray E. D. Group A streptococcal bacteriocin. Production, purification, and mode of action. J Exp Med. 1973 Nov 1;138(5):1168–1183. doi: 10.1084/jem.138.5.1168. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tagg J. R., McGiven A. R. Assay system for bacteriocins. Appl Microbiol. 1971 May;21(5):943–943. doi: 10.1128/am.21.5.943-943.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tagg J. R., McGiven A. R. Some possible autoimmune mechanisms in rheumatic carditis. Lancet. 1972 Sep 30;2(7779):686–688. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(72)92091-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tagg J. R., Mushin R. Epidemiology of Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection in hospitals. 1. Pyocine typing of Ps. aeruginosa. Med J Aust. 1971 Apr 17;1(16):847–852. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tagg J. R., Pihl E. A., McGiven A. R. Morphological changes in a susceptible strain of Streptococcus pyogenes treated with streptocin A. J Gen Microbiol. 1973 Nov;79(1):167–169. doi: 10.1099/00221287-79-1-167. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tagg J. R., Read R. S., McGiven A. R. Bacteriocin of a group A streptococcus: partial purification and properties. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1973 Sep;4(3):214–221. doi: 10.1128/aac.4.3.214. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takagaki Y., Kunugita K., Matsuhashi M. Evidence for the direct action of colicin K on aerobic 32 P i uptake in Escherichia coli in vivo and in vitro. J Bacteriol. 1973 Jan;113(1):42–50. doi: 10.1128/jb.113.1.42-50.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeya K., Tokiwa H. Bacteriocin-typing of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1974 Feb;109(2):304–305. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1974.109.2.304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tashpulatova N. V., Krylova M. D. Bakteriotsiny difteriinykh bakterii. Zh Mikrobiol Epidemiol Immunobiol. 1967 May;44(5):78–80. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tramer J. Inhibitory effect of Lactobacillus acidophilus. Nature. 1966 Jul 9;211(5045):204–205. doi: 10.1038/211204a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trust T. J. Antagonism by a gram-positive coccus. Can J Microbiol. 1970 Aug;16(8):661–665. doi: 10.1139/m70-114. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tubylewicz H. Antigenic properties of the bacteriocine preparations obtained from type A Cl. perfringens strains. Bull Acad Pol Sci Biol. 1970;18(5):253–256. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tubylewicz H. Experimental studies on bacteriocinogeneity in Cl. perfringens type A. 3. Chemical structure of isolated bacteriocines. Bull Acad Pol Sci Biol. 1968;16(5):279–284. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tubylewicz H. Experimental studies on bacteriocinogeneity in Clostridium perfringens type A. I. Isolation of bacteriocines and their antibacterial spectrum. Bull Acad Pol Sci Biol. 1966;14(1):31–36. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tubylewicz H. Experimental studies on the bacteriocinogeneity in Cl. perfringens type A. II. Properties of isolated bacteriocines. Bull Acad Pol Sci Biol. 1966;14(7):467–473. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turnowsky F., Drews J., Eich F., Högenauer G. In vitro inactivation of ascites ribosomes by colicin E 3. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1973 May 1;52(1):327–334. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(73)90991-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tzannetis S. E., Papavassiliou J., Papanayiotou P. Naturally occurring antibodies against colicines in human sera. J Med Microbiol. 1972 Aug;5(3):275–281. doi: 10.1099/00222615-5-3-275. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tzannetis S., Dimitracopoulos G., Papavassiliou J. Occurrence of staphylococcin production in staphylococci. Boll Ist Sieroter Milan. 1974 Jan-Feb;50(1):26–29. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tzannetis S., Leonardopoulos J., Papavassiliou J. Enterocinogeny and lysogeny in enterococci. J Appl Bacteriol. 1970 Jun;33(2):358–362. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1970.tb02207.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tzannetis S., Poulaki-Tsontou A., Papavassiliou J. Bacteriocine production in group B streptococci. Pathol Microbiol (Basel) 1974;41(1):51–57. doi: 10.1159/000162563. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Upreti G. C., Hinsdill R. D. Isolation and characterization of a bacteriocin from a homofermentative Lactobacillus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1973 Oct;4(4):487–494. doi: 10.1128/aac.4.4.487. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Upreti G. C., Hinsdill R. D. Production and mode of action of lactocin 27: bacteriocin from a homofermentative Lactobacillus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1975 Feb;7(2):139–145. doi: 10.1128/aac.7.2.139. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VASSILIADIS P., TZAMOURANIS N. [Antibiotic activity of a Staphylococcus albus strain]. Arch Inst Pasteur Hell. 1961 Dec;7:105–113. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VINCENT J. G., VEOMETT R. C., RILEY R. F. Antibacterial activity associated with Lactobacillus acidophilus. J Bacteriol. 1959 Oct;78:477–484. doi: 10.1128/jb.78.4.477-484.1959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vianu I. Etudes préliminaires sur le transfert de la bactériocinogenèse des staphylocoques. Arch Roum Pathol Exp Microbiol. 1969 Dec;28(4):1097–1101. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WHEATER D. M., HIRSCH A., MATTICK A. T. R. Possible identity of lactobacillin with hydrogen peroxide produced by lactobacilli. Nature. 1952 Oct 11;170(4328):623–624. doi: 10.1038/170623a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wadström T., Hisatsune K. Bacteriolytic enzymes from Staphylococcus aureus. Purification of an endo-beta-N-acetylglucosaminidase. Biochem J. 1970 Dec;120(4):725–734. doi: 10.1042/bj1200725. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walstad D. L., Reitz R. C., Sparling P. F. Growth inhibition among strains of Neisseria gonorrhoeae due to production of inhibitory free fatty acids and lysophosphatidylethanolamine: absence of bacteriocins. Infect Immun. 1974 Sep;10(3):481–488. doi: 10.1128/iai.10.3.481-488.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warren R., Rogolsky M., Wiley B. B., Glasgow L. A. Effect of ethidium bromide on elimination of exfoliative toxin and bacteriocin production in Staphylococcus aureus. J Bacteriol. 1974 Jun;118(3):980–985. doi: 10.1128/jb.118.3.980-985.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weltzien H. U., Jesaitis M. A. The nature of the cilicin K receptor of Escherichia coli Cullen. J Exp Med. 1971 Mar 1;133(3):534–553. doi: 10.1084/jem.133.3.534. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White R. J., Hurst A. The location of nisin in the producer organism, Streptococcus lactis. J Gen Microbiol. 1968 Sep;53(2):171–179. doi: 10.1099/00221287-53-2-171. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolff L. F., Duncan J. L. Studies on a bactericidal substance produced by group A streptococci. J Gen Microbiol. 1974 Apr;81(2):413–424. doi: 10.1099/00221287-81-2-413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Barjac H., Lajudie J. Mise en évidence de facteurs antagonistes du type des bactériocines chez Bacillus thuringiensis. Ann Microbiol (Paris) 1974 Dec;125(4):529–537. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Klerk H. C., Smit J. A. Properties of a Lactobacillus fermenti bacteriocin. J Gen Microbiol. 1967 Aug;48(2):309–316. doi: 10.1099/00221287-48-2-309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


