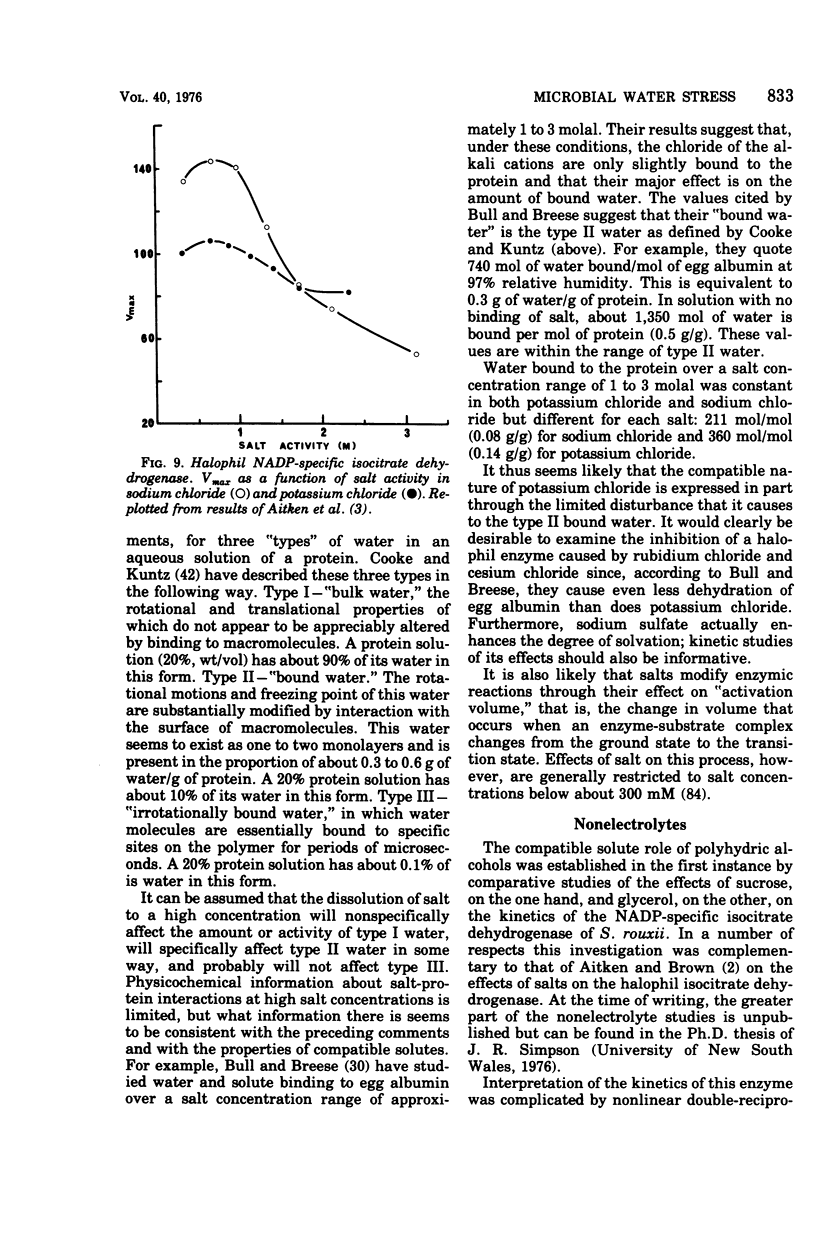
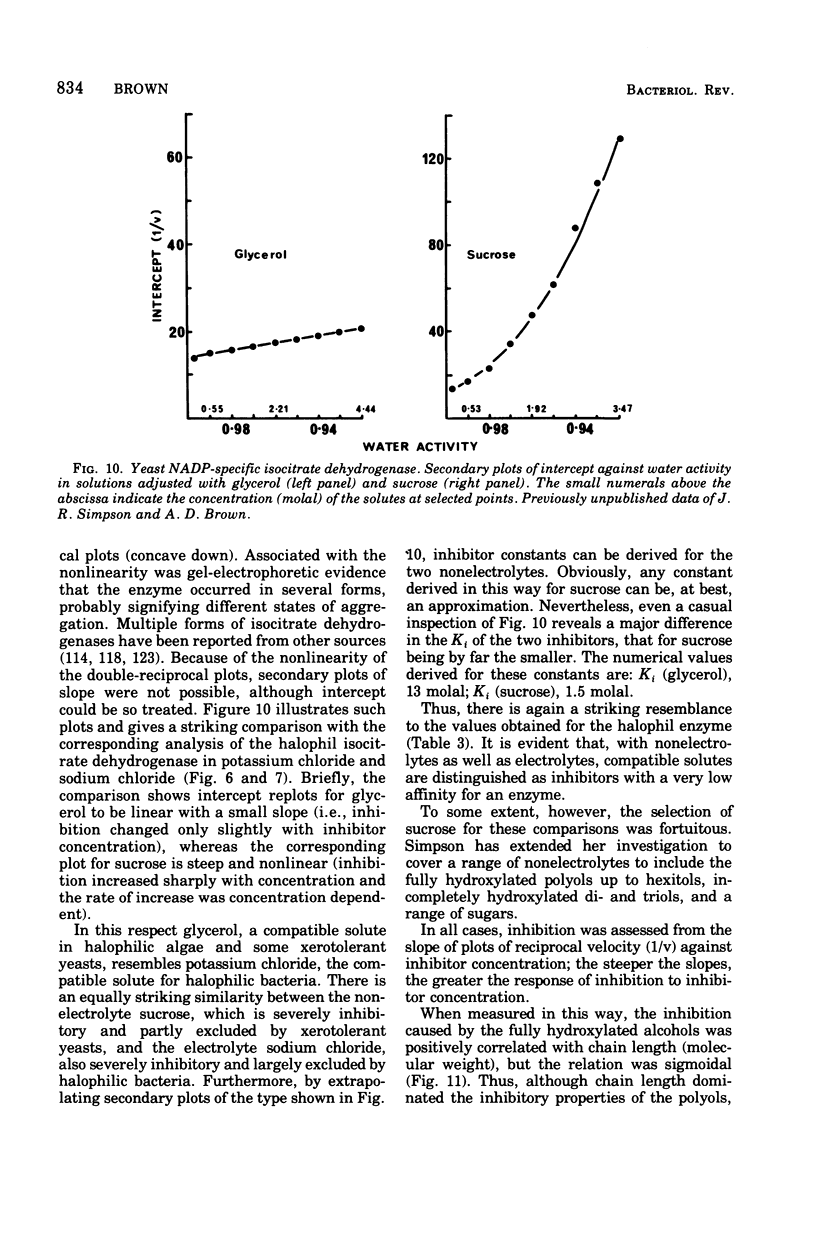
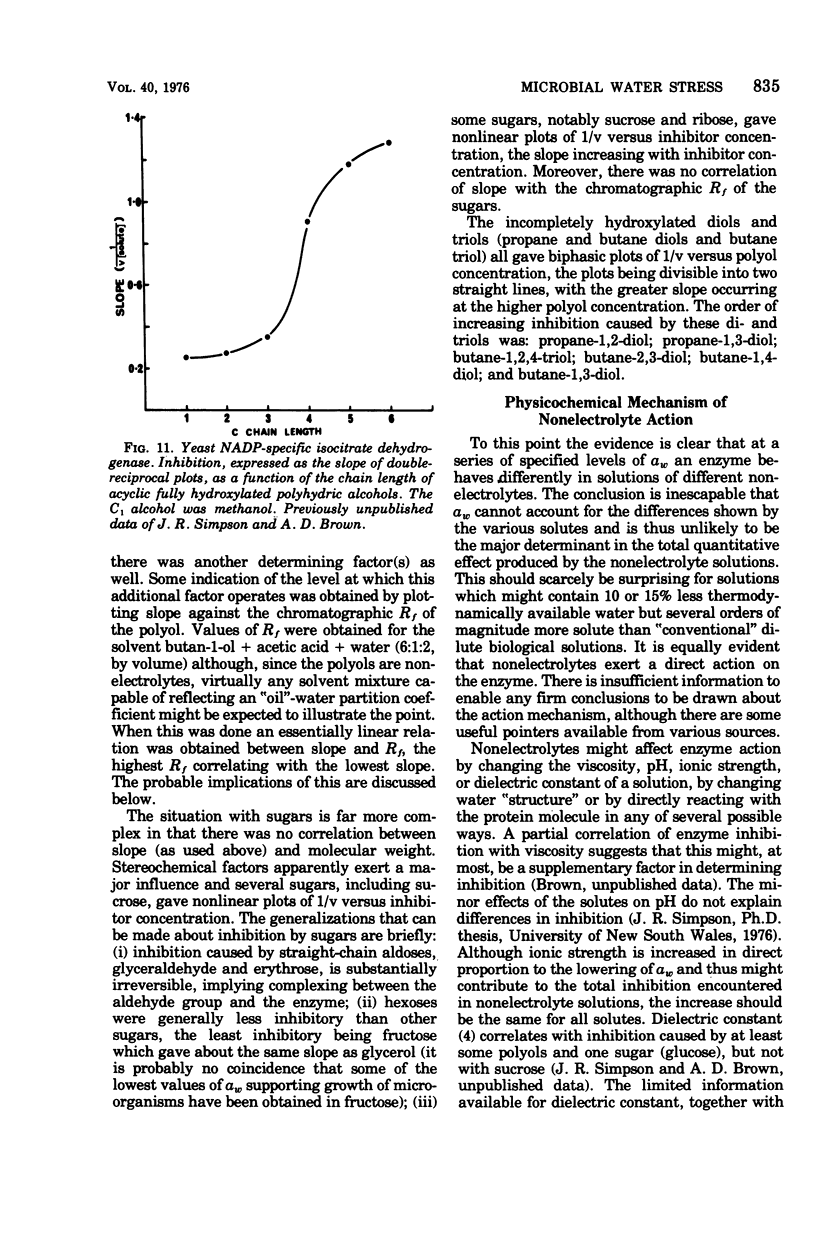
Full text
PDF

















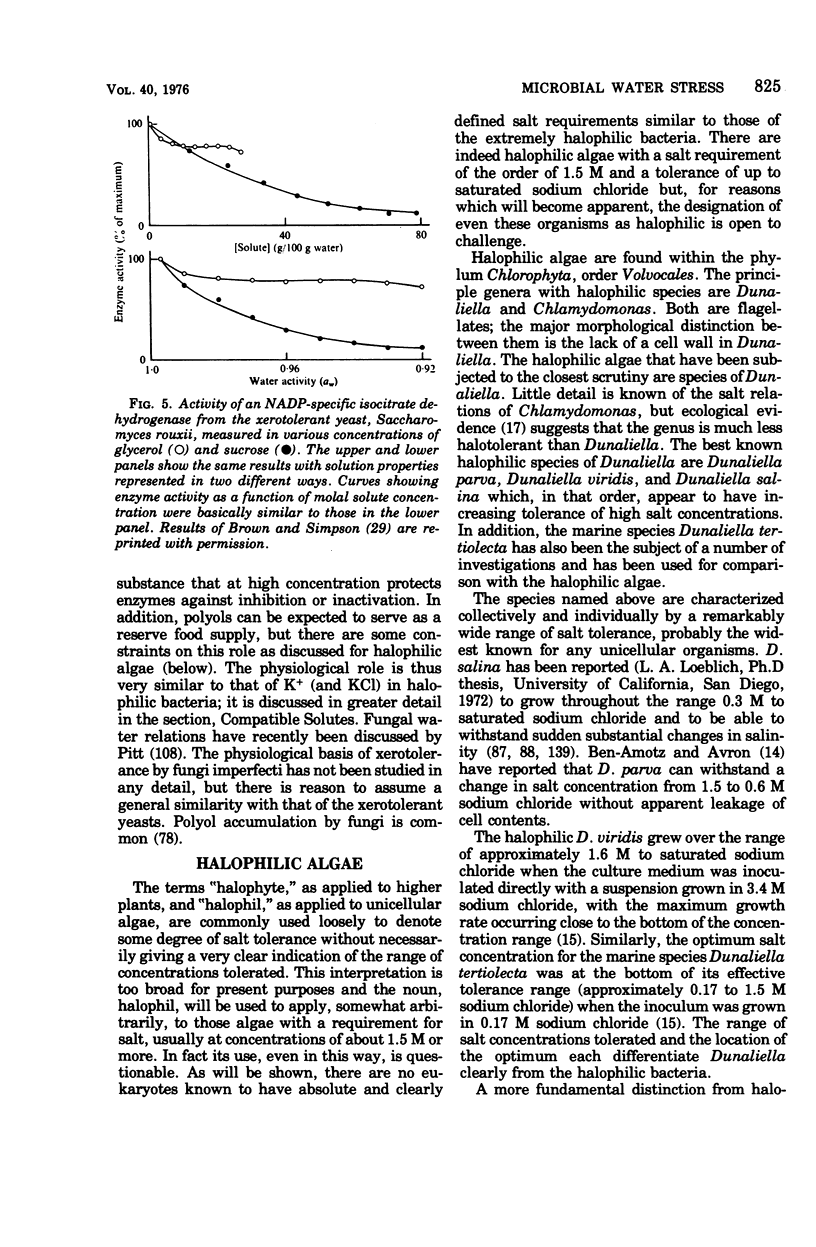




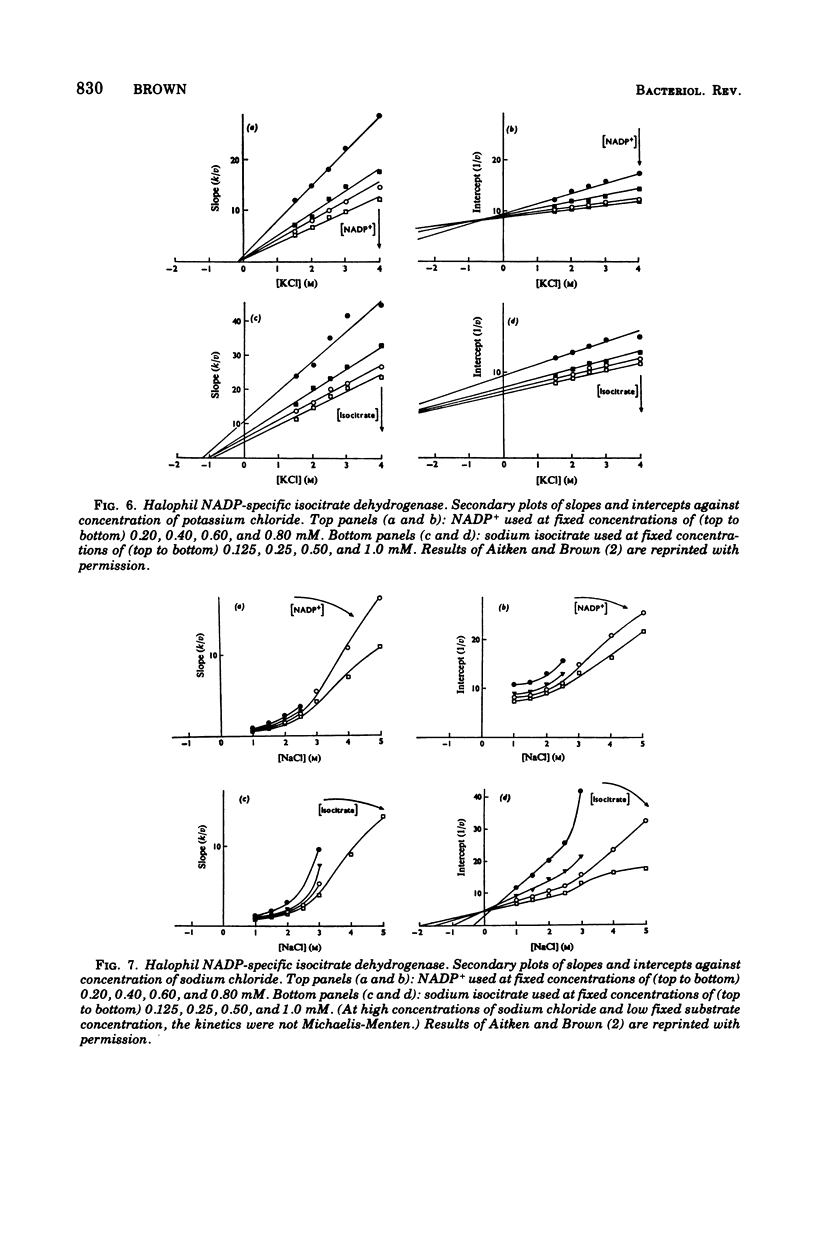
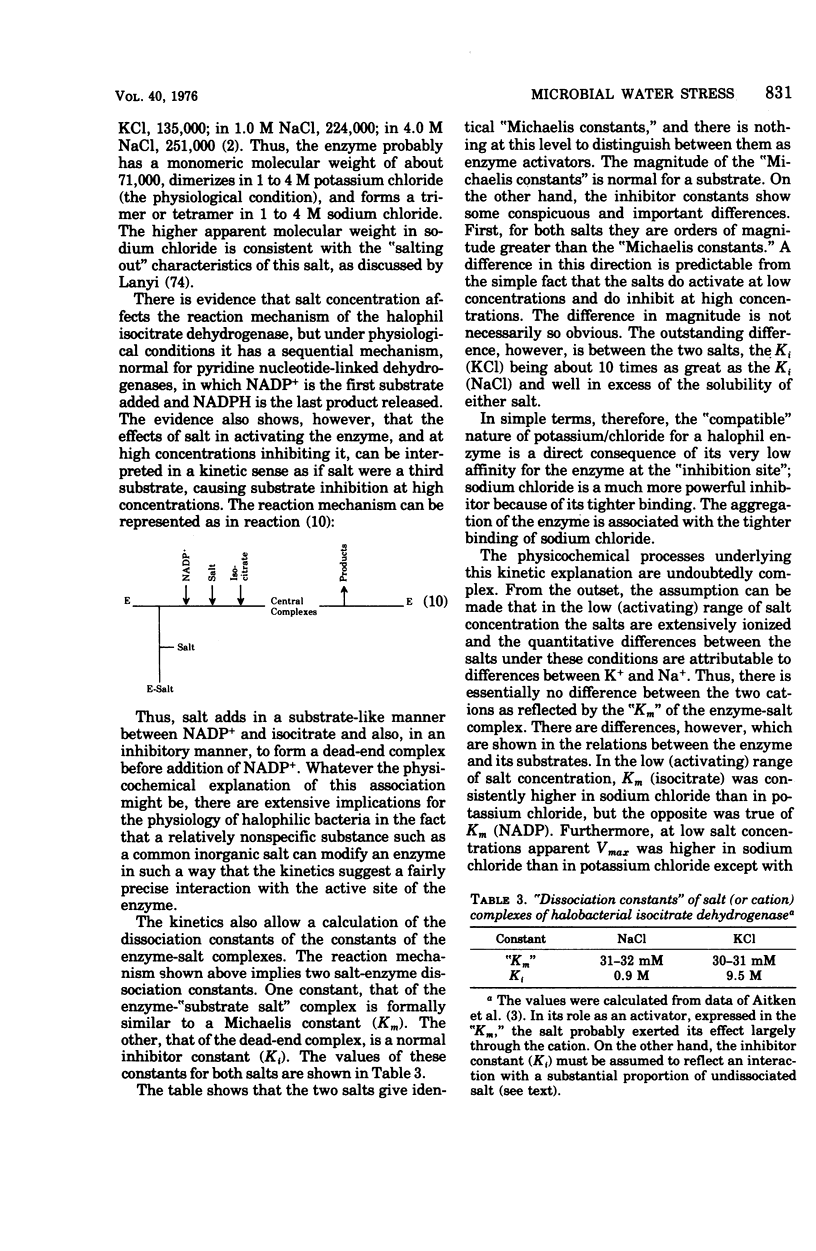
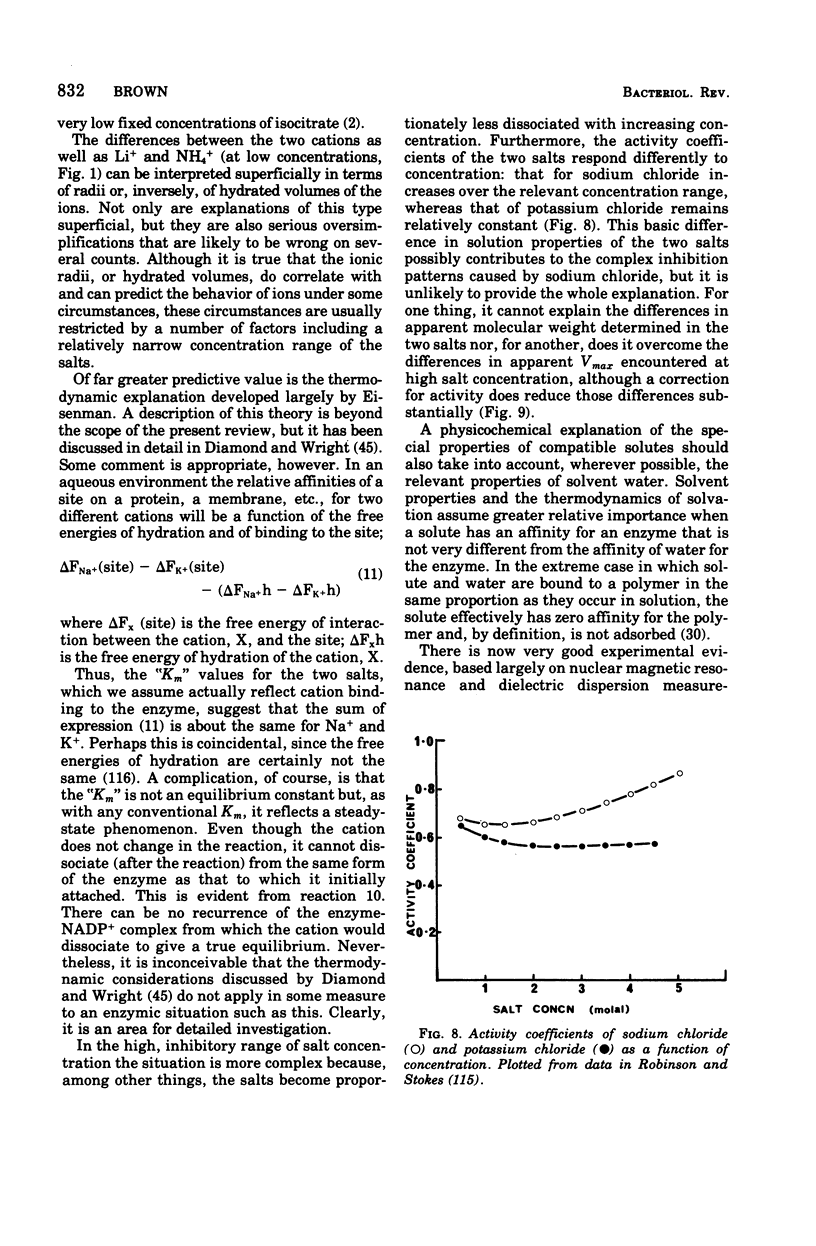











Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aitken D. M., Brown A. D. Properties of halophil nicotinamide-adenine dinucleotide phosphate-specific isocitrate dehydrogenase. True Michaelis constants, reaction mechanisms and molecular weights. Biochem J. 1972 Dec;130(3):645–662. doi: 10.1042/bj1300645. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aitken D. M., Wicken A. J., Brown A. D. Properties of a halophil nicotinamide--adenine dinucleotide phosphate-specific isocitrate dehydrogenase. Preliminary studies of the salt relations and kinetics of the crude enzyme. Biochem J. 1970 Jan;116(1):125–134. doi: 10.1042/bj1160125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BAXTER R. M. An interpretation of the effects of salts on the lactic dehydrogenase of Halobacterium salinarium. Can J Microbiol. 1959 Feb;5(1):47–57. doi: 10.1139/m59-006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRITTEN R. J., McCLURE F. T. The amino acid pool in Escherichia coli. Bacteriol Rev. 1962 Sep;26:292–335. doi: 10.1128/br.26.3.292-335.1962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BROWN A. D. ASPECTS OF BACTERIAL RESPONSE TO THE IONIC ENVIRONMENT. Bacteriol Rev. 1964 Sep;28:296–329. doi: 10.1128/br.28.3.296-329.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BROWN A. D. HYDROGEN ION TITRATIONS OF INTACT AND DISSOLVED LIPOPROTEIN MEMBRANES. J Mol Biol. 1965 Jun;12:491–508. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(65)80272-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BROWN A. D., SHOREY C. D. THE CELL ENVELOPES OF TWO EXTREMELY HALOPHILIC BACTERIA. J Cell Biol. 1963 Sep;18:681–689. doi: 10.1083/jcb.18.3.681. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BROWN A. D. THE DEVELOPMENT OF HALOPHILIC PROPERTIES IN BACTERIAL MEMBRANES BY ACYLATION. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1964 Oct 9;93:136–142. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(64)90267-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BROWN A. D. THE PERIPHERAL STRUCTURES OF GRAM-NEGATIVE BACTERIA.IV. THE CATION-SENSITIVE DISSOLUTION OF THE CELL MEMBRANE OF THE HALOPHILIC BACTERIUM, HALOBACTERIUM HALOBIUM. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1963 Nov 29;75:425–435. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(63)90630-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ben-Amotz A., Avron M. NADP specific dihydroxyacetone reductase from Dunaliella parva. FEBS Lett. 1973 Jan 15;29(2):153–155. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(73)80548-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ben-Amotz A., Avron M. Photosynthetic Activities of the Halophilic Alga Dunaliella parva. Plant Physiol. 1972 Feb;49(2):240–243. doi: 10.1104/pp.49.2.240. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ben-Amotz A., Avron M. The Role of Glycerol in the Osmotic Regulation of the Halophilic Alga Dunaliella parva. Plant Physiol. 1973 May;51(5):875–878. doi: 10.1104/pp.51.5.875. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borowitzka L. J., Brown A. D. The salt relations of marine and halophilic species of the unicellular green alga, Dunaliella. The role of glycerol as a compatible solute. Arch Mikrobiol. 1974 Mar 1;96(1):37–52. doi: 10.1007/BF00590161. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown A. D., Cho K. Y. The walls of the extremely halophilic cocci: gram-positive bacteria lacking muramic acid. J Gen Microbiol. 1970 Aug;62(2):267–270. doi: 10.1099/00221287-62-2-267. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown A. D. Microbial water relations. Effects of solute concentration on the respiratory activity of sugar-tolerant and non-tolerant yeasts. J Gen Microbiol. 1975 Feb;86(2):241–249. doi: 10.1099/00221287-86-2-241. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown A. D. Microbial water relations: features of the intracellular composition of sugar-tolerant yeasts. J Bacteriol. 1974 Jun;118(3):769–777. doi: 10.1128/jb.118.3.769-777.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown A. D., Netschey A. Sedimentation, viscosity and partial specific volumes of membrane proteins and lipoproteins. Biochem J. 1967 Apr;103(1):24–28. doi: 10.1042/bj1030024. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown A. D., Pearce R. F. Preliminary fractionation by gel electrophoresis of the membrane proteins and lipoproteins of Halobacterium halobium. Can J Biochem. 1969 Sep;47(9):833–837. doi: 10.1139/o69-131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown A. D., Shorey C. D., Turner H. P. An alternative method of isolating the membrane of a halophilic bacterium. J Gen Microbiol. 1965 Nov;41(2):225–231. doi: 10.1099/00221287-41-2-225. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown A. D., Simpson J. R. Water relations of sugar-tolerant yeasts: the role of intracellular polyols. J Gen Microbiol. 1972 Oct;72(3):589–591. doi: 10.1099/00221287-72-3-589. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bull H. B., Breese K. Water and solute binding by proteins. 1. Electrolytes. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1970 Apr;137(2):299–305. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(70)90443-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHRISTIAN J. H., WALTHO J. A. Solute concentrations within cells of halophilic and non-halophilic bacteria. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1962 Dec 17;65:506–508. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(62)90453-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHRISTIAN J. H., WALTHO J. A. THE COMPOSITION OF STAPHYLOCOCCUS AUREUS IN RELATION TO THE WATER ACTIVITY OF THE GROWTH MEDIUM. J Gen Microbiol. 1964 May;35:205–213. doi: 10.1099/00221287-35-2-205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHRISTIAN J. H., WALTHO J. A. The sodium and potassium content of non-halophilic bacteria in relation to salt tolerance. J Gen Microbiol. 1961 May;25:97–102. doi: 10.1099/00221287-25-1-97. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheah K. S. The membrane-bound carbon monoxide-reactive hemoproteins in the extreme halophiles. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Jan 13;197(1):84–86. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(70)90011-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cho K. Y., Doy C. H., Mercer E. H. Ultrastructure of the obligate halophilic bacterium Halobacterium halobium. J Bacteriol. 1967 Jul;94(1):196–201. doi: 10.1128/jb.94.1.196-201.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christian J. H., Waltho J. A. Water relations of Salmonella oranienburg; stimulation of respiration by amino acids. J Gen Microbiol. 1966 Jun;43(3):345–355. doi: 10.1099/00221287-43-3-345. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Contaxis C. C., Reithel F. J. Studies on protein multimers. II. A study of the mechanism of urease dissociation in 1,2-propanediol: comparative studies with ethylene glycol and glycerol. J Biol Chem. 1971 Feb 10;246(3):677–685. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooke R., Kuntz I. D. The properties of water in biological systems. Annu Rev Biophys Bioeng. 1974;3(0):95–126. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.03.060174.000523. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danon A., Stoeckenius W. Photophosphorylation in Halobacterium halobium. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Apr;71(4):1234–1238. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.4.1234. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamond J. M., Wright E. M. Biological membranes: the physical basis of ion and nonelectrolyte selectivity. Annu Rev Physiol. 1969;31:581–646. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.31.030169.003053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Douzou P. The use of subzero temperatures in biochemistry: slow reactions. Methods Biochem Anal. 1974;22:401–512. doi: 10.1002/9780470110423.ch9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ginzburg M. The unusual membrane permeability of two halophilic unicellular organisms. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969 Apr;173(3):370–376. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(69)90002-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gochnauer M. B., Kushner D. J. Growth and nutrition of extremely halophilic bacteria. Can J Microbiol. 1969 Oct;15(10):1157–1165. doi: 10.1139/m69-211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gochnauer M. B., Leppard G. G., Komaratat P., Kates M., Novitsky T., Kushner D. J. Isolation and characterization of Actinopolyspora halophila, gen. et sp. nov., an extremely halophilic actinomycete. Can J Microbiol. 1975 Oct;21(10):1500–1511. doi: 10.1139/m75-222. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOUWINK A. L. Flagella, gas vacuoles and cell-wall structure in Halobacterium halobium; an electron microscope study. J Gen Microbiol. 1956 Aug;15(1):146–150. doi: 10.1099/00221287-15-1-146. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hellingwerf K. J., Michels P. A., Dorpema J. W., Konings W. N. Transport of amino acids in membrane vesicles of Rhodopseudomonas spheroides energized by respiratory and cyclic electron flow. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Jul 1;55(2):397–406. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb02175.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson R., Unwin P. N. Three-dimensional model of purple membrane obtained by electron microscopy. Nature. 1975 Sep 4;257(5521):28–32. doi: 10.1038/257028a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hescox M. A., Carlberg D. M. Photoreactivation in Halobacterium cutirubrum. Can J Microbiol. 1972 Jul;18(7):981–985. doi: 10.1139/m72-152. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hildebrand E., Dencher N. Two photosystems controlling behavioural responses of Halobacterium halobium. Nature. 1975 Sep 4;257(5521):46–48. doi: 10.1038/257046a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JOSHI J. G., GUILD W. R., HANDLER P. The presence of two species of DNA in some halobacteria. J Mol Biol. 1963 Jan;6:34–38. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(63)80079-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson M. K., Johnson E. J., MacElroy R. D., Speer H. L., Bruff B. S. Effects of salts on the halophilic alga Dunaliella viridis. J Bacteriol. 1968 Apr;95(4):1461–1468. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.4.1461-1468.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaneshiro E. S., Holz G. G., Jr, Dunham P. B. Osmoregulation in a marine ciliate, Miamiensis avidus. II. Regulation of intracellular free amino acids. Biol Bull. 1969 Aug;137(1):161–169. doi: 10.2307/1539939. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kauss H. Turnover of galactosylglycerol and osmotic balance in ochromonas. Plant Physiol. 1973 Dec;52(6):613–615. doi: 10.1104/pp.52.6.613. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kientz M. L., Bigelow C. C. The effect of ethylene glycol on the structure of beta-lactoglobulin. Biochemistry. 1966 Nov;5(11):3494–3500. doi: 10.1021/bi00875a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kushner D. J. Halophilic bacteria. Adv Appl Microbiol. 1968;10:73–99. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2164(08)70189-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langworthy T. A., Mayberry W. R., Smith P. F. Long-chain glycerol diether and polyol dialkyl glycerol triether lipids of Sulfolobus acidocaldarius. J Bacteriol. 1974 Jul;119(1):106–116. doi: 10.1128/jb.119.1.106-116.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langworthy T. A., Smith P. F., Mayberry W. R. Lipids of Thermoplasma acidophilum. J Bacteriol. 1972 Dec;112(3):1193–1200. doi: 10.1128/jb.112.3.1193-1200.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanyi J. K. Salt-dependent properties of proteins from extremely halophilic bacteria. Bacteriol Rev. 1974 Sep;38(3):272–290. doi: 10.1128/br.38.3.272-290.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Louis B. G., Fitt P. S. Isolation and properties of highly purified Halobacterium cutirubrum deoxyribonucleic acid-dependent ribonucleic acid polymerase. Biochem J. 1972 Mar;127(1):69–80. doi: 10.1042/bj1270069. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Louis B. G., Fitt P. S. Nucleic acid enzymology of extremely halophilic bacteria. Halobacterium cutirubrum deoxyribonucleic acid-dependent ribonucleic acid polymerase. Biochem J. 1971 Feb;121(4):621–627. doi: 10.1042/bj1210621. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Louis B. G., Fitt P. S. Nucleic acid enzymology of extremely halophilic bacteria. Halobacterium cutirubrum ribonucleic acid-dependent ribonucleic acid polymerase. Biochem J. 1971 Feb;121(4):629–633. doi: 10.1042/bj1210629. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Louis B. G., Fitt P. S. Purification and properties of the ribonucleic acid-dependent ribonucleic acid polymerase from Halobacterium cutirubrum. Biochem J. 1972 Jul;128(4):755–762. doi: 10.1042/bj1280755. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Louis B. G., Fitt P. S. The role of Halobacterium cutirubrum deoxyribonucleic acid-dependent ribonucleic acid polymerase subunits in initiation and polymerization. Biochem J. 1972 Mar;127(1):81–86. doi: 10.1042/bj1270081. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Low P. S., Somero G. N. Activation volumes in enzymic catalysis: their sources and modification by low-molecular-weight solutes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Aug;72(8):3014–3018. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.8.3014. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Low P. S., Somero G. N. Protein hydration changes during catalysis: a new mechanism of enzymic rate-enhancement and ion activation/inhibition of catalysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Sep;72(9):3305–3309. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.9.3305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacDonald R. E., Lanyi L. K. Light-induced leucine transport in Halobacterium halobium envelope vesicles: a chemiosmotic system. Biochemistry. 1975 Jul;14(13):2882–2889. doi: 10.1021/bi00684a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall C. L., Brown A. D. The membrane lipids of Halobacterium halobium. Biochem J. 1968 Dec;110(3):441–448. doi: 10.1042/bj1100441. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall C. L., Wicken A. J., Brown A. D. The outer layer of the cell envelope of Halobacterium halobium. Can J Biochem. 1969 Jan;47(1):71–74. doi: 10.1139/o69-013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Measures J. C. Role of amino acids in osmoregulation of non-halophilic bacteria. Nature. 1975 Oct 2;257(5525):398–400. doi: 10.1038/257398a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mescher M. F., Strominger J. L. Bacitracin induces sphere formation in Halobacterium species which lack a wall peptidoglycan. J Gen Microbiol. 1975 Aug;89(2):375–378. doi: 10.1099/00221287-89-2-375. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer G. H., Morrow M. B., Wyss O., Berg T. E., Littlepage J. L. Antarctica: The Microbiology of an Unfrozen Saline Pond. Science. 1962 Dec 7;138(3545):1103–1104. doi: 10.1126/science.138.3545.1103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore R. L., McCarthy B. J. Characterization of the deoxyribonucleic acid of various strains of halophilic bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1969 Jul;99(1):248–254. doi: 10.1128/jb.99.1.248-254.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakanishi S., Adhya S., Gottesman M., Pastan I. Activation of transcription at specific promoters by glycerol. J Biol Chem. 1974 Jul 10;249(13):4050–4056. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nozaki Y., Tanford C. The solubility of amino acids and related compounds in aqueous thylene glycol solutions. J Biol Chem. 1965 Sep;240(9):3568–3575. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OKAMOTO H., SUZUKI Y. INTRACELLULAR CONCENTRATION OF IONS IN A HALOPHILIC STRAIN OF CHLAMYDOMONAS. I. CONCENTRATION OF NA, K AND CL IN THE CELL. Z Allg Mikrobiol. 1964;4:350–357. doi: 10.1002/jobm.3630040503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ONISHI H., MCCANCE E., GIBBONS N. E. A SYNTHETIC MEDIUM FOR EXTREMELY HALOPHILIC BACTERIA. Can J Microbiol. 1965 Apr;11:365–373. doi: 10.1139/m65-044. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ONISHI H. OSMOPHILIC YEASTS. Adv Food Res. 1963;12:53–94. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oesterhelt D., Stoeckenius W. Rhodopsin-like protein from the purple membrane of Halobacterium halobium. Nat New Biol. 1971 Sep 29;233(39):149–152. doi: 10.1038/newbio233149a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oesterhelt D. The purple membrane of Halobacterium halobium: a new system for light energy conversion. Ciba Found Symp. 1975;(31):147–167. doi: 10.1002/9780470720134.ch9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olivares W., McQuarrie D. A. On the theory of ionic solutions. Biophys J. 1975 Feb;15(2 Pt 1):143–162. doi: 10.1016/s0006-3495(75)85798-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pitt J. I., Christian J. H. Water relations of xerophilic fungi isolated from prunes. Appl Microbiol. 1968 Dec;16(12):1853–1858. doi: 10.1128/am.16.12.1853-1858.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Postgate J. R. Recent advances in the study of the sulfate-reducing bacteria. Bacteriol Rev. 1965 Dec;29(4):425–441. doi: 10.1128/br.29.4.425-441.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pugh E. L., Wassef M. K., Kates M. Inhibition of fatty acid synthetase in Halobacterium cutirubrum and Escherichia coli by high salt concentrations. Can J Biochem. 1971 Aug;49(8):953–958. doi: 10.1139/o71-138. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Racker E., Stoeckenius W. Reconstitution of purple membrane vesicles catalyzing light-driven proton uptake and adenosine triphosphate formation. J Biol Chem. 1974 Jan 25;249(2):662–663. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raymond J. C., Sistrom W. R. ctothiorhodospira halophila: a new species ofthe genus Ectothiorhodospira. Arch Mikrobiol. 1969;69(2):121–126. doi: 10.1007/BF00409756. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reeves H. C., Brehmeyer B. A., Ajl S. J. Multiple forms of bacterial NADP-specific isocitrate dehydrogenase. Science. 1968 Oct 18;162(3851):359–360. doi: 10.1126/science.162.3851.359. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothfield L., Romeo D. Role of lipids in the biosynthesis of the bacterial cell envelope. Bacteriol Rev. 1971 Mar;35(1):14–38. doi: 10.1128/br.35.1.14-38.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowe J. J., Reeves H. C. Electrophoretic heterogeneity of bacterial nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate-specific isocitrate dehydrogenases. J Bacteriol. 1971 Nov;108(2):824–827. doi: 10.1128/jb.108.2.824-827.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SEHGAL S. N., KATES M., GIBBONS N. E. Lipids of Halobacterium cutirubrum. Can J Biochem Physiol. 1962 Jan;40:69–81. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Self C. H., Weitzman P. D. The isocitrate dehydrogenases of Acinetobacter lwoffi. Separation and properties of two nicotinamide-adenine dinucleotide phosphate-linked isoenzymes. Biochem J. 1972 Nov;130(1):211–219. doi: 10.1042/bj1300211. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shkedy-Vinkler C., Avi-Dor Y. Betaine-induced stimulation of respiration at high osmolarities in a halotolerant bacterium. Biochem J. 1975 Aug;150(2):219–226. doi: 10.1042/bj1500219. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith P. F., Langworth T. A., Mayberry W. R., Houghland A. E. Characterization of the membranes of Thermoplasma acidophilum. J Bacteriol. 1973 Nov;116(2):1019–1028. doi: 10.1128/jb.116.2.1019-1028.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spencer J. F. Production of polyhydric alcohols by yeasts. Prog Ind Microbiol. 1968;7:1–42. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steber J., Schleifer K. H. Halococcus morrhuae: a sulfated heteropolysaccharide as the structural component of the bacterial cell wall. Arch Microbiol. 1975 Oct 27;105(2):173–177. doi: 10.1007/BF00447133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoeckenius W., Rowen R. A morphological study of Halobacterium halobium and its lysis in media of low salt concentration. J Cell Biol. 1967 Jul;34(1):365–393. doi: 10.1083/jcb.34.1.365. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoner L. C., Dunham P. B. Regulation of cellular osmolarity and volume in Tetrahymena. J Exp Biol. 1970 Oct;53(2):391–399. doi: 10.1242/jeb.53.2.391. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tempest D. W., Meers J. L., Brown C. M. Influence of environment on the content and composition of microbial free amino acid pools. J Gen Microbiol. 1970 Dec;64(2):171–185. doi: 10.1099/00221287-64-2-171. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thierry O. C., Cooney J. J. Physicochemical factors influencing growth and pigment synthesis by Micrococcus roseus. Can J Microbiol. 1966 Aug;12(4):691–698. doi: 10.1139/m66-095. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torsvik T., Dundas I. D. Bacteriophage of Halobacterium salinarium. Nature. 1974 Apr 19;248(5450):680–681. doi: 10.1038/248680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WILBRANDT W. Transport through biological membranes. Annu Rev Physiol. 1963;25:601–630. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.25.030163.003125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wais A. C., Kon M., MacDonald R. E., Stollar B. D. Salt-dependent bacteriophage infecting Halobacterium cutirubrum and H. halobium. Nature. 1975 Jul 24;256(5515):314–315. doi: 10.1038/256314a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walsby A. E. Structure and function of gas vacuoles. Bacteriol Rev. 1972 Mar;36(1):1–32. doi: 10.1128/br.36.1.1-32.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wegmann K. Osmotic regulation of photosynthetic glycerol production in Dunaliella. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Jun 15;234(3):317–323. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(71)90197-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodrow G. C., Cheung H. T., Cho K. Y. Phospholipid of an extremely halophilic bacterium, Sarcina morrhuae. Aust J Biol Sci. 1973 Aug;26(4):787–792. doi: 10.1071/bi9730787. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



