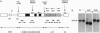Abstract
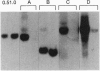
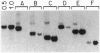
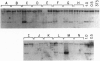
Retrovirus-mediated gene transfer into hematopoietic cells may provide a means of treating both inherited and acquired diseases involving hematopoietic cells. Implementation of this approach for disorders resulting from mutations affecting the beta-globin gene (e.g., beta-thalassemia and sickle cell anemia), however, has been hampered by the inability to generate recombinant viruses able to efficiently and faithfully transmit the necessary sequences for appropriate gene expression. We have addressed this problem by carefully examining the interactions between retroviral and beta-globin gene sequences which affect vector transmission, stability, and expression. First, we examined the transmission properties of a large number of different recombinant proviral genomes which vary both in the precise nature of vector, beta-globin structural gene, and locus control region (LCR) core sequences incorporated and in the placement and orientation of those sequences. Through this analysis, we identified one specific vector, termed M beta 6L, which carries both the human beta-globin gene and core elements HS2, HS3, and HS4 from the LCR and faithfully transmits recombinant proviral sequences to cells with titers greater than 10(6) per ml. Populations of murine erythroleukemia (MEL) cells transduced by this virus expressed levels of human beta-globin transcript which, on a per gene copy basis, were 78% of the levels detected in an MEL-derived cell line, Hu11, which carries human chromosome 11, the site of the beta-globin locus. Analysis of individual transduced MEL cell clones, however, indicated that, while expression was detected in every clone tested (n = 17), the levels of human beta-globin treatment varied between 4% and 146% of the levels in Hu11. This clonal variation in expression levels suggests that small beta-globin LCR sequences may not provide for as strict chromosomal position-independent expression of beta-globin as previously suspected, at least in the context of retrovirus-mediated gene transfer.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Auffray C., Rougeon F. Purification of mouse immunoglobulin heavy-chain messenger RNAs from total myeloma tumor RNA. Eur J Biochem. 1980 Jun;107(2):303–314. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb06030.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bender M. A., Gelinas R. E., Miller A. D. A majority of mice show long-term expression of a human beta-globin gene after retrovirus transfer into hematopoietic stem cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Apr;9(4):1426–1434. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.4.1426. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bender M. A., Miller A. D., Gelinas R. E. Expression of the human beta-globin gene after retroviral transfer into murine erythroleukemia cells and human BFU-E cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Apr;8(4):1725–1735. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.4.1725. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blom van Assendelft G., Hanscombe O., Grosveld F., Greaves D. R. The beta-globin dominant control region activates homologous and heterologous promoters in a tissue-specific manner. Cell. 1989 Mar 24;56(6):969–977. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90630-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bodine D. M., Karlsson S., Nienhuis A. W. Combination of interleukins 3 and 6 preserves stem cell function in culture and enhances retrovirus-mediated gene transfer into hematopoietic stem cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Nov;86(22):8897–8901. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.22.8897. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchman A. R., Berg P. Comparison of intron-dependent and intron-independent gene expression. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Oct;8(10):4395–4405. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.10.4395. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caterina J. J., Ciavatta D. J., Donze D., Behringer R. R., Townes T. M. Multiple elements in human beta-globin locus control region 5' HS 2 are involved in enhancer activity and position-independent, transgene expression. Nucleic Acids Res. 1994 Mar 25;22(6):1006–1011. doi: 10.1093/nar/22.6.1006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caterina J. J., Ryan T. M., Pawlik K. M., Palmiter R. D., Brinster R. L., Behringer R. R., Townes T. M. Human beta-globin locus control region: analysis of the 5' DNase I hypersensitive site HS 2 in transgenic mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Mar 1;88(5):1626–1630. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.5.1626. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang J. C., Liu D., Kan Y. W. A 36-base-pair core sequence of locus control region enhances retrovirally transferred human beta-globin gene expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Apr 1;89(7):3107–3110. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.7.3107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charnay P., Treisman R., Mellon P., Chao M., Axel R., Maniatis T. Differences in human alpha- and beta-globin gene expression in mouse erythroleukemia cells: the role of intragenic sequences. Cell. 1984 Aug;38(1):251–263. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90547-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collis P., Antoniou M., Grosveld F. Definition of the minimal requirements within the human beta-globin gene and the dominant control region for high level expression. EMBO J. 1990 Jan;9(1):233–240. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08100.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crossley M., Orkin S. H. Regulation of the beta-globin locus. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 1993 Apr;3(2):232–237. doi: 10.1016/0959-437x(93)90028-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curtin P. T., Liu D. P., Liu W., Chang J. C., Kan Y. W. Human beta-globin gene expression in transgenic mice is enhanced by a distant DNase I hypersensitive site. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Sep;86(18):7082–7086. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.18.7082. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danos O., Mulligan R. C. Safe and efficient generation of recombinant retroviruses with amphotropic and ecotropic host ranges. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Sep;85(17):6460–6464. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.17.6460. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dillon N., Grosveld F. Transcriptional regulation of multigene loci: multilevel control. Trends Genet. 1993 Apr;9(4):134–137. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(93)90208-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dranoff G., Jaffee E., Lazenby A., Golumbek P., Levitsky H., Brose K., Jackson V., Hamada H., Pardoll D., Mulligan R. C. Vaccination with irradiated tumor cells engineered to secrete murine granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor stimulates potent, specific, and long-lasting anti-tumor immunity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Apr 15;90(8):3539–3543. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.8.3539. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dzierzak E. A., Papayannopoulou T., Mulligan R. C. Lineage-specific expression of a human beta-globin gene in murine bone marrow transplant recipients reconstituted with retrovirus-transduced stem cells. Nature. 1988 Jan 7;331(6151):35–41. doi: 10.1038/331035a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engel J. D. Developmental regulation of human beta-globin gene transcription: a switch of loyalties? Trends Genet. 1993 Sep;9(9):304–309. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(93)90248-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felsenfeld G. Chromatin as an essential part of the transcriptional mechanism. Nature. 1992 Jan 16;355(6357):219–224. doi: 10.1038/355219a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forrester W. C., Novak U., Gelinas R., Groudine M. Molecular analysis of the human beta-globin locus activation region. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(14):5439–5443. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.14.5439. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forrester W. C., Takegawa S., Papayannopoulou T., Stamatoyannopoulos G., Groudine M. Evidence for a locus activation region: the formation of developmentally stable hypersensitive sites in globin-expressing hybrids. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Dec 23;15(24):10159–10177. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.24.10159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraser P., Hurst J., Collis P., Grosveld F. DNaseI hypersensitive sites 1, 2 and 3 of the human beta-globin dominant control region direct position-independent expression. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Jun 25;18(12):3503–3508. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.12.3503. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaensler K. M., Kitamura M., Kan Y. W. Germ-line transmission and developmental regulation of a 150-kb yeast artificial chromosome containing the human beta-globin locus in transgenic mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Dec 1;90(23):11381–11385. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.23.11381. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grosveld F., van Assendelft G. B., Greaves D. R., Kollias G. Position-independent, high-level expression of the human beta-globin gene in transgenic mice. Cell. 1987 Dec 24;51(6):975–985. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90584-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guild B. C., Finer M. H., Housman D. E., Mulligan R. C. Development of retrovirus vectors useful for expressing genes in cultured murine embryonal cells and hematopoietic cells in vivo. J Virol. 1988 Oct;62(10):3795–3801. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.10.3795-3801.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikuta T., Kan Y. W. In vivo protein-DNA interactions at the beta-globin gene locus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Nov 15;88(22):10188–10192. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.22.10188. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karlsson S., Bodine D. M., Perry L., Papayannopoulou T., Nienhuis A. W. Expression of the human beta-globin gene following retroviral-mediated transfer into multipotential hematopoietic progenitors of mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Aug;85(16):6062–6066. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.16.6062. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu D., Chang J. C., Moi P., Liu W., Kan Y. W., Curtin P. T. Dissection of the enhancer activity of beta-globin 5' DNase I-hypersensitive site 2 in transgenic mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 May 1;89(9):3899–3903. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.9.3899. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu X., Mertz J. E. Polyadenylation site selection cannot occur in vivo after excision of the 3'-terminal intron. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Nov 11;21(22):5256–5263. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.22.5256. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller A. D., Bender M. A., Harris E. A., Kaleko M., Gelinas R. E. Design of retrovirus vectors for transfer and expression of the human beta-globin gene. J Virol. 1988 Nov;62(11):4337–4345. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.11.4337-4345.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller J. L., Walsh C. E., Ney P. A., Samulski R. J., Nienhuis A. W. Single-copy transduction and expression of human gamma-globin in K562 erythroleukemia cells using recombinant adeno-associated virus vectors: the effect of mutations in NF-E2 and GATA-1 binding motifs within the hypersensitivity site 2 enhancer. Blood. 1993 Sep 15;82(6):1900–1906. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moi P., Kan Y. W. Synergistic enhancement of globin gene expression by activator protein-1-like proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Nov;87(22):9000–9004. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.22.9000. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nandi A. K., Roginski R. S., Gregg R. G., Smithies O., Skoultchi A. I. Regulated expression of genes inserted at the human chromosomal beta-globin locus by homologous recombination. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jun;85(11):3845–3849. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.11.3845. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ney P. A., Sorrentino B. P., McDonagh K. T., Nienhuis A. W. Tandem AP-1-binding sites within the human beta-globin dominant control region function as an inducible enhancer in erythroid cells. Genes Dev. 1990 Jun;4(6):993–1006. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.6.993. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishioka Y., Leder P. The complete sequence of a chromosomal mouse alpha--globin gene reveals elements conserved throughout vertebrate evolution. Cell. 1979 Nov;18(3):875–882. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90139-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novak U., Harris E. A., Forrester W., Groudine M., Gelinas R. High-level beta-globin expression after retroviral transfer of locus activation region-containing human beta-globin gene derivatives into murine erythroleukemia cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 May;87(9):3386–3390. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.9.3386. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson K. R., Clegg C. H., Huxley C., Josephson B. M., Haugen H. S., Furukawa T., Stamatoyannopoulos G. Transgenic mice containing a 248-kb yeast artificial chromosome carrying the human beta-globin locus display proper developmental control of human globin genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Aug 15;90(16):7593–7597. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.16.7593. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Philipsen S., Pruzina S., Grosveld F. The minimal requirements for activity in transgenic mice of hypersensitive site 3 of the beta globin locus control region. EMBO J. 1993 Mar;12(3):1077–1085. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05749.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Philipsen S., Talbot D., Fraser P., Grosveld F. The beta-globin dominant control region: hypersensitive site 2. EMBO J. 1990 Jul;9(7):2159–2167. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07385.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plavec I., Papayannopoulou T., Maury C., Meyer F. A human beta-globin gene fused to the human beta-globin locus control region is expressed at high levels in erythroid cells of mice engrafted with retrovirus-transduced hematopoietic stem cells. Blood. 1993 Mar 1;81(5):1384–1392. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pruzina S., Hanscombe O., Whyatt D., Grosveld F., Philipsen S. Hypersensitive site 4 of the human beta globin locus control region. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Apr 11;19(7):1413–1419. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.7.1413. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reddy P. M., Shen C. K. Protein-DNA interactions in vivo of an erythroid-specific, human beta-globin locus enhancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Oct 1;88(19):8676–8680. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.19.8676. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryan T. M., Behringer R. R., Martin N. C., Townes T. M., Palmiter R. D., Brinster R. L. A single erythroid-specific DNase I super-hypersensitive site activates high levels of human beta-globin gene expression in transgenic mice. Genes Dev. 1989 Mar;3(3):314–323. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.3.314. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryan T. M., Behringer R. R., Townes T. M., Palmiter R. D., Brinster R. L. High-level erythroid expression of human alpha-globin genes in transgenic mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jan;86(1):37–41. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.1.37. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern P. J., Berg P. Transformation of mammalian cells to antibiotic resistance with a bacterial gene under control of the SV40 early region promoter. J Mol Appl Genet. 1982;1(4):327–341. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strauss E. C., Orkin S. H. In vivo protein-DNA interactions at hypersensitive site 3 of the human beta-globin locus control region. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jul 1;89(13):5809–5813. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.13.5809. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Talbot D., Collis P., Antoniou M., Vidal M., Grosveld F., Greaves D. R. A dominant control region from the human beta-globin locus conferring integration site-independent gene expression. Nature. 1989 Mar 23;338(6213):352–355. doi: 10.1038/338352a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Talbot D., Grosveld F. The 5'HS2 of the globin locus control region enhances transcription through the interaction of a multimeric complex binding at two functionally distinct NF-E2 binding sites. EMBO J. 1991 Jun;10(6):1391–1398. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07659.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Talbot D., Philipsen S., Fraser P., Grosveld F. Detailed analysis of the site 3 region of the human beta-globin dominant control region. EMBO J. 1990 Jul;9(7):2169–2177. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07386.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuan D., Solomon W., Li Q., London I. M. The "beta-like-globin" gene domain in human erythroid cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Oct;82(19):6384–6388. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.19.6384. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zinn K., DiMaio D., Maniatis T. Identification of two distinct regulatory regions adjacent to the human beta-interferon gene. Cell. 1983 Oct;34(3):865–879. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90544-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]