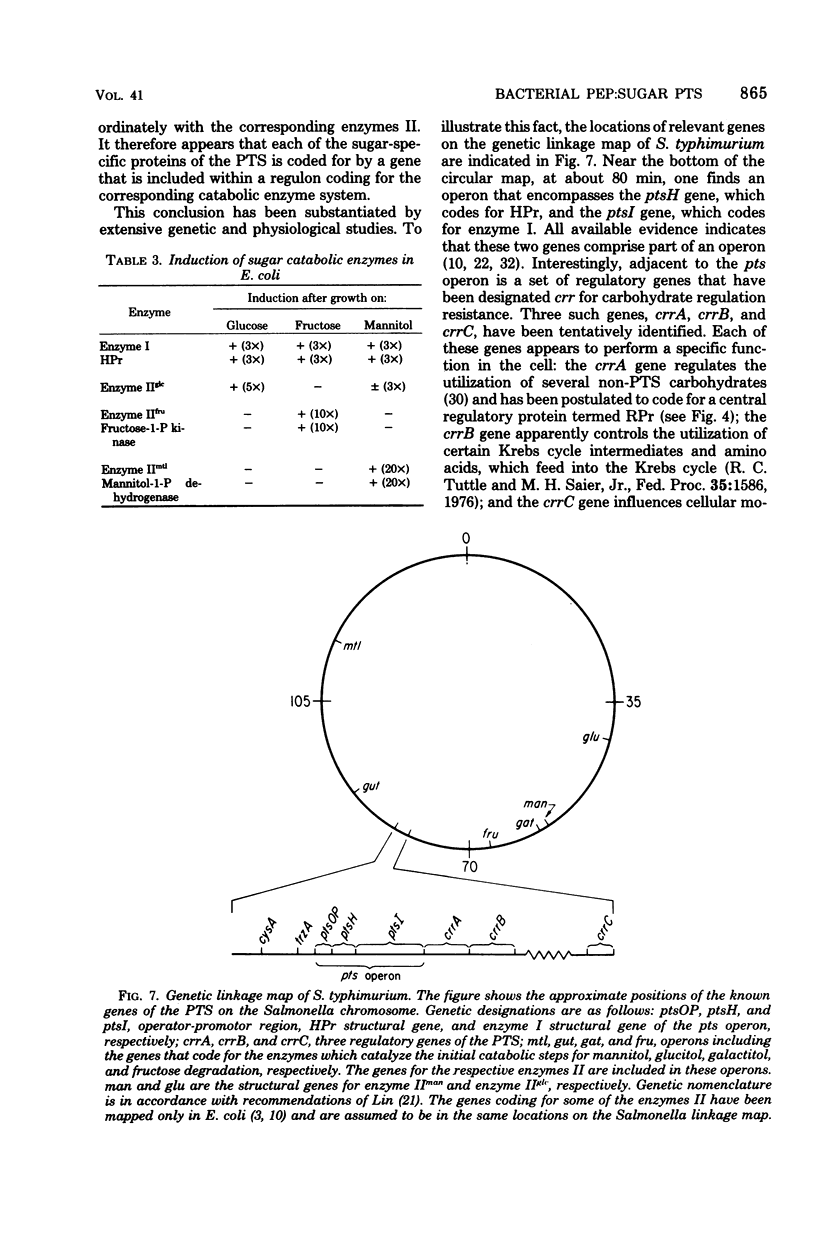
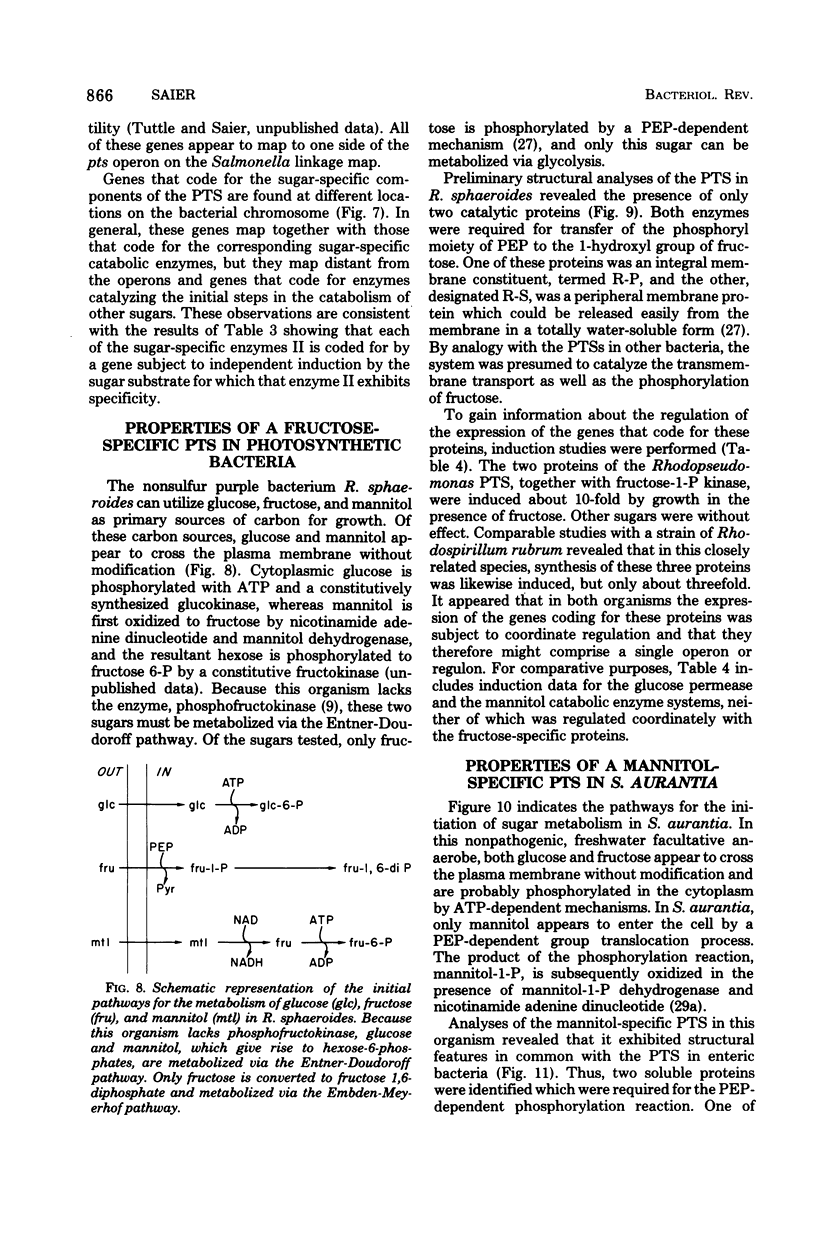
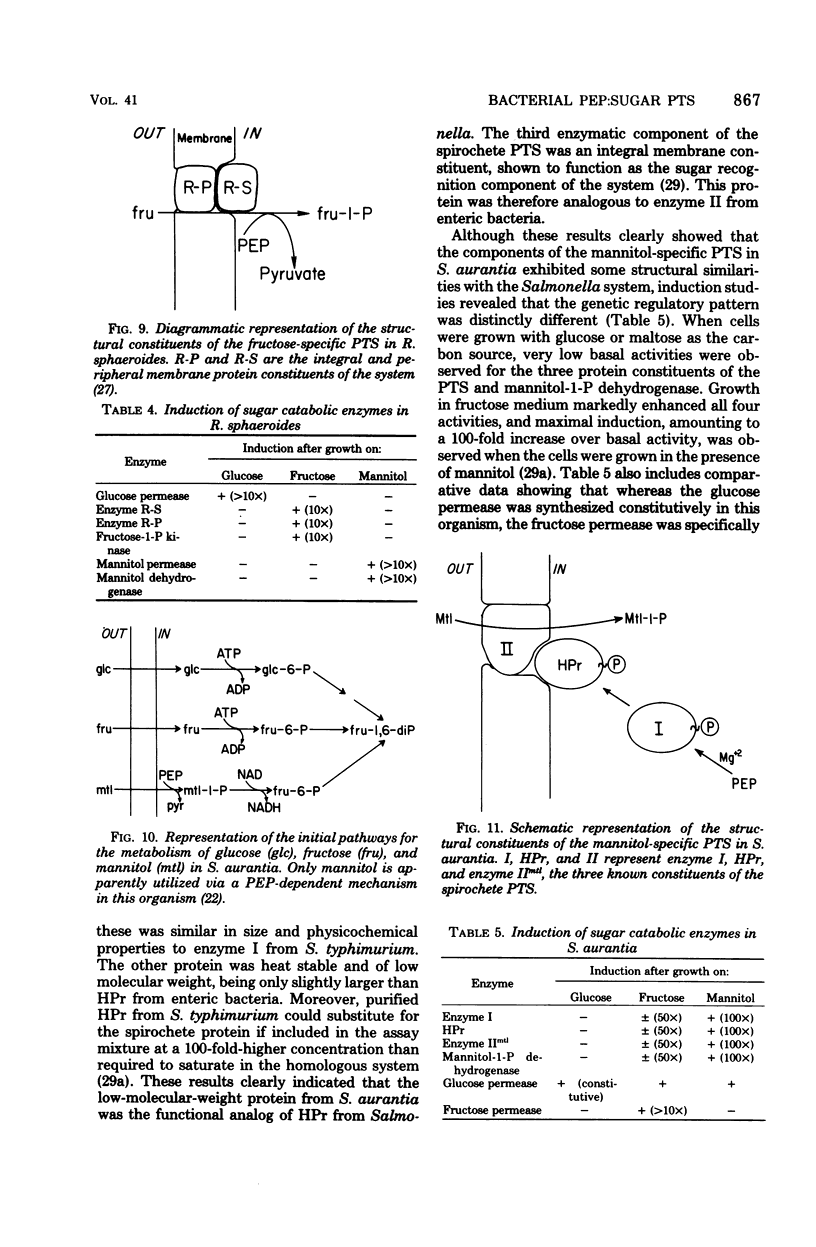
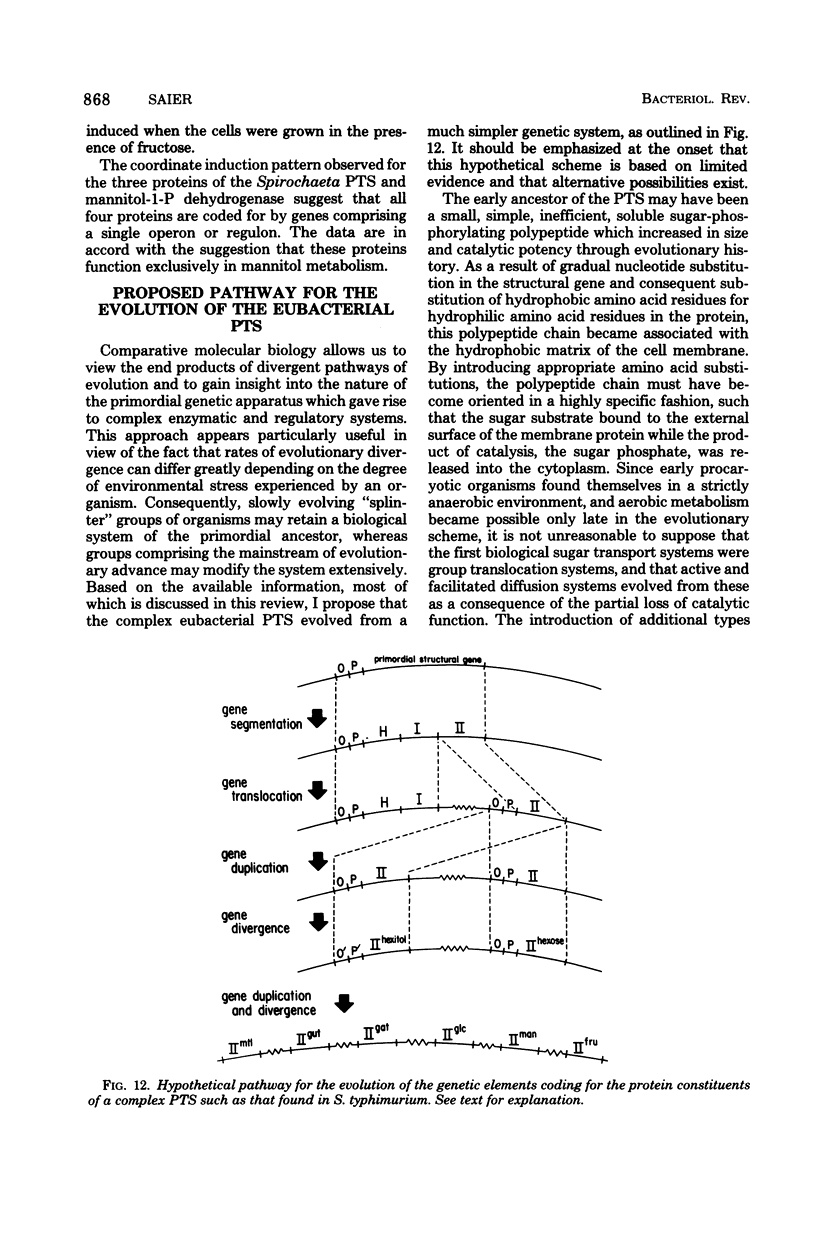
Full text
PDF

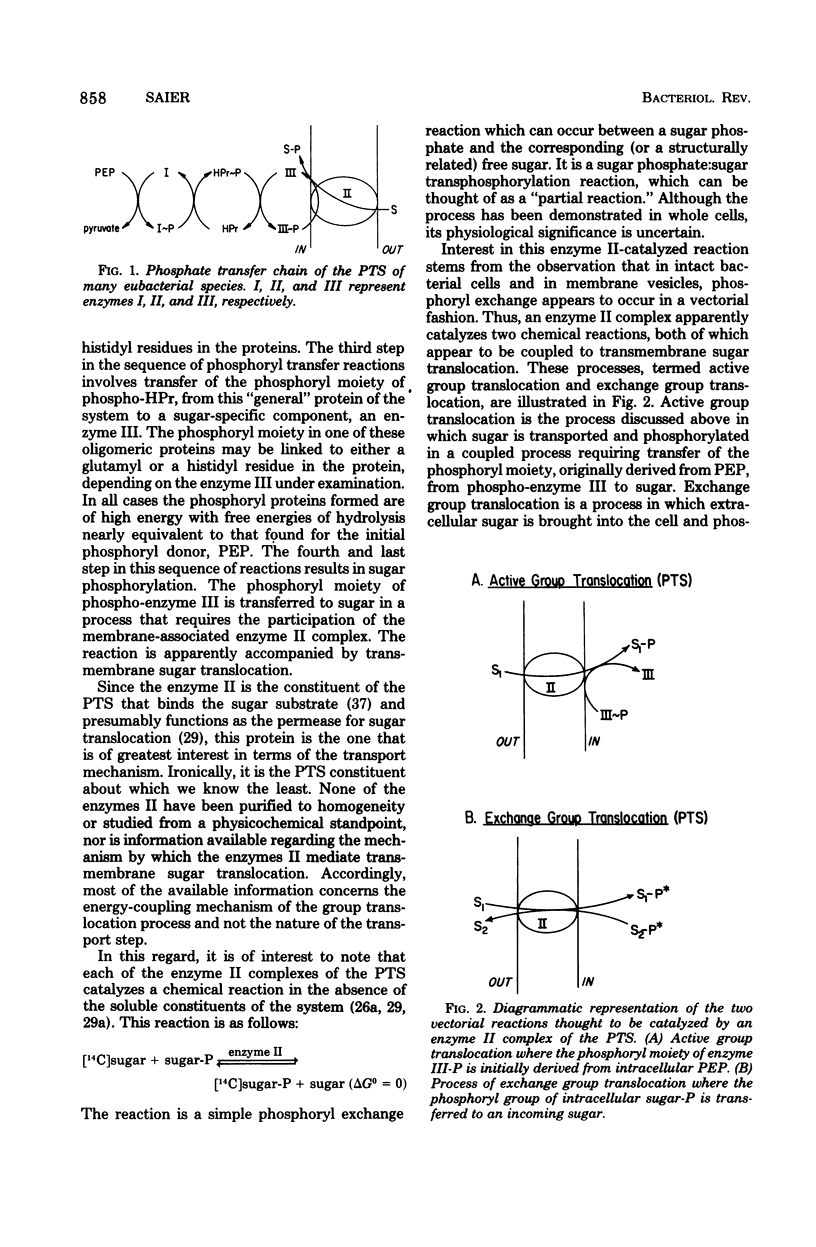


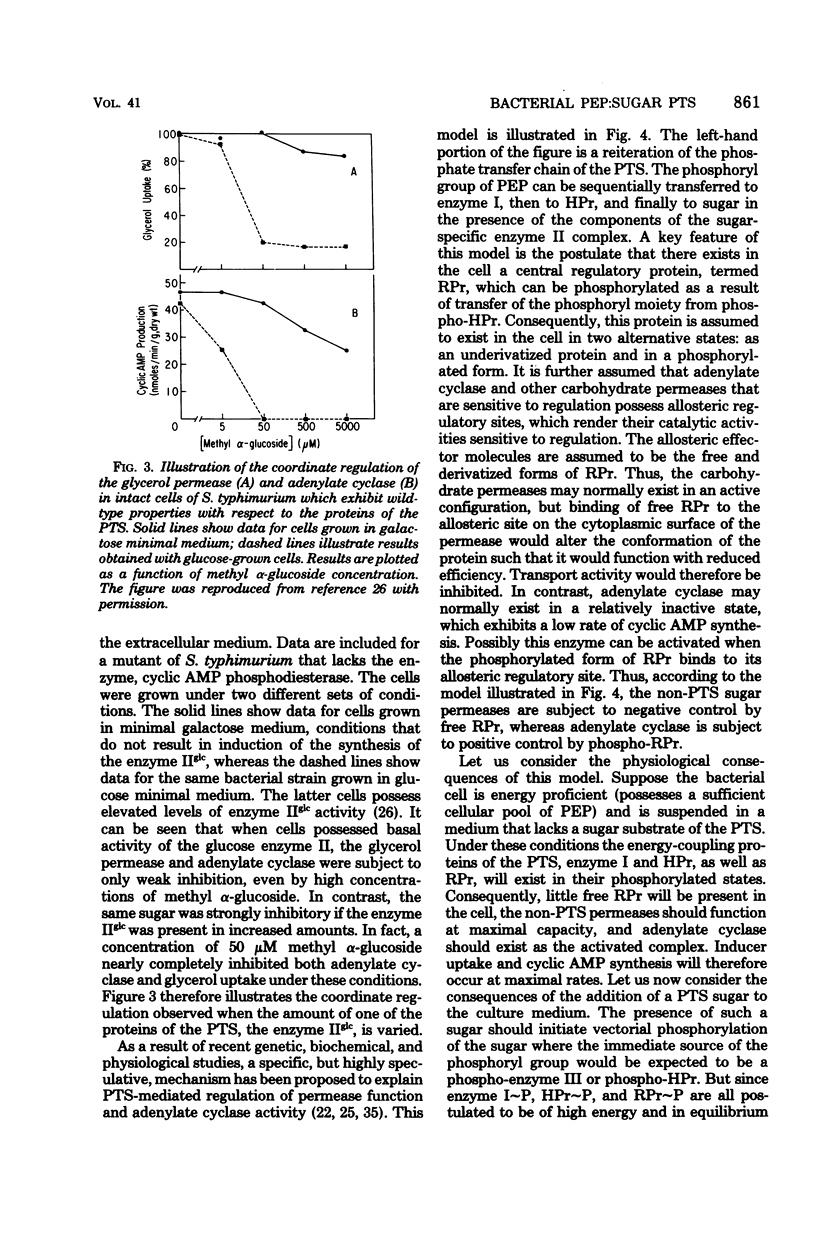
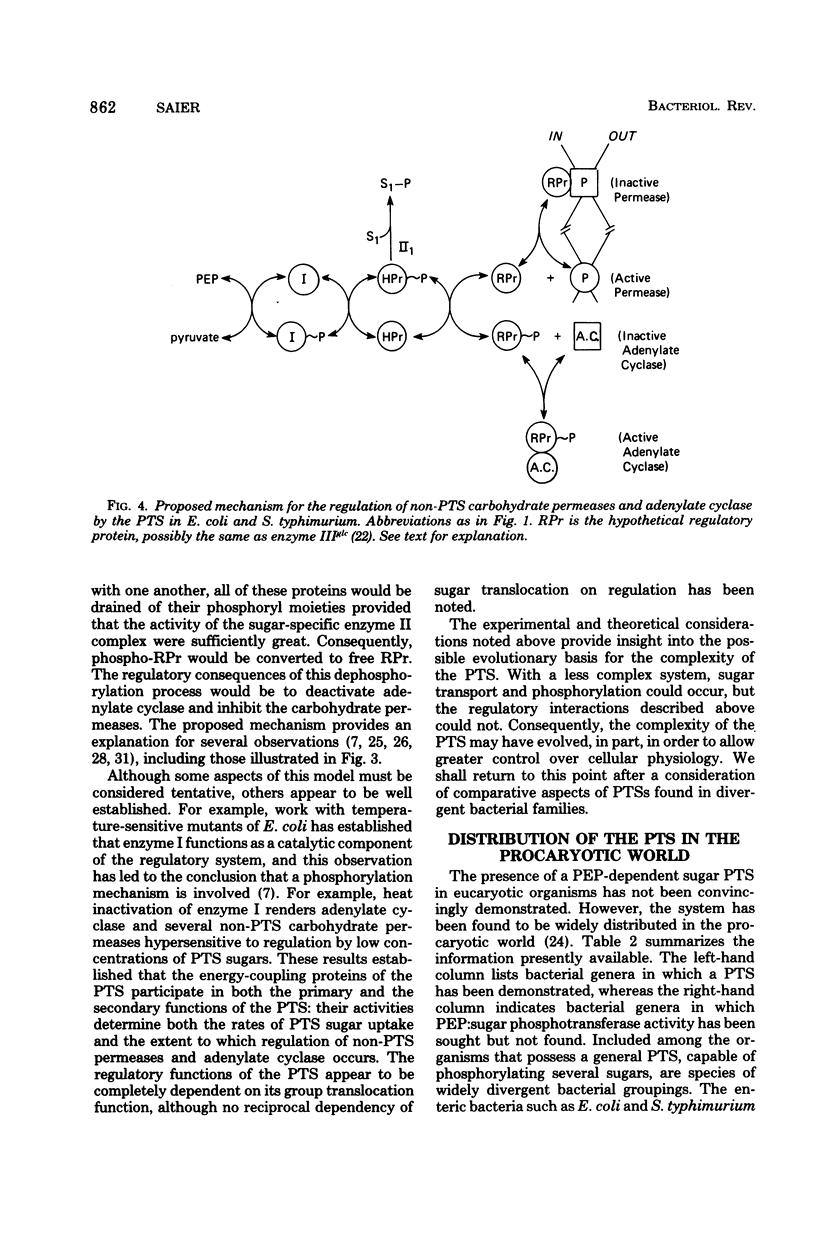

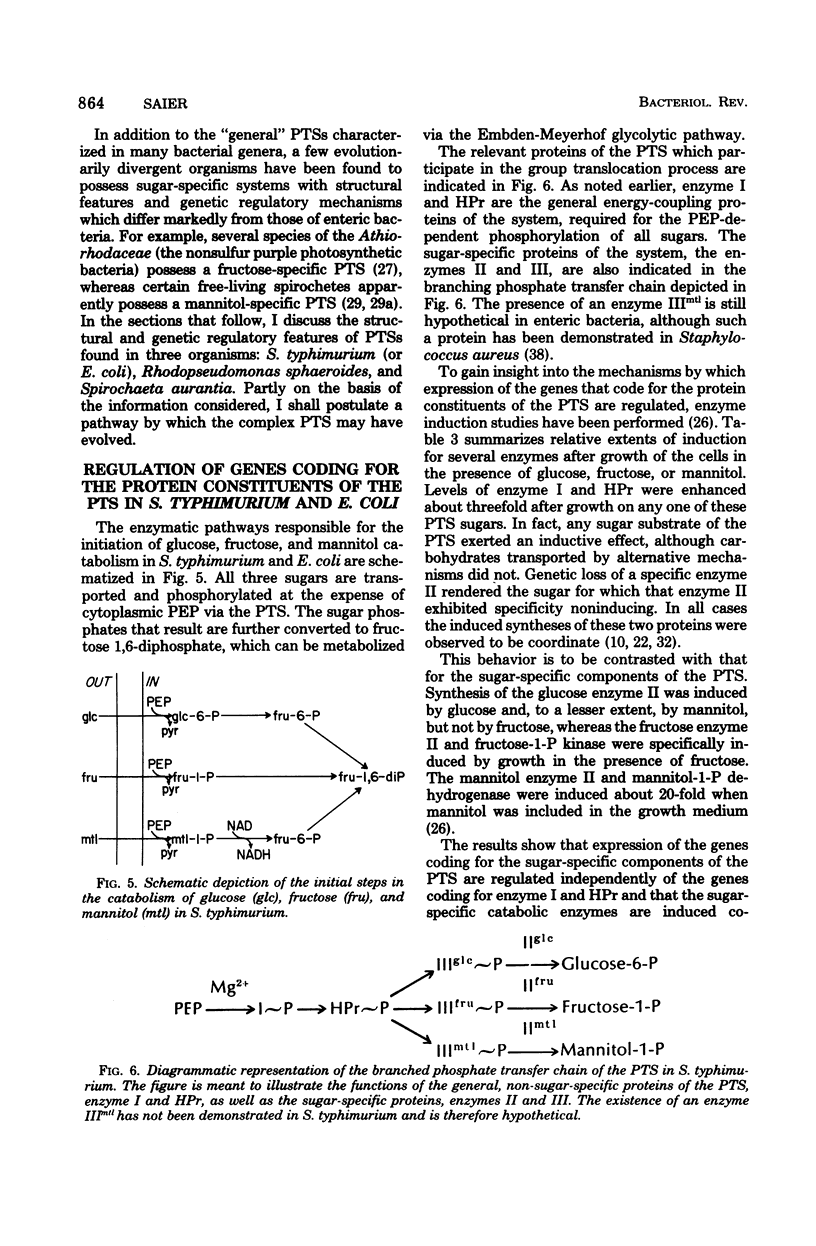



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adler J., Epstein W. Phosphotransferase-system enzymes as chemoreceptors for certain sugars in Escherichia coli chemotaxis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Jul;71(7):2895–2899. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.7.2895. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andrews K. J., Lin E. C. Selective advantages of various bacterial carbohydrate transport mechanisms. Fed Proc. 1976 Aug;35(10):2185–2189. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bachmann B. J., Low K. B., Taylor A. L. Recalibrated linkage map of Escherichia coli K-12. Bacteriol Rev. 1976 Mar;40(1):116–167. doi: 10.1128/br.40.1.116-167.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baumann P., Baumann L. Catabolism of D-fructose and D-ribose by Pseudomonas doudoroffii. I. Physiological studies and mutant analysis. Arch Microbiol. 1975 Nov 7;105(3):225–240. doi: 10.1007/BF00447141. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boos W. Bacterial transport. Annu Rev Biochem. 1974;43(0):123–146. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.43.070174.001011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calhoun D. H. Autoregulation of gene expression. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1975;29:275–299. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.29.100175.001423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castro L., Feucht B. U., Morse M. L., Saier M. H., Jr Regulation of carbohydrate permeases and adenylate cyclase in Escherichia coli. Studies with mutant strains in which enzyme I of the phosphoenolpyruvate:sugar phosphotransferase system is thermolabile. J Biol Chem. 1976 Sep 25;251(18):5522–5527. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cirillo V. P., Razin S. Distribution of a phosphoenolypyruvate-dependent sugar phosphotransferase system in mycoplasms. J Bacteriol. 1973 Jan;113(1):212–217. doi: 10.1128/jb.113.1.212-217.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conrad R., Schlegel H. G. Different pathways for fructose and glucose utilization in Rhodopseudomonas capsulata and demonstration of 1-phosphofructokinase in phototrophic bacteria. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Jul 17;358(1):221–225. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(74)90273-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cordaro C. Genetics of the bacterial phosphoenolpyruvate: glycose phosphotransferase system. Annu Rev Genet. 1976;10:341–359. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.10.120176.002013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crawford I. P. Gene rearrangements in the evolution of the tryptophan synthetic pathway. Bacteriol Rev. 1975 Jun;39(2):87–120. doi: 10.1128/br.39.2.87-120.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delobbe A., Chalumeau H., Claverie J. M., Gay P. Phosphorylation of intracellular fructose in Bacillus subtilis mediated by phosphoenolpyruvate-1-fructose phosphotransferase. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Jul 15;66(3):485–491. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10573.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gee D. L., Baumann P., Baumann L. Enzymes of D-fructose catabolism in species of Beneckea and Photobacterium. Arch Microbiol. 1975 Apr 7;103(2):205–207. doi: 10.1007/BF00436351. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hochstadt-Ozer J. The regulation of purine utilization in bacteria. IV. Roles of membrane-localized and pericytoplasmic enzymes in the mechanism of purine nucleoside transport across isolated Escherichia coli membranes. J Biol Chem. 1972 Apr 25;247(8):2419–2426. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koch A. L. Local and non-local interactions of fluxes mediated by the glucose and galactoside permeases of Escherichia coli. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Oct 12;249(1):197–215. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(71)90097-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kundig W., Roseman S. Sugar transport. I. Isolation of a phosphotransferase system from Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1971 Mar 10;246(5):1393–1406. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kundig W., Roseman S. Sugar transport. II. Characterization of constitutive membrane-bound enzymes II of the Escherichia coli phosphotransferase system. J Biol Chem. 1971 Mar 10;246(5):1407–1418. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levinson S. L., Krulwich T. A. Metabolism of L-rhamnose in Arthrobacter pyridinolis. J Gen Microbiol. 1976 Aug;96(2):277–286. doi: 10.1099/00221287-95-2-277. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin E. C. The genetics of bacterial transport systems. Annu Rev Genet. 1970;4:225–262. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.04.120170.001301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Postma P. W., Roseman S. The bacterial phosphoenolpyruvate: sugar phosphotransferase system. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Dec 14;457(3-4):213–257. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(76)90001-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rader R. L., Hochstadt J. Regulation of purine utilization in bacteria. VII. Involvement of membrane-associated nucleoside phosphorylase in the uptake and the base-mediated loss of the ribose moiety of nucleosides by Salmonella typhimurium membrane vesicles. J Bacteriol. 1976 Oct;128(1):290–301. doi: 10.1128/jb.128.1.290-301.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romano A. H., Eberhard S. J., Dingle S. L., McDowell T. D. Distribution of the phosphoenolpyruvate: glucose phosphotransferase system in bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1970 Nov;104(2):808–813. doi: 10.1128/jb.104.2.808-813.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saier M. H., Jr, Feucht B. U. Coordinate regulation of adenylate cyclase and carbohydrate permeases by the phosphoenolpyruvate:sugar phosphotransferase system in Salmonella typhimurium. J Biol Chem. 1975 Sep 10;250(17):7078–7080. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saier M. H., Jr, Feucht B. U., Hofstadter L. J. Regulation of carbohydrate uptake and adenylate cyclase activity mediated by the enzymes II of the phosphoenolpyruvate: sugar phosphotransferase system in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1976 Feb 10;251(3):883–892. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saier M. H., Jr, Feucht B. U., Mora W. K. Sugar phosphate: sugar transphosphorylation and exchange group translocation catalyzed by the enzyme 11 complexes of the bacterial phosphoenolpyruvate: sugar phosphotransferase system. J Biol Chem. 1977 Dec 25;252(24):8899–8907. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saier M. H., Jr, Feucht B. U., Roseman S. Phosphoenolpyruvate-dependent fructose phosphorylation in photosynthetic bacteria. J Biol Chem. 1971 Dec 25;246(24):7819–7821. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saier M. H., Jr, Newman M. J. Direct transfer of the phosphoryl moiety of mannitol 1-phosphate to [14C]mannitol catalyzed by the enzyme II complexes of the phosphoenolpyruvate: mannitol phosphotransferase systems in Spirochaeta aurantia and Salmonella typhimurium. J Biol Chem. 1976 Jun 25;251(12):3834–3837. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saier M. H., Jr, Newman M. J., Rephaeli A. W. Properties of a phosphoenolpyruvate: mannitol phosphotransferase system in Spirochaeta aurantia. J Biol Chem. 1977 Dec 25;252(24):8890–8898. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saier M. H., Jr, Roseman S. Sugar transport. 2nducer exclusion and regulation of the melibiose, maltose, glycerol, and lactose transport systems by the phosphoenolpyruvate:sugar phosphotransferase system. J Biol Chem. 1976 Nov 10;251(21):6606–6615. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saier M. H., Jr, Roseman S. Sugar transport. The crr mutation: its effect on repression of enzyme synthesis. J Biol Chem. 1976 Nov 10;251(21):6598–6605. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saier M. H., Jr, Simoni R. D., Roseman S. The physiological behavior of enzyme I and heat-stable protein mutants of a bacterial phosphotransferase system. J Biol Chem. 1970 Nov 10;245(21):5870–5873. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saier M. H., Jr, Staley J. T. Phosphoenolpyruvate:sugar phosphotransferase system in Ancalomicrobium adetum. J Bacteriol. 1977 Aug;131(2):716–718. doi: 10.1128/jb.131.2.716-718.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simoni R. D., Hays J. B., Nakazawa T., Roseman S. Sugar transport. VI. Phosphoryl transfer in the lactose phosphotransferase system of Staphylococcus aureus. J Biol Chem. 1973 Feb 10;248(3):957–965. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simoni R. D., Roseman S., Saier M. H., Jr Sugar transport. Properties of mutant bacteria defective in proteins of the phosphoenolpyruvate: sugar phosphotransferase system. J Biol Chem. 1976 Nov 10;251(21):6584–6597. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simoni R. D., Smith M. F., Roseman S. Resolution of a staphylococcal phosphotransferase system into four protein components and its relation to sugar transport. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1968 Jun 10;31(5):804–811. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(68)90634-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer S. J. The molecular organization of membranes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1974;43(0):805–833. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.43.070174.004105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stock J., Roseman S. A sodium-dependent sugar co-transport system in bacteria. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1971 Jul 2;44(1):132–138. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(71)80168-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walter R. W., Jr, Anderson R. L. Evidence that the inducible phosphoenolpyruvate:D-fructose 1-phosphotransferase system of Aerobacter aerogenes does not require "HPr". Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1973 May 1;52(1):93–97. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(73)90958-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winkler H. H., Wilson T. H. Inhibition of beta-galactoside transport by substrates of the glucose transport system in Escherichia coli. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1967;135(5):1030–1051. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(67)90073-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



