Abstract
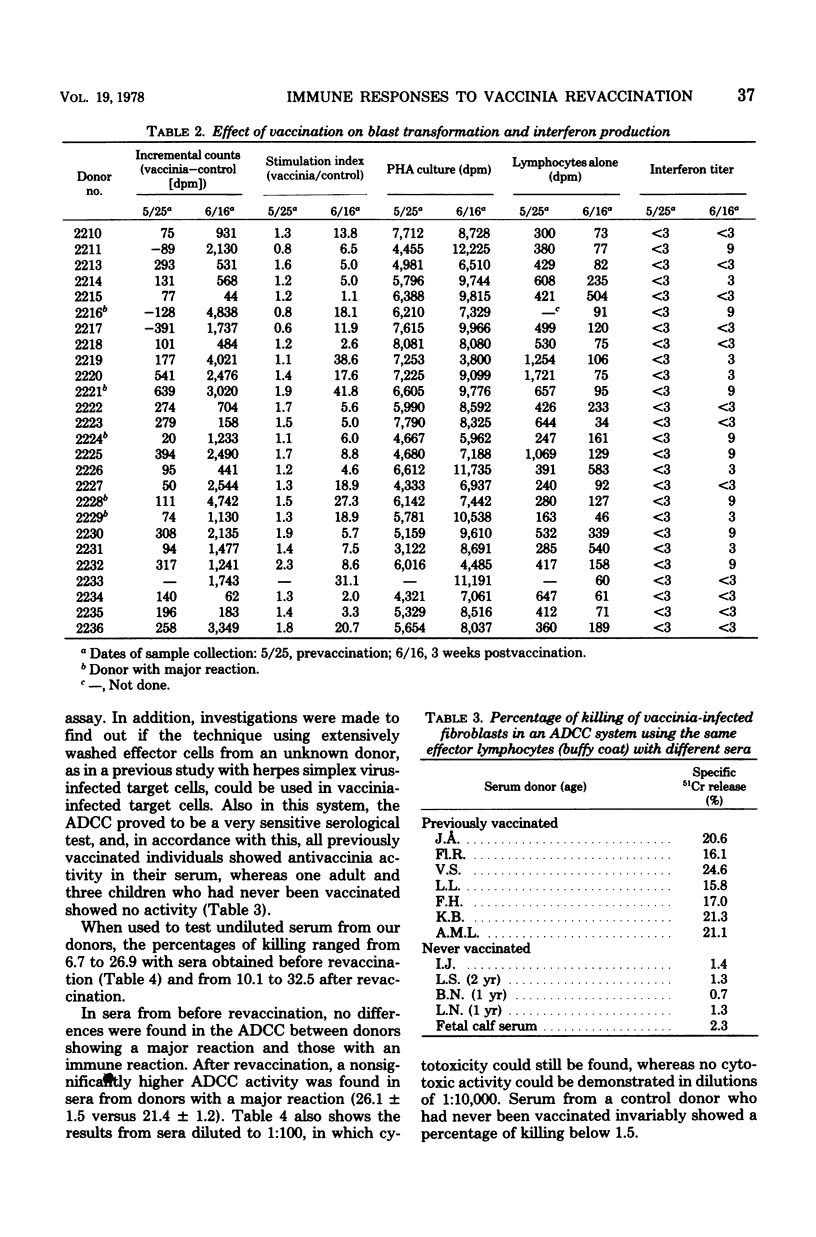
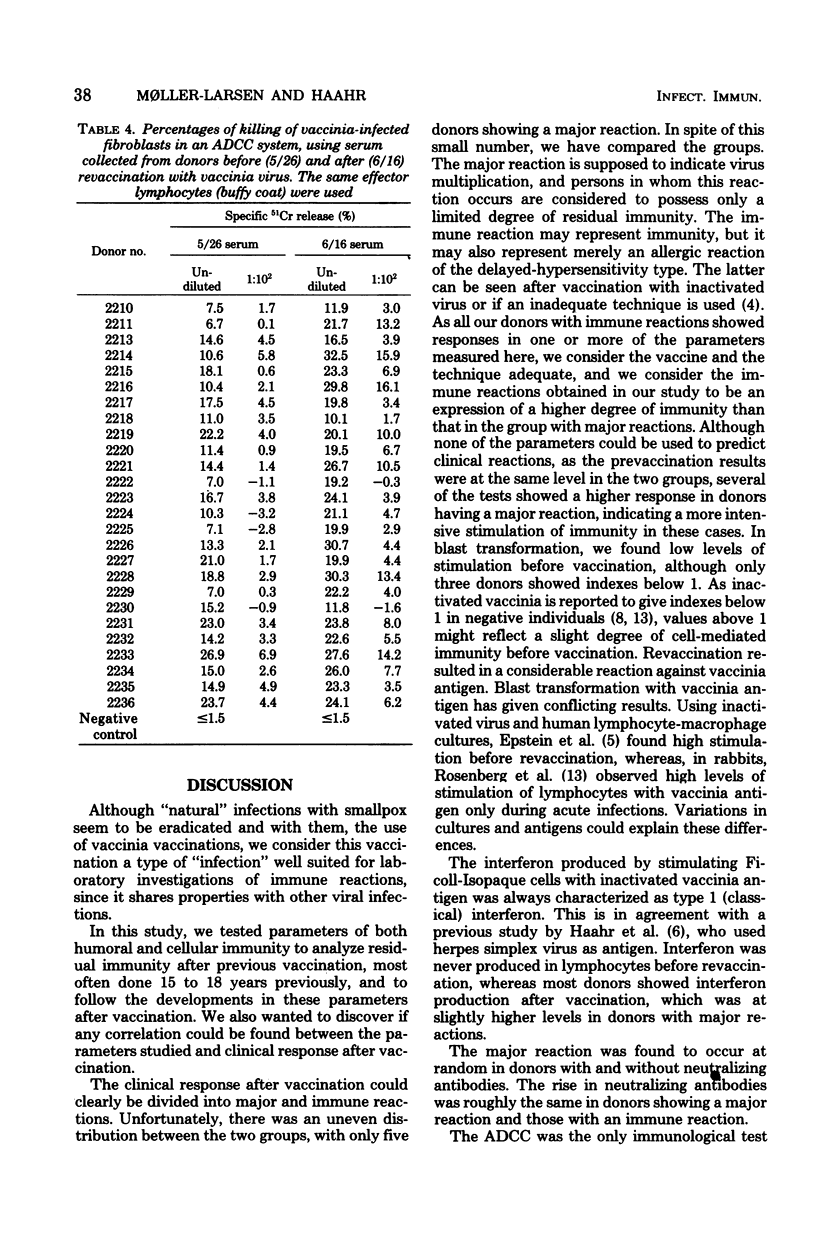
Twenty-six healthy males vaccinated 15 to 18 years ago with vaccinia virus were revaccinated. Blood samples were collected before vaccination and 3 weeks after. The lymphocytes were tested in a blast transformation assay with vaccinia antigen and phytohemagglutinin, and interferon production was measured. The sera were subjected to neutralization and antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC) tests. All results were compared with clinical responses. The only test showing immunity in all donors before vaccination was the ADCC. The other tests showed a very limited residual immunity or no immunity at all. After revaccination, immunity reactions were found in all tests in most of the donors. None of the tests made before vaccination could be used to predict clinical reactions. The ADCC is recommended as a sensitive serological test.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andersson T., Stejskal V., Harfast B. An in vitro method for study of human lymphocyte cytotoxicity against mumps-virus-infected target cells. J Immunol. 1975 Jan;114(1 Pt 1):237–243. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böyum A. Isolation of leucocytes from human blood. Further observations. Methylcellulose, dextran, and ficoll as erythrocyteaggregating agents. Scand J Clin Lab Invest Suppl. 1968;97:31–50. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiba Y., Dzierba J. L., Morag A., Ogra P. L. Cell-mediated immune response to mumps virus infection in man. J Immunol. 1976 Jan;116(1):12–15. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epstein L. B., Stevens D. A., Merigan T. C. Selective increase in lymphocyte interferon response to vaccinia antigen after revaccination. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Sep;69(9):2632–2636. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.9.2632. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haahr S., Rasmussen L., Merigan T. C. Lymphocyte transformation and interferon production in human mononuclear cell microcultures for assay of cellular immunity to herpes simplex virus. Infect Immun. 1976 Jul;14(1):47–54. doi: 10.1128/iai.14.1.47-54.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heron I., Moller-Larsen A., Berg K. Effector cell involved in cell-mediated cytotoxicity to cells infected with herpes simplex virus type 1. Infect Immun. 1977 Apr;16(1):48–53. doi: 10.1128/iai.16.1.48-53.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLaren C., Cheng H., Spicer D. L., Tompkins W. A. Lymphocyte and macrophage responses after vaccinia virus infections. Infect Immun. 1976 Oct;14(4):1014–1021. doi: 10.1128/iai.14.4.1014-1021.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merigan T. C. Host defenses against viral disease. N Engl J Med. 1974 Feb 7;290(6):323–329. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197402072900608. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moller-Larsen A., Heron I., Haahr S. Cell-mediated cytotoxicity to herpes-infected cells in humans: dependence on antibodies. Infect Immun. 1977 Apr;16(1):43–47. doi: 10.1128/iai.16.1.43-47.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rager-Zisman B., Allison A. C. Mechanism of immunologic resistance to herpes simplex virus 1 (HSV-1) infection. J Immunol. 1976 Jan;116(1):35–40. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg G. L., Farber P. A., Notkins A. L. In vitro stimulation of sensitized lymphocytes by herpes simplex virus and vaccinia virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Mar;69(3):756–760. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.3.756. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valle M. J., Jordan G. W., Haahr S., Merigan T. C. Characteristics of immune interferon produced by human lymphocyte cultures compared to other human interferons. J Immunol. 1975 Jul;115(1):230–233. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



