Abstract
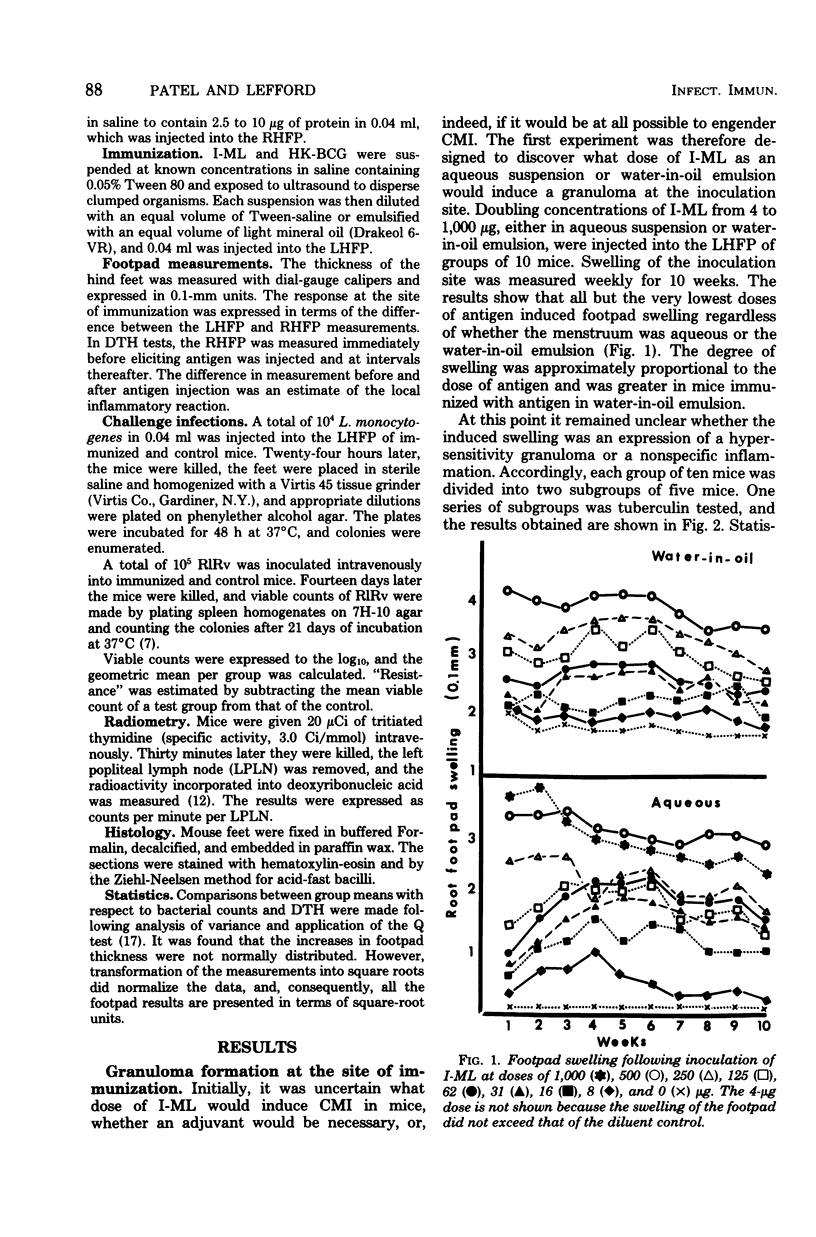
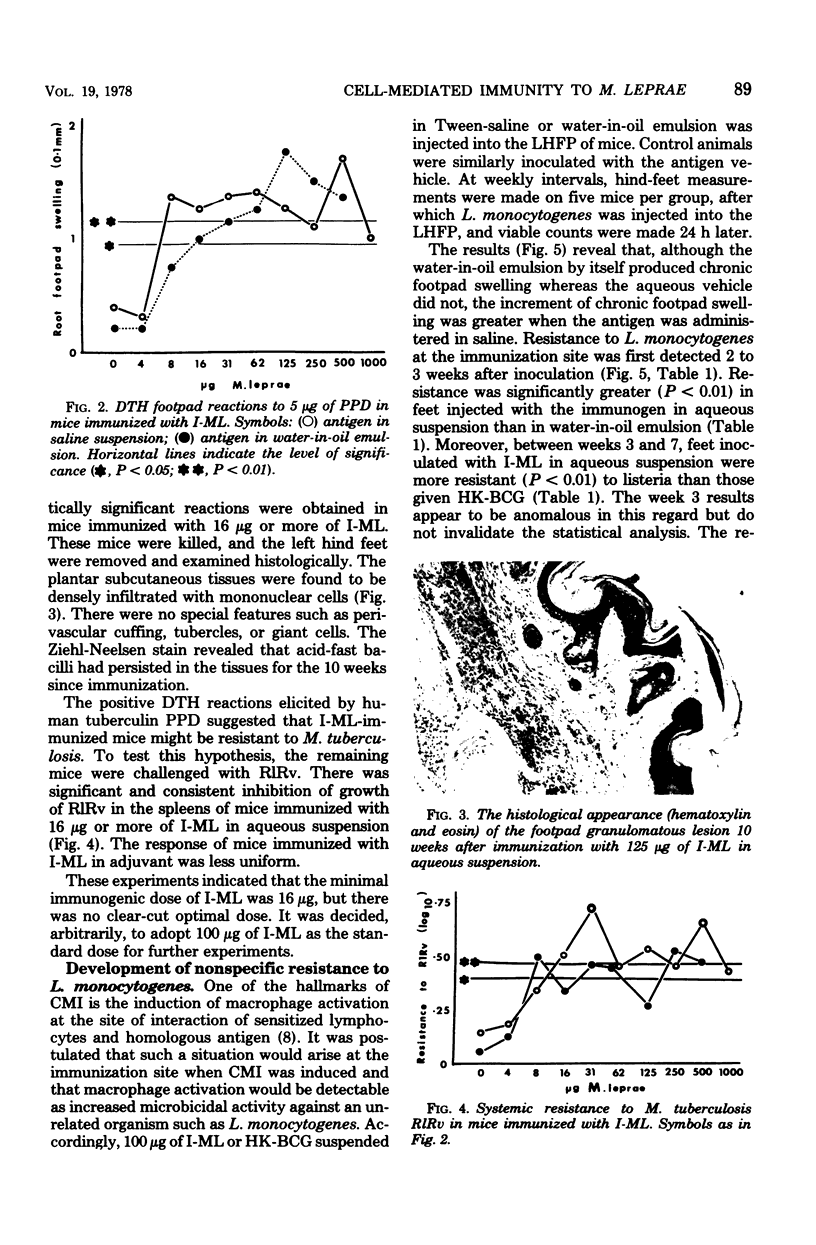
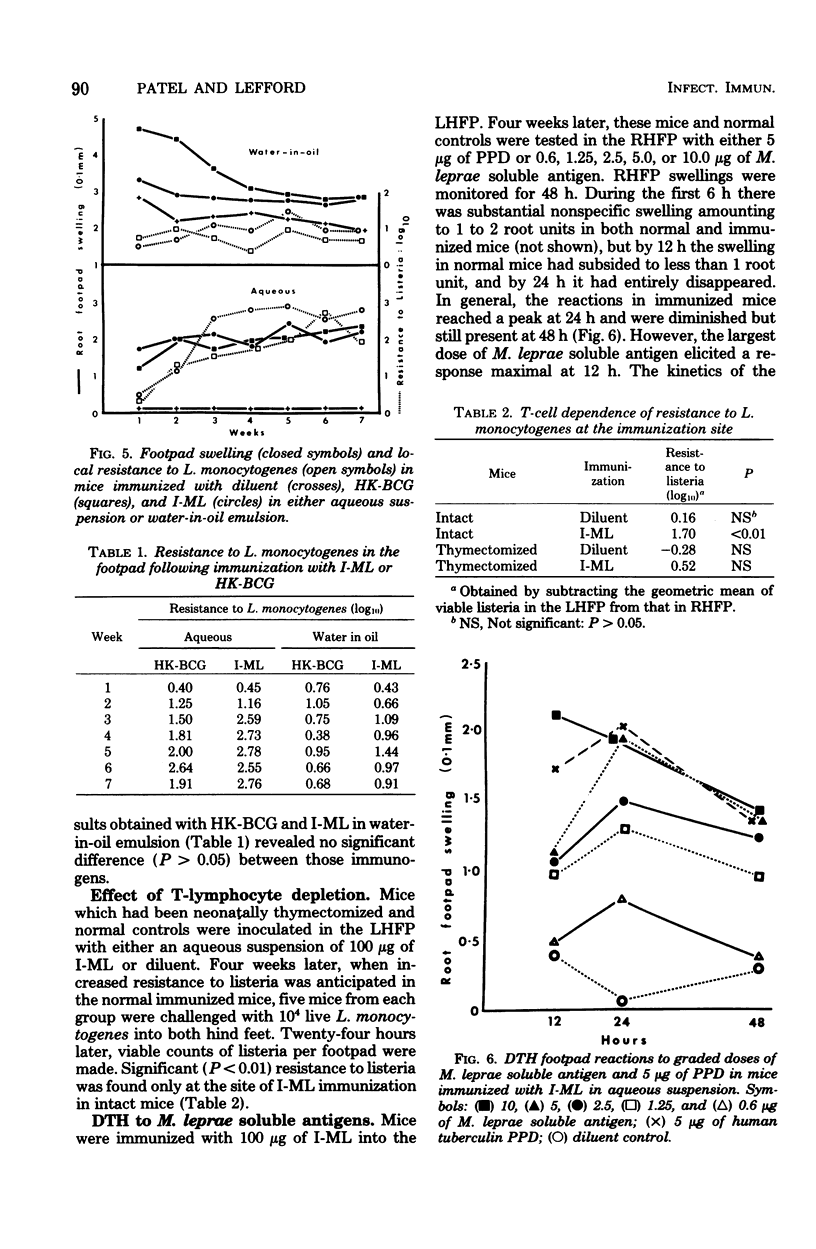
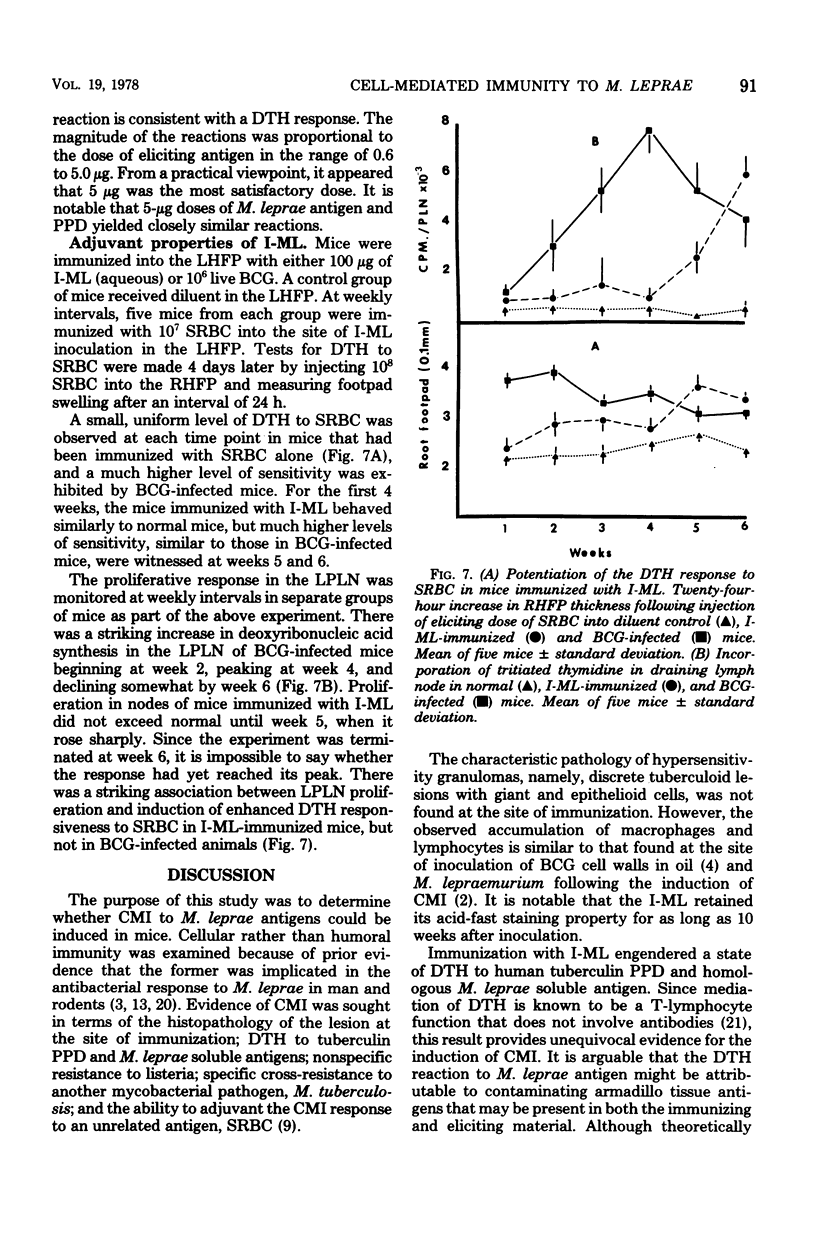
The immune response of mice to armadillo-derived, irradiation-killed Mycobacterium leprae (I-ML) was investigated. Following injection of 100 microgram of I-ML into the left hind footpads of mice, a state of cell-mediated immunity (CMI) was engendered to antigens of M. leprae. The evidence for CMI was as follows: (i) development of delayed-type hypersensitivity to both human tuberculin purified protein derivative and soluble M. leprae antigens; (ii) T-lymphocyte-dependent macrophage activation at the inoculation site; (iii) specific systemic resistance to the cross-reactive species M. tuberculosis; and (iv) immunopotentiation of the delayed-type hypersensitivity response to an unrelated antigen. The CMI induced by I-ML in aqueous suspension was greater than that obtained with the same antigen in water-in-oil emulsion, even though the latter generated a more severe reaction at the site of immunization. I-ML also induced a stronger CMI response than the corresponding dose of heat-killed BCG.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blanden R. V., Lefford M. J., Mackaness G. B. The host response to Calmette-Guérin bacillus infection in mice. J Exp Med. 1969 May 1;129(5):1079–1107. doi: 10.1084/jem.129.5.1079. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Closs O., Haugen O. A. Experimental murine leprosy. 3. Early local reaction to mycobacterium lepraemurium in C3H and C57/BL mice. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand A. 1975 Jan;83(1):51–58. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fieldsteel A. H., Levy L. Neonatally thymectomized Lewis rats infected with Mycobacterium leprae: response to primary infection, secondary challenge, and large inocula. Infect Immun. 1976 Sep;14(3):736–741. doi: 10.1128/iai.14.3.736-741.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granger D. L., Brehmer W., Brehmer W., Yamamoto K., Ribi E. Cutaneous granulomatous response to BCG cell walls with reference to cancer immunotherapy. Infect Immun. 1976 Feb;13(2):543–553. doi: 10.1128/iai.13.2.543-553.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kronvall G., Stanford J. L., Walsh G. P. Studies of mycobacterial antigens, with special reference to Mycobacterium leprae. Infect Immun. 1976 Apr;13(4):1132–1138. doi: 10.1128/iai.13.4.1132-1138.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lefford M. J. Transfer of adoptive immunity to tuberculosis in mice. Infect Immun. 1975 Jun;11(6):1174–1181. doi: 10.1128/iai.11.6.1174-1181.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackaness G. B., Lagrange P. H., Ishibashi T. The modifying effect of BCG on the immunological induction of T cells. J Exp Med. 1974 Jun 1;139(6):1540–1552. doi: 10.1084/jem.139.6.1540. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackaness G. B. The influence of immunologically committed lymphoid cells on macrophage activity in vivo. J Exp Med. 1969 May 1;129(5):973–992. doi: 10.1084/jem.129.5.973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller T. E., Mackaness G. B., Lagrange P. H. Immunopotentiation with BCG. II. Modulation of the response to sheep red blood cells. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1973 Nov;51(5):1669–1676. doi: 10.1093/jnci/51.5.1669. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- North R. J., Kirstein D. P. T-cell-mediated concomitant immunity to syngeneic tumors. I. Activated macrophages as the expressors of nonspecific immunity to unrelated tumors and bacterial parasites. J Exp Med. 1977 Feb 1;145(2):275–292. doi: 10.1084/jem.145.2.275. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rees R. J. Enhanced susceptibility of thymectomized and irradiated mice to infection with Mycobacterium leprae. Nature. 1966 Aug 6;211(5049):657–658. doi: 10.1038/211657a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHEPARD C. C. VACCINATION AGAINST EXPERIMENTAL INFECTION WITH MYCOBACTERIUM LEPRAE. Am J Epidemiol. 1965 Mar;81:150–163. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a120504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shepard C. C. Vaccination of mice against M. leprae infection. Int J Lepr Other Mycobact Dis. 1976 Jan-Jun;44(1-2):222–226. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spitalny G. L., North R. J. Subversion of host defense mechanisms by malignant tumors: an established tumor as a privileged site for bacterial growth. J Exp Med. 1977 May 1;145(5):1264–1277. doi: 10.1084/jem.145.5.1264. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanford J. L. Immunodiffusion analysis--a rational basis for the taxonomy of mycobacteria. Ann Soc Belg Med Trop. 1973;53(4):321–330. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turk J. L., Bryceson A. D. Immunological phenomena in leprosy and related diseases. Adv Immunol. 1971;13:209–266. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60185-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Youdim S., Stuntman O., Good R. A. Thymus dependency of cells involved in transfer of delayed hypersensitivity to Listeria monocytogenes in mice. Cell Immunol. 1973 Sep;8(3):395–402. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(73)90129-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



