Abstract
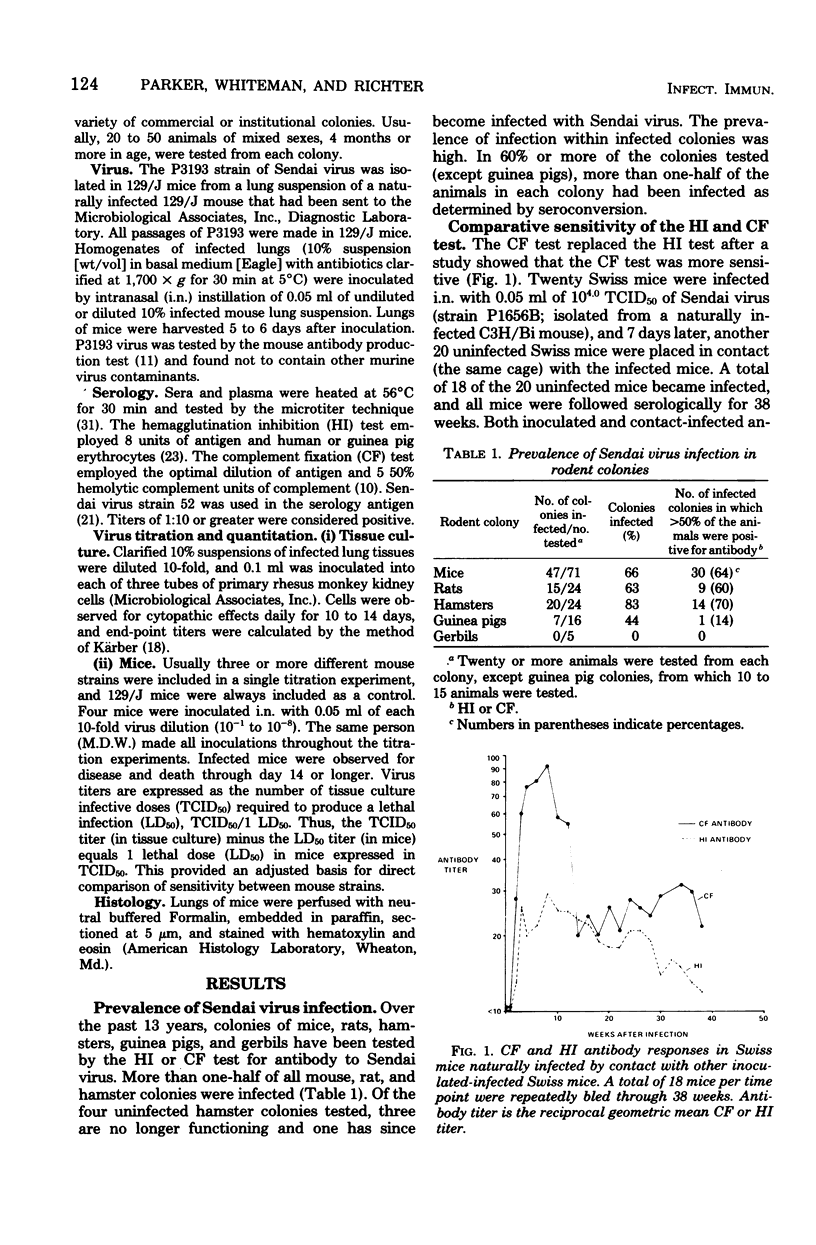
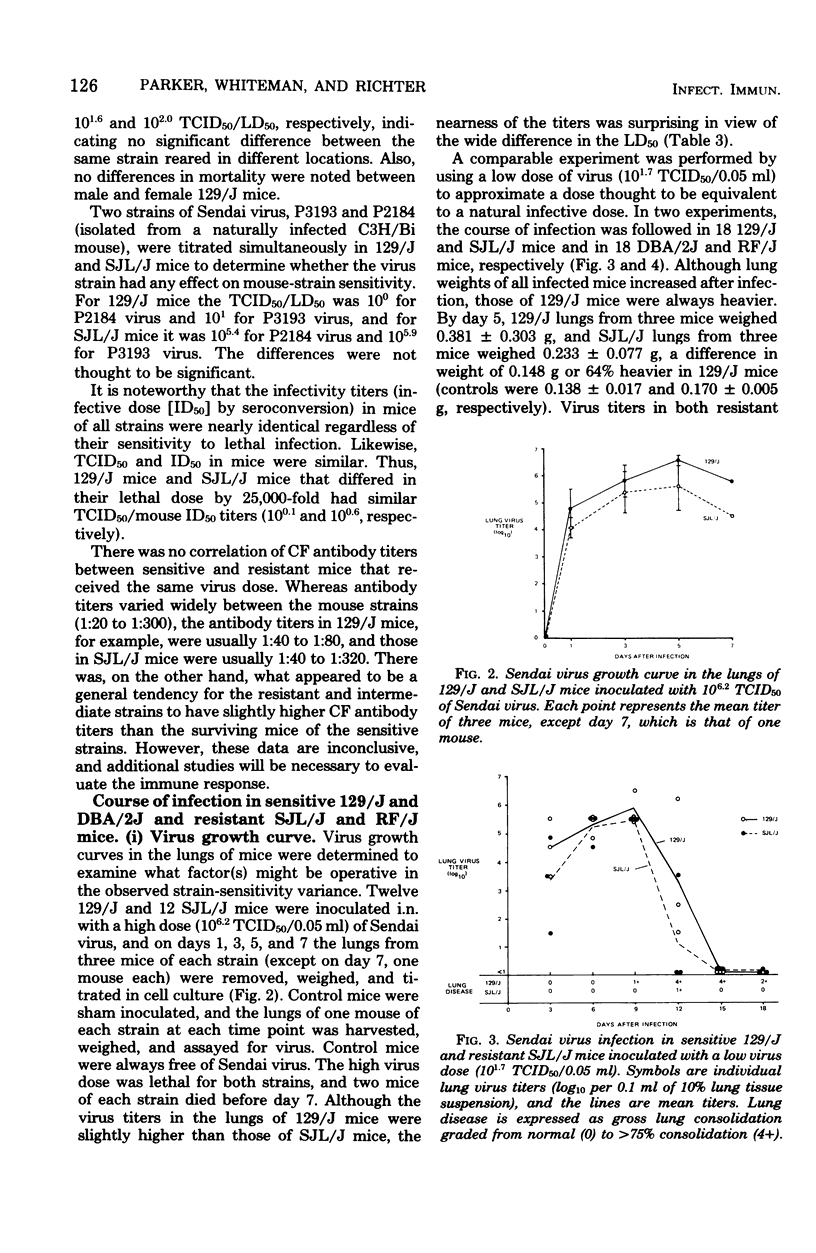
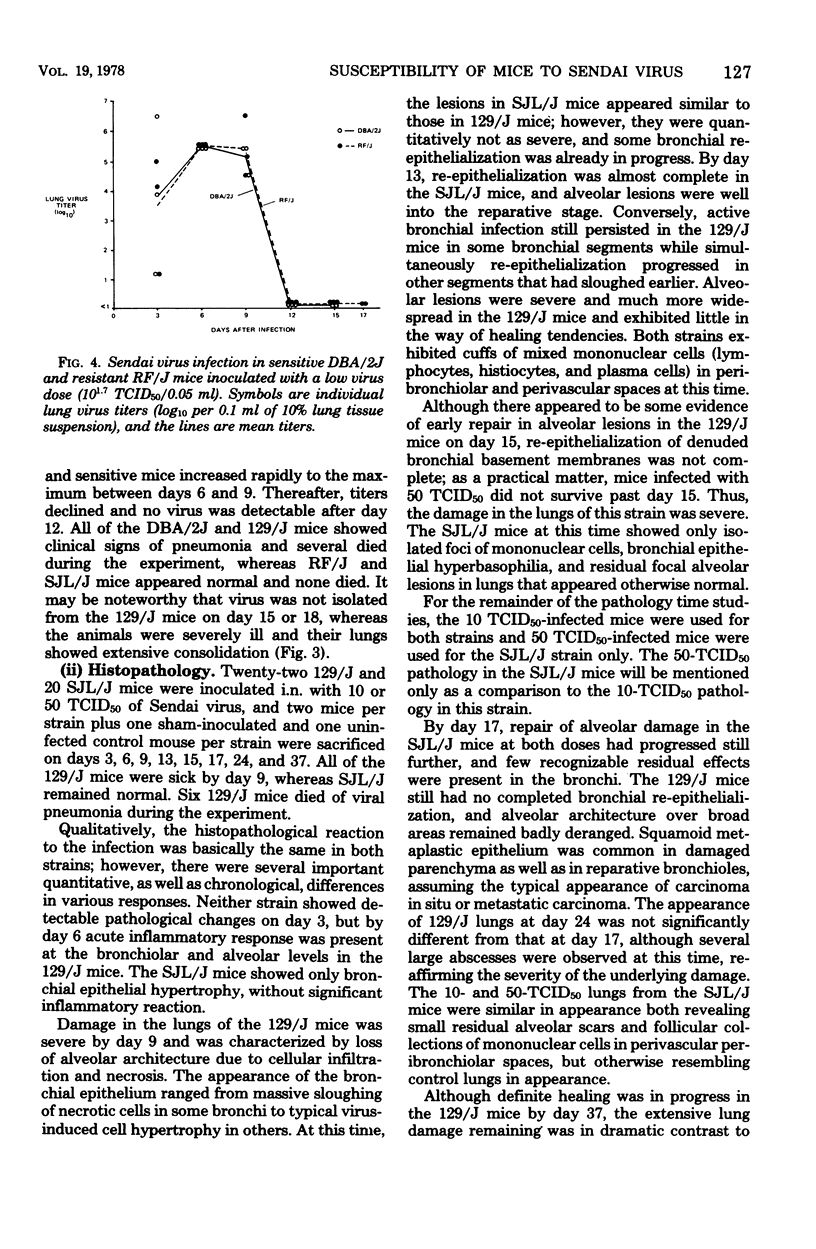
Sendai virus is one of the more prevalent and serious virus infections of rodents. Infection was found in 66% of the mouse, 63% of the rat, 83% of the hamster, and 44% of the guinea pig colonies examined. Twenty-four inbred and outbred strains of mice were tested for their sensitivity to lethal Sendai virus infection. The 129/J mice tested were approximately 25,000-fold more sensitive than SJL/J mice; however, both mouse strains were similarly permissive in support of viral replication in their lung tissues. Histopathological studies revealed that whereas lesions in both sensitive and resistant mice were qualitatively similar, the lesions in the more sensitive 129/J mice appeared earlier, were much more extensive, and persisted longer than in the resistant SJL/J mice. These results suggest that the observed variance in sensitivity is not the result of a genetic restriction on virus infection and replication but rather is the result of a physiological factor(s) possibly related to some aberration of strain difference in the humoral or cell-mediated immune response.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson M. J., Bainbridge D. R., Pattison J. R., Heath R. B. Cell-mediated immunity to Sendai virus infection in mice. Infect Immun. 1977 Jan;15(1):239–244. doi: 10.1128/iai.15.1.239-244.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Appell L. H., Kovatch R. M., Reddecliff J. M., Gerone P. J. Pathogenesis of Sendai virus infection in mice. Am J Vet Res. 1971 Nov;32(11):1835–1841. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Argyris B. Maturation of immunological responsiveness to transplantation antigens. Transplantation. 1965 Sep;3(5):618–626. doi: 10.1097/00007890-196509000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhatt P. N., Jonas A. M. An epizootic of Sendai infection with mortality in a barrier-maintained mouse colony. Am J Epidemiol. 1974 Sep;100(3):222–229. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a112031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blandford G., Cureton R. J., Heath R. B. Studies of the immune respnse in Sendai virus infection of mice. J Med Microbiol. 1971 Aug;4(3):351–356. doi: 10.1099/00222615-4-3-351. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blandford G., Heath R. B. Studies on the immune response and pathogenesis of Sendai virus infection of mice. I. The fate of viral antigens. Immunology. 1972 Apr;22(4):637–649. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blandford G., Heath R. B. Studies on the immune response and pathogenesis of Sendai virus infection of mice. II. The immunoglobulin class of plasma cells in the bronchial sub-mucosa. Immunology. 1974 Mar;26(3):667–671. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blandford G. Studies on the immune response and pathogenesis of Sendai virus infection of mice. III. The effects of cyclophosphamide. Immunology. 1975 May;28(5):871–883. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins M. J., Jr, Parker J. C. Murine virus contaminants of leukemia viruses and transplantable tumors. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1972 Oct;49(4):1139–1143. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FUKUMI H., NISHIKAWA F., KITAYAMA T. A pneumotropic virus from mice causing hemagglutination. Jpn J Med Sci Biol. 1954 Aug;7(4):345–363. doi: 10.7883/yoken1952.7.345. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fenner F. Genetic aspects of viral diseases of animals. Prog Med Genet. 1972;8:1–60. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GALLILY R., WARWICK A., BANG F. B. EFFECT OF CORTISONE OF GENETIC RESISTANCE TO MOUSE HEPATITIS VIRUS IN VIVO AND IN VITRO. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1964 Jun;51:1158–1164. doi: 10.1073/pnas.51.6.1158. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grunert R. R. Isolation of sendai virus as a latent respiratory virus in mice. Lab Anim Care. 1967 Apr;17(2):164–171. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JAHKOLA M. NATURE AND INHERITANCE OF THE RESISTANCE OF INBRED MICE TO TUMOR INDUCTION BY POLYOMA VIRUS. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand Suppl. 1965;173:SUPPL 173–17469. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LAW L. W., TING R. C. IMMUNOLOGIC COMPETENCE AND INDUCTION OF NEOPLASMS BY POLYOMA VIRUS. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1965 Jul;119:823–830. doi: 10.3181/00379727-119-30311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Makino S., Seko S., Nakao H., Mikazuki K. [An epizootic of Sendai virus infection in a rat colony (author's transl)]. Jikken Dobutsu. 1973 Oct;22(4):275–280. doi: 10.1538/expanim1957.22.4_275. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mims C. A., Murphy F. A. Parainfluenza virus Sendai infection in macrophages, ependyma, choroid plexus, vascular endothelium and respiratory tract of mice. Am J Pathol. 1973 Mar;70(3):315–328. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PARKER J. C., TENNANT R. W., WARD T. G., ROWE W. P. ENZOOTIC SENDAI VIRUS INFECTIONS IN MOUSE BREEDER COLONIES WITHIN THE UNITED STATES. Science. 1964 Nov 13;146(3646):936–938. doi: 10.1126/science.146.3646.936. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PARKER J. C., TENNANT R. W., WARD T. G., ROWE W. P. VIRUS STUDIES WITH GERMFREE MICE. I. PREPARATION OF SEROLOGIC DIAGNOSTIC REAGENTS AND SURVEY OF GERMFREE AND MONOCONTAMINATED MICE FOR INDIGENOUS MURINE VIRUSES. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1965 Mar;34:371–380. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker J. C., Reynolds R. K. Natural history of Sendai virus infection in mice. Am J Epidemiol. 1968 Jul;88(1):112–125. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a120859. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker J. C., Tennant R. W., Ward T. G. Prevalence of viruses in mouse colonies. Natl Cancer Inst Monogr. 1966 Feb;20:25–45. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Profeta M. L., Lief F. S., Plotkin S. A. Enzootic sendai infection in laboratory hamsters. Am J Epidemiol. 1969 Mar;89(3):316–324. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a120944. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson T. W., Cureton R. J., Heath R. B. The effect of cyclophosphamide on Sendai virus infection of mice. J Med Microbiol. 1969 May;2(2):137–145. doi: 10.1099/00222615-2-2-137. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson T. W., Cureton R. J., Heath R. B. The pathogenesis of Sendai virus infection in the mouse lung. J Med Microbiol. 1968 Aug;1(1):89–95. doi: 10.1099/00222615-1-1-89. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHELL K. Studies on the innate resistance of mice to infection with mousepox. I. Resistance and antibody production. Aust J Exp Biol Med Sci. 1960 Aug;38:271–288. doi: 10.1038/icb.1960.29. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHELL K. Studies on the innate resistance of mice to infection with mousepox. II. Route of inoculation and resistance; and some observations on the inheritance of resistance. Aust J Exp Biol Med Sci. 1960 Aug;38:289–299. doi: 10.1038/icb.1960.30. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SEVER J. L. Application of a microtechnique to viral serological investigations. J Immunol. 1962 Mar;88:320–329. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward J. M., Houchens D. P., Collins M. J., Young D. M., Reagan R. L. Naturally-occurring Sendai virus infection of athymic nude mice. Vet Pathol. 1976;13(1):36–46. doi: 10.1177/030098587601300105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward J. M. Naturally occurring Sendai virus disease of mice. Lab Anim Sci. 1974 Dec;24(6):938–942. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willenborg D. O., Shah K. V., Bang F. B. Effect of cyclophosphamide on the genetic resistance of C 3 H mice to mouse hepatitis virus. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1973 Mar;142(3):762–766. doi: 10.3181/00379727-142-37111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


