Abstract
The development of humoral and cell-mediated immune responses to Eikenella corrodens (a bacterium that causes periodontal lesions in gnotobiotic rats) was measured and compared with the rate of appearance of macroscopic lesions. A possible inverse relationship was found. A strong cell-mediated immune response, as measured by skin reactivity and lymphocyte mitogenesis, occurred between 4 and 6 weeks after infection and subsided soon thereafter to a low response level. Humoral antibodies to endotoxin from E. corrodens could not be detected at any time. The disease developed only after the cell-mediated immune response diminished, thus suggesting that lack of an efficient immune response may permit the development of the disease. This is seemingly in contradiction to the assumption that tissue destruction in such cases is caused by the immune response and its products. We are inclined to believe, based on our findings reported here, that the lack of immune responsiveness to the bacterium and/or its products is the major causative factor in the development of periodontitis. At the same time, we wish to emphasize that occurrence of both phenomena during the long development of periodontal disease is possible.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- GUPTA O. P., SHAW J. H. [Periodontal disease in the rice rat. II. Methods for the evaluation of the extent of periodontal disease]. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol. 1956 Jul;9(7):727–735. doi: 10.1016/0030-4220(56)90249-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garant P. R. Light and electron microscopic observations of osteoclastic alveolar bone resorption in rats monoinfected with Actinomyces naeslundii. J Periodontol. 1976 Dec;47(12):717–723. doi: 10.1902/jop.1976.47.12.717. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbons R. J., Berman K. S., Knoettner P., Kapsimalis B. Dental caries and alveolar bone loss in gnotobiotic rats infected with capsule forming streptococci of human origin. Arch Oral Biol. 1966 Jun;11(6):549–560. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(66)90220-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hausmann E., Raisz L. G., Miller W. A. Endotoxin: stimulation of bone resorption in tissue culture. Science. 1970 May 15;168(3933):862–864. doi: 10.1126/science.168.3933.862. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horton J. E., Oppenheim J. J., Mergenhagen S. E. Elaboration of lymphotoxin by cultured human peripheral blood leucocytes stimulated with dental-plaque deposits. Clin Exp Immunol. 1973 Mar;13(3):383–393. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horton J. E., Raisz L. G., Simmons H. A., Oppenheim J. J., Mergenhagen S. E. Bone resorbing activity in supernatant fluid from cultured human peripheral blood leukocytes. Science. 1972 Sep 1;177(4051):793–795. doi: 10.1126/science.177.4051.793. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inbar M., Shinitzky M. Cholesterol as a bioregulator in the development and inhibition of leukemia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Oct;71(10):4229–4231. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.10.4229. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inbar M., Shinitzky M. Increase of cholesterol level in the surface membrane of lymphoma cells and its inhibitory effect on ascites tumor development. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 May;71(5):2128–2130. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.5.2128. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
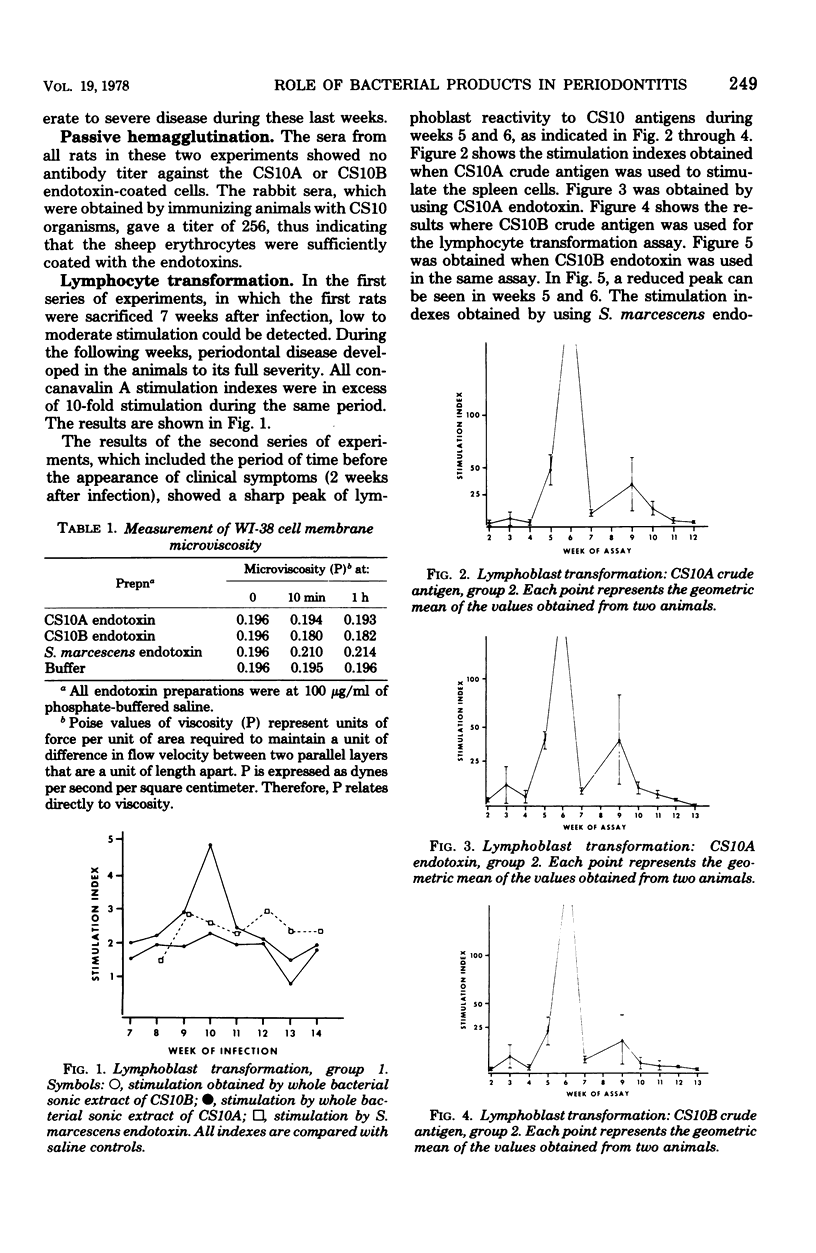
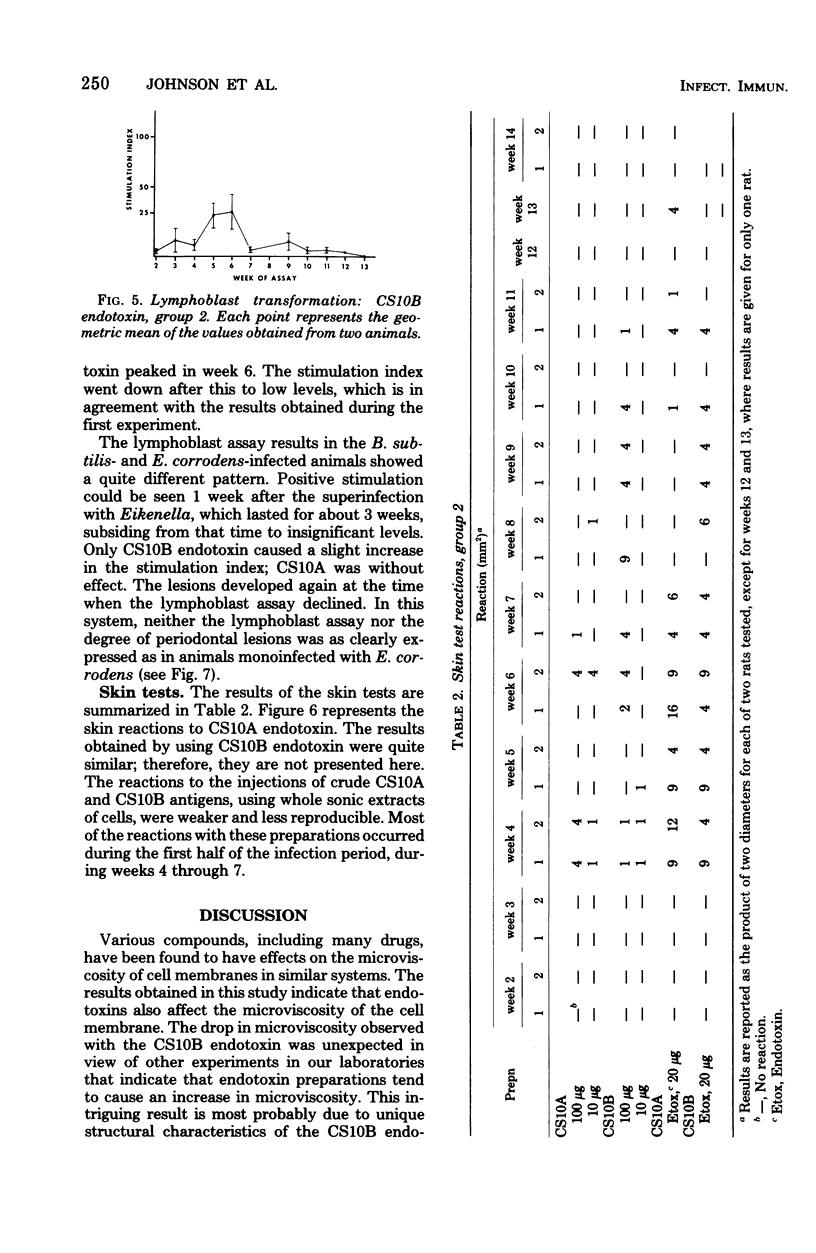
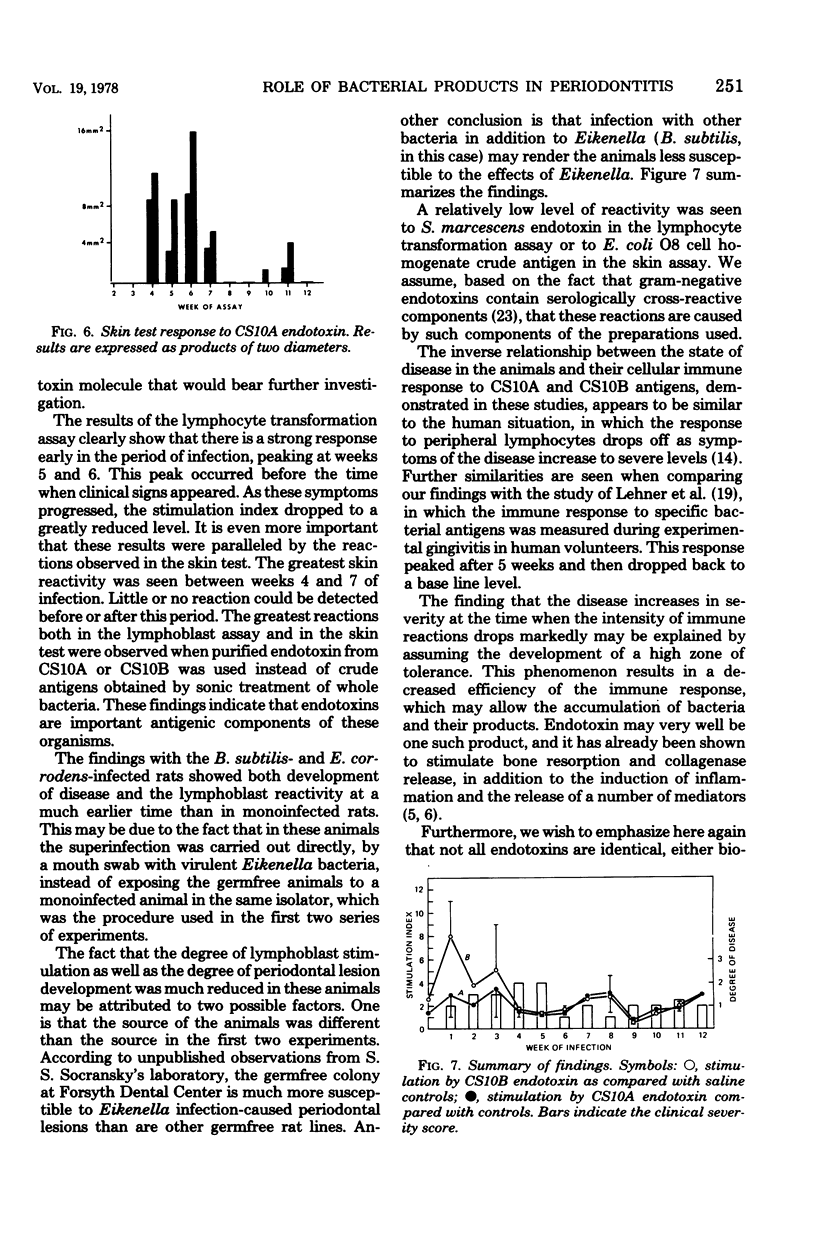
- Irving J. T., Newman M. G., Socransky S. S., Heely J. D. Histological changes in experimental periodontal disease in rats mono-infected with a gram-negative organism. Arch Oral Biol. 1975 Mar;20(3):219–220. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(75)90013-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irving J. T., Socransky S. S., Heeley J. D. Histological changes in experimental periodontal disease in gnotobiotic rats and conventional hamsters. J Periodontal Res. 1974;9(2):73–80. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0765.1974.tb00656.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ivanyi L., Lehner T. Lymphocyte transformation by sonicates of dental plaque in human periodontal disease. Arch Oral Biol. 1971 Sep;16(9):1117–1121. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(71)90216-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ivanyi L., Lehner T. Stimulation of lymphocyte transformation by bacterial antigens in patients with periodontal disease. Arch Oral Biol. 1970 Nov;15(11):1089–1096. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(70)90121-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ivanyi L., Lehner T. The significance of serum factors in stimulation of lymphocytes from patients with periodontal disease by Veillonella alcalescens. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1971;41(4):620–627. doi: 10.1159/000230554. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ivanyi L., Wilton J. M., Lehner T. Cell-mediated immunity in periodontal disease; cytotoxicity, migration inhibition and lymphocyte transformation studies. Immunology. 1972 Jan;22(1):141–145. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson D. A., Chen C. L., Dombrowski J. C., Nowotny A. Role of bacterial products in periodontitis. I. Endotoxin content and immunogenicity of human plaque. J Periodontal Res. 1976 Nov;11(6):349–359. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0765.1976.tb00089.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jordan H. V., Keyes P. H., Bellack S. Periodontal lesions in hamsters and gnotobiotic rats infected with actinomyces of human origin. J Periodontal Res. 1972;7(1):21–28. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0765.1972.tb00627.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jordan H. V. Rodent model systems in periodontal disease research. J Dent Res. 1971 Mar-Apr;50(2):236–242. doi: 10.1177/00220345710500021301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehner T., Wilton J. M., Challacombe S. J., Ivanyi L. Sequential cell-mediated immune responses in experimental gingivitis in man. Clin Exp Immunol. 1974 Mar;16(3):481–492. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levin J., Poore T. E., Zauber N. P., Oser R. S. Detection of endotoxin in the blood of patients with sepsis due to gran-negative bacteria. N Engl J Med. 1970 Dec 10;283(24):1313–1316. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197012102832404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NETER E., BERTRAM L. F., ZAK D. A., MURDOCK M. R., ARBESMAN C. E. Studies on hemagglutination and hemolysis by escherichia coli antisera. J Exp Med. 1952 Jul;96(1):1–15. doi: 10.1084/jem.96.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ng A. K., Chen C. L., Chang C. M., Nowotny A. Relationship of structure to function in bacterial endotoxins: serologically cross-reactive components and their effect on protection of mice against some gram-negative infections. J Gen Microbiol. 1976 May;94(1):107–116. doi: 10.1099/00221287-94-1-107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHULTZ-HAUDT S. D., SCHERP H. W. Lysis of collagen by human gingival bacteria. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1955 Aug;89(4):697–770. doi: 10.3181/00379727-89-21920. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz J., Stinson F. L., Parker R. B. The passage of tritiated bacterial endotoxin across intact gingival crevicular epithelium. J Periodontol. 1972 May;43(5):270–276. doi: 10.1902/jop.1972.43.5.270. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seligman S. J. In vitro susceptibility of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus to sulfamethoxazole and trimethoprim. J Infect Dis. 1973 Nov;128(Suppl):543–p. doi: 10.1093/infdis/128.supplement_3.s543. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Socransky S. S., Hubersak C., Propas D. Induction of periodontal destruction in gnotobiotic rats by a human oral strain of Actinomyces naeslundii. Arch Oral Biol. 1970 Oct;15(10):993–995. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(70)90095-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Socransky S. S. Relationship of bacteria to the etiology of periodontal disease. J Dent Res. 1970 Mar-Apr;49(2):203–222. doi: 10.1177/00220345700490020401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tripodi D., Nowotny A. Relation of structure to function in bacterial O-antigens. V. Nature of active sites in endotoxic lipopolysaccharides of Serratia marcescens. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1966 Jun 30;133(2):604–621. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1966.tb52392.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



