Abstract
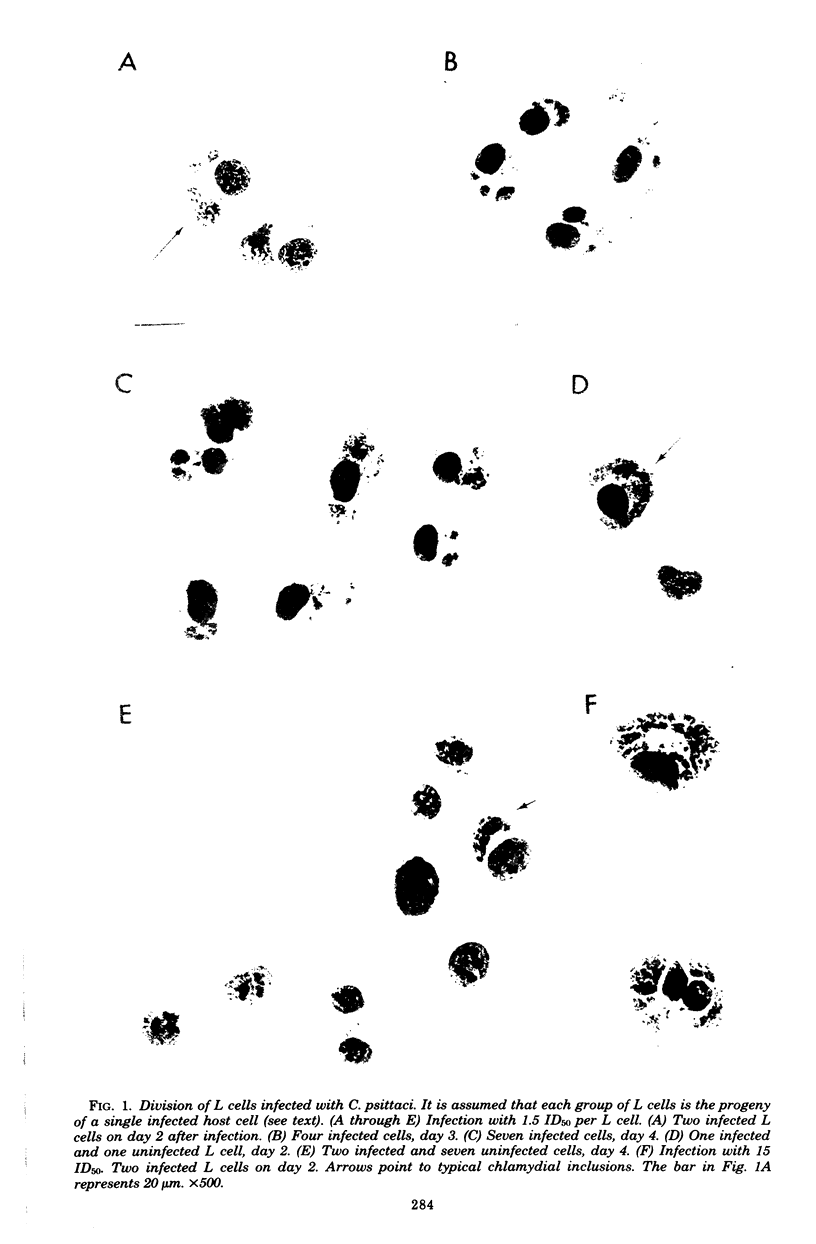
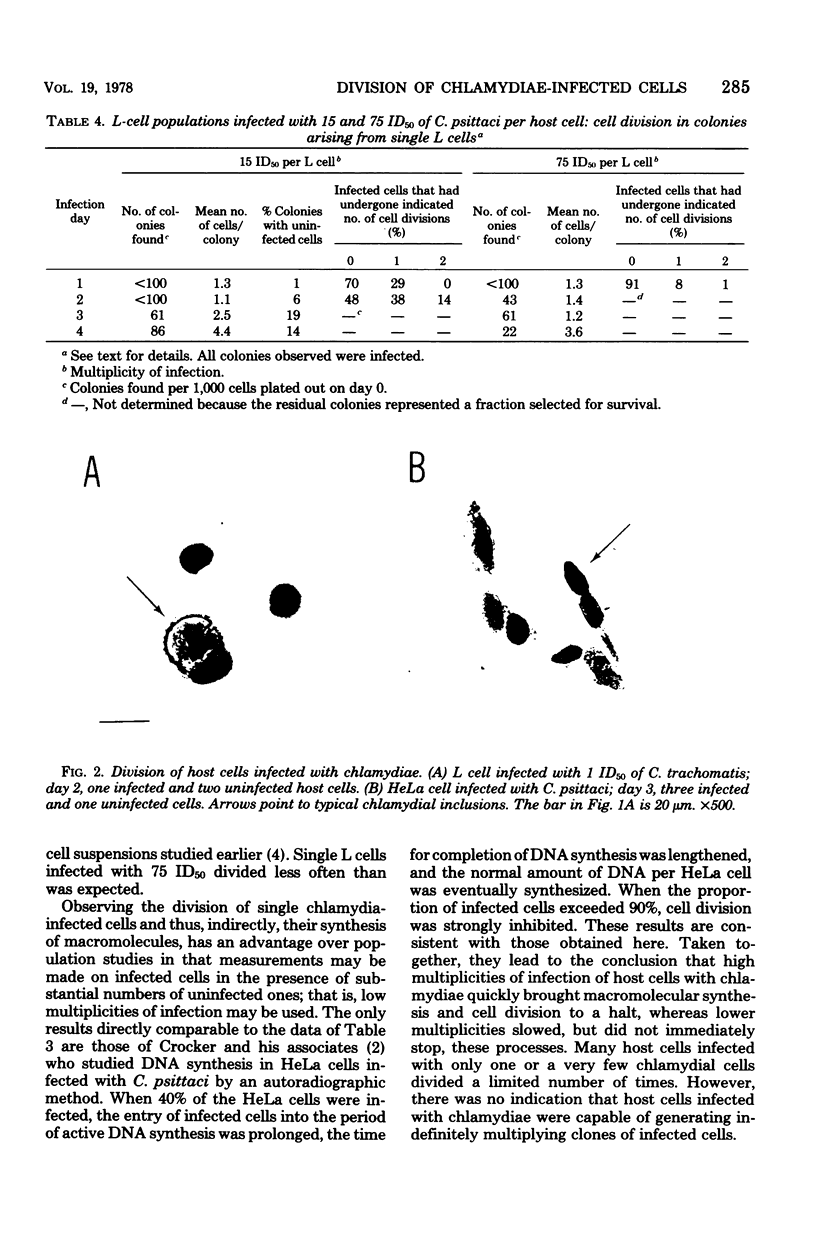
Mouse fibroblasts (L cells) were infected in suspension with Chlamydia psittaci (6BC) and then plated out on a solid substrate at a density of 80 cells per cm2 so that the effect of chlamydial infection on the division of single host cells and their progeny could be determined. Uninfected L cells multiplied with a mean generation time of 15 h. The generation time of single L cells infected with 1.5 50% infectious units (ID50) of C. psittaci was over twice as long. Half of the infected L cells had divided once by day 4 after infection, and the rest had divided more than once. Division of infected cells frequently produced one infected and one uninfected daughter. About half of the L cells infected with 15 ID50 of C. psittaci divided at least once before most of them detached from their substrate before observation on day 3. Less than 10% of the L cells infected with 75 ID50 of C. psittaci divided before they were lost from their substrate by day 2. Comparable results were obtained with single L cells infected with a lymphogranuloma venereum (440L) strain of C. trachomatis and with single HeLa 229 cells infected with C. psittaci. It was concluded that high multiplicities of infection of host cells with chlamydiae quickly bring cell division to a halt, whereas lower multiplicities slow but do not immediately stop the division of host cells. However, indefinitely multiplying clones of chlamydia-infected host cells were not observed. The method used here should be applicable to other studies on the division of cells in culture.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alexander J. J. Separation of protein synthesis in meningopneumonitisgent from that in L cells by differential susceptibility to cycloheximide. J Bacteriol. 1968 Feb;95(2):327–332. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.2.327-332.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CROCKER T. T., PELC S. R., NIELSEN B. I., EASTWOOD J. M., BANKS J. POPULATION DYNAMICS AND DEOXYRIBONUCLEIC ACID SYNTHESIS IN HELA CELLS INFECTED WITH AN ORNITHOSIS AGENT. J Infect Dis. 1965 Apr;115:105–122. doi: 10.1093/infdis/115.2.105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatch T. P. Competition between Chlamydia psittaci and L cells for host isoleucine pools: a limiting factor in chlamydial multiplication. Infect Immun. 1975 Jul;12(1):211–220. doi: 10.1128/iai.12.1.211-220.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kellogg K. R., Horoschak K. D., Moulder J. W. Toxicity of low and moderate multiplicities of Chlamydia psittaci for mouse fibroblasts (L cells). Infect Immun. 1977 Nov;18(2):531–541. doi: 10.1128/iai.18.2.531-541.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin H. S. Inhibition of thymidine kinase activity and deoxyribonucleic acid synthesis in L cells infected with the meningopneumonitis agent. J Bacteriol. 1968 Dec;96(6):2054–2065. doi: 10.1128/jb.96.6.2054-2065.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OFFICER J. E., BROWN A. Serial changes in virus and cells in cultures chronically infected with psittacosis virus. Virology. 1961 May;14:88–99. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(61)90136-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schechter E. M. Synthesis of nucleic acid and protein in L cells infected with the agent of meningopneumonitis. J Bacteriol. 1966 May;91(5):2069–2080. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.5.2069-2080.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TAMURA A., IWANAGA M. RNA SYNTHESIS IN CELLS INFECTED WITH THE MENINGOPNEUMONITIS AGENT. J Mol Biol. 1965 Jan;11:97–108. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(65)80175-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tribby I. I., Moulder J. W. Inhibition of Deoxyribonucleic Acid Synthesis in Synchronized Populations of L Cells Infected with Chlamydia psittaci. Infect Immun. 1971 Feb;3(2):363–364. doi: 10.1128/iai.3.2.363-364.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]