Abstract
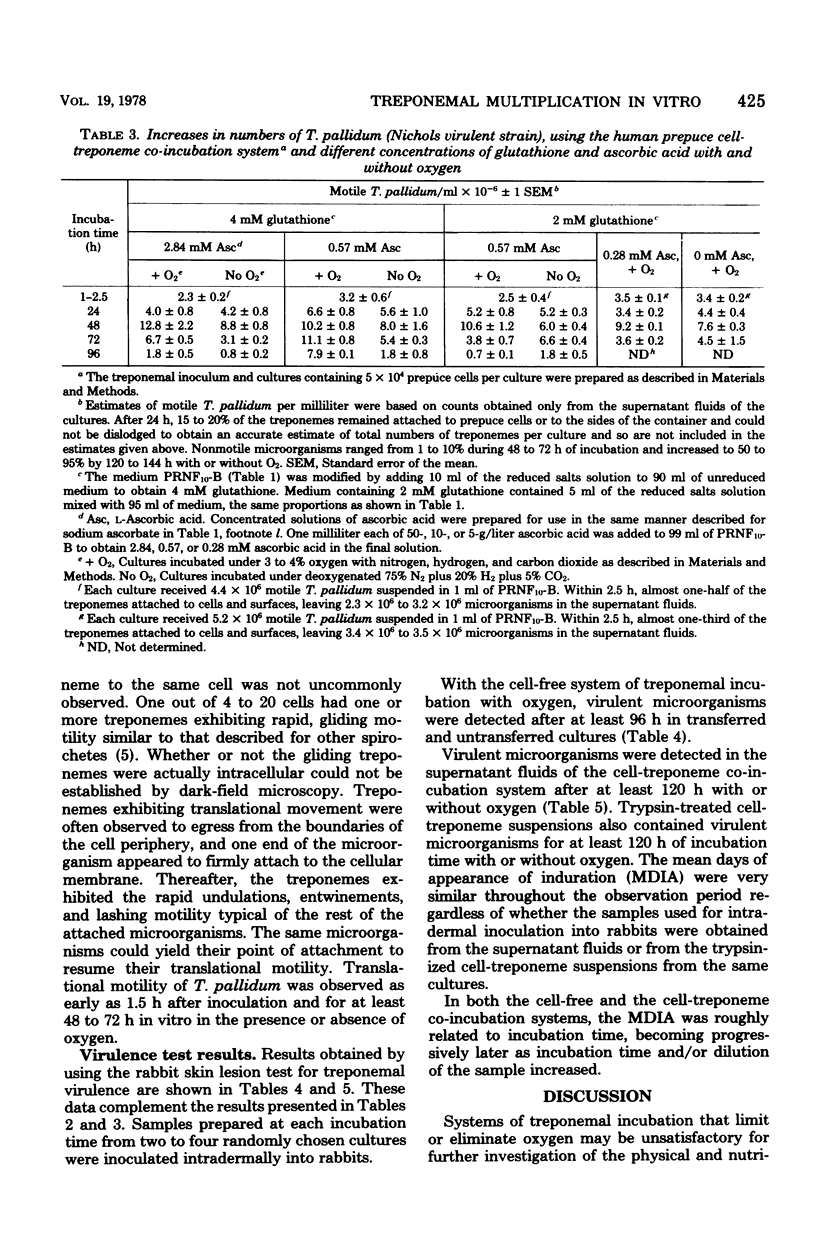
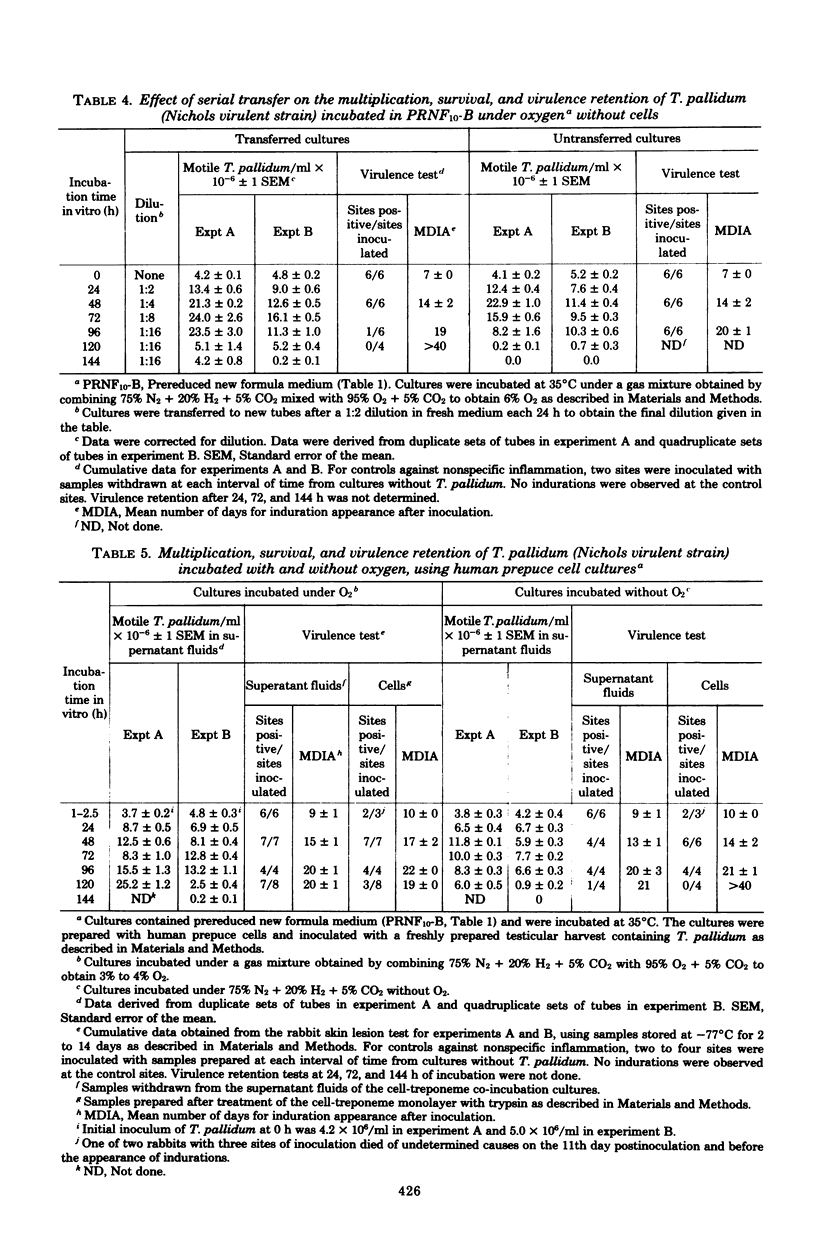
Treponema pallidum (Nichols virulent strain) was incubated with or without oxygen using a modified medium supplemented with reduced glutathione and a variety of nutrients (PRNF10-B). Two- to fourfold increases in treponemal numbers were observed in cultures without mammalian cells within 96 h of incubation under 5 to 6% oxygen. Treponemal motility and multiplication were maintained more satisfactorily in cultures that were diluted and transferred daily, using an equal volume of fresh medium. Treponemes incubated without oxygen did not significantly increase in number. Virulent microorganisms were detected for at least 96 h in the cell-free system. In the presence of 3 to 4% oxygen, two- to fivefold increases in treponemal numbers were observed in the supernatant fluids of cultures containing human prepuce cells after 48 to 120 h at 35 degrees C. Without oxygen, treponemal numbers rarely approached a threefold increase. Virulent treponemes were detected by the rabbit skin lesion test after at least 120 h in vitro. Regardless of the system of incubation, increases in treponemal numbers could not be sustained for longer than 120 h, and treponemal virulence decreased as a function of time in vitro.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baseman J. B., Hayes N. S. Protein synthesis by Treponema pallidum extracted from infected rabbit tissue. Infect Immun. 1974 Dec;10(6):1350–1355. doi: 10.1128/iai.10.6.1350-1355.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baseman J. B., Nichols J. C., Hayes N. C. Virulent Treponema pallidum: aerobe or anaerobe. Infect Immun. 1976 Mar;13(3):704–711. doi: 10.1128/iai.13.3.704-711.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baseman J. B., Nichols J. C., Rumpp J. W., Hayes N. S. Purification of Treponema pallidum from Infected Rabbit Tissue: Resolution into Two Treponemal Populations. Infect Immun. 1974 Nov;10(5):1062–1067. doi: 10.1128/iai.10.5.1062-1067.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baseman J. B. Summary of the workshop on the biology of Treponema pallidum: cultivation and vaccine development. J Infect Dis. 1977 Aug;136(2):308–311. doi: 10.1093/infdis/136.2.308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CROSS B. A., SILVER I. A. Neurovascular control of oxygen tension in the testis and epididymis. J Reprod Fertil. 1962 Jun;3:377–395. doi: 10.1530/jrf.0.0030377. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Canale-Parola E. Physiology and evolution of spirochetes. Bacteriol Rev. 1977 Mar;41(1):181–204. doi: 10.1128/br.41.1.181-204.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox C. D., Barber M. K. Oxygen uptake by Treponema pallidum. Infect Immun. 1974 Jul;10(1):123–127. doi: 10.1128/iai.10.1.123-127.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EAGLE H. Amino acid metabolism in mammalian cell cultures. Science. 1959 Aug 21;130(3373):432–437. doi: 10.1126/science.130.3373.432. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fieldsteel A. H., Becker F. A., Stout J. G. Prolonged survival of virulent Treponema pallidum (Nichols strain) in cell-free and tissue culture systems. Infect Immun. 1977 Oct;18(1):173–182. doi: 10.1128/iai.18.1.173-182.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitzgerald T. J., Cleveland P., Johnson R. C., Miller J. N., Sykes J. A. Scanning electron microscopy of Treponema pallidum (Nichols strain) attached to cultured mammalian cells. J Bacteriol. 1977 Jun;130(3):1333–1344. doi: 10.1128/jb.130.3.1333-1344.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitzgerald T. J., Johnson R. C., Sykes J. A., Miller J. N. Interaction of Treponema pallidum (Nichols strain) with cultured mammalian cells: effects of oxygen, reducing agents, serum supplements, and different cell types. Infect Immun. 1977 Feb;15(2):444–452. doi: 10.1128/iai.15.2.444-452.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitzgerald T. J., Miller J. N., Sykes J. A. Treponema pallidum (Nichols strain) in tissue cultures: cellular attachment, entry, and survival. Infect Immun. 1975 May;11(5):1133–1140. doi: 10.1128/iai.11.5.1133-1140.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graves S. R., Sandok P. L., Jenkin H. M., Johnson R. C. Retention of motility and virulence of Treponema pallidum (Nichols strain) in vitro. Infect Immun. 1975 Nov;12(5):1116–1120. doi: 10.1128/iai.12.5.1116-1120.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayes N. S., Muse K. E., Collier A. M., Baseman J. B. Parasitism by virulent Treponema pallidum of host cell surfaces. Infect Immun. 1977 Jul;17(1):174–186. doi: 10.1128/iai.17.1.174-186.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson R. C., Ritzi D. M., Livermore B. P. Outer envelope of virulent Treponema pallidum. Infect Immun. 1973 Aug;8(2):291–295. doi: 10.1128/iai.8.2.291-295.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones R. H., Finn M. A., Thomas J. J., Folger C. Growth and subculture of pathogenic T. pallidum (Nichols strain) in BHK-21 cultured tissue cells. Br J Vener Dis. 1976 Feb;52(1):18–23. doi: 10.1136/sti.52.1.18. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Király K., Horváth I. Survival of T. pallidum under microaerobic conditions in cell and tissue cultures. Zentralbl Bakteriol Orig A. 1976 Aug;235(4):500–505. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lysko P. G., Cox C. D. Terminal electron transport in Treponema pallidum. Infect Immun. 1977 Jun;16(3):885–890. doi: 10.1128/iai.16.3.885-890.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Onderdonk A. B., Johnston J., Mayhew J. W., Gorbach S. L. Effect of dissolved oxygen and Eh and Bacteroides fragilis during continuous culture. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1976 Feb;31(2):168–172. doi: 10.1128/aem.31.2.168-172.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandok P. L., Jenkin H. M., Graves S. R., Knight S. T. Retention of motility of Treponema pallidum (Nichols virulent strain) in an anaerobic cell culture system and in a cell-free system. J Clin Microbiol. 1976 Jan;3(1):72–74. doi: 10.1128/jcm.3.1.72-74.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandok P. L., Knight S. T., Jenkin H. M. Examination of various cell culture techniques for co-incubation of virulent Treponema pallidum (Nichols I strain) under anaerobic conditions. J Clin Microbiol. 1976 Oct;4(4):360–371. doi: 10.1128/jcm.4.4.360-371.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro H. M. Redox balance in the body: an approach to quantitation. J Surg Res. 1972 Sep;13(3):138–152. doi: 10.1016/0022-4804(72)90057-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith H. Microbial surfaces in relation to pathogenicity. Bacteriol Rev. 1977 Jun;41(2):475–500. doi: 10.1128/br.41.2.475-500.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEBER M. M. Factors influencing the in vitro survival of Treponema pallidum. Am J Hyg. 1960 May;71:401–417. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a120123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willcox R. R., Guthe T. Treponema pallidum. A bibliographical review of the morphology, culture and survival of T. pallidum and associated organisms. Bull World Health Organ. 1966;35:1–169. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeigler J. A., Jones A. M., Jones R. H., Kubica K. M. Demonstration of extracellular material at the surface of pathogenic T. pallidum cells. Br J Vener Dis. 1976 Feb;52(1):1–8. doi: 10.1136/sti.52.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



