Abstract
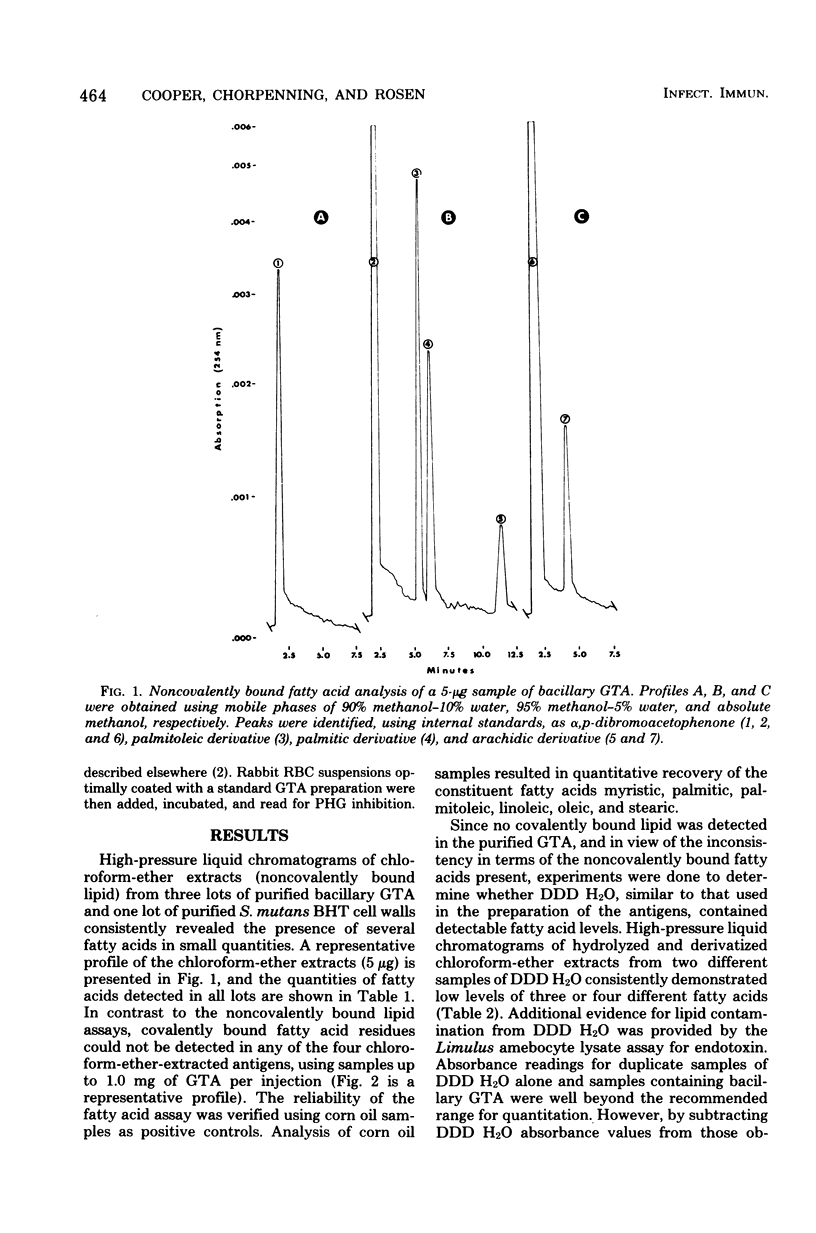
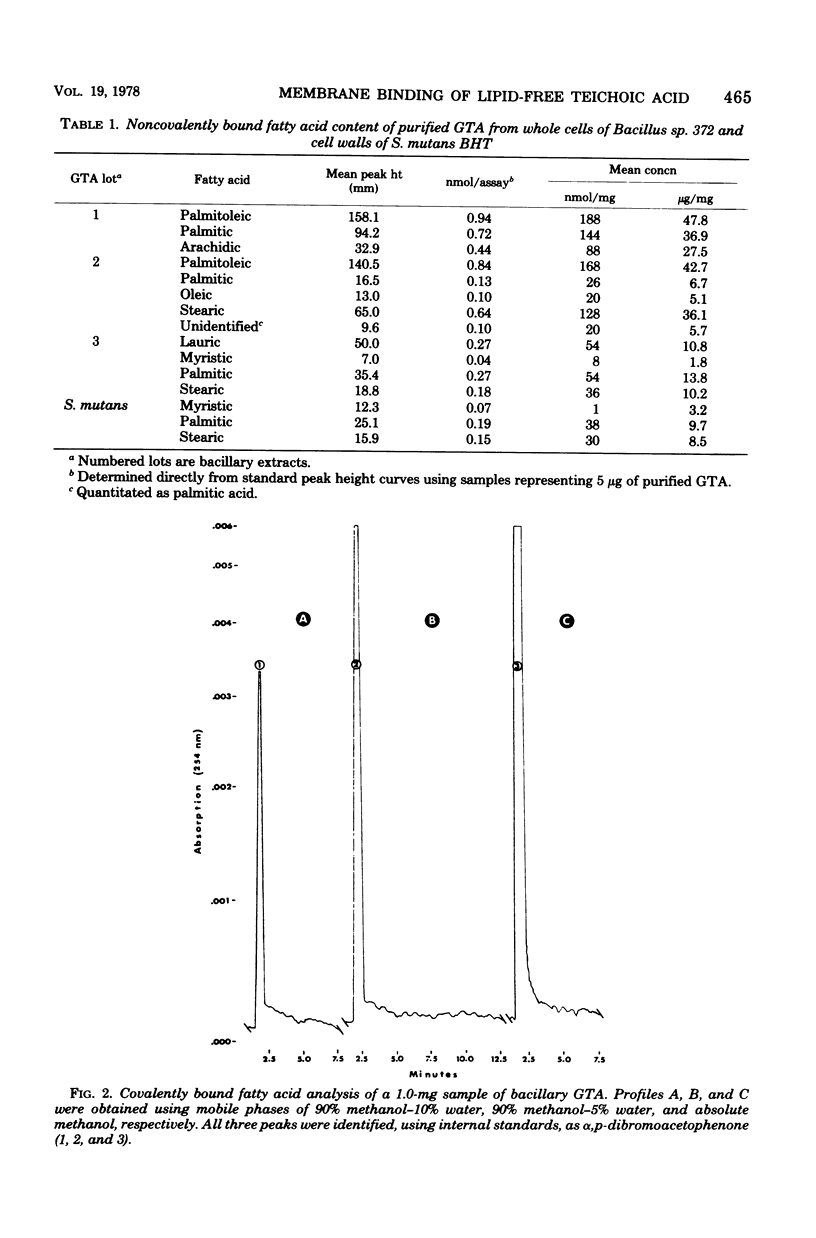
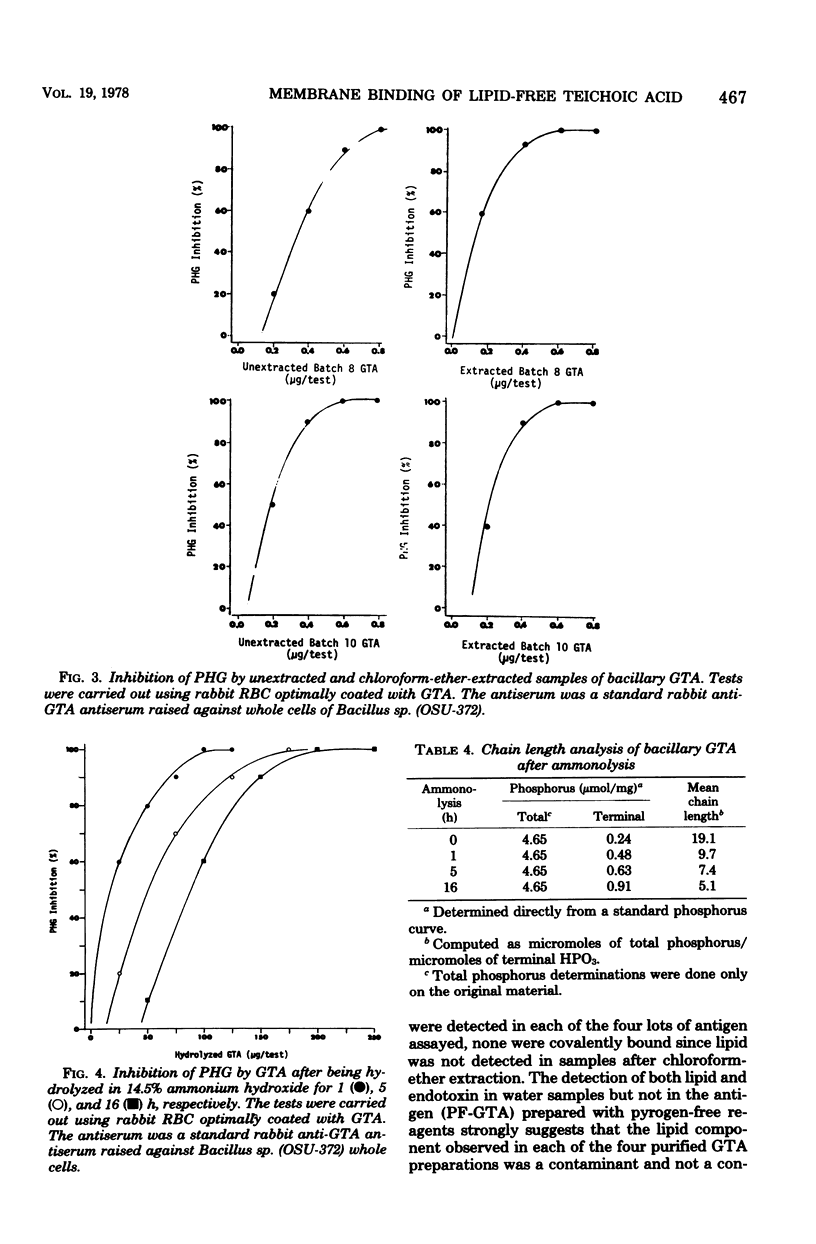
Lipid analysis of several glycerol teichoic acid preparations strongly indicated that covalently bound lipid is not required for spontaneous adsorption of glycerol teichoic acid to erythrocyte membranes. Although fatty acids were detected in each of four batches, none were covalently bound. Chloroform-ether-extracted antigens retained potent erythrocyte membrane-binding activity as measured by passive hemagglutination, even though they were shown to contain less than one fatty acid residue per 4,869 teichoic acid chains. Mild ammonolysis abolished erythrocyte-sensitizing activity in passive hemagglutination, but further studies indicated the loss of activity was due to partial destruction of the polyglycerophosphate backbone and not to the removal of esterified lipid. The amount of hydrolyzed antigen required to produce 100% passive hemagglutination inhibition was between 170 and 330 times the amount required to produce the same result using unhydrolyzed glycerol teichoic acid. The average chain length was reduced from 19.1 to 9.7, 7.4, and 5.1 glycerophosphate residues for antigen samples hydrolyzed for 1, 5, and 16 h, respectively.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Archibald A. R., Baddiley J. The teichoic acids. Adv Carbohydr Chem Biochem. 1966;21:323–375. doi: 10.1016/s0096-5332(08)60320-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chorpenning F. W., Cooper H. R., Rosen S. Cross-reactions of Streptococcus mutans due to cell wall teichoic acid. Infect Immun. 1975 Sep;12(3):586–591. doi: 10.1128/iai.12.3.586-591.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chorpenning F. W., Stamper H. B. Spontaneous adsorption of teichoic acid to erythrocytes. Immunochemistry. 1973 Jan;10(1):15–20. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(73)90245-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper H. R., Chorpenning F. W., Rosen S. Preparation and chemical composition of the cell walls of Streptococcus mutans. Infect Immun. 1975 Apr;11(4):823–828. doi: 10.1128/iai.11.4.823-828.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Decker G. P., Chorpenning F. W., Frederick G. T. Naturally-occurring antibodies to bacillary teichoic acids. J Immunol. 1972 Jan;108(1):214–222. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Durst H. D., Milano M., Kikta E. J., Jr, Connelly S. A., Grushka E. Phenacyl esters of fatty acids via crown ether catalysts for enhanced ultraviolet detection in liquid chromatography. Anal Chem. 1975 Sep;47(11):1797–1801. doi: 10.1021/ac60361a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hewett M. J., Knox K. W., Wicken A. J. Studies on the group F antigen of lactobacilli: detection of antibodies by haemagglutination. J Gen Microbiol. 1970 Mar;60(3):315–322. doi: 10.1099/00221287-60-3-315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson R. W., Moskowitz M. Nature of a red cell sensitizing substance from streptococci. J Bacteriol. 1966 Jun;91(6):2205–2209. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.6.2205-2209.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knox K. W., Wicken A. J. Immunological properties of teichoic acids. Bacteriol Rev. 1973 Jun;37(2):215–257. doi: 10.1128/br.37.2.215-257.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEVIN J., BANG F. B. THE ROLE OF ENDOTOXIN IN THE EXTRACELLULAR COAGULATION OF LIMULUS BLOOD. Bull Johns Hopkins Hosp. 1964 Sep;115:265–274. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuno T., Slade H. D. Group a streptococcal polysaccharide antigens. Infect Immun. 1971 Mar;3(3):385–389. doi: 10.1128/iai.3.3.385-389.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller G. A., Jackson R. W. The effect of a streptococcus pyogenes teichoic acid on the immune response of mice. J Immunol. 1973 Jan;110(1):148–156. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller G. A., Urban J., Jackson R. W. Effects of a streptococcal lipoteichoic acid on host responses in mice. Infect Immun. 1976 May;13(5):1408–1417. doi: 10.1128/iai.13.5.1408-1417.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moskowitz M. Separation and properties of a red cell sensitizing substance from streptococci. J Bacteriol. 1966 Jun;91(6):2200–2204. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.6.2200-2204.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ne'eman N., Ginsburg I. Red cell-sensitizing antigen of group A streptococci. II. Immunological and immunopathological properties. Isr J Med Sci. 1972 Nov;8(11):1807–1816. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ofek I., Beachey E. H., Jefferson W., Campbell G. L. Cell membrane-binding properties of group A streptococcal lipoteichoic acid. J Exp Med. 1975 May 1;141(5):990–1003. doi: 10.1084/jem.141.5.990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stamper H. B., Jr, Chorpenning F. W. An experimentally pathogenic Bacillus species. I. Description and characterization of the organism. Can J Microbiol. 1975 Apr;21(4):485–489. doi: 10.1139/m75-068. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaught R. M., Bleiweis A. S. Antigens of Streptococcus mutans. II. Characterization of an antigen resembling a glycerol teichoic acid in walls of strain BHT. Infect Immun. 1974 Jan;9(1):60–67. doi: 10.1128/iai.9.1.60-67.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wicken A. J., Knox K. W. Lipoteichoic acids: a new class of bacterial antigen. Science. 1975 Mar 28;187(4182):1161–1167. doi: 10.1126/science.46620. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wicken A. J., Knox K. W. Studies on the group F antigen of lactobacilli: isolation of a teichoic acid-lipid complex from Lactobacillus fermenti NCTC 6991. J Gen Microbiol. 1970 Mar;60(3):293–301. doi: 10.1099/00221287-60-3-293. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


