Abstract
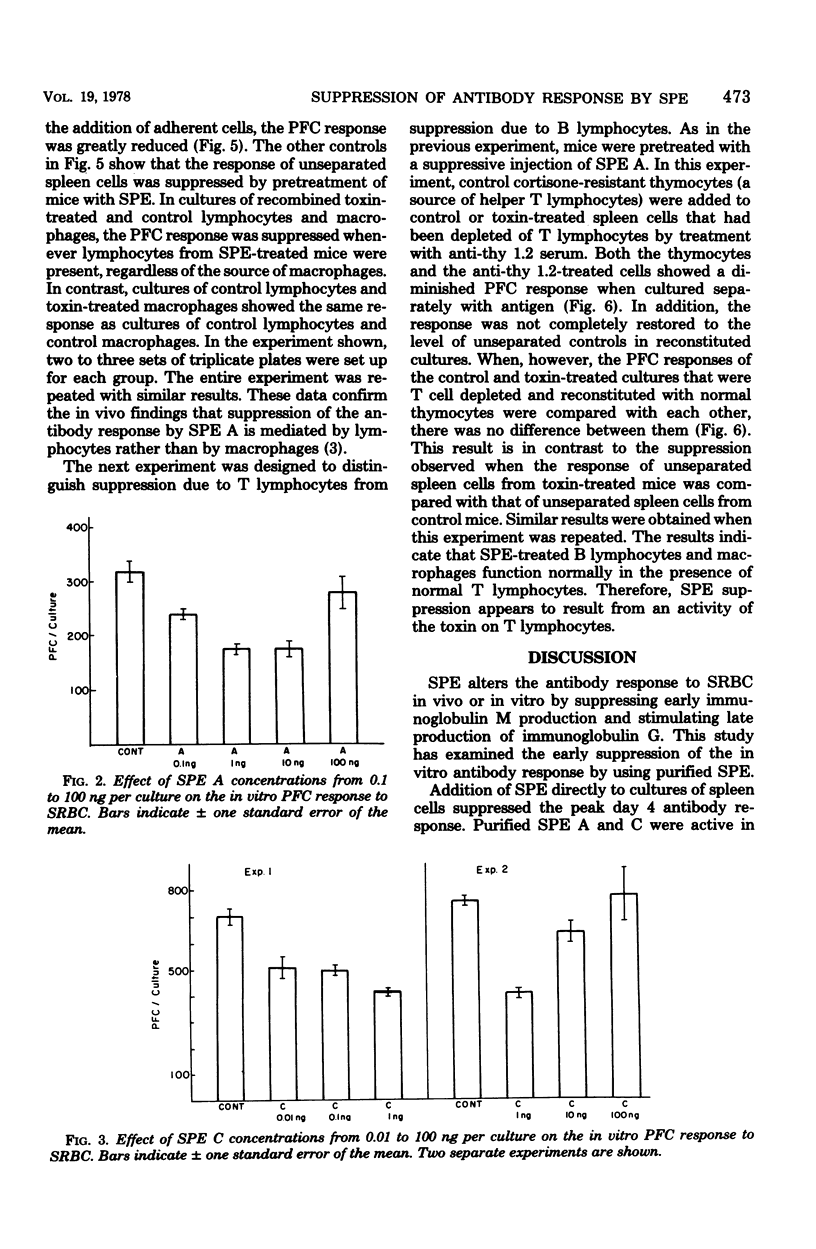
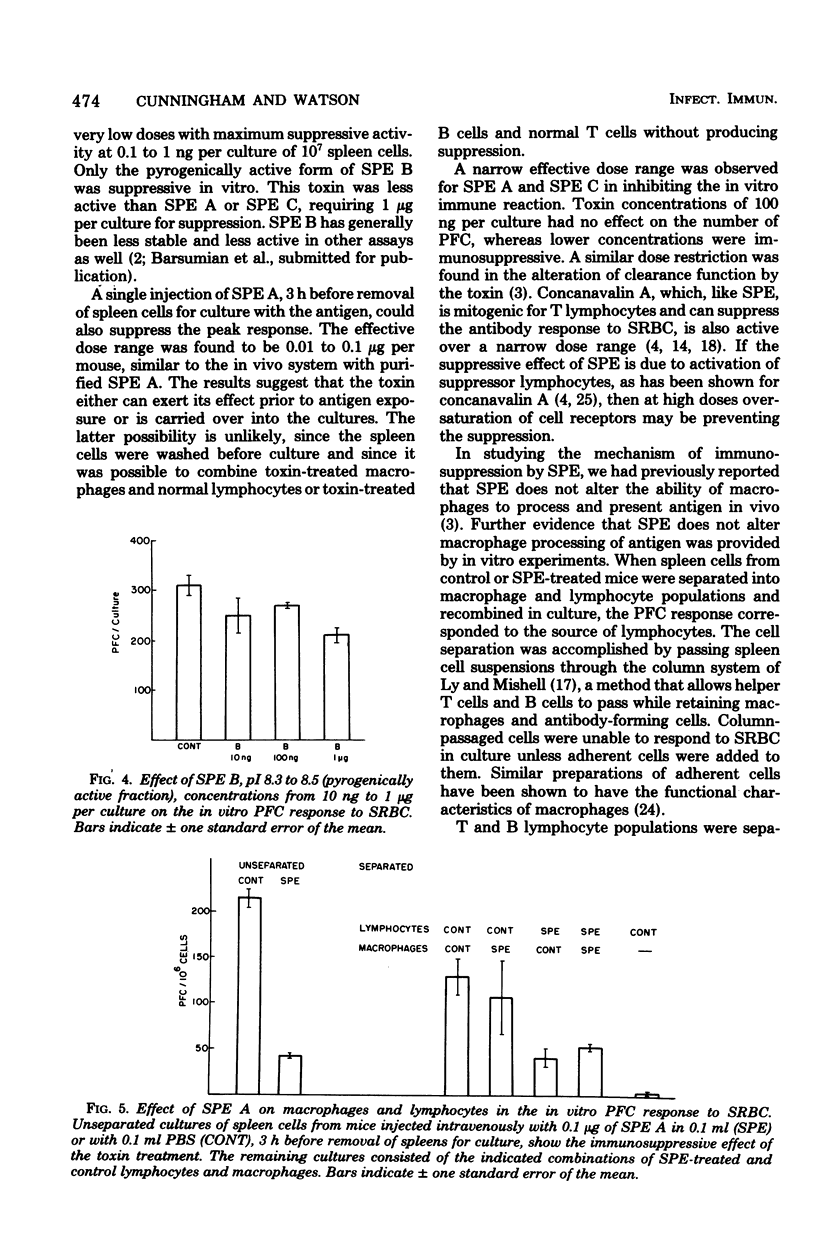
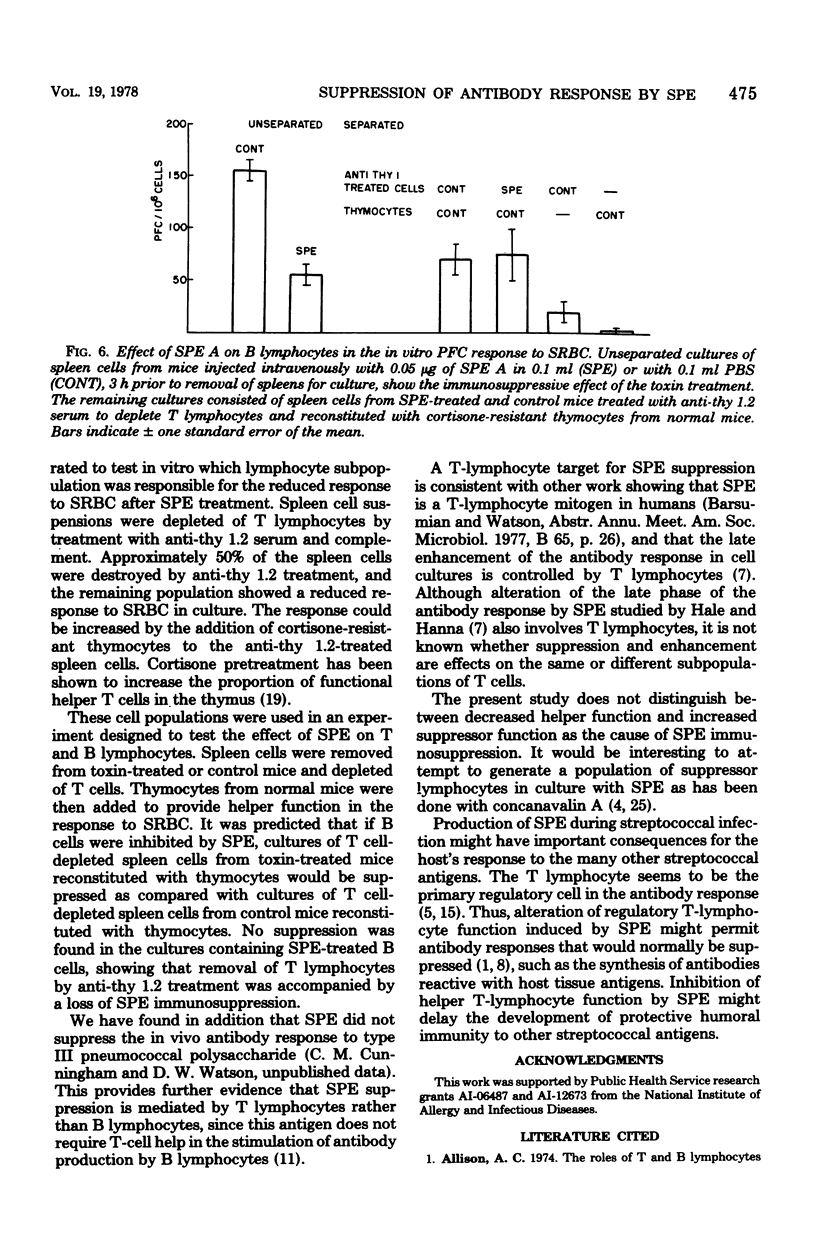
The effect of purified streptococcal pyrogenic exotoxins (SPE) on the antibody response to sheep erythrocytes was studied in cultures of mouse spleen cells. Purified SPE types A, B, and C shared the ability to suppress the day 4 direct plaque-forming cell response when added to cultures. SPE A and C were most suppressive at concentrations of 0.1 to 1 ng per culture, while SPE B was active at 1 microgram per culture. Pretreatment of mice with SPE A, 3 h before removal of their spleens for culture, also produced suppression. Cell populations were separated from spleens of normal and toxin-treated mice and recombined in culture to test the cellular site of action of SPE immunosuppression. When nonadherent cells (lymphocytes) and adherent cells (macrophages) from control and SPE-treated mice were separated and recombined, the plaque-forming cell response depended on the source of lymphocytes. Macrophages from toxin-treated mice functioned normally in the presence of control lymphocytes. In a further experiment, toxin pretreatment failed to suppress the plaque-forming cell response of spleen cells that were T-cell depleted and reconstituted with control thymocytes. When the T lymphocytes were removed from toxin-treated spleen cell suspensions, the remaining cells were able to respond normally to antigen if normal helper T cells were provided. The results suggest that the suppressive activity of SPE on antibody production is mediated by altered activity of T lymphocytes.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cunningham C. M., Barsumian E. L., Watson D. W. Further purification of group A streptococcal pyrogenic exotoxin and characterization of the purified toxin. Infect Immun. 1976 Sep;14(3):767–775. doi: 10.1128/iai.14.3.767-775.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cunningham C. M., Watson D. W. Alteration of clearance function by group A streptococcal pyrogenic exotoxin and its relation to suppression of the antibody response. Infect Immun. 1978 Jan;19(1):51–57. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.1.51-57.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dutton R. W. Inhibitory and stimulatory effects of concanavalin A on the response of mouse spleen cell suspensions to antigen. I. Characterization of the inhibitory cell activity. J Exp Med. 1972 Dec 1;136(6):1445–1460. doi: 10.1084/jem.136.6.1445. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gershon R. K. T cell control of antibody production. Contemp Top Immunobiol. 1974;3:1–40. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4684-3045-5_1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ginsburg I. Mechanisms of cell and tissue injury induced by group A streptococci: relation to poststreptococcal sequelae. J Infect Dis. 1972 Sep;126(3):294–340. doi: 10.1093/infdis/126.3.294. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HANNA E. E., WATSON D. W. HOST-PARASITE RELATIONSHIPS AMONG GROUP A STREPTOCOCCI. 3. DEPRESSION OF RETICULOENDOTHELIAL FUNCTION BY STREPTOCOCCAL PYROGENIC EXOTOXINS. J Bacteriol. 1965 Jan;89:154–158. doi: 10.1128/jb.89.1.154-158.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hale M. L., Hanna E. E. Deregulation of mouse antibody-forming cells by streptococcal pyrogenic exotoxin. II. Modification of spleen T-cell-complemented nude mouse PFC responses. Cell Immunol. 1976 Oct;26(2):168–177. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(76)90361-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanna E. E., Hale M. Deregulation of mouse antibody-forming cells in vivo in cell culture by streptococcal pyrogenic exotoxin. Infect Immun. 1975 Feb;11(2):265–272. doi: 10.1128/iai.11.2.265-272.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanna E. E., Watson D. W. Enhanced immune response after immunosuppression by Streptococcal pyrogenic exotoxin. Infect Immun. 1973 Jun;7(6):1009–1011. doi: 10.1128/iai.7.6.1009-1011.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanna E. E., Watson D. W. Host-parasite relationships among group A streptococci. IV. Suppression of antibody response by streptococcal pyrogenic exotoxin. J Bacteriol. 1968 Jan;95(1):14–21. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.1.14-21.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard J. G., Christie G. H., Courtenay B. M., Leuchars E., Davies A. J. Studies on immunological paralysis. VI. Thymic-independence of tolerance and immunity to type 3 pneumococcal polysaccharide. Cell Immunol. 1971 Dec;2(6):614–626. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(71)90009-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hríbalová V., Pospísil M. Lymphocyte-stimulating activity of scarlet fever toxin. Experientia. 1973 Jun 15;29(6):704–705. doi: 10.1007/BF01944787. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson H. M., Stanton G. J., Baron S. Relative ability of mitogens to stimulate production of interferon by lymphoid cells and to induce suppression of the in vitro immune response. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1977 Jan;154(1):138–141. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz D. H., Benacerraf B. The regulatory influence of activated T cells on B cell responses to antigen. Adv Immunol. 1972;15:1–94. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60683-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim Y. B., Watson D. W. A purified group A streptococcal pyrogenic exotoxin. Physiochemical and biological properties including the enhancement of susceptibility to endotoxin lethal shock. J Exp Med. 1970 Mar 1;131(3):611–622. doi: 10.1084/jem.131.3.611. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ly I. A., Mishell R. I. Separation of mouse spleen cells by passage through columns of sephadex G-10. J Immunol Methods. 1974 Aug;5(3):239–247. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(74)90108-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClain D. A., Edelman G. M. Analysis of the stimulation-inhibition paradox exhibited by lymphocytes exposed to concanavalin A. J Exp Med. 1976 Dec 1;144(6):1494–1508. doi: 10.1084/jem.144.6.1494. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller J. F., Basten A., Sprent J., Cheers C. Interaction between lymphocytes in immune responses. Cell Immunol. 1971 Oct;2(5):469–495. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(71)90057-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mishell R. I., Dutton R. W. Immunization of dissociated spleen cell cultures from normal mice. J Exp Med. 1967 Sep 1;126(3):423–442. doi: 10.1084/jem.126.3.423. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosier D. E. A requirement for two cell types for antibody formation in vitro. Science. 1967 Dec 22;158(3808):1573–1575. doi: 10.1126/science.158.3808.1573. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosier D. E., Pierce C. W. Functional maturation of thymic lymphocyte populations in vitro. J Exp Med. 1972 Dec 1;136(6):1484–1500. doi: 10.1084/jem.136.6.1484. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierce C. W. Immune responses in vitro. VI. Cell interactions in the development of primary IgM, IgG and IgA plaque-forming cell responses in vitro. Cell Immunol. 1973 Dec;9(3):453–464. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(73)90060-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierce C. W., Kapp J. A., Wood D. D., Benacerraf B. Immune responses in vitro. X. Functions of macrophages. J Immunol. 1974 Mar;112(3):1181–1189. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rich R. R., Pierce C. W. Biological expressions of lymphocyte activation. II. Generation of a population of thymus-derived suppressor lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 1973 Mar 1;137(3):649–659. doi: 10.1084/jem.137.3.649. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlievert P. M., Bettin K. M., Watson D. W. Purification and characterization of group A streptococcal pyrogenic exotoxin type C. Infect Immun. 1977 May;16(2):673–679. doi: 10.1128/iai.16.2.673-679.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WATSON D. W. Host-parasite factors in group A streptococcal infections. Pyrogenic and other effects of immunologic distinct exotoxins related to scarlet fever toxins. J Exp Med. 1960 Feb 1;111:255–284. doi: 10.1084/jem.111.2.255. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



