Abstract
The antibacterial potential of fresh serum obtained from young animals during a pre-antibody period of development was assessed against two smooth and two rough strains of gram-negative bacteria. The bactericidal capacity of serum from 3- to 4-week-old guinea pigs and 4- to 5-week-old rabbits was compared with that of serum from adults. Serum from young animals was deficient in natural antibodies, and in conventional dilution assays the bactericidal action was unimpressive, especially against the smooth strains. However, when decimal increments of bacteria were incubated in fresh undiluted serum, killing of both smooth and rough strains proved substantial. This finding may have particular meaning in the very young animal when natural antibodies are at ebb: cellular defense mechanisms may function less efficiently at this time and effect a greater reliance on humoral antibacterial systems.
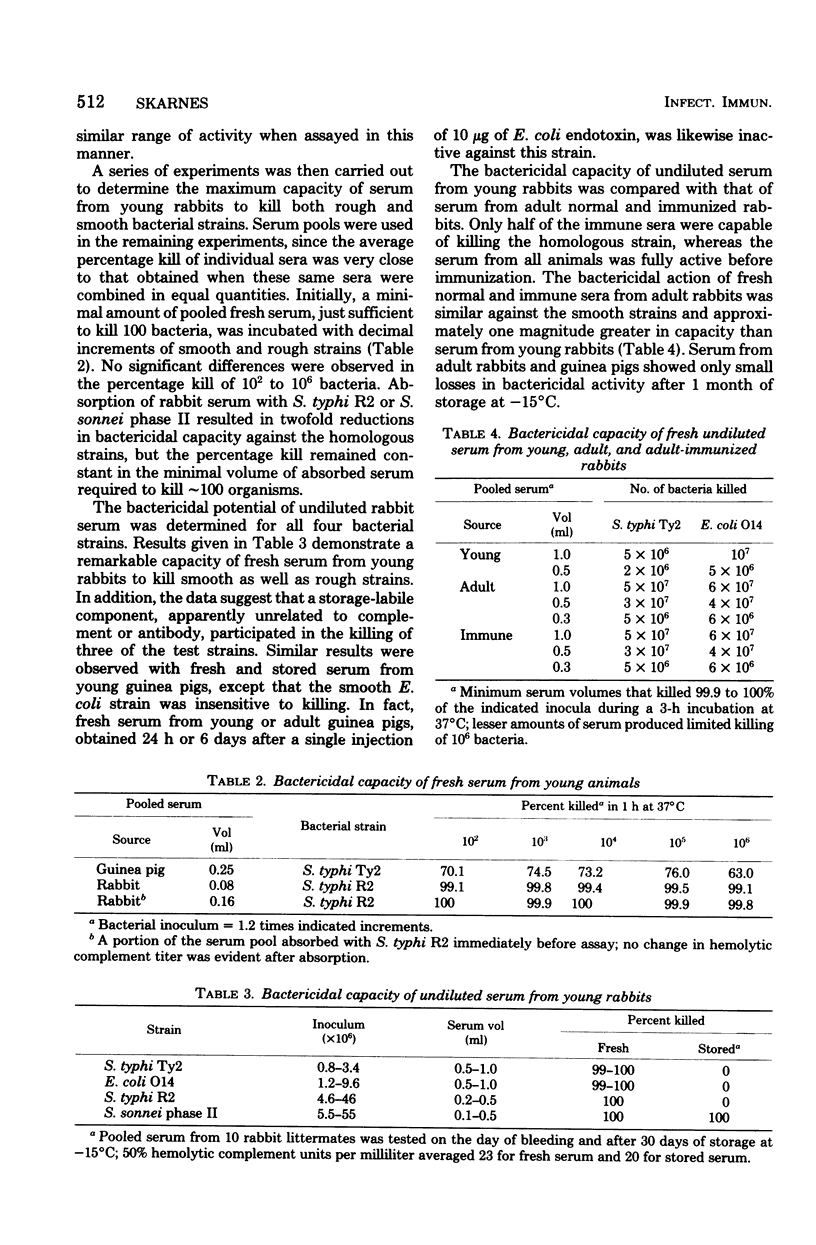
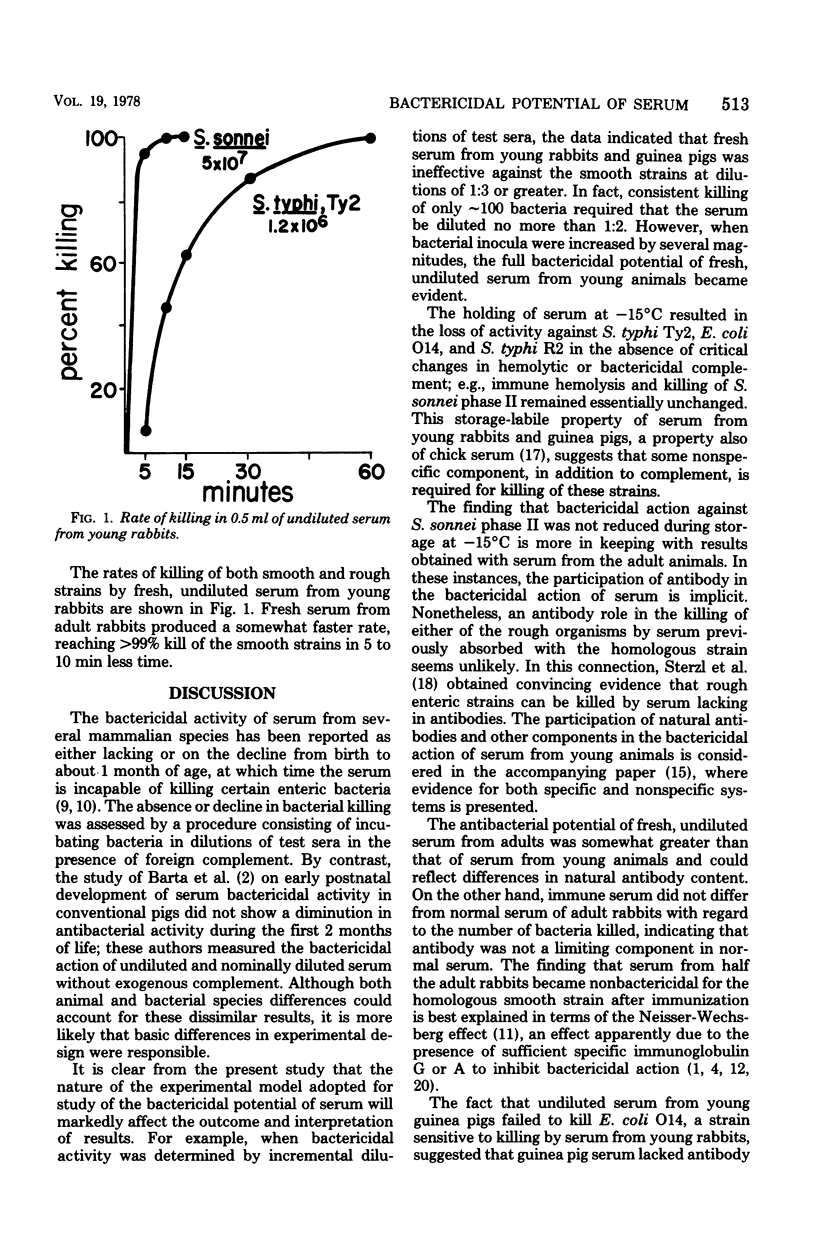
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ADLER F. L. Studies on the bactericidal reaction. I. Bactericidal action of normal sera against a strain of Salmonella typhosa. J Immunol. 1953 Jan;70(1):69–78. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barta O., Barta V., Miniats O. P., Ingram D. G. Bactericidal activity of conventional and germfree pig serum against smooth and rough strains of Escherichia coli. Am J Vet Res. 1971 Jul;32(7):1077–1082. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eddie D. S., Schulkind M. L., Robbins J. B. The isolation and biologic activities of purified secretory IgA and IgG anti-Salmonella typhimurium "O" antibodies from rabbit intestinal fluid and colostrum. J Immunol. 1971 Jan;106(1):181–190. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glynn A. A., Howard C. J. The sensitivity to complement of strains of Escherichia coli related to their K antigens. Immunology. 1970 Mar;18(3):331–346. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joos R. W., Hall W. H. Bactericidal action of fresh rabbit blood against Brucella abortus. J Bacteriol. 1968 Oct;96(4):881–885. doi: 10.1128/jb.96.4.881-885.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LANDY M., MICHAEL J. G., WHITBY J. L. Bactericidal method for the measurement in normal serum of antibody to gramnegative bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1962 Mar;83:631–640. doi: 10.1128/jb.83.3.631-640.1962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MICHAEL J. G., WHITBY J. L., LANDY M. Studies on natural antibodies to gram-negative bacteria. J Exp Med. 1962 Jan 1;115:131–146. doi: 10.1084/jem.115.1.131. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Normann B., Stendahl O., Tagesson C., Edebo L. Characteristics of the inhibition by rabbit immune serum of the bactericidal effect of cattle normal serum on Salmonella typhimurium 395 MRO. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B Microbiol Immunol. 1972;80(6):891–899. doi: 10.1111/j.0365-5563.1973.tb00016.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OSAWA E., MUSCHEL L. H. STUDIES RELATING TO THE SERUM RESISTANCE OF CERTAIN GRAM-NEGATIVE BACTERIA. J Exp Med. 1964 Jan 1;119:41–51. doi: 10.1084/jem.119.1.41. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SKARNES R. C., WATSON D. W. Antimicrobial factors of normal tissues and fluids. Bacteriol Rev. 1957 Dec;21(4):273–294. doi: 10.1128/br.21.4.273-294.1957. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STERZL J., KOSTKA J., LANC A. Development of bactericidal properties against gram-negative organisms in the serum of young animals. Folia Microbiol (Praha) 1962 May;7:162–174. doi: 10.1007/BF02928237. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STEWARD J. P., COLLIS L. R., ROANTREE R. J. EFFECTS OF ACTIVE IMMUNIZATION AND OF TOTAL BODY X-IRRADIATION UPON THE HUMORAL BACTERICIDAL SYSTEM OF THE GUINEA PIG AS MEASURED WITH STRAINS OF ENTERIC BACILLI. J Immunol. 1964 Apr;92:616–625. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skarnes R. C. Humoral bactericidal systems: nonspecific and specific mechanisms. Infect Immun. 1978 Feb;19(2):515–522. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.2.515-522.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skarnes R. C. Non specific hemolysis of erythrocytes modified with bacterial endotoxins. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1965 Jul;109(1):66–79. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solomon J. B. Immunity to Salmonella gallinarum during ontogeny of the chicken. 3. Bactericidal antibody. Immunology. 1968 Aug;15(2):219–226. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor P. W. Isolation and characterization of a serum antibactericidal factor. Clin Sci. 1972 Nov;43(5):705–708. doi: 10.1042/cs0430705. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEIDANZ W. P., LANDY M. A SIMPLIFIED METHOD FOR BACTERICIDAL ASSAY OF NATURAL ANTIBODIES AGAINST GRAM-NEGATIVE BACTERIA. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1963 Aug-Sep;113:861–867. doi: 10.3181/00379727-113-28513. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



