Abstract
Phagocytosis of the 6BC strain of Chlamydia psittaci and the lymphogranuloma venereum 440L strain of Chlamydia trachomatis by L cells and HeLa 229 cells occurred at rates and to extents that were 10 to 100 times greater than those observed for the phagocytosis of Escherichia coli and polystyrene latex spheres. Both species of Chlamydia were efficiently taken up by host cells of a type they had not previously encountered. Phagocytosis of chlamydiae was brought about by the interaction of parasite surface ligands with elements of the host cell surface. The chlamydial ligands were readily denatured by heat, were masked by antibody, and were resistant to proteases and detergents. The host cell components were reversibly removed by proteases. Chlamydial phagocytosis was inhibited when host cells were incubated for many hours with cycloheximide. It was suggested that the presence on the chlamydial cell surface of ligands with high affinity for normal, ubiquitously occurring structures on the surface of host cells is an evolutionary adaptation to intracellular existence. The term parasite-specified phagocytosis was used to describe the efficient phagocytosis of chlamydiae by nonprofessional phagocytes and to distinguish it from the host-specified immunological and non-immunological phagocytosis carried out by professional phagocytes.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ARMSTRONG J. A., REED S. E. NATURE AND ORIGIN OF INITIAL BODIES IN LYMPHOGRANULOMA VENEREUM. Nature. 1964 Jan 25;201:371–373. doi: 10.1038/201371a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BOVARNICK M. R., MILLER J. C. Oxidation and transamination of glutamate by typhus rickettsiae. J Biol Chem. 1950 Jun;184(2):661–676. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
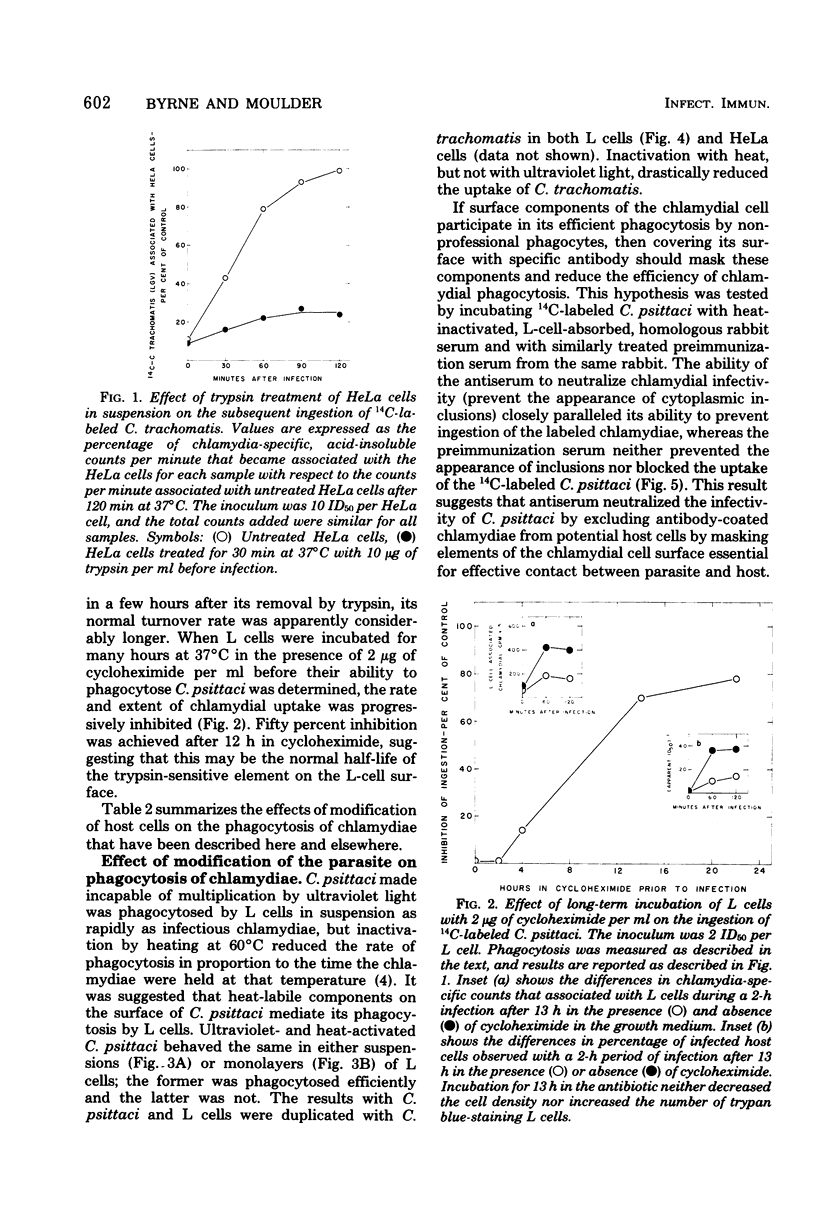
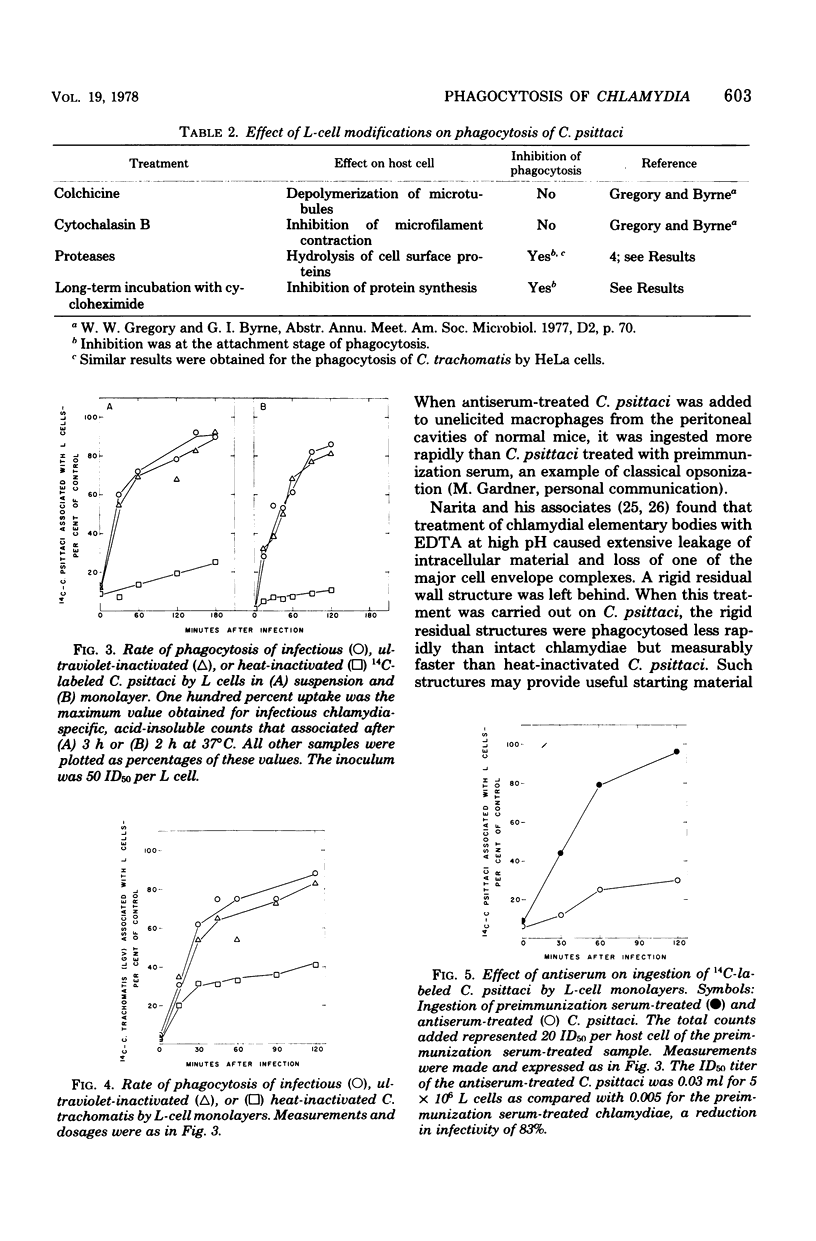
- Byrne G. I. Kinetics of phagocytosis of Chlamydia psittaci by mouse fibroblasts (L cells): separation of the attachment and ingestion stages. Infect Immun. 1978 Feb;19(2):607–612. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.2.607-612.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Byrne G. I. Requirements for ingestion of Chlamydia psittaci by mouse fibroblasts (L cells). Infect Immun. 1976 Sep;14(3):645–651. doi: 10.1128/iai.14.3.645-651.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COHN Z. A., BOZEMAN F. M., CAMPBELL J. M., HUMPHRIES J. W., SAWYER T. K. Study on growth of Rickettsia. V. Penetration of Rickettsia tsutsugamushi into mammalian cells in vitro. J Exp Med. 1959 Mar 1;109(3):271–292. doi: 10.1084/jem.109.3.271. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dales S. Early events in cell-animal virus interactions. Bacteriol Rev. 1973 Jun;37(2):103–135. doi: 10.1128/br.37.2.103-135.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doughri A. M., Storz J., Altera K. P. Mode of entry and release of chlamydiae in infections of intestinal epithelial cells. J Infect Dis. 1972 Dec;126(6):652–657. doi: 10.1093/infdis/126.6.652. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friis R. R. Interaction of L cells and Chlamydia psittaci: entry of the parasite and host responses to its development. J Bacteriol. 1972 May;110(2):706–721. doi: 10.1128/jb.110.2.706-721.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldman R. Lectin-mediated attachment and ingestion of yeast cells and erythrocytes by hamster fibroblasts. Exp Cell Res. 1977 Feb;104(2):325–334. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(77)90098-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grayston J. T., Wang S. New knowledge of chlamydiae and the diseases they cause. J Infect Dis. 1975 Jul;132(1):87–105. doi: 10.1093/infdis/132.1.87. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffin F. M., Jr, Griffin J. A., Leider J. E., Silverstein S. C. Studies on the mechanism of phagocytosis. I. Requirements for circumferential attachment of particle-bound ligands to specific receptors on the macrophage plasma membrane. J Exp Med. 1975 Nov 1;142(5):1263–1282. doi: 10.1084/jem.142.5.1263. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffin F. M., Jr, Griffin J. A., Silverstein S. C. Studies on the mechanism of phagocytosis. II. The interaction of macrophages with anti-immunoglobulin IgG-coated bone marrow-derived lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 1976 Sep 1;144(3):788–809. doi: 10.1084/jem.144.3.788. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffin F. M., Jr, Silverstein S. C. Segmental response of the macrophage plasma membrane to a phagocytic stimulus. J Exp Med. 1974 Feb 1;139(2):323–336. doi: 10.1084/jem.139.2.323. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HIGASHI N. ELECTRON MICROSCOPIC STUDIES ON THE MODE OF REPRODUCTION OF TRACHOMA VIRUS AND PSITTACOSIS VIRUS IN CELL CULTURES. Exp Mol Pathol. 1965 Feb;76:24–39. doi: 10.1016/0014-4800(65)90021-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatch T. P. Competition between Chlamydia psittaci and L cells for host isoleucine pools: a limiting factor in chlamydial multiplication. Infect Immun. 1975 Jul;12(1):211–220. doi: 10.1128/iai.12.1.211-220.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatch T. P. Utilization of L-cell nucleoside triphosphates by Chlamydia psittaci for ribonucleic acid synthesis. J Bacteriol. 1975 May;122(2):393–400. doi: 10.1128/jb.122.2.393-400.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones T. C., Yeh S., Hirsch J. G. The interaction between Toxoplasma gondii and mammalian cells. I. Mechanism of entry and intracellular fate of the parasite. J Exp Med. 1972 Nov 1;136(5):1157–1172. doi: 10.1084/jem.136.5.1157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kellogg K. R., Horoschak K. D., Moulder J. W. Toxicity of low and moderate multiplicities of Chlamydia psittaci for mouse fibroblasts (L cells). Infect Immun. 1977 Nov;18(2):531–541. doi: 10.1128/iai.18.2.531-541.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kingsbury D. T., Weiss E. Lack of deoxyribonucleic acid homology between species of the genus Chlamydia. J Bacteriol. 1968 Oct;96(4):1421–1423. doi: 10.1128/jb.96.4.1421-1423.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuo C. C., Grayston T. Interaction of Chlamydia trachomatis organisms and HeLa 229 cells. Infect Immun. 1976 Apr;13(4):1103–1109. doi: 10.1128/iai.13.4.1103-1109.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuo C. C., Wang S. P., Grayston J. T. Effect of polycations, polyanions and neuraminidase on the infectivity of trachoma-inclusin conjunctivitis and lymphogranuloma venereum organisms HeLa cells: sialic acid residues as possible receptors for trachoma-inclusion conjunction. Infect Immun. 1973 Jul;8(1):74–79. doi: 10.1128/iai.8.1.74-79.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LITWIN J. The growth cycle of the psittacosis group of micro-organisms. J Infect Dis. 1959 Sep-Oct;105:129–160. doi: 10.1093/infdis/105.2.129. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moulder J. W., Hatch T. P., Byrne G. I., Kellogg K. R. Immediate toxicity of high multiplicities of Chlamydia psittaci for mouse fibroblasts (L cells). Infect Immun. 1976 Jul;14(1):277–289. doi: 10.1128/iai.14.1.277-289.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Narita T., Manire G. P. Protein-carbohydrate-lipid complex isolated from the cell envelopes of Chlamydia psittaci in alkaline buffer and ethylenediaminetetraacetate. J Bacteriol. 1976 Jan;125(1):308–316. doi: 10.1128/jb.125.1.308-316.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Narita T., Wyrick P. B., Manire G. P. Effect of alkali on the structure of cell envelopes of Chlamydia psittaci elementary bodies. J Bacteriol. 1976 Jan;125(1):300–307. doi: 10.1128/jb.125.1.300-307.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schachter J., Meyer K. F. Lymphogranuloma venereum. II. Characterization of some recently isolated strains. J Bacteriol. 1969 Sep;99(3):636–638. doi: 10.1128/jb.99.3.636-638.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stossel T. P. Phagocytosis: recognition and ingestion. Semin Hematol. 1975 Jan;12(1):83–116. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamura A., Manire G. P. Hemagglutinin in cell walls of Chlamydia psittaci. J Bacteriol. 1974 Apr;118(1):144–148. doi: 10.1128/jb.118.1.144-148.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tribby I. I. Cell Wall Synthesis by Chlamydia psittaci Growing in L Cells. J Bacteriol. 1970 Dec;104(3):1176–1188. doi: 10.1128/jb.104.3.1176-1188.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


