Abstract
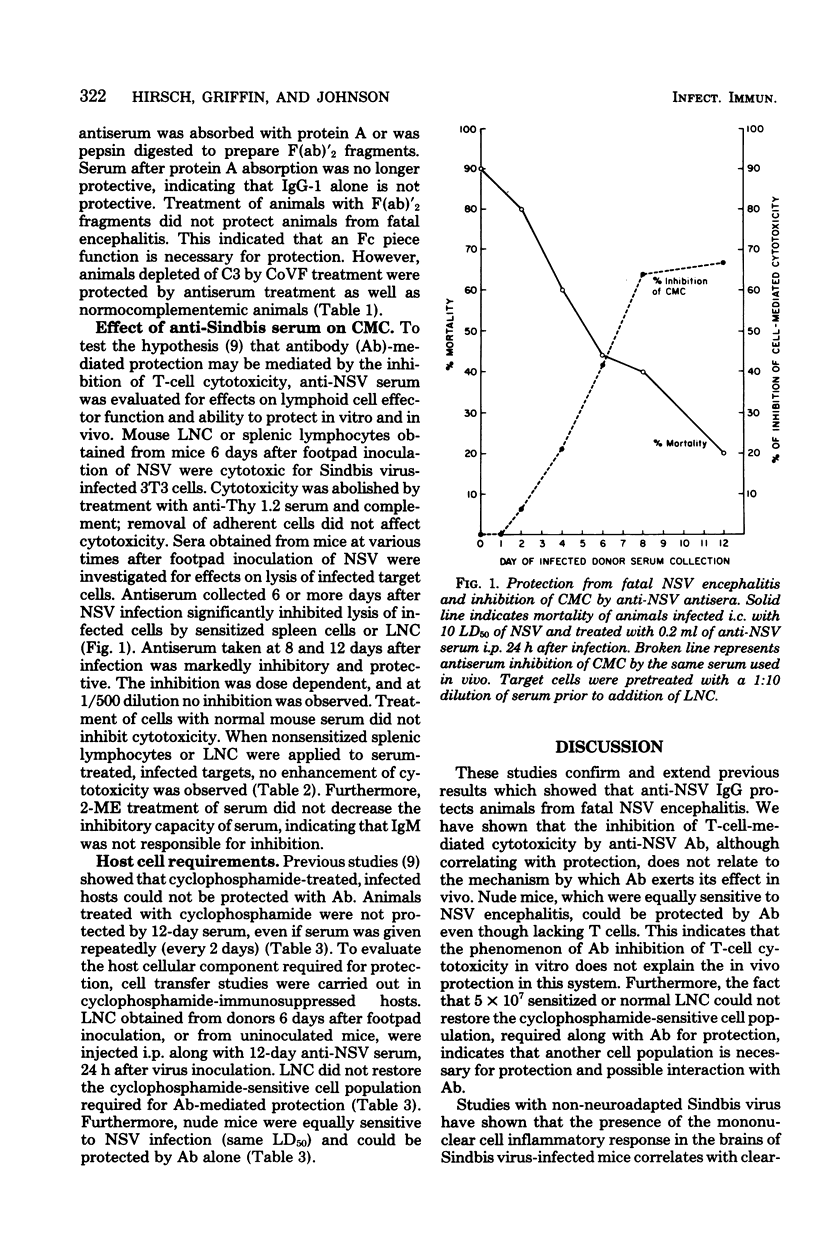
Transfer of anti-Sindbis virus serum, obtained from peripherally inoculated donors, protected mice from an otherwise fatal intracerebral infection with neuroadapted Sindbis virus (NSV). F(ab)'2 preparations of serum were not protective, indicating that the Fc piece of immunoglobulin G was important. Complement-depleted animals were protected with anti-NSV serum, ruling out as essential the complement-fixing function of the Fc piece. The presence of protective antibody correlated with the ability of serum to inhibit T-cell cytotoxicity. However, experiments using athymic nude mice showed that T cells played no role in killing the mice since the 50% lethal dose was the same as that in normal BALB/c mice, and that T cells were not required for protection since athymic nude mice were protected with antibody alone. Cyclophosphamide treatment of NSV-infected mice ablated the protective capacity of anti-NSV serum. Therefore, a non-T cell, cyclophosphamide-sensitive cell was required for antibody-mediated protection.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blanden R. V., Mims C. A. Macrophage activation in mice infected with ectromelia or lymphocytic choriomeningitis viruses. Aust J Exp Biol Med Sci. 1973 Jun;51(3):393–398. doi: 10.1038/icb.1973.35. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böyum A. Isolation of leucocytes from human blood. Further observations. Methylcellulose, dextran, and ficoll as erythrocyteaggregating agents. Scand J Clin Lab Invest Suppl. 1968;97:31–50. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ennis F. A., Martin W. J., Verbonitz M. W., Butchko G. M. Specificity studies on cytotoxic thymus-derived lymphocytes reactive with influenza virus-infected cells: evidence for dual recognition of H-2 and viral hemagglutinin antigens. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Jul;74(7):3006–3010. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.7.3006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuson E. W., Whitten H. D., Ayers R. D., Lamon E. W. Antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity by human lymphocytes. I. Comparison of IgM- and IgG-induced cytotoxicity. J Immunol. 1978 May;120(5):1726–1732. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorini G., Medgyesi G. A., Doria G. Heterogeneity of mouse myeloma gamma G globulins as revealed by enzymatic proteolysis. J Immunol. 1969 Nov;103(5):1132–1142. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg S. B., Criswell B. S., Six H. R., Couch R. B. Lymphocyte cytotoxicity to influenza virus-infected cells: response to vaccination and virus infection. Infect Immun. 1978 Jun;20(3):640–645. doi: 10.1128/iai.20.3.640-645.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffin D. E., Johnson R. T. Cellular immune response to viral infection: in vitro studies of lymphocytes from mice infected with Sindbis virus. Cell Immunol. 1973 Dec;9(3):426–434. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(73)90057-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffin D. E., Johnson R. T. Role of the immune response in recovery from Sindbis virus encephalitis in mice. J Immunol. 1977 Mar;118(3):1070–1075. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffin D. E. Role of the immune response in age-dependent resistance of mice to encephalitis due to Sindbis virus. J Infect Dis. 1976 Apr;133(4):456–464. doi: 10.1093/infdis/133.4.456. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirsch R. L., Griffin D. E., Winkelstein J. A. The effect of complement depletion on the course of Sindbis virus infection in mice. J Immunol. 1978 Oct;121(4):1276–1278. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson R. T., McFarland H. F., Levy S. E. Age-dependent resistance to viral encephalitis: studies of infections due to Sindbis virus in mice. J Infect Dis. 1972 Mar;125(3):257–262. doi: 10.1093/infdis/125.3.257. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jonsson S., Kronvall G. The use of protein A-containing Staphylococcus aureus as a solid phase anti-IgG reagent in radioimmunoassays as exemplified in the quantitation of alpha-fetoprotein in normal human adult serum. Eur J Immunol. 1974 Jan;4(1):29–33. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830040108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kronvall G., Grey H. M., Williams R. C., Jr Protein A reactivity with mouse immunoglobulins. Structural relationship between some mouse and human immunoglobulins. J Immunol. 1970 Nov;105(5):1116–1123. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macfarlan R. I., Burns W. H., White D. O. Two cytotoxic cells in peritoneal cavity of virus-infected mice: antibody-dependent macrophages and nonspecific killer cells. J Immunol. 1977 Nov;119(5):1569–1574. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McFarland H. F., Griffin D. E., Johnson R. T. Specificity of the inflammatory response in viral encephalitis. I. Adoptive immunization of immunosuppressed mice infected with Sindbis virus. J Exp Med. 1972 Aug 1;136(2):216–226. doi: 10.1084/jem.136.2.216. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McFarland H. F. In vitro studies of cell-mediated immunity in an acute viral infection. J Immunol. 1974 Jul;113(1):173–180. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oldstone M. B. Virus neutralization and virus-induced immune complex disease. Virus-antibody union resulting in immunoprotection or immunologic injury--two sides of the same coin. Prog Med Virol. 1975;19:84–119. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reinarz A. B., Broome M. G., Sagik B. P. Age-dependent resistance of mice to sindbis virus infection: viral replication as a function of host age. Infect Immun. 1971 Feb;3(2):268–273. doi: 10.1128/iai.3.2.268-273.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shin H. S., Gewurz H., Snyderman R. Reaction of a cobra venom factor with guinea pig complement and generation of an activity chemotactic for polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1969 May;131(1):203–207. doi: 10.3181/00379727-131-33840. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vassar P. S., Levy E. M., Brooks D. E. Studies on the electrophoretic separability of B and T human lymphocytes. Cell Immunol. 1976 Feb;21(2):257–271. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(76)90055-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welsh R. M., Jr Cytotoxic cells induced during lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus infection of mice. I. Characterization of natural killer cell induction. J Exp Med. 1978 Jul 1;148(1):163–181. doi: 10.1084/jem.148.1.163. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



