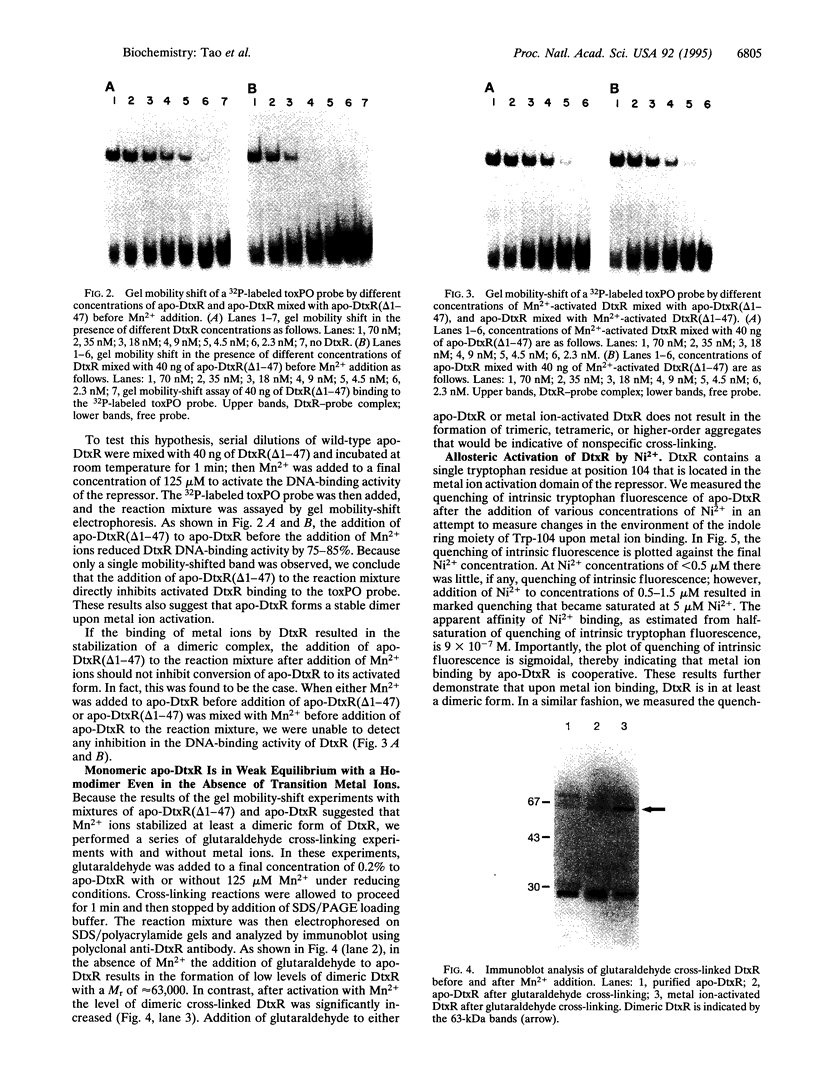
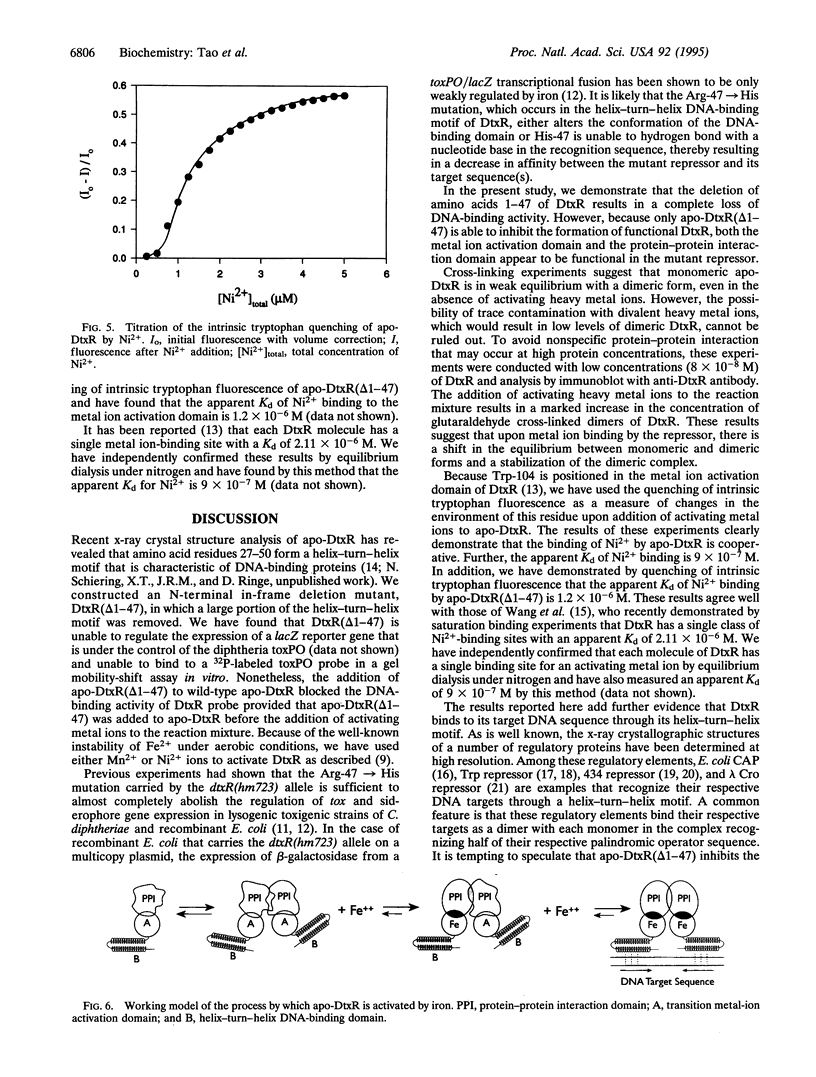
Abstract
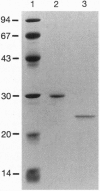
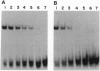
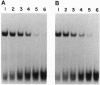
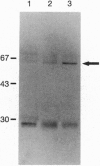
The diphtheria tox repressor (DtxR) is a transition metal ion-dependent regulatory element that controls the expression of diphtheria toxin and several genes involved in the synthesis of siderophores in Corynebacterium diphtheriae. In the presence of transition metal ions apo-DtxR becomes activated and specifically binds to its target DNA sequences. We demonstrate by glutaraldehyde cross-linking that monomeric apo-DtxR is in weak equilibrium with a dimeric form and that upon addition of activating metal ions to the reaction mixture a dimeric complex is stabilized. Addition of the DNA-binding-defective mutant apo-DtxR(delta 1-47) to apo-DtxR in the absence of transition metal ions inhibits conversion of the apo-repressor to its activated DNA-binding form. We also show that the binding of Ni2+ to both apo-DtxR and apo-DtxR(delta 1-47) is cooperative and that upon ion binding there is a conformational change in the environment of the indole ring moiety of Trp-104. For the wild-type repressor the consequences of this conformational change include a shift in equilibrium toward dimer formation and activation of target DNA binding by the repressor. We conclude that the formation of DtxR homodimers is mediated through a protein-protein interaction domain that is also activated on metal ion binding.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aggarwal A. K., Rodgers D. W., Drottar M., Ptashne M., Harrison S. C. Recognition of a DNA operator by the repressor of phage 434: a view at high resolution. Science. 1988 Nov 11;242(4880):899–907. doi: 10.1126/science.3187531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson J. E., Ptashne M., Harrison S. C. Structure of the repressor-operator complex of bacteriophage 434. 1987 Apr 30-May 6Nature. 326(6116):846–852. doi: 10.1038/326846a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson W. F., Ohlendorf D. H., Takeda Y., Matthews B. W. Structure of the cro repressor from bacteriophage lambda and its interaction with DNA. Nature. 1981 Apr 30;290(5809):754–758. doi: 10.1038/290754a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyd J. M., Hall K. C., Murphy J. R. DNA sequences and characterization of dtxR alleles from Corynebacterium diphtheriae PW8(-), 1030(-), and C7hm723(-). J Bacteriol. 1992 Feb;174(4):1268–1272. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.4.1268-1272.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyd J., Oza M. N., Murphy J. R. Molecular cloning and DNA sequence analysis of a diphtheria tox iron-dependent regulatory element (dtxR) from Corynebacterium diphtheriae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Aug;87(15):5968–5972. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.15.5968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brennan R. G., Matthews B. W. The helix-turn-helix DNA binding motif. J Biol Chem. 1989 Feb 5;264(4):1903–1906. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKay D. B., Steitz T. A. Structure of catabolite gene activator protein at 2.9 A resolution suggests binding to left-handed B-DNA. Nature. 1981 Apr 30;290(5809):744–749. doi: 10.1038/290744a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otwinowski Z., Schevitz R. W., Zhang R. G., Lawson C. L., Joachimiak A., Marmorstein R. Q., Luisi B. F., Sigler P. B. Crystal structure of trp repressor/operator complex at atomic resolution. Nature. 1988 Sep 22;335(6188):321–329. doi: 10.1038/335321a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiering N., Tao X., Murphy J. R., Petsko G. A., Ringe D. Crystallization and preliminary X-ray studies of the diphtheria Tox repressor from Corynebacterium diphtheriae. J Mol Biol. 1994 Dec 16;244(5):654–656. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1994.1760. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmitt M. P., Holmes R. K. Characterization of a defective diphtheria toxin repressor (dtxR) allele and analysis of dtxR transcription in wild-type and mutant strains of Corynebacterium diphtheriae. Infect Immun. 1991 Nov;59(11):3903–3908. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.11.3903-3908.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmitt M. P., Holmes R. K. Cloning, sequence, and footprint analysis of two promoter/operators from Corynebacterium diphtheriae that are regulated by the diphtheria toxin repressor (DtxR) and iron. J Bacteriol. 1994 Feb;176(4):1141–1149. doi: 10.1128/jb.176.4.1141-1149.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmitt M. P., Holmes R. K. Iron-dependent regulation of diphtheria toxin and siderophore expression by the cloned Corynebacterium diphtheriae repressor gene dtxR in C. diphtheriae C7 strains. Infect Immun. 1991 Jun;59(6):1899–1904. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.6.1899-1904.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmitt M. P., Twiddy E. M., Holmes R. K. Purification and characterization of the diphtheria toxin repressor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Aug 15;89(16):7576–7580. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.16.7576. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tai S. P., Krafft A. E., Nootheti P., Holmes R. K. Coordinate regulation of siderophore and diphtheria toxin production by iron in Corynebacterium diphtheriae. Microb Pathog. 1990 Oct;9(4):267–273. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(90)90015-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tao X., Boyd J., Murphy J. R. Specific binding of the diphtheria tox regulatory element DtxR to the tox operator requires divalent heavy metal ions and a 9-base-pair interrupted palindromic sequence. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jul 1;89(13):5897–5901. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.13.5897. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tao X., Murphy J. R. Binding of the metalloregulatory protein DtxR to the diphtheria tox operator requires a divalent heavy metal ion and protects the palindromic sequence from DNase I digestion. J Biol Chem. 1992 Oct 25;267(30):21761–21764. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tao X., Murphy J. R. Cysteine-102 is positioned in the metal binding activation site of the Corynebacterium diphtheriae regulatory element DtxR. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Sep 15;90(18):8524–8528. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.18.8524. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tao X., Murphy J. R. Determination of the minimal essential nucleotide sequence for diphtheria tox repressor binding by in vitro affinity selection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Sep 27;91(20):9646–9650. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.20.9646. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang Z., Schmitt M. P., Holmes R. K. Characterization of mutations that inactivate the diphtheria toxin repressor gene (dtxR). Infect Immun. 1994 May;62(5):1600–1608. doi: 10.1128/iai.62.5.1600-1608.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang R. G., Joachimiak A., Lawson C. L., Schevitz R. W., Otwinowski Z., Sigler P. B. The crystal structure of trp aporepressor at 1.8 A shows how binding tryptophan enhances DNA affinity. Nature. 1987 Jun 18;327(6123):591–597. doi: 10.1038/327591a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]