Abstract
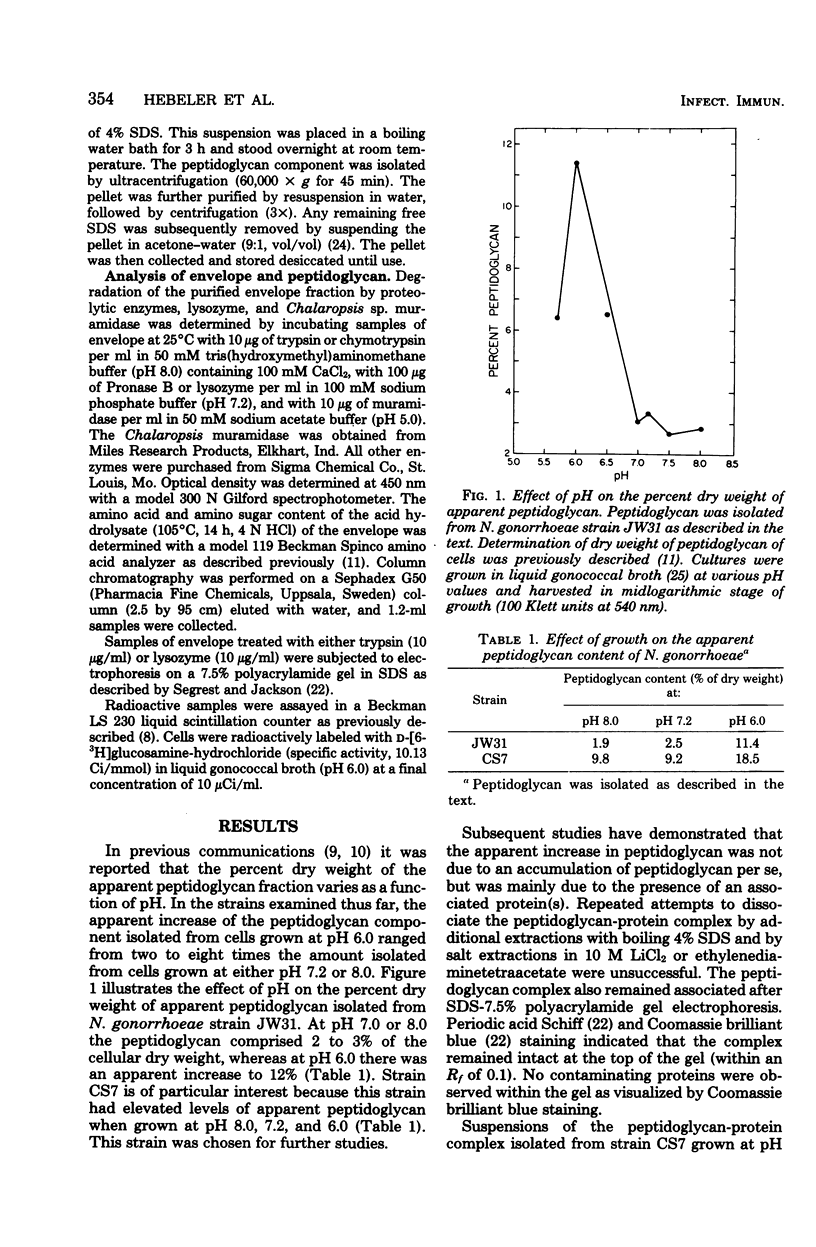
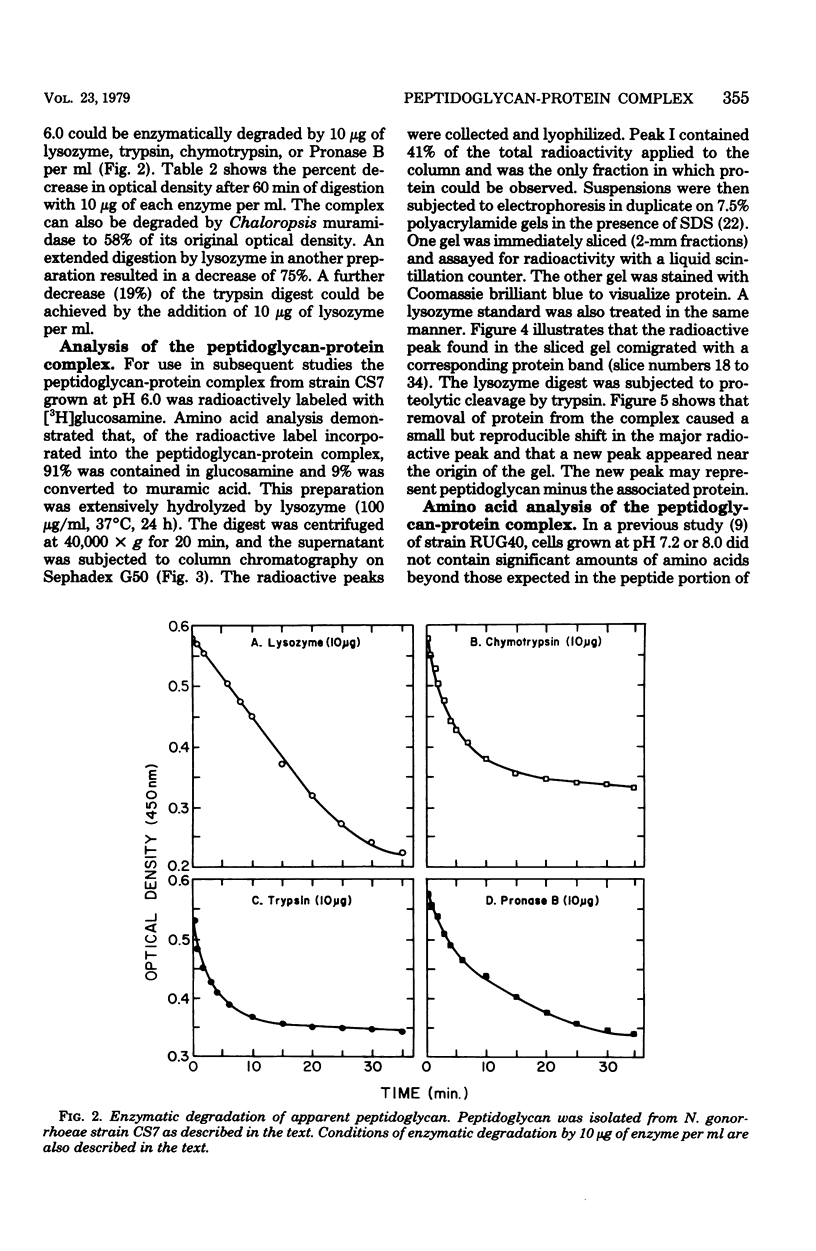
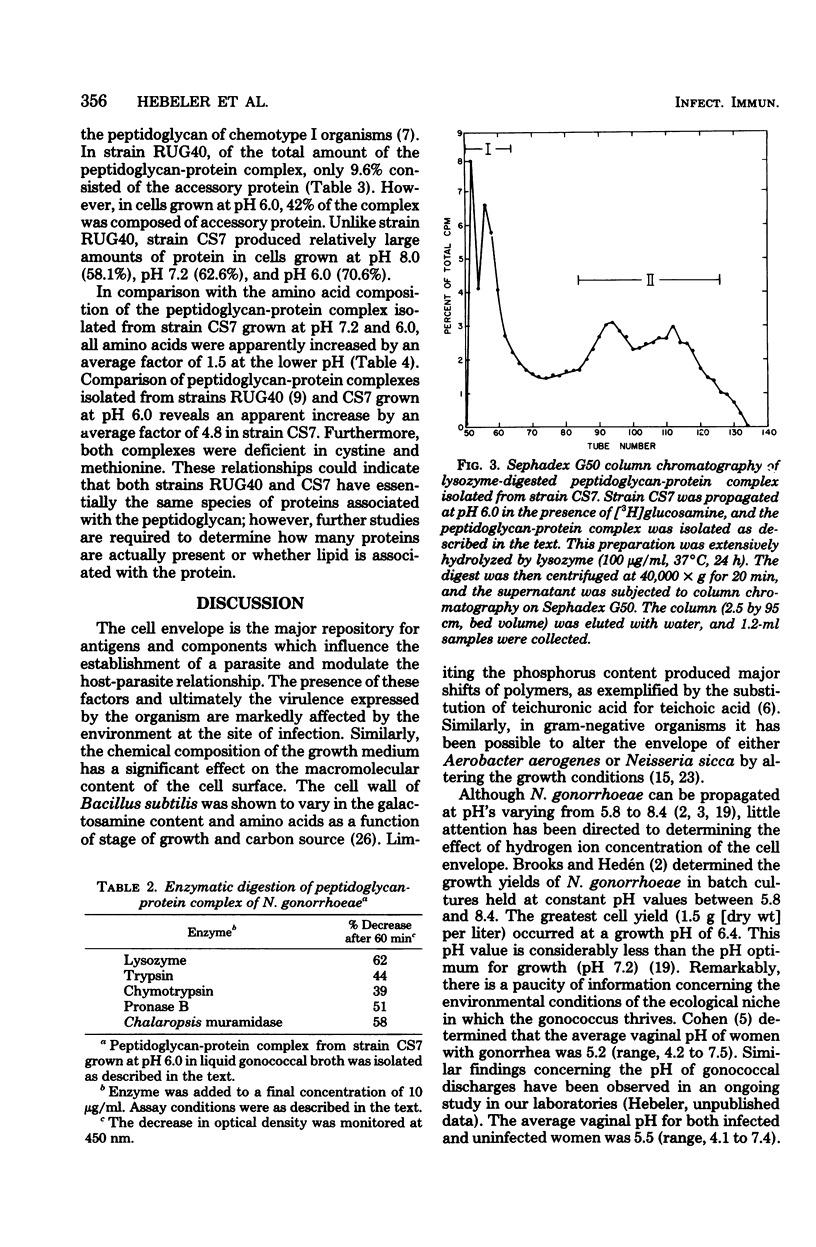
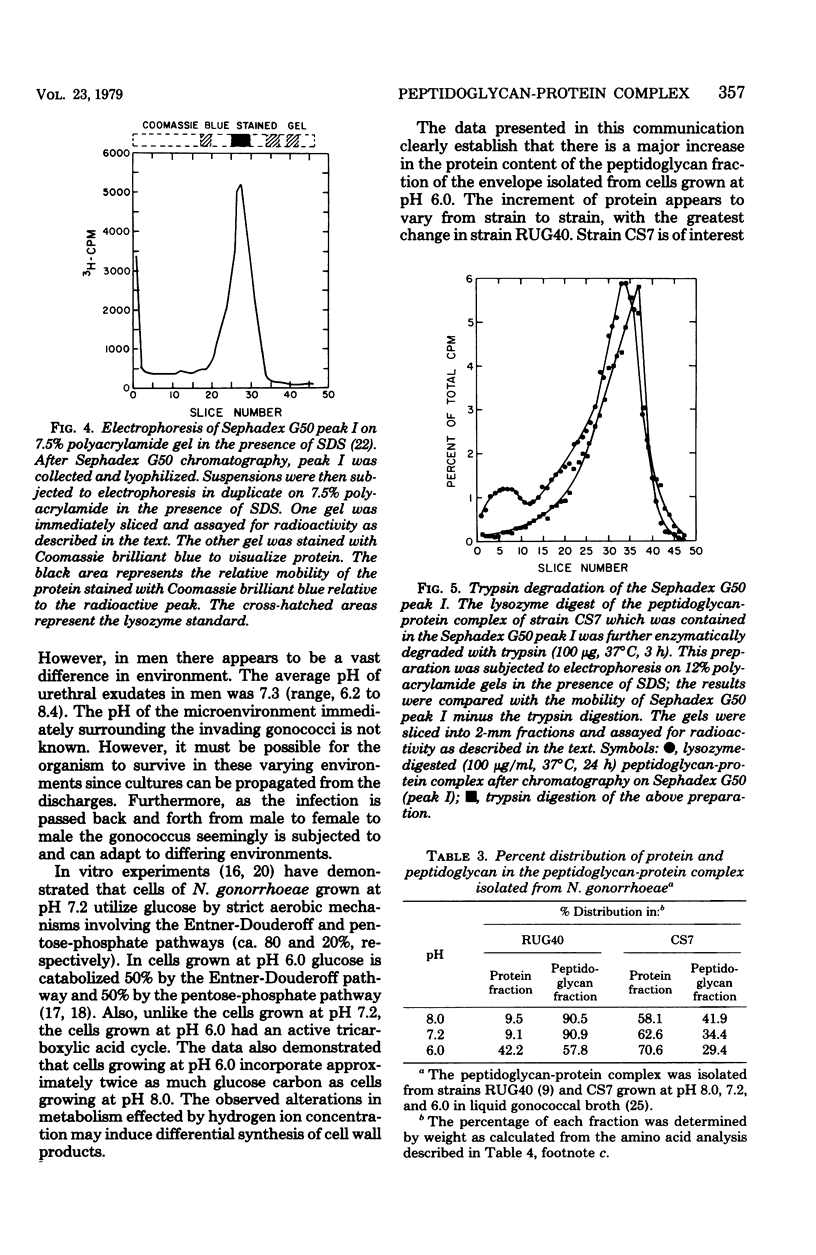
Treatment of cells grown to exponential phase with 4% sodium dodecyl sulfate for 3 h at 100 degrees C resulted in solubilization of all cellular components except for peptidoglycan. In most strains, cells cultured in liquid gonococcal broth at pH 7.2 yielded a peptidoglycan composed primarily of N-acetylmuramic acid N-acetylglucosamine, alanine, glutamic acid, and diaminopimelic acid in a molar ratio of 1:1:2:1:1. The peptidoglycan in these cells accounted for 1 to 2% (dry weight) of the cells. However, in cells cultured at pH 6.0, the dry weight of peptidoglycan increased to 4 to 13%. Preliminary investigations indicated that the apparent increase in weight is strain dependent and is due in part to associated protein(s). Neisseria gonorrhoeae strain CS7 had elevated amounts of protein associated with the peptidoglycan regardless of growth pH. The peptidoglycan-protein complex could not be dissociated by additional extraction with sodium dodecyl sulfate, 10 M LiCl2, or ethylenediaminetetraacetate or by 7.5% polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. The complex could be degraded by lysozyme, trypsin, chymotrypsin, Pronase B, and Chalaropsis sp. muramidase.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Braun V., Bosch V. Sequence of the murein-lipoprotein and the attachment site of the lipid. Eur J Biochem. 1972 Jun 23;28(1):51–69. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1972.tb01883.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brookes R., Hedén C. G. Dense cultures of Neisseria gonorrhoeae in liquid medium. Appl Microbiol. 1967 Mar;15(2):219–223. doi: 10.1128/am.15.2.219-223.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brookes R., Sikyta B. Influence of pH on the growth characteristics of Neisseria gonorrhoeae in continuous culture. Appl Microbiol. 1967 Mar;15(2):224–227. doi: 10.1128/am.15.2.224-227.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen L. Influence of pH on vaginal discharges. Br J Vener Dis. 1969 Sep;45(3):241–247. doi: 10.1136/sti.45.3.241. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellwood D. C., Tempest D. W. Control of teichoic acid and teichuronic acid biosyntheses in chemostat cultures of Bacillus subtilis var. niger. Biochem J. 1969 Jan;111(1):1–5. doi: 10.1042/bj1110001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghuysen J. M. Use of bacteriolytic enzymes in determination of wall structure and their role in cell metabolism. Bacteriol Rev. 1968 Dec;32(4 Pt 2):425–464. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hebeler B. H., Chatterjee A. N., Young F. E. Regulation of the bacterial cell wall: effect of antibiotics on lipid biosynthesis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1973 Sep;4(3):346–353. doi: 10.1128/aac.4.3.346. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hebeler B. H., Morse S. A., Wong W., Young F. E. Evidence for peptidoglycan-associated protein(s) in Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 Apr 14;81(3):1011–1017. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(78)91451-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hebeler B. H., Young F. E. Chemical composition and turnover of peptidoglycan in Neisseria gonorrhoeae. J Bacteriol. 1976 Jun;126(3):1180–1185. doi: 10.1128/jb.126.3.1180-1185.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herbold D. R., Glaser L. Bacillus subtilis N-acetylmuramic acid L-alanine amidase. J Biol Chem. 1975 Mar 10;250(5):1676–1682. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston K. H., Gotschlich E. C. Isolation and characterization of the outer membrane of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. J Bacteriol. 1974 Jul;119(1):250–257. doi: 10.1128/jb.119.1.250-257.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston K. H., Holmes K. K., Gotschlich E. C. The serological classification of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. I. Isolation of the outer membrane complex responsible for serotypic specificity. J Exp Med. 1976 Apr 1;143(4):741–758. doi: 10.1084/jem.143.4.741. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonald I. J., Adams G. A. Influence of cultural conditions on the lipopolysaccharide composition of Neisseria sicca. J Gen Microbiol. 1971 Feb;65(2):201–207. doi: 10.1099/00221287-65-2-201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morse S. A., Hebeler B. H. Effect of pH on the growth and glucose metabolism of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Infect Immun. 1978 Jul;21(1):87–95. doi: 10.1128/iai.21.1.87-95.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morse S. A., Stein S., Hines J. Glucose metabolism in Neisseria gonorrhoeae. J Bacteriol. 1974 Nov;120(2):702–714. doi: 10.1128/jb.120.2.702-714.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novotny P., Short J. A., Walker P. D. An electron-microscope study of naturally occurring and cultured cells of Neisseria Gonorrhoeae. J Med Microbiol. 1975 Aug;8(3):413–427. doi: 10.1099/00222615-8-3-413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tempest D. W., Ellwood D. C. The influence of growth conditions on the composition of some cell wall components of Aerobacter aerogenes. Biotechnol Bioeng. 1969 Sep;11(5):775–783. doi: 10.1002/bit.260110507. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Osborn M. The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4406–4412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wegener W. S., Hebeler B. H., Morse S. A. Cell envelope of Neisseria gonorrhoeae: relationship between autolysis in buffer and the hydrolysis of peptidoglycan. Infect Immun. 1977 Oct;18(1):210–219. doi: 10.1128/iai.18.1.210-219.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young F. E. Variation in the chemical composition of the cell walls of Bacillus subtilis during growth in different media. Nature. 1965 Jul 3;207(992):104–105. doi: 10.1038/207104b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



