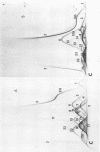
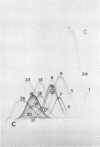
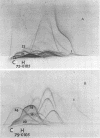
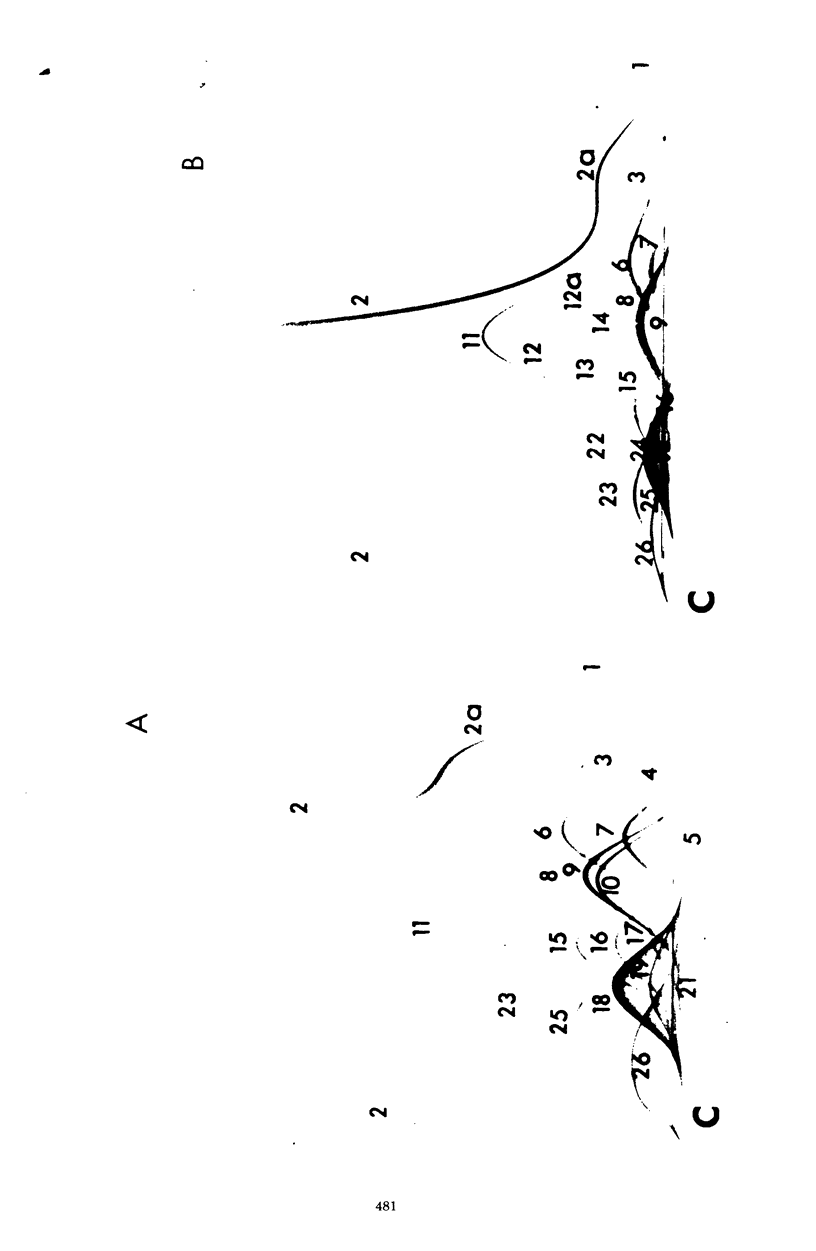
Abstract
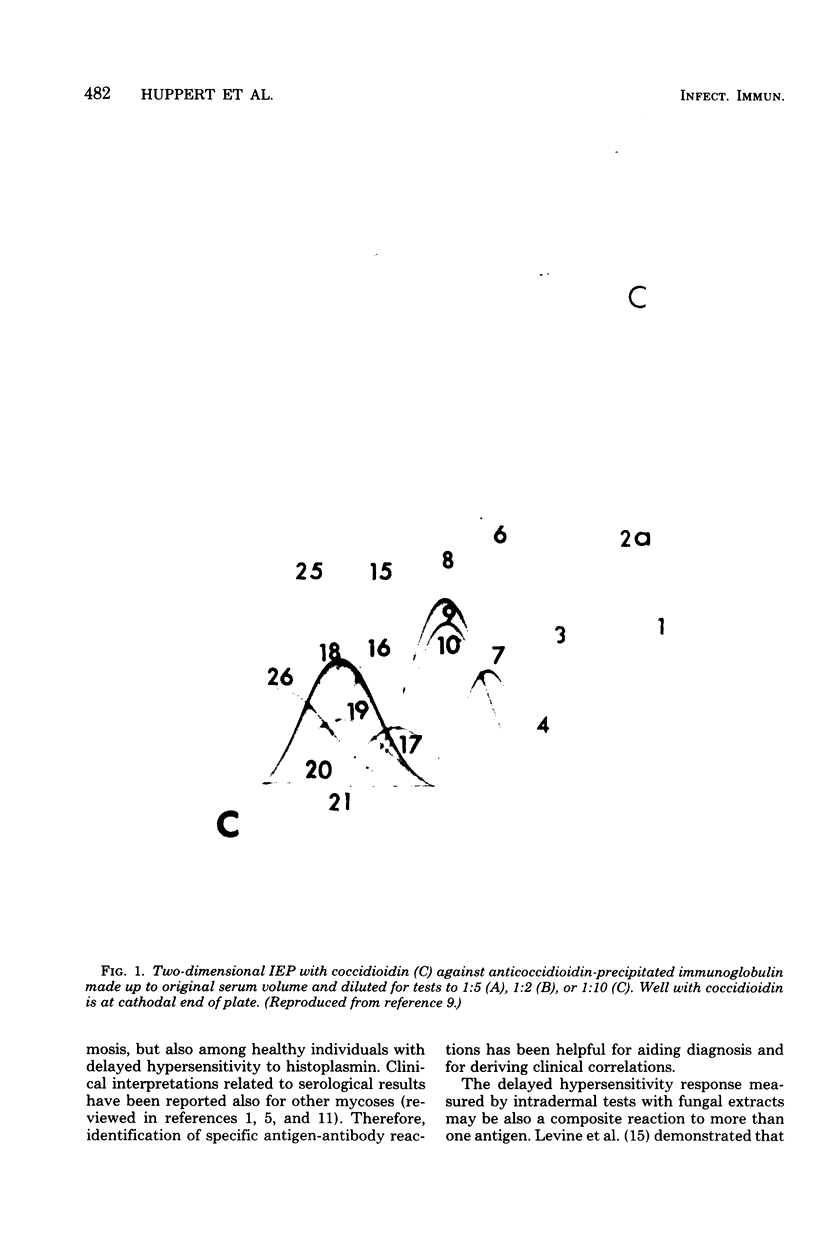
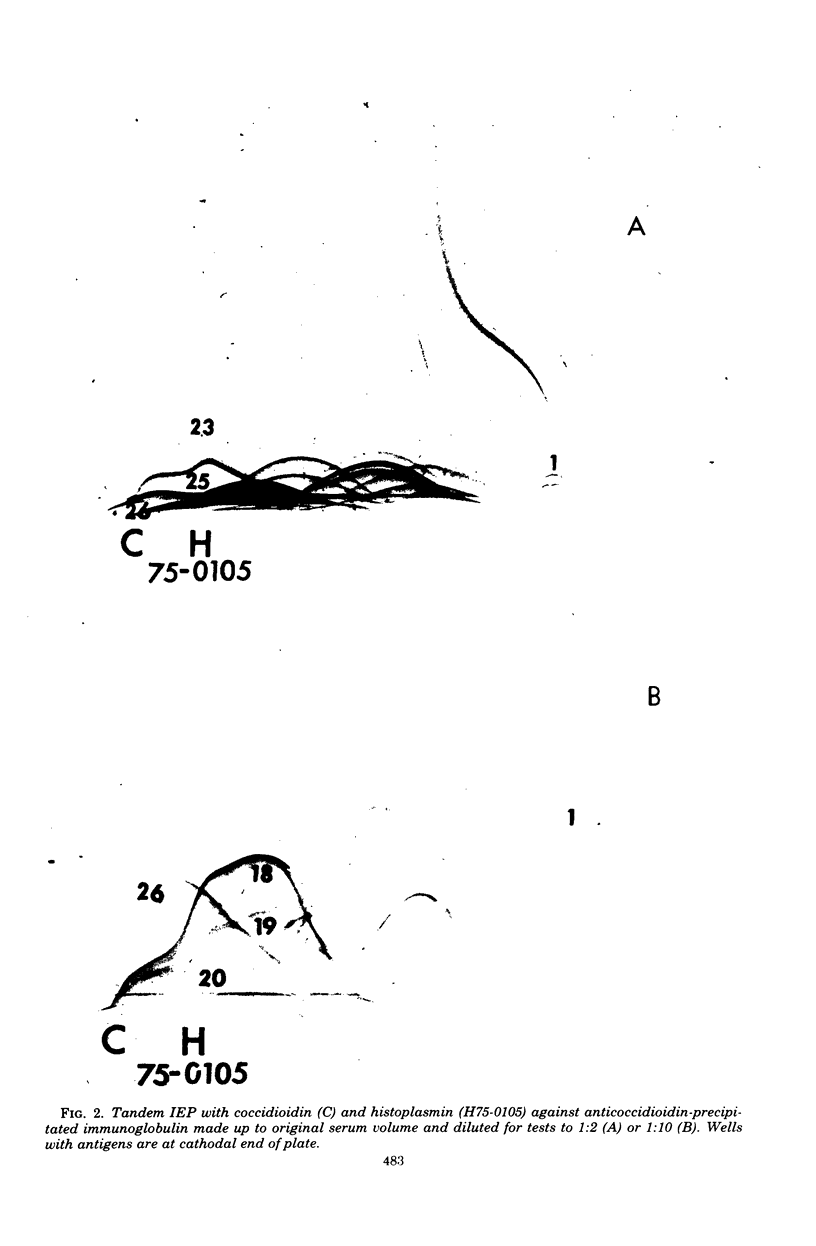
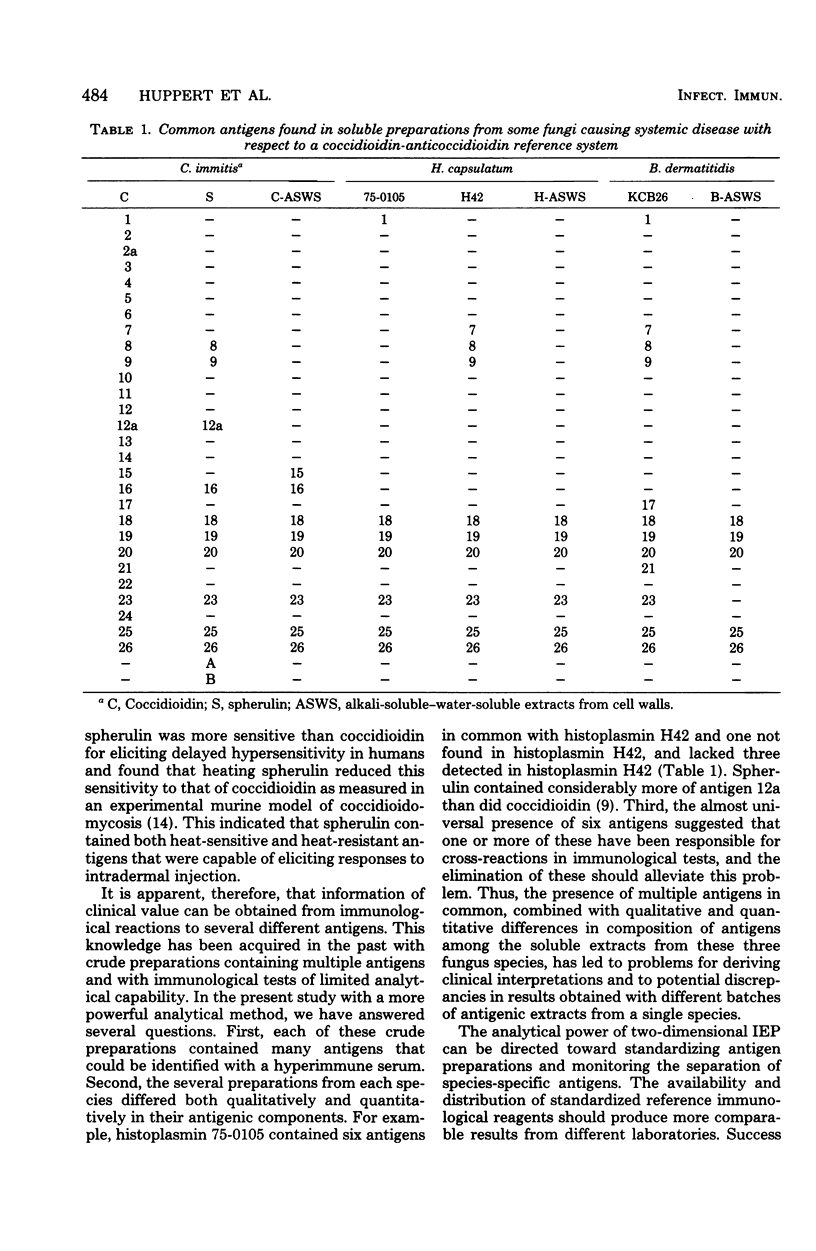
The interpretation of immunological results in systemic mycoses has been complicated by cross-reactions among specimens from patients with blastomycosis, coccidioidomycosis, and histoplasmosis. The fungal preparations used in these tests evidently contained one or more antigens in common. Two-dimensional immunoelectrophoresis techniques were used to determine the number of antigens contained in several soluble extracts from Blastomyces dermatitidis and Histoplasma capsulatum that were common with those demonstrable in a coccidiodin-anticoccidioidin reference system. A total of 12 and 10 common antigens were found in preparations from B. dermatitidis and H. capsulatum, respectively. In addition, the crude preparations from each species of fungus exhibited some qualitative and quantitative differences in composition of antigens. Use of two-dimensional immunoelectrophoresis for standardization of fungus extracts, for monitoring separation of species-specific antigens, and for testing humoral antibody response should add further refinement to correlations with clinical disease.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- CAMPBELL C. C. The accuracy of serologic methods in diagnosis. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1960 Aug 27;89:163–177. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1960.tb20139.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chick E. W., Baum G. L., Furcolow M. L., Huppert M., Kaufman L., Pappagianis R. Scientific Assembly statement. The use of skin tests and serologic tests in histoplasmosis, coccidioidomycosis, and blastomycosis, 1973. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1973 Jul;108(1):156–159. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1973.108.1.156. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox R. A., Best G. K. Cell wall composition of two strains of Blastomyces dermatitidis exhibiting differences in virulence for mice. Infect Immun. 1972 Apr;5(4):449–453. doi: 10.1128/iai.5.4.449-453.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HEINER D. C. Diagnosis of histoplasmosis using precipitin reactions in agargel. Pediatrics. 1958 Oct;22(4 Pt 1):616–627. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huppert M., Spratt N. S., Vukovich K. R., Sun S. H., Rice E. H. Antigenic analysis of coccidioidin and spherulin determined by two-dimensional immunoelectrophoresis. Infect Immun. 1978 May;20(2):541–551. doi: 10.1128/iai.20.2.541-551.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan P., Graybill J. R., Thor D. Disseminated histoplasmosis followed by disseminated coccidioidomycosis. Chest. 1977 Aug;72(2):238–241. doi: 10.1378/chest.72.2.238. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufman L., McLaughlin D. W., Clark M. J., Blumer S. Specific immunodiffusion test for blastomycosis. Appl Microbiol. 1973 Sep;26(3):244–247. doi: 10.1128/am.26.3.244-247.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine H. B., Cobb J. M., Scalarone G. M. Spherule coccidioidin in delayed dermal sensitivity reactions of experimental animals. Sabouraudia. 1969 Feb;7(1):20–32. doi: 10.1080/00362177085190051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine H. B., Gonzalez-Ochoa A., Ten Eyck D. R. Dermal sensitivity to Coccidioides immitis. A comparison of responses elicited in man by spherulin and coccidioidin. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1973 Mar;107(3):379–386. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1973.107.3.379. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PAPPAGIANIS D., LINDSEY N. J., SMITH C. E., SAITO M. T. ANTIBODIES IN HUMAN COCCIDIOIDOMYCOSIS: IMMUNOELECTROPHORETIC PROPERTIES. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1965 Jan;118:118–122. doi: 10.3181/00379727-118-29773. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SMITH C. E., SAITO M. T. Histoplasmin sensitivity and coccidioidal infection; occurrence of cross-reaction. Am J Public Health Nations Health. 1949 Jun;39(6):722–736. doi: 10.2105/ajph.39.6.722. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawaki Y., Huppert M., Bailey J. W., Yagi Y. Patterns of human antibody reactions in coccidioidomycosis. J Bacteriol. 1966 Jan;91(1):422–427. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.1.422-427.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- The current status of serologic, immunologic and skin tests in the diagnosis of pulmonary mycoses. Report of the Committee on Fungus Diseases and Subcommittee on Criteria for Clinical Diagnosis--American College of Chest Physicians. Chest. 1973 Feb;63(2):259–270. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward E. R., Jr, Cox R. A., Schmitt J. A., Jr, Huppert M., Sun S. H. Delayed-type hypersensitivity responses to a cell wall fraction of the mycelial phase of Coccidioides immitis. Infect Immun. 1975 Nov;12(5):1093–1097. doi: 10.1128/iai.12.5.1093-1097.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]