Abstract
The rate and degree of interferon action on mouse embryo (ME), mouse L, and human amnion (WISH) cells were found to be dependent on the cell density. The most precipitous drop in interferon action occurred just below cell confluency. This effect was shown with both vesicular stomatitis virus and Sindbis virus and at both constant and variable input multiplicities of infection. At both "high" and "low" cell densities, cells attached to a surface develop viral resistance faster than suspended cells. These data indicate that either cell contact or close cell proximity is required for maximal interferon activity. These results are discussed in relation to interferon-induced transfer of viral resistance.
Full text
PDF
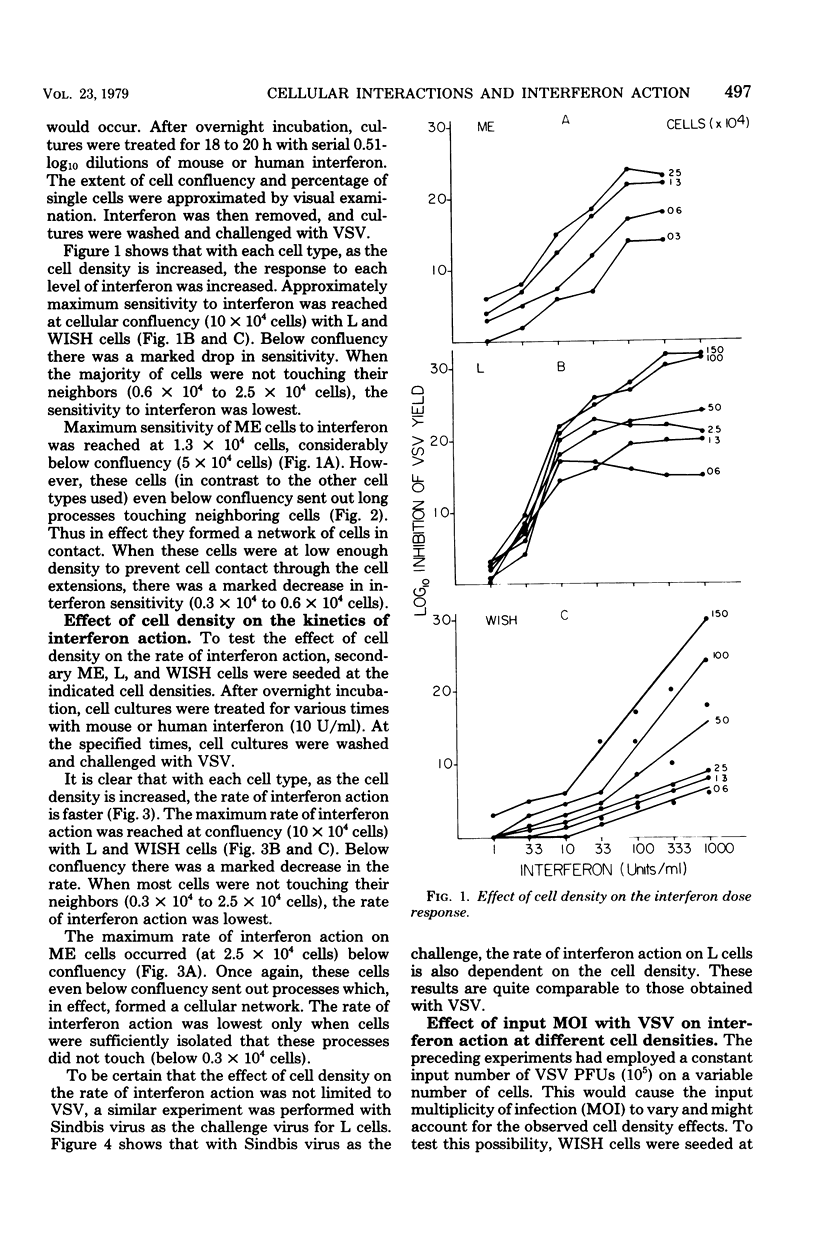

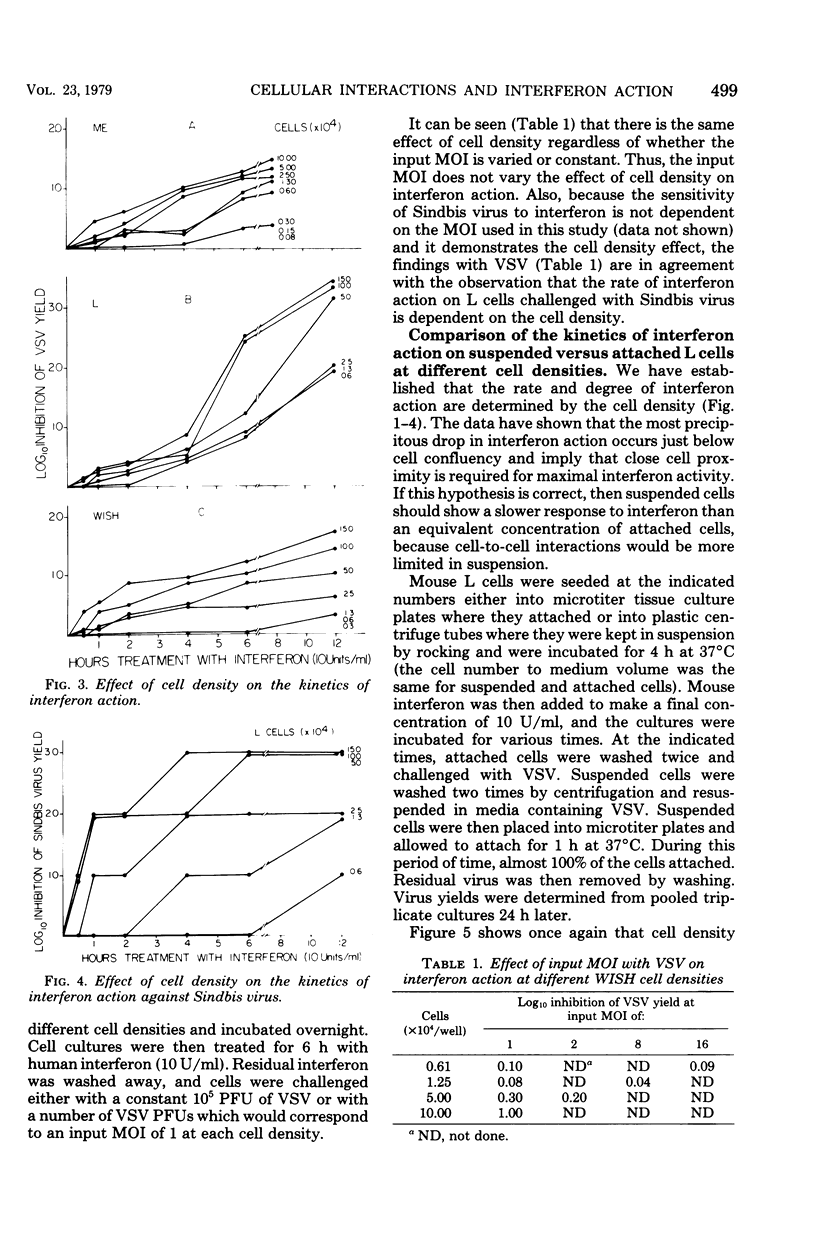
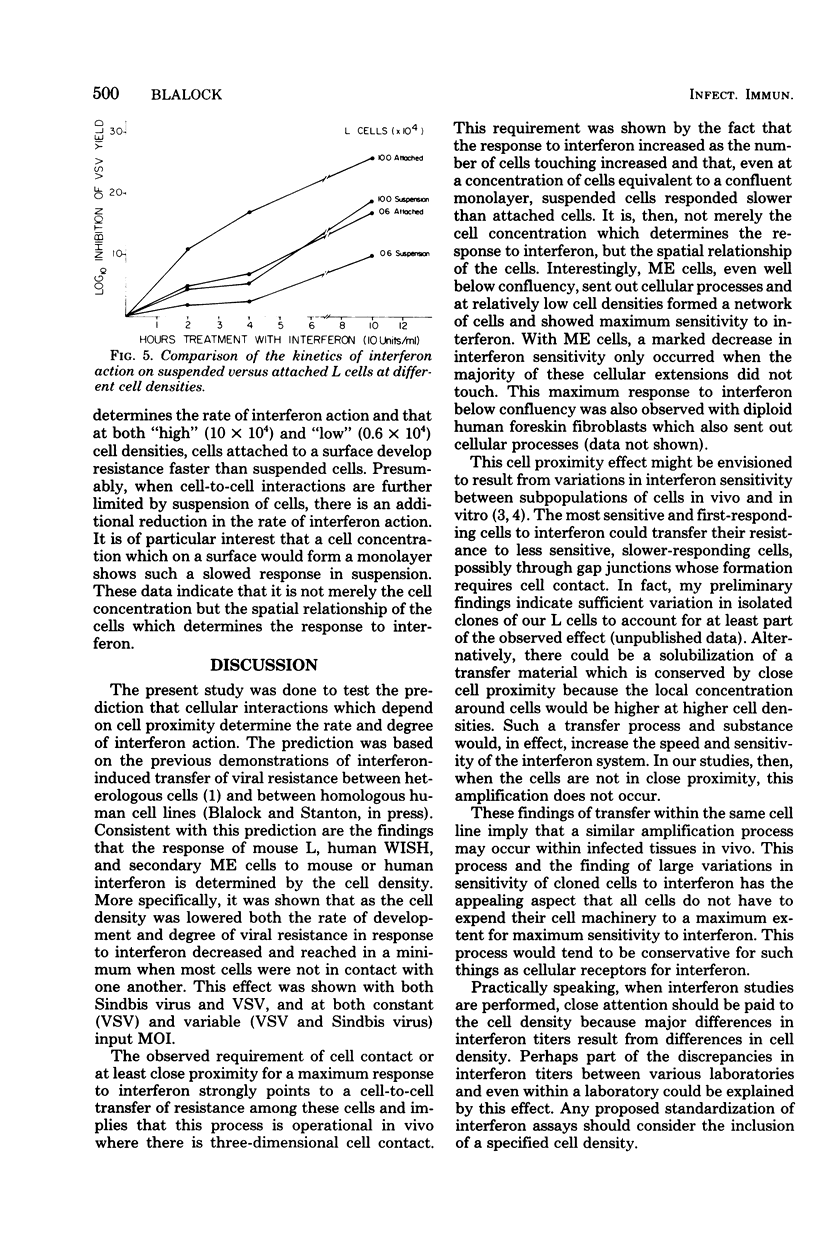

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blalock J. E., Baron S. Interferon-induced transfer of viral resistance between animal cells. Nature. 1977 Sep 29;269(5627):422–425. doi: 10.1038/269422a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CANTELL K., PAUCKER K. Studies on viral interference in two lines of HeLa cells. Virology. 1963 Jan;19:81–87. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(63)90027-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell J. B., Grunberger T., Kochman M. A., White S. L. A microplaque reduction assay for human and mouse interferon. Can J Microbiol. 1975 Aug;21(8):1247–1253. doi: 10.1139/m75-186. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOCKART R. Z., Jr VARIATIONS IN THE ABILITIES OF SEVERAL LINES OF L CELLS TO PRODUCE AND TO BE AFFECTED BY INTERFERON. J Bacteriol. 1965 Jan;89:117–122. doi: 10.1128/jb.89.1.117-122.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossman T. G., Vilcek J. Influence of the rate of cell growth and cell density on interferon action in chick embryo cells. J Virol. 1969 Jul;4(1):7–11. doi: 10.1128/jvi.4.1.7-11.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




