Abstract
Objective
Action potentials and local field potentials (LFPs) recorded in primary motor cortex contain information about the direction of movement. LFPs are assumed to be more robust to signal instabilities than action potentials, which makes LFPs along with action potentials a promising signal source for brain-computer interface applications. Still, relatively little research has directly compared the utility of LFPs to action potentials in decoding movement direction in human motor cortex.
Approach
We conducted intracortical multielectrode recordings in motor cortex of two persons (T2 and [S3]) as they performed a motor imagery task. We then compared the offline decoding performance of LFPs and spiking extracted from the same data recorded across a one-year period in each participant.
Main results
We obtained offline prediction accuracy of movement direction and endpoint velocity in multiple LFP bands, with the best performance in the highest (200–400Hz) LFP frequency band, presumably also containing low-pass filtered action potentials. Cross-frequency correlations of preferred directions and directional modulation index showed high similarity of directional information between action potential firing rates (spiking) and high frequency LFPs (70–400Hz), and increasing disparity with lower frequency bands (0–7, 10–40 and 50–65Hz). Spikes predicted the direction of intended movement more accurately than any individual LFP band, however combined decoding of all LFPs was statistically indistinguishable from spike based performance. As the quality of spiking signals (i.e. signal amplitude) and the number of significantly modulated spiking units decreased, the offline decoding performance decreased 3.6[5.65]%/month (for T2 and [S3] respectively). The decrease in the number of significantly modulated LFP signals and their decoding accuracy followed a similar trend (2.4[2.85]%/month, ANCOVA, p=0.27[0.03]).
Significance
Field potentials provided comparable offline decoding performance to unsorted spikes. Thus, LFPs may provide useful external device control using current human intracortical recording technology. (Clinical trial registration number: NCT00912041)
Keywords: motor control, brain-machine interface, brain-computer interface, intracortical, spikes, local field potential, stability, open-loop, offline decoding, tetraplegia
Introduction
Brain computer interface (BCI) systems based on intracortically derived neural signals offer a promising means to control external devices by decoding intended movement related activity with high temporal and spatial resolution. An advantage of intracortical sensors is their ability to record both action potentials (spikes) and lower frequency local field potentials (LFPs), which may provide multiple, independent information channels to generate commands for applications (Pesaran et al., 2002, Bansal et al., 2012, Andersen et al., 2004). To date, human intracortical BCIs have largely focused on the commands derived from ensembles of spiking neurons (Truccolo et al., 2008). For instance, spike-based pilot stage BCI systems have allowed people with tetraplegia to use a computer for point and click actions and to perform simple actions by controlling assistive technologies (Hochberg et al., 2012, Hochberg et al., 2006, Collinger et al., 2013). Applications for these BCIs may range from a simple cursor control system for people with locked-in syndrome to a rich control signal that allows reach and grasp with a prosthetic limb. However, BCIs for clinical or daily real-world use will be practical only if the system can function reliably every day.
Recording stable spiking activity poses challenges both on a minute-by-minute time scale and longer (hours to years) periods (Dickey et al., 2009, Chestek et al., 2011) first, because electrodes must remain in the proximity of the recorded neurons and second, the electrode’s material characteristics must remain stable. Shifts in the sampled neuronal population and unmodeled changes in spike rate introduce decoding errors and impair neuroprosthetic performance (Perge et al., 2013). This problem might be mitigated by improved sensors, better recording technology, decoding or signal processing techniques (Fraser et al., 2009, Jarosiewicz et al., 2013), adaptive algorithms (Homer et al., 2011, Gurel and Mehring, 2012, Li et al., 2011) or by using LFP signals simultaneously available from intracortical recordings.
Local field potentials (LFPs) in area M1 contain information about voluntary arm movements (O’Leary and Hatsopoulos, 2006), and the offline decoded movement or muscle activity in monkeys appears to approach or even rival the decoding performance of spikes (Bansal et al., 2012, Bansal et al., 2011, Mehring et al., 2003, Rickert et al., 2005, Zhuang et al., 2010a, Flint et al., 2012a, Flint et al., 2012b, Slutzky et al., 2011, Stark and Abeles, 2007). In monkeys, LFP signal power at higher frequencies (>100Hz) demonstrate increased kinematic information and better decoding performance than signal power at lower frequencies (Zhuang et al., 2010b, Bansal et al., 2012) presumably because high frequency LFP signals contain spiking activity (Belitski et al., 2008, Ray et al., 2008a, Liu and Newsome, 2006, Schomburg et al., 2012, Nir et al., 2007), as well as oscillations related to network-level synaptic activity (Buzsaki et al., 2012, Buzsaki and Draguhn, 2004). This suggests that high frequency LFP could be a proxy for the population firing rate (Ray et al., 2008b, Manning et al., 2009, Whittingstall and Logothetis, 2009). In contrast, lower frequency LFPs (<30Hz) might correspond to the activity of a distinct neural population with different tuning properties, and encoding different information (Lashgari et al., 2012). This might provide an additional information channel, beyond spiking, for BCI control. Although the type of information and the stability of motor cortical LFP signals in humans with tetraplegia are unknown, this information is now available by analyzing chronic intracortical multielectrode recordings from people with tetraplegia engaged in the BrainGate pilot clinical trial.
We compared the temporal stability of directional information in LFPs and spiking ensembles obtained from the primary motor cortex (MI) of two people with tetraplegia. The results show that despite several years of paralysis, motor cortical LFPs were functionally modulated in multiple frequency bands during intended movement of the arm or hand. Assessed by continuous trajectory decoding using a Kalman filter and discrete target decoding with a naïve Bayesian classifier, we found that LFPs contained information about intended movement direction similar to spiking. When decoders were recalibrated each day, LFP signals retained offline decoding performance and reliability over time similar to spiking signals, indicating that decoding approaches could benefit from the use of LFPs.
Methods
2.1 Trial participants and dataset
Electrophysiological recordings were collected from two BrainGate clinical trial participants (T2 and [S3], ages 66[56] at the time of the recordings). We analyzed a total of 25 research sessions, 12[14] sessions spanning more than one year in each participant from day 46–467[974–1293] after implantation. Both participants were diagnosed with extensive pontine infarction due to thrombosis of the basilar artery 9[6] years prior to trial recruitment. Both participants were tetraplegic and anarthric. The usual form of communication was through eye movements. This research was conducted with Institutional Review Board (IRB) approval and an Investigational Device Exemption from the U.S. Food and Drug Administration. (Caution: Investigational device. Limited by federal (USA) law to investigational use.) The pilot clinical trial is registered at clinicaltrials.gov/NCT00912041. Detailed description of the BrainGate BCI is presented elsewhere (Simeral et al., 2011).
2.2 Decoder calibration and closed-loop control
The results presented in this paper are based on offline analysis of open and spike-based closed-loop data recorded in the context of the BrainGate pilot clinical trials (Hochberg et al., 2012, Simeral et al., 2011, Hochberg et al., 2006). Participants performed a four direction center-out-and-back target acquisition task (Kim et al., 2008). At the outset of each session, termed the ‘open-loop phase’, a linear mapping was derived between spiking activity and cursor movements (see also section 2.5). Specifically, the participant watched a computer-generated sequence of cursor movements (‘training cursor’) while attempting arm motions that would produce the observed cursor action. Neural firing rates recorded during this attempted arm/hand movement together with the training cursor velocity were used to calibrate a Kalman filter based decoding model (Wu et al., 2006, Malik et al., 2011). Once established, this mapping was used for closed-loop control to convert the participant’s subsequently observed neural firing into real time cursor motion in two dimensions.
Online, closed-loop voluntary control over the neural cursor was tested by a radial-4 center-out-back target acquisition task (Kim et al., 2008). The goal of this task was to move the neural cursor to one of four circularly arranged peripheral targets that were discs on a screen. The cursor was centered on the screen to begin a trial (i.e. cursor movement to a new target), and the participant was asked to direct the cursor to the target (indicated by color change), then direct the cursor back to the center and wait to begin a new trial (Fig. 1A). The results of closed-loop cursor control based on spiking activity has been reported elsewhere (Kim et al., 2008, Perge et al., 2013, Simeral et al., 2011, Hochberg et al., 2006).
Fig. 1. Motor cortical field potentials in humans with tetraplegia are task modulated.
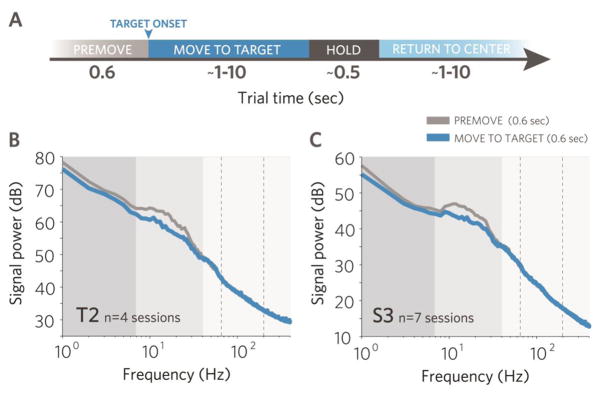
A. Time representation of task. B and C. Data from participants T2 and S3. Signal power decreased in the medium frequency range during movement (∼7–40Hz) more substantially than at lower frequencies (0.3–7Hz). Vertical bands indicate approximate frequency boundaries in the medium frequency range that guided our band selection for this study. Power spectral densities were generated with fast Fourier transform and averaged across significantly modulated channels over four sessions in T2 and seven sessions in S3 (27,000 and [10,000] data segments per figure).
2.3 Signal acquisition
Motor cortical activity was recorded with a 10×10 array of platinum-tipped silicon microelectrodes (1.5 mm length, 400 μm spacing, 96 active electrodes, Blackrock Microsystems, Salt Lake City, Utah) chronically implanted into M1 arm/hand area (Hochberg et al., 2006). Recorded electrical signals were passed externally through a titanium percutaneous connector that was secured to the skull. Cabling (94 cm long) attached to the connector and equipped with a unity-gain isolation stage routed signals to an amplifier, where ‘raw data’ signals were analog filtered (0.3–7500 Hz), digitized at 30kHz sampling rate and optically transferred to a series of computers for further processing, as described previously (Perge et al., 2013, Simeral et al., 2011).
To obtain unsorted spikes (i.e. multiple single unit activity), analog signals from each channel were referenced to the mean of all 96 channels then bandpass filtered at 750–7500Hz. Referencing was used to eliminate large electrical artifacts and improve signal to noise ratio. Times when this filtered voltage signal crossed a 4.5 root-mean-squared threshold triggered the storage of a 1.6-ms long spike waveform. For the offline analysis presented here, no further spike sorting or discrimination in spike shape was performed, thus time stamps of the threshold crossing events, i.e. multiunit spiking activity was used in decoding.
2.4 LFP processing
The same raw data used to obtain spiking was referenced to the mean of all 96 channels, low pass filtered with a 400 Hz cutoff with an 8th order Chebyshev filter (Parks and Burrus, 1987) and down-sampled to 1 kHz. To examine systematic variations of the amplitude spectrum at different frequencies, we computed spectrograms of LFP data segments time aligned to the onset of one of four targets. All spectral analyses were based on time-frequency decomposition using short-term fast Fourier transform with time windows of 300ms, overlaps of 120ms and frequency steps of 1–10Hz (steps of 1Hz for frequencies <10Hz, steps of 3Hz for frequencies <70Hz and steps of 10Hz above 70Hz).
We differentiated five non-overlapping frequency bands of interest (low: <5Hz, medium: 10–40Hz, gamma1: 45–65Hz, gamma2: 70–200Hz, epsilon: 200–400Hz). These frequency intervals were determined based on a characteristic drop of signal power in the ∼10–40Hz frequency range in the average power spectral density when compared between premovement and movement conditions (Fig. 1, arrows). In addition, we apportioned gamma and higher bands (>50Hz) arbitrarily as an additional survey on potential differences between these bands. This was motivated by reports showing that these bands may behave differently (Ray and Maunsell, 2010).
Signal amplitude within each frequency bin of the spectrogram was z-scored (i.e. the mean signal amplitude within the bin across all trials and all times was subtracted from individual trials, and the signal segments were divided by the standard deviation of all of the values). This normalization step was used to bring the different spectral features into the same scale, as cortical field potentials show a 1/f pink-noise like decay of signal power (Henrie and Shapley, 2005, Pesaran et al., 2002). In addition, subtracting the mean also eliminated static (and therefore non-informative) components of the signal such as line noise. Z-scoring gave essentially the same decoding results as normalization by dividing the bin’s value by the average signal amplitude of a 1 sec long premovement (rest) period of that frequency bin. Histograms of spiking activity were similarly z-scored for each recording channel, thus each electrode (channel) provided six signal types: five LFP features and one spike rate feature.
The normalized spectrograms for individual trials within each recording channel served to calculate signal power within the five frequency bands at 0.3–2.3sec following target onset. The preferred direction of a feature on a given recording channel was determined by fitting the trial-to-trial measurements over the four directions with a cosine function. To quantify the strength of directional modulation we calculated a directional modulation index, i.e., the peak-to-peak amplitude of the cosine fit divided by the standard deviation of the error residuals of the fit.
2.5 Offline decoding
To ensure that results are independent of the decoding approach, we used two types of decoders in this study, a naïve Bayesian direction classifier with an assumption of Gaussian distributed data (Chestek et al., 2011) and a velocity-based Kalman filter (Bansal et al., 2011, Zhuang et al., 2010a, Malik et al., 2011). Each decoder was evaluated with five-fold cross validation. Classification performance was evaluated in terms of the percent of target directions that were correctly classified, while the Kalman filter decoding performance was evaluated by the Pearson’s correlation coefficient between estimated and actual cursor velocity both in the horizontal and vertical direction. To simplify presentation, we reported the average of the horizontal and vertical velocity correlation coefficients.
The state-space model for the Kalman filter was:
| (1) |
| (2) |
where represents the velocity of cursor at time tk = kΔt (time bin Δt = 100 ms), zk denotes the features of neural signals at time tk (spectral power of LFP in each frequency band or firing rate in a 300ms window); C is the observation matrix that linearly relates the cursor state to the features of neural signals, A is the state transition matrix that linearly relates the cursor velocity at time tk + 1 to the velocity at time tk; pk ∼ N(0, T) and qk ∼ N(0, W) are the observation and state Gaussian noise respectively with covariance matrices T and W. LFP features and firing rates used in Kalman decoding were computed in a 300ms sliding window with steps of 100ms.
LFP features usually outnumbered measurements or trials (480 LFP features vs. ∼200–300 trials per session), which necessitated feature selection to avoid overfitting. For this purpose, we ranked features according to their individual decoding performance (based on the percent correctly classified movement directions or Pearson’s correlation coefficient) from best to worst then calculated decoding performance starting with the best performing feature and adding features incrementally for decoding. Increasing the number of features in directional classification showed performance improvement that saturated at ∼15 features, with a performance plateau between ∼20–30 features and occasional performance decrease above ∼30 features, in close agreement with non-human primates studies (Bansal et al., 2011). For this reason, we selected the 20 best-performing features in all analyses with directional classification. The results were relatively robust to this choice of feature number. For instance, directional classification using thirty features instead of 20 over the first four research sessions in T2 showed no significant difference at any frequency band or spike (paired t-test, p>0.05).
The same feature selection protocol was used for continuous decoding using the Kalman filter, except that decoding performance saturated with a slower pace and reached a plateau at a higher feature number (50–100 depending on the session). For this reason we used 30 features for continuous decoding. A greedy selection paradigm (Bansal et al., 2011) eliminated highly redundant features and improved decoding performance by ∼10%, however both in the cross-frequency and time comparison analyses (see below) it provided highly similar results. Therefore, due to its simplicity, we used rank-based feature selection in all subsequent decoding analysis.
Classifying movement direction, when decoded from either open-loop or spike-based closed-loop trials showed practically the same result (Suppl. Fig. 1). For instance, offline decoding performance was not significantly different between open or closed-loop data in T2 (t-test, p>0.05 for any frequency bands or spikes) while we found a weak but significant difference in S3 only in two out of ten LFP bands (t-test, 0.3–5Hz: p=0.03, 45–65Hz: p=0.04, Suppl. Fig. 1, stars). Due to this high similarity, we combined open and closed-loop trials in all subsequent analyses.
To establish significance levels of the decoding results, we used a bootstrap procedure. In short, we decoded movement direction (Bayesian classification among four directions) or cursor velocity (Kalman filter) based on neural data after we randomized the sequence of movement directions (five-fold cross validation). One thousand iterations resulted in a smooth surrogate distribution of decoding performance, where the mean of the distribution (0.25 in four-directional classification and 0 in Kalman filter Pearson’s correlation coefficient accuracy) and the 95% confidence interval marked our significance level.
3.0 Results
We compared motor cortical spiking activity and multiple bands of local field potentials (LFPs) recorded from two clinical trial participants T2 and [S3] performing center-out tasks (Methods), including 12 sessions from participant T2 (trial days 46–467, one year and two months study period) and 14 sessions from participant S3 (trial days 974–1330 after implantation, one year study period). Below, we describe the directional tuning and decoding performance in spiking activity and LFPs, followed by a comparison of offline decoding stability across research sessions.
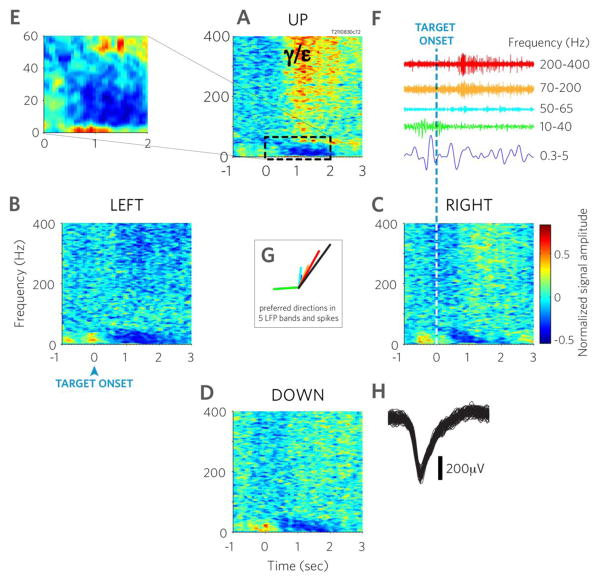
The power spectral density of the signal prior to and during attempted movement showed characteristic changes in different frequency bands (Fig. 1) and showed at least three characteristic types of modulation during movement imagery (Fig. 2). First, LFPs at low frequency (0.3–7Hz) showed a transient increase followed by tonic decrease in signal power after cue onset. Second, signal power decreased markedly at medium frequency (∼10–30Hz), referred to in motor cortex as beta suppression or event-related beta desynchronization (Pfurtscheller and Lopes da Silva, 1999). Third, higher frequencies, generally labeled as gamma, high gamma and epsilon bands (∼50Hz and higher) showed increased signal power, in a directionally specific manner. This higher frequency regime contained a strong component of spiking activity (Fig. 2F) and the directional modulation showed an upper boundary at ∼1–3kHz (data not shown), which most likely marked the high end of frequency components of spikes.
Fig. 2. Motor cortical LFPs in a person with tetraplegia are functionally modulated in multiple frequency bands.
A–D Trial averaged time-frequency spectrograms to four movement directions (direction indicated at top of each panel) recorded on a representative electrode. Power increase in the high frequency bands gamma and epsilon is highly directional selective, as it occurs mostly in the upward movement condition (‘γ/ɛ’) on this electrode. E. inset of panel A with higher magnification. F. Bandpass filtered data segments from representative trials within the five frequency windows used in this study. Time scale is identical to that of the spectrograms. G. center plot: preferred directions obtained by fitting the LFP features at each frequency band with a cosine function. The length of the bars indicate the amplitude of the cosine fit (arbitrary units). All frequency bands and spiking were significantly modulated (1-way ANOVA, p<0.01). Colors correspond to the frequency bands plotted in F. Black: spiking activity. H. Spike waveforms recorded on the same channel. Figure is based on a single channel in one session and 71–73 trials per spectrogram.
To describe directional information across the frequency spectrum of the field potentials, we sampled the signal power in five non-overlapping frequency bins of the spectrograms at 0.3–2.3sec following cue onset (‘low’: 0.3–5Hz, ‘medium’: 10–40Hz, ‘gamma 1’: 50–65Hz, ‘high gamma’: 70–200Hz, ‘epsilon: 200–400Hz, Methods). The average z-scored signal power within these time-frequency windows and z-scored spike rates were calculated for each electrode. The LFP and spike features (five LFP frequency bins and one spiking activity per channel) with significant modulation across the four stimulus conditions (one-way ANOVA, p<0.01) were selected for directional analysis. Directional modulation indices (Methods) were extracted for all significantly modulated features, and movement directions were decoded based on a single type of feature or the combination of all types (see below).
3.1 Comparison of directional modulation in spiking and LFPs
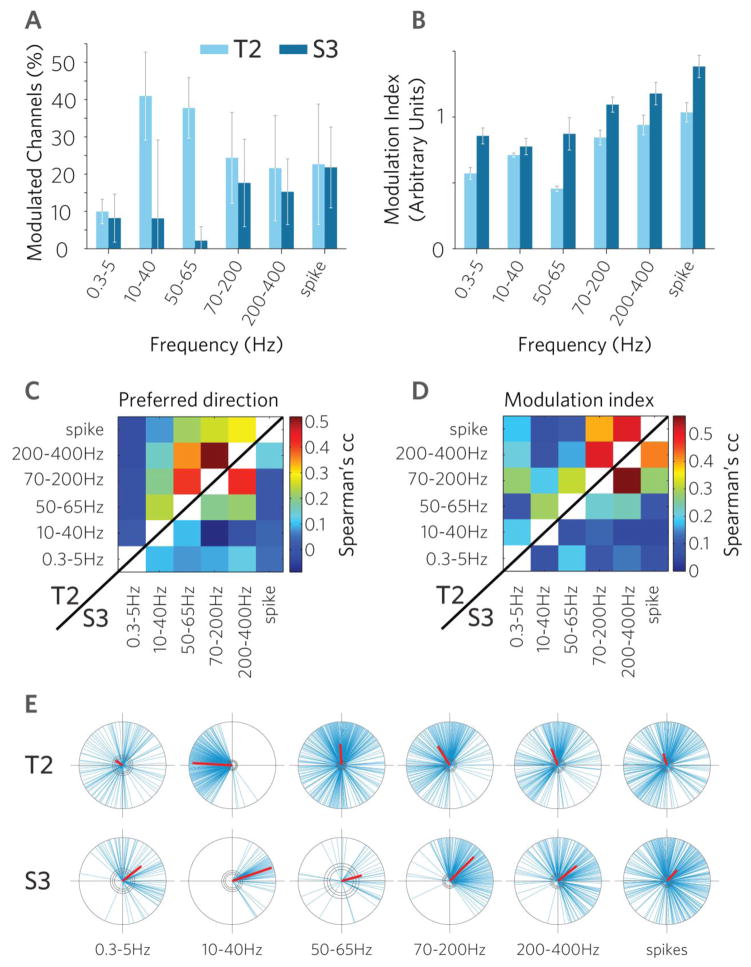
The total number of significantly modulated LFP features (1-way ANOVA p<0.01) outnumbered spiking features by 2.95[1.5]-fold (Table 1.). Stratified to individual feature types, the number of significantly modulated channels was more than twice as high at high frequency (∼20% of all modulated channels in features >70Hz) than at low frequency (<10% at <5Hz, Fig. 3A), while features in the intermediate frequency range (10–65Hz) showed a high number of modulated channels in T2 (∼38%) and low number in S3 (∼5%, Fig. 3A). Directional modulation index (Methods) increased with signal frequency and was highest in spikes (Fig. 3B).
Table 1. Frequent co-modulation in LFPs and spiking.
Significant tuning was calculated with 1-way ANOVA (p<0.01). Data based on 12[14] research sessions. High gamma: 70–200Hz. Epsilon: 200–400Hz LFP band. Values were rounded to single digit precision.
| Significantly tuned | T2 | S3 |
|---|---|---|
| % of all channels | ||
| LFPs or spike | 71 | 37 |
|
| ||
| LFPs | 68 | 30 |
|
| ||
| spike | 23 | 22 |
|
| ||
| LFPs and spike | 20 | 15 |
|
| ||
| spike but not LFPs | 2 | 7 |
|
| ||
| LFPs but not spike | 48 | 15 |
|
| ||
| spike but not epsilon | 6 | 11 |
|
| ||
| epsilon but not spike | 5 | 4 |
|
| ||
| spike and epsilon | 16 | 11 |
|
| ||
| epsilon not high gamma | 5 | 5 |
Fig. 3. Cross-frequency comparisons of direction tuning show high similarity among higher frequency bands and spikes.
A. Number of significantly modulated channels (1-way ANOVA p<0.01). Error bars indicate 95% confidence intervals as determined by bootstrapping. B. Directional modulation index (Methods). C. Cross-frequency correlations of preferred direction within the same channel. Upper left half: participant T2. Bottom right half: participant S3. D. Cross-frequency correlations of modulation index within the same channel, in both participants. Same conventions as C. E. The distribution of preferred directions at the group level. Blue lines: preferred directions of individual, significantly modulated features. Red bars indicate the vector sum of all preferred directions. Center circles: p=0.001, 0.01 and 0.05 significance levels (Rayleigh test). Radius denotes unity. Data is taken from 0.3–2.3sec following cue onset of all trials, recorded over 12[14] research sessions.
Simultaneous modulation in multiple LFP bands was common. One-third of the channels showing significant modulation in any signal type (Table 1., ‘LFPs or spike’) were simultaneously modulated both in LFPs and spikes (‘LFPs and spike’). Importantly, 48 [15]% of the channels showed modulation in at least one of the five LFP frequency bands, even in the absence of modulation in spiking activity on the same channel. A fraction of channels (16[11]%) that showed modulation in spiking also showed significant modulation in epsilon.
Similarity across spiking and different LFPs was also captured by directional correlations (preferred direction and modulation index) within the same channel and across frequencies (Fig. 3). With respect to the preferred direction, we found the strongest directional correlations between the high frequency range (70–200 and 200–400Hz). Correlations in directional modulation index (Methods) across frequency bands within the same channel showed high similarity between spikes and high gamma frequency, and high gamma and epsilon (70–200Hz and 200–400Hz) but less correlation between low and high gamma (50–65Hz and 70–200Hz). Directional correlations (both the preferred direction and modulation index) between high and low frequencies within the same channel were relatively small, indicating a disparity of kinematic information between these signal components. These results were comparable to studies in primary visual cortex reporting that low frequency LFPs and spikes contain independent information (Lashgari et al., 2012, Belitski et al., 2008).
Preferred directions were not homogenously distributed (p<0.001 Rayleigh-test for all but T2 low frequency which was significant at the 0.05 level), instead all distributions were unimodal (Fig. 3E). High frequency bands (45–400) and spiking distributions shared a common mean direction with no significant difference between the peaks (two-sample Watson-Williams test, p>0.05) although preferred directions in spiking activity showed significantly broader spread, i.e. a larger variability of preferred directions, which would make spiking signals especially suitable for multidirectional decoding. In contrast, despite the relatively high number of significantly tuned channels in the 10–40Hz range (T2, Fig. 3A), the preferred directions were highly clustered in both participants (Fig. 3E second column of polar plots). This indicates high redundancy of directional information in this band, and as we show below, this band also provided poorer directional decoding performance. The most common preferred direction changed between participants and likely depended on recording location, considering that M1 shows spatial clustering of preferred directions (Eisenberg et al., 2010, Amirikian and Georgopoulos, 2003, Georgopoulos et al., 2007, Ben-Shaul et al., 2003)
We also intended to ensure that a clustering of preferred directions or differences in decoding performance across frequency bands was not an artifact of common average referencing, which we applied to eliminate synchronous noise artifacts (Methods). Therefore we performed the same directional tuning analysis on unreferenced signals, which also showed similar inhomogeneity in the distribution of preferred directions (Rayleigh-test, p<0.001 for all but S3 50–65Hz range). Thus, while we observed that common average referencing decreased the overall signal power preferentially at low frequencies, neither the distribution of preferred directions, nor the decoding performance (see section 3.6) were altered by this data processing.
3.2 Decoding results
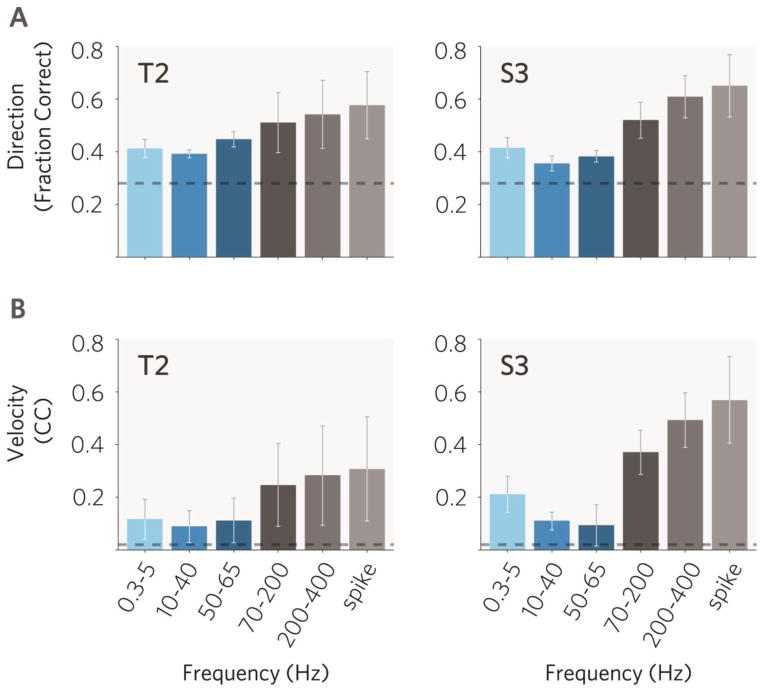
We further measured information content in different bands by comparing the offline decoding accuracy of the intended target direction with a naïve Bayesian classifier in each band. Decoding movement direction showed the highest performance in spikes with 56±22[70±22]% correct performance (n=12[14] sessions), and a gradually decreasing performance at lower frequencies, with the exception of the 10–40Hz band, where the performance was the lowest (35±2[32±4]%) in both participants (Fig. 4A). Decoding performance of the highest frequency LFP feature (epsilon band, 200–400Hz) was statistically indifferent from spike-based performance (paired t-test, p=0.06[0.17]), while spikes marginally, though significantly, outperformed all other LFP bands (p<0.05 in all bands and both participants).
Fig. 4. Decoding performance in high frequency LFPs is comparable to spikes and gradually decreases at lower frequencies.
A. Directional classification using a naïve Bayesian classifier. B. Continuous decoding using a Kalman filter. Individual LFP or spike features were ranked according to their decoding performance, and the best 20 features were selected to generate performance results for each frequency band and spikes. Error bars indicate 95% confidence intervals as determined by bootstrapping. Dashed line indicates chance level and 95% confidence interval as determined by bootstrapping (Methods).
Sorted single-unit spiking activity might provide different performance than multiunit spikes, and knowing this difference would be important from a practical standpoint. To compare multiunit spiking to sorted single unit spikes in our study, we manually re-sorted the action potentials of the entire data set (Perge et al., 2013), and repeated directional classification using single-unit spiking activity. Sorted spikes improved decoding performance by 1–5% in the early sessions, in accordance to previous studies (Fraser et al., 2009). However, as signal quality decreased over the study period, decoding performance fell below multiunit spike decoding. The mean decoding performance over the entire study period using sorted spikes was 12[18]% lower (p=0.007[0.03], paired t-test) than multiunit spikes.
To ensure that decoding results are independent of the choice of the decoding algorithm, we also performed continuous decoding of cursor movement velocity using a Kalman filter. This showed an identical tendency to the Bayesian classifier, i.e. high offline decoding performance in multiunit spikes and high frequency LFPs, while gradually decreasing performance at lower frequencies (Fig. 4B). Performance in the epsilon band was statistically indistinguishable from spikes (t-test, p=0.32[0.31]) while spikes outperformed all other LFP bands (p<0.05 in all bands and both participants). Both the classification and continuous decoding results confirmed non-human primate studies investigating directional information in macaque M1 LFP frequency bands (Mehring et al., 2003, Rickert et al., 2005).
3.3 Comparison of long term decoding stability of movement direction in spiking and LFPs
To compare the long term stability of spiking and LFP signals, we assessed changes in offline decoding performance (naïve Bayesian classifier, percent correctly classified target directions) across all research sessions of this study over the duration of one year in both participants (Fig. 5). In this case we decoded movement direction using an optimal subset of features selected from all LFP bands, spikes or a mixture of both LFPs and spikes (‘hybrid decoding’) using a rank-based feature selection (see Methods). In other words, all feature types from all electrodes were pooled together in the observation vector for the decoder, assuming statistical independence.
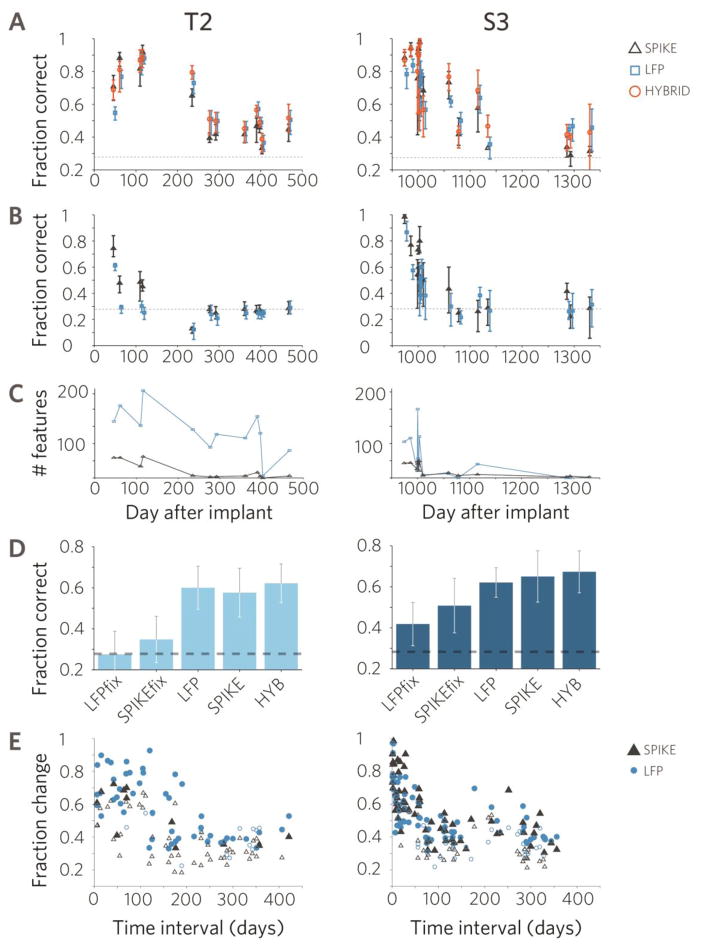
Fig. 5. Reliability of LFP-based offline decoding is similar to spike-based offline performance.
A. Directional decoding using a classifier recalibrated in each research session. Error bars indicate 95% confidence intervals obtained from bootstrapping the five-fold cross validation results. Dashed lines show chance level B. Offline decoding performance using the same classifier calibrated on the first session. C. Number of significantly modulated features co-vary between spikes and LFPs. D. Summary performance of the five classifiers tested over the study period reveals similar performance for spikes and LFPs. E. Offline decoding performance using the same decoder decreases by 60% over time periods of ∼2 months but remains significantly different from chance level (Methods) both in spikes and LFPs. Larger, filled symbols indicate statistically different performance from chance level. Fraction change indicates the proportional change in decoding performance respect to the calibration session.
Combined LFP decoding performance using daily recalibration of the decoder was statistically indistinguishable from spike-based performance in 75[76]% of the sessions (Fig. 5A and B, t-test on cross-validation results, p>0.05). In 25[20]% of the sessions spikes outperformed LFPs and in 0[6]% of the sessions LFPs significantly outperformed spikes. Both LFP and spike-based performance showed a significant decrease over time in both participants. The rate of performance decrease in spiking signals and LFPs was similar in participant T2 (linear fit, spike: 3.6%/month, LFPs 2.4%/month, ANCOVA, p=0.27), while ∼3% slower in LFPs in participant S3 (spike: 5.65%/month, LFPs: 2.85%/month, ANCOVA, p=0.03). Thus, in the majority of sessions, LFPs provided similar offline decoding performance to spikes.
Signal stability was also reflected in the number of significantly tuned features (Fig. 5. C). On a long time scale (months to year), both spike and LFP features in both participants showed an overall decrease in number (least-square regression, r2>0.3, p<0.05 in each case). Although the reason for this change was unknown, we noticed a gradual decrease in action potential amplitude and electrode impedance (unpublished observation) as also described in a macaque study (Chestek et al., 2011), indicating that electrode integrity or other parameters of the recording conditions might have changed over multiple months. Despite the decline, it is notable that the array in participant S3 continued to provide useful signals through more than five years (Hochberg et al., 2012).
On a medium time scale (days to weeks), feature counts showed large inter-session variability in both signal types (Fig. 5C), and the changes were significantly correlated between LFP and spike feature counts (Pearson’s cc = 0.76[0.87], p=0.00003[0.002]). Most notably, significantly modulated spike features in T2 decreased from 40±14(n=4 sessions) to 3±3units (n=8, remaining sessions) between day 116 and day 235 after implantation (4th session, or at the 4th month of this study period) while spike-based decoding performance decreased from 83±10% to 44±9%. In parallel, the number of significantly tuned LFP features and LFP decoding performance also decreased (129±88 to 112±49, performance change: 77±16% to 51±10%). In summary, feature counts and decoding performance fluctuated in a similar fashion across LFPs and spikes both on a long and at a medium time scale. On a short time scale, i.e., within a research session, fluctuations in spike amplitudes and firing rates have been previously reported (Perge et al., 2013).
3.4 Comparison of decoding stability in spiking and LFPs using fixed decoders
As a further comparison of reliability between spike and LFP features, we trained a classifier based on data from the first session and used the same classifier (i.e. fixed its features and weights) for the remaining sessions. Change in offline decoding performance reflected signal instability, as unmodeled signal changes introduce decoding error, thus decreasing the performance of a fixed decoder (Perge et al., 2013). The offline performance of both the spike and LFP-based classifiers in both participants fell to chance level over time separations of about two months or longer (Fig. 5B). Since recalibration outperformed fixed decoders in both participants, these results verify that the daily recalibration, performed with the intent of optimizing performance was a reasonable approach during the closed-loop sessions.
To further characterize the effective time window within which the same decoder provided reliable offline decoding, we decoded the intended movement direction in one session using a decoder calibrated in an earlier session. In other words, we compared pairs of sessions with increasing level of temporal separation, and investigated the effect of inter session time on prediction accuracy. This test revealed that calibration and testing performed with short time intervals (days to weeks) showed higher performance therefore a more comparable set of features than sessions performed months apart. Prediction accuracy fell by 60% compared to the original training performance within ∼100 days of intersession separation both in spiking and LFPs and in both participants (Fig. 5E), although significant performance remained even at longer intersession intervals in both participants and signal types (Fig. 5E large filled symbols). Decoding performance was significantly different from chance level in 77[71]% of the tested session combinations for LFPs, and 20[64]% of the session pairs for spike decoding which indicates increased stability of LFP signals compared to spiking in participant T2 and comparable performance in S3.
3.5 Hybrid spike-LFP decoding
Given the large number of significantly tuned LFP features and the stronger directional modulation in spiking (Fig. 3), we asked if a joint spike-LFP (hybrid) decoding would improve offline decoding performance. In each session, we selected twenty features with the highest individual decoding performance, irrespective of whether that feature was spiking or LFP, then used these features to recalibrate a decoder in that session. Decoding movement direction (with a naïve Bayesian classifier) using this hybrid input signal yielded a similarly high offline performance as the best performing component (spiking or LFPs) alone (Fig. 5A). That is, hybrid performance was not statistically significantly different from the best performing signal type alone in any of the research sessions (t-test on cross-validation results, p>0.05). In addition, we calculated regression lines on performance data presented in Fig. 5A. Regression slopes compared between spike-hybrid or LFP-hybrid performance were statistically indistinguishable in both participants (ANCOVA, p>0.05).
Feature types were not represented in equal number in the selection of the 20 most informative features. The most common feature types were low gamma (50–65Hz) in T2 (41% of all selected features) and spikes in S3 (43%) followed by epsilon (200–400Hz) in both participants (15[19]%, Table 2). Higher number of selected features from a given feature type also indicated stronger contribution to decoding performance, because leaving one type of feature out of the feature selection process (i.e. selecting 20 most informative features but ignoring one feature type at a time) revealed the largest performance drop for the exclusion of low gamma in T2 (50–65Hz, 6% decrease) and spiking in S3 (7.7% decrease, Table 2). The lack of performance improvement using hybrid signals over either spikes or LFPs further supported our earlier findings of high redundancy in kinematic information (Fig. 3) across these signal types.
Table 2. Contribution of signal types to hybrid decoding.
Signals that were frequently selected for decoding (left columns) where also more detrimental on performance when removed (right columns). Right columns indicate performance change when a given feature type is omitted from feature selection. Asterisks indicate statistically significant performance decrease by removing a given signal type (paired t-test, p<0.05).
| Signal Type | % All Selected Features | Performance Change (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| T2 | S3 | T2 | S3 | |
| 0.3–5Hz | 1.25 | 9.3 | −0.5 | −2.3 |
|
| ||||
| 10–40Hz | 14.2 | 6.7 | −2.2* | 0.8 |
|
| ||||
| 50–65Hz | 41.6 | 8 | −6* | 0.7 |
|
| ||||
| 70–200Hz | 10 | 13.3 | 0.1 | 1.6 |
|
| ||||
| 200–400Hz | 15 | 19 | −0.2 | −1.6 |
|
| ||||
| spikes | 17.9 | 43.7 | −3.5* | −7.7* |
3.6 Noise correlations and decoding performance
The slightly lower decoding performance of LFPs in the early research sessions might be explained by noise correlations, namely synchronous signal fluctuations across electrodes that carry no kinematic information (Hwang and Andersen, 2013). To estimate the impact of noise correlations on decoding performance, we randomly shuffled LFP features within the same electrode, same feature and same target trials. This way we preserved the directional content of the signal, but de-correlated the synchronous noise that might occur across electrodes and within the same electrode but in different frequency bands. Decoding performance based on de-correlated input showed no significant improvement, (t-test p>0.05 at all signal types, Supplementary Fig. 2). This result might be explained by common average referencing that we applied on all of our data (Methods), which removed synchronized interelectrode signal fluctuations mostly at lower frequencies. Yet, performing the same analysis on unreferenced signals showed no significant improvement at any frequency band (paired t-test, p>0.05 at all signal types). In summary, eliminating noise correlations in our LFP signals did not improve decoding performance.
Discussion
Reliability will be a key factor in the utility of neural interfaces in clinical practice. Our results with clinical trial participants with tetraplegia confirm in offline analysis what other studies reported in able-bodied monkey motor cortex: LFP-based decoding performance could rival spike-based performance (Flint et al., 2012b, Slutzky et al., 2011). This could make LFPs an alternative signal source –now also confirmed in human clinical trial participants –for intracortical brain-computer interface applications.
Action potential-based decoding of intended movements from human motor cortex show conceptually similar performance to intact nonhuman primates (Hochberg et al., 2012, Taylor et al., 2002, Serruya et al., 2002); the present offline study now also confirms the potential for using LFPs. Directional information in LFPs is reported in rat (Slutzky et al., 2011, Ludwig et al., 2011) and monkey motor cortex (Ince et al., 2010, Rickert et al., 2005, Donoghue et al., 1998, Zhuang et al., 2010a) with high decoding accuracy at low (<5Hz) and high frequencies (>63Hz), while the 16–42Hz band showed poor directional tuning (Rickert et al., 2005). In addition, our results show that including LFP frequencies above 200Hz may be beneficial (Zhuang et al., 2010a). For instance 5[4]% of the channels showed significant modulation in the 200–400Hz range, when significant modulation was absent from the spiking activity of the same channel, and 5[5]% of the channels were modulated in the 200–400Hz range but not modulated at 70–200Hz (Table 1). This could happen if tuned multiunit spiking activity is too attenuated to be detectable with threshold crossing of highpass-filtered signals, but still well detectable in signal power at lower frequencies, such as in the upper range of our reported field potentials.
Long term stability of spiking and LFP signals
Many LFP studies –including this paper –have been motivated by the belief that LFPs are better long-term signal types than spikes. Indeed, the rate of performance decrease was slower using LFPs in S3 (indicating more robust decoding, section 3.4), and intersession signal comparison showed increased stability of LFPs in participant T2 (section 3.5). However, these improvements were modest, with variable success in the two participants. In addition, direction tuning, the level of decoding performance and long term fluctuations in performance were tightly correlated between spikes and high-frequency LFPs above 70Hz, which could be explained by the presence of action potentials in LFP signals (Ray et al., 2008a, Ray et al., 2008b). Regardless of their stability or origin, LFPs carried as much movement related information as spikes, which confirms the utility of LFPs in neuroprosthetic applications.
Voluntary movements in able-bodied monkeys can be reliably decoded online from LFPs over a year using the same recording channels and a fixed decoder (Flint et al., 2013). Fixed decoders could then allow the user to adapt to inconsistencies arising from signal instabilities, and to improve control proficiency by learning (Flint et al., 2013, Ganguly and Carmena, 2009). These acquired motor skills might be less easily transferred with repeated recalibration of the system. This motivates further research into the development of fixed, LFP-inclusive neuroprosthetic applications for people with movement disabilities.
Sources of signal instability
Somewhat inconsistently with similar studies in non-human primates (Flint et al., 2012b), the session-to-session offline decoding performance in our study showed large fluctuations both in spiking and LFPs. Array micro-movement might explain part of the large session-to-session variability, as 40% of the sessions show signs of array micro-movements within the session (Perge et al., 2013). While electrode impedance remained in the operational range during this study (100–1000 kOhm per manufacturer), the topographic arrangement of spiking units on the array changed across research sessions (unpublished observation), indicating a shifting neural population or other technical factors. In addition, micro movements might be more detrimental to high frequency signal components, as the recording sphere of high frequency LFPs and spikes is smaller (∼100μm), (Csicsvari et al., 2003, Gold et al., 2006, Harris et al., 2001) than lower frequency signals (∼250μm or greater) (Katzner et al., 2009). Thus micro movements on a range of tens of microns might change the readout of directional information in spiking and higher frequency LFPs, while lower frequency LFPs might remain relatively unchanged. In support of this idea, the decoding performance of higher frequency signals across sessions was more variable (Fig. 4, error bars).
Animal studies recording from smaller brains might overestimate recording stability in humans. For instance, in smaller brains of mice, rats and cats, the presence of the array and wire bundle may reduce brain movement. Recording from larger and older human brains –which we performed here –might face increased mechanical instability, because aging brains shrink significantly in a fixed intracranial space (Wanifuchi et al., 2002, Ge et al., 2002), in turn the increased subarachnoid space fills up with more cerebrospinal fluid. This would allow larger movements with respect to the skull, thus age-related volume changes could impact recording stability as well. While monkeys move considerably more than our participants did, we note that participants could sneeze, cough or were regularly transferred between chairs, beds and bathrooms during a day; the impact of these activities on recording stability remains to be determined.
Leveraging decoder stability in the setting of signal variability
Based on our offline analysis, it remains unclear to what extent closed-loop online decoding using the same decoder repeatedly would have improved stability. Performance improvement using a fixed decoder might be considerable (Ganguly and Carmena, 2009), but the improvement is more modest (<10%) when starting with a well calibrated decoder (Flint et al., 2012b). Improvement on this magnitude is unlikely to compensate for larger inter-session variability and the >50% offline performance decrease in the studied time period. In addition, such an approach, especially if it utilizes only a small number of channels (Ganguly and Carmena, 2009) strictly depends on long term signal stability. This indicates that the decision whether to recalibrate daily or to use a fixed decoder might depend on two factors: the magnitude of unmodeled signal changes between the uses of the neuroprosthetic device and the user’s plasticity to compensate for decoding errors introduced by those signal changes. Small magnitude signal changes and a high level of plasticity could justify a fixed decoder while large signal nonstationarities would benefit from frequent recalibration or adaptive decoding (Homer et al., 2013, Homer et al., 2011, Gurel and Mehring, 2012, Li et al., 2011, Jarosiewicz et al., 2013).
Hybrid decoding of spikes and LFPs
Irrespective of their stability, if LFPs convey additional kinematic information unavailable in spikes, combining these signal types in decoding could increase information and improve motor prosthetic performance and reliability. Low frequency LFPs and spikes convey independent information (Lashgari et al., 2012, Belitski et al., 2008) while high frequency LFPs are linked to spiking activity (Ray et al., 2008a, Ray et al., 2008b). Accordingly, the combination of low and high frequency LFPs provided the highest decoding performance in a monkey study (Rickert et al., 2005). However, decoding performance also depends on cortical lamina (Buffalo et al., 2011, Smith et al., 2013, Markowitz et al., 2011) thus the lower performance of the <5Hz LFP in our study might be partially explained by differences in recording depth.
Lower decoding performance in the <5Hz LFP in our study might also explain why combining spikes and LFPs (or low and high LFPs) did not significantly improve offline decoding accuracy beyond its components (Fig. 5). Both spikes and LFPs contained considerable directional information. The majority of this information was redundant across spikes and the higher frequency bands (Fig. 3), thus joint decoding did not increase the available information and decoding performance. However, in this work we studied only LFP power changes, while further improvement in decoding performance might be achievable by exploring phase information of specific LFP bands (Belitski et al., 2008) or by cross-frequency coupling (Molter et al., 2012, de Hemptinne et al., 2013, Saleh et al., 2010, Belluscio et al., 2012).
Conclusion
Offline LFP-based decoding in people with paralysis performed as reliably as spike-based decoding, emphasizing the utility of LFPs in online neuroprosthetic control. While the hybrid offline decoding approach in this study did not outperform spike or LFP-based decoding, we believe that complementary knowledge about the movement plan extracted across different frequency bands of the recorded intracortical signals could increase information throughput and therefore increase decoding performance and robustness. Brain computer interfaces will likely benefit from the integration of multiple signal types recorded simultaneously or at different time scales within the same or even different brain areas, by combining different aspects of the same motor action or even different modalities. An integrated approach using multiple signal types should operate more reliably, because such a system would not depend on any one signal type with its individual instabilities.
Supplementary Material
Suppl. Fig. 1. Offline decoding of open-loop and closed-loop trials yield similar prediction of movement direction. Open-loop calibration data (light blue bars) refers to trials during which participants watched a computer generated sequence of linear cursor movements to four cardinal targets and imagined moving their own arm as if they were controlling the cursor. Spike-based closed-loop data (dark blue) refers to retrospective analysis of broadband recordings during which participants voluntarily controlled neural cursor velocity based on intracortical spiking activity. Compared to open-loop calibration, cursor movements during spike-based closed-loop control had more variance. However, the average direction of the neural cursor within the two second time window closely approximated the actual target direction. This allowed us to retrospectively analyze broadband data from the spike-based closed-loop trials the same way as we did with open-loop trials, i.e., using the same frequency bands and four cardinal targets. Data are from n=12[14] research sessions. Only two conditions in participant S3 (right panel) showed statistically significant difference between open and spike-based closed-loop offline decoding performance (asterisks, paired t-test, 0.3–5Hz: p=0.03, 50–65Hz: p=0.04). Error bars indicate 95% confidence intervals as determined by bootstrapping.
Suppl. Fig. 2. Removing noise correlations does not improve decoding performance. A. Data with common average referencing (Methods). B. Data without referencing. Non-shuffled data is identical to Fig. 4. Shuffling retained directional information, but removed interelectrode correlations. Error bars indicate 95% confidence intervals as determined by bootstrapping.
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to the Boston Home and participants T2 and S3 for their dedication to this research. This work was supported by the Rehabilitation Research and Development Service, Office of Research and Development, Department of Veterans Affairs (B6453R, A6779I, B6459L, B6310N), Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute Of Child Health & Human Development (RC1HD063931, NCMRR - N01HD53403 & N01HD10018), NIDCD (R01DC009899), TATRC, DARPA REPAIR (N66001-10-C-2010), Doris Duke Charitable Foundation, MGH-Deane Institute, Katie Samson Foundation, the State Scholarship Fund from the China Scholarship Council (No.201206325014) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No.31371001). The pilot clinical trial from which these data are derived was sponsored in part by Cyberkinetics Neurotechnology Systems, Inc. JPD is a former Chief Scientific Officer and director of Cyberkinetics Neurotechnology Systems, Inc. (CKI); he held stocks and received compensation. LRH received research support from Massachusetts General and Spaulding Rehabilitation Hospitals, which in turn received clinical trial support from CKI. CKI ceased operations in 2009. The content is solely the responsibility of the authors and does not necessarily represent the official views of the Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute Of Child Health & Human Development, the National Institutes of Health, or the Department of Veterans Affairs or the United States Government.
References
- AMIRIKIAN B, GEORGOPOULOS AP. Modular organization of directionally tuned cells in the motor cortex: is there a short-range order? Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 2003;100:12474–9. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2037719100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ANDERSEN RA, MUSALLAM S, PESARAN B. Selecting the signals for a brain-machine interface. Current opinion in neurobiology. 2004;14:720–6. doi: 10.1016/j.conb.2004.10.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BANSAL AK, TRUCCOLO W, VARGAS-IRWIN CE, DONOGHUE JP. Decoding 3D reach and grasp from hybrid signals in motor and premotor cortices: spikes, multiunit activity, and local field potentials. J Neurophysiol. 2012;107:1337–55. doi: 10.1152/jn.00781.2011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BANSAL AK, VARGAS-IRWIN CE, TRUCCOLO W, DONOGHUE JP. Relationships among low-frequency local field potentials, spiking activity, and three-dimensional reach and grasp kinematics in primary motor and ventral premotor cortices. J Neurophysiol. 2011;105:1603–19. doi: 10.1152/jn.00532.2010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BELITSKI A, GRETTON A, MAGRI C, MURAYAMA Y, MONTEMURRO MA, LOGOTHETIS NK, PANZERI S. Low-frequency local field potentials and spikes in primary visual cortex convey independent visual information. J Neurosci. 2008;28:5696–709. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0009-08.2008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BELLUSCIO MA, MIZUSEKI K, SCHMIDT R, KEMPTER R, BUZSAKI G. Cross-frequency phase-phase coupling between theta and gamma oscillations in the hippocampus. J Neurosci. 2012;32:423–35. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4122-11.2012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BEN-SHAUL Y, STARK E, ASHER I, DRORI R, NADASDY Z, ABELES M. Dynamical organization of directional tuning in the primate premotor and primary motor cortex. J Neurophysiol. 2003;89:1136–42. doi: 10.1152/jn.00364.2002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BUFFALO EA, FRIES P, LANDMAN R, BUSCHMAN TJ, DESIMONE R. Laminar differences in gamma and alpha coherence in the ventral stream. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 2011;108:11262–7. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1011284108. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BUZSAKI G, ANASTASSIOU CA, KOCH C. The origin of extracellular fields and currents–EEG, ECoG, LFP and spikes. Nature reviews Neuroscience. 2012;13:407–20. doi: 10.1038/nrn3241. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BUZSAKI G, DRAGUHN A. Neuronal oscillations in cortical networks. Science (New York, N Y) 2004;304:1926–9. doi: 10.1126/science.1099745. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHESTEK CA, GILJA V, NUYUJUKIAN P, FOSTER JD, FAN JM, KAUFMAN MT, CHURCHLAND MM, RIVERA-ALVIDREZ Z, CUNNINGHAM JP, RYU SI, SHENOY KV. Long-term stability of neural prosthetic control signals from silicon cortical arrays in rhesus macaque motor cortex. J Neural Eng. 2011;8:045005. doi: 10.1088/1741-2560/8/4/045005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COLLINGER JL, WODLINGER B, DOWNEY JE, WANG W, TYLER-KABARA EC, Weber DJ, MCMORLAND AJ, VELLISTE M, BONINGER ML, SCHWARTZ AB. High-performance neuroprosthetic control by an individual with tetraplegia. Lancet. 2013;381:557–64. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(12)61816-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CSICSVARI J, HENZE DA, JAMIESON B, HARRIS KD, SIROTA A, BARTHO P, WISE KD, BUZSAKI G. Massively parallel recording of unit and local field potentials with silicon-based electrodes. J Neurophysiol. 2003;90:1314–23. doi: 10.1152/jn.00116.2003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DE HEMPTINNE C, RYAPOLOVA-WEBB ES, AIR EL, GARCIA PA, MILLER KJ, OJEMANN JG, OSTREM JL, GALIFIANAKIS NB, STARR PA. Exaggerated phase-amplitude coupling in the primary motor cortex in Parkinson disease. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 2013;110:4780–5. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1214546110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DICKEY AS, SUMINSKI A, AMIT Y, HATSOPOULOS NG. Single-unit stability using chronically implanted multielectrode arrays. J Neurophysiol. 2009;102:1331–9. doi: 10.1152/jn.90920.2008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DONOGHUE JP, SANES JN, HATSOPOULOS NG, GAAL G. Neural discharge and local field potential oscillations in primate motor cortex during voluntary movements. J Neurophysiol. 1998;79:159–73. doi: 10.1152/jn.1998.79.1.159. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EISENBERG M, SHMUELOF L, VAADIA E, ZOHARY E. Functional organization of human motor cortex: directional selectivity for movement. J Neurosci. 2010;30:8897–905. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0007-10.2010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FLINT RD, LINDBERG EW, JORDAN LR, MILLER LE, SLUTZKY MW. Accurate decoding of reaching movements from field potentials in the absence of spikes. J Neural Eng. 2012a;9:046006. doi: 10.1088/1741-2560/9/4/046006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FLINT RD, WRIGHT ZA, SCHEID MR, SLUTZKY MW. Long term, stable brain machine interface performance using local field potentials and multiunit spikes. J Neural Eng. 2013;10:056005. doi: 10.1088/1741-2560/10/5/056005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FLINT RD, WRIGHT ZA, SLUTZKY MW. Control of a Biomimetic Brain Machine Interface with Local Field Potentials: Performance and Stability of a Static Decoder Over 200 Days. 34th Annual International Conference of the IEEE EMBS; 2012b; San Diego, California USA. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRASER GW, CHASE SM, WHITFORD A, SCHWARTZ AB. Control of a brain-computer interface without spike sorting. J Neural Eng. 2009;6:055004. doi: 10.1088/1741-2560/6/5/055004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GANGULY K, CARMENA JM. Emergence of a stable cortical map for neuroprosthetic control. PLoS biology. 2009;7:e1000153. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.1000153. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GE Y, GROSSMAN RI, BABB JS, RABIN ML, MANNON LJ, KOLSON DL. Age-related total gray matter and white matter changes in normal adult brain. Part I: volumetric MR imaging analysis. AJNR American journal of neuroradiology. 2002;23:1327–33. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GEORGOPOULOS AP, MERCHANT H, NASELARIS T, AMIRIKIAN B. Mapping of the preferred direction in the motor cortex. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 2007;104:11068–72. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0611597104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOLD C, HENZE DA, KOCH C, BUZSAKI G. On the origin of the extracellular action potential waveform: A modeling study. J Neurophysiol. 2006;95:3113–28. doi: 10.1152/jn.00979.2005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GUREL T, MEHRING C. Unsupervised adaptation of brain-machine interface decoders. Frontiers in neuroscience. 2012;6:164. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2012.00164. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HARRIS KD, HIRASE H, LEINEKUGEL X, HENZE DA, BUZSAKI G. Temporal interaction between single spikes and complex spike bursts in hippocampal pyramidal cells. Neuron. 2001;32:141–9. doi: 10.1016/s0896-6273(01)00447-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HENRIE JA, SHAPLEY R. LFP power spectra in V1 cortex: the graded effect of stimulus contrast. J Neurophysiol. 2005;94:479–90. doi: 10.1152/jn.00919.2004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOCHBERG LR, BACHER D, JAROSIEWICZ B, MASSE NY, SIMERAL JD, VOGEL J, HADDADIN S, LIU J, CASH SS, VAN DER SMAGT P, DONOGHUE JP. Reach and grasp by people with tetraplegia using a neurally controlled robotic arm. Nature. 2012;485:372–5. doi: 10.1038/nature11076. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOCHBERG LR, SERRUYA MD, FRIEHS GM, MUKAND JA, SALEH M, CAPLAN AH, BRANNER A, CHEN D, PENN RD, DONOGHUE JP. Neuronal ensemble control of prosthetic devices by a human with tetraplegia. Nature. 2006;442:164–71. doi: 10.1038/nature04970. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOMER ML, PERGE JA, BLACK MJ, HARRISON MT, CASH S, HOCHBERG LR. IEEE Trans Neural Syst Rehabil Eng. 2013. Adaptive offset correction for intracortical brain computer interfaces. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOMER ML, PERGE JA, HOCHBERG LR. Mitigating nonstationarities during neural cursor control with noise offset correction. Society for Neuroscience Annual Meeting; 2011. 142.03/E18. [Google Scholar]
- HWANG EJ, ANDERSEN RA. The utility of multichannel local field potentials for brain-machine interfaces. J Neural Eng. 2013;10:046005. doi: 10.1088/1741-2560/10/4/046005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- INCE NF, GUPTA R, ARICA S, TEWFIK AH, ASHE J, PELLIZZER G. High accuracy decoding of movement target direction in non-human primates based on common spatial patterns of local field potentials. PloS one. 2010;5:e14384. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0014384. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JAROSIEWICZ B, MASSE NY, BACHER D, DONOGHUE J, HOCHBERG LR. Advantages of closed-loop filter calibration in neural interfaces for people with paralysis. J Neural Eng. 2013;10(4):046012. doi: 10.1088/1741-2560/10/4/046012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KATZNER S, NAUHAUS I, BENUCCI A, BONIN V, RINGACH DL, CARANDINI M. Local origin of field potentials in visual cortex. Neuron. 2009;61:35–41. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2008.11.016. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KIM SP, SIMERAL JD, HOCHBERG LR, DONOGHUE JP, BLACK MJ. Neural control of computer cursor velocity by decoding motor cortical spiking activity in humans with tetraplegia. J Neural Eng. 2008;5:455–76. doi: 10.1088/1741-2560/5/4/010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LASHGARI R, LI X, CHEN Y, KREMKOW J, BERESHPOLOVA Y, SWADLOW HA, ALONSO JM. Response properties of local field potentials and neighboring single neurons in awake primary visual cortex. J Neurosci. 2012;32:11396–413. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0429-12.2012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LI Z, O’DOHERTY JE, LEBEDEV MA, NICOLELIS MAL. Adaptive decoding for brain-machine interfaces through Bayesian parameter updates. Neural computation. 2011;23:3162–204. doi: 10.1162/NECO_a_00207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LIU J, NEWSOME WT. Local field potential in cortical area MT: stimulus tuning and behavioral correlations. J Neurosci. 2006;26:7779–90. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5052-05.2006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LUDWIG KA, MIRIANI RM, LANGHALS NB, MARZULLO TC, KIPKE DR. Use of a Bayesian maximum-likelihood classifier to generate training data for brain-machine interfaces. Journal of neural engineering. 2011;8:046009. doi: 10.1088/1741-2560/8/4/046009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MALIK WQ, TRUCCOLO W, BROWN EN, HOCHBERG LR. Efficient decoding with steady-state Kalman filter in neural interface systems. IEEE Trans Neural Syst Rehabil Eng. 2011;19:25–34. doi: 10.1109/TNSRE.2010.2092443. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MANNING JR, JACOBS J, FRIED I, KAHANA MJ. Broadband shifts in local field potential power spectra are correlated with single-neuron spiking in humans. J Neurosci. 2009;29:13613–20. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2041-09.2009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARKOWITZ DA, WONG YT, GRAY CM, PESARAN B. Optimizing the decoding of movement goals from local field potentials in macaque cortex. J Neurosci. 2011;31:18412–22. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4165-11.2011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MEHRING C, RICKERT J, VAADIA E, CARDOSA DE OLIVEIRA S, AERTSEN A, ROTTER S. Inference of hand movements from local field potentials in monkey motor cortex. Nature neuroscience. 2003;6:1253–4. doi: 10.1038/nn1158. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MOLTER C, O’NEILL J, YAMAGUCHI Y, HIRASE H, LEINEKUGEL X. Rhythmic modulation of theta oscillations supports encoding of spatial and behavioral information in the rat hippocampus. Neuron. 2012;75:889–903. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2012.06.036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NIR Y, FISCH L, MUKAMEL R, GELBARD-SAGIV H, ARIELI A, FRIED I, MALACH R. Coupling between neuronal firing rate, gamma LFP, and BOLD fMRI is related to interneuronal correlations. Curr Biol. 2007;17:1275–85. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2007.06.066. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O’LEARY JG, HATSOPOULOS NG. Early visuomotor representations revealed from evoked local field potentials in motor and premotor cortical areas. Journal of neurophysiology. 2006;96:1492–506. doi: 10.1152/jn.00106.2006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PARKS TW, BURRUS CS. Digital Filter Design. John Wiley & Sons; 1987. [Google Scholar]
- PERGE JA, HOMER ML, MALIK WQ, CASH S, ESKANDAR E, FRIEHS G, DONOGHUE JP, HOCHBERG LR. Intra-day signal instabilities affect decoding performance in an intracortical neural interface system. J Neural Eng. 2013;10:036004. doi: 10.1088/1741-2560/10/3/036004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PESARAN B, PEZARIS JS, SAHANI M, MITRA PP, ANDERSEN RA. Temporal structure in neuronal activity during working memory in macaque parietal cortex. Nature neuroscience. 2002;5:805–11. doi: 10.1038/nn890. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PFURTSCHELLER G, LOPES DA SILVA FH. Event-related EEG/MEG synchronization and desynchronization: basic principles. Clinical neurophysiology : official journal of the International Federation of Clinical Neurophysiology. 1999;110:1842–57. doi: 10.1016/s1388-2457(99)00141-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RAY S, CRONE NE, NIEBUR E, FRANASZCZUK PJ, HSIAO SS. Neural correlates of high-gamma oscillations (60–200 Hz) in macaque local field potentials and their potential implications in electrocorticography. J Neurosci. 2008a;28:11526–36. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2848-08.2008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RAY S, HSIAO SS, CRONE NE, FRANASZCZUK PJ, NIEBUR E. Effect of stimulus intensity on the spike-local field potential relationship in the secondary somatosensory cortex. J Neurosci. 2008b;28:7334–43. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1588-08.2008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RAY S, MAUNSELL JHR. Differences in gamma frequencies across visual cortex restrict their possible use in computation. Neuron. 2010;67:885–96. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2010.08.004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RICKERT J, OLIVEIRA SC, VAADIA E, AERTSEN A, ROTTER S, MEHRING C. Encoding of movement direction in different frequency ranges of motor cortical local field potentials. J Neurosci. 2005;25:8815–24. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0816-05.2005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SALEH M, REIMER J, PENN R, OJAKANGAS CL, HATSOPOULOS NG. Fast and slow oscillations in human primary motor cortex predict oncoming behaviorally relevant cues. Neuron. 2010;65:461–71. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2010.02.001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHOMBURG EW, ANASTASSIOU CA, BUZSAKI G, KOCH C. The spiking component of oscillatory extracellular potentials in the rat hippocampus. J Neurosci. 2012;32:11798–811. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0656-12.2012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SERRUYA MD, HATSOPOULOS NG, PANINSKI L, FELLOWS MR, DONOGHUE JP. Instant neural control of a movement signal. Nature. 2002;416:141–2. doi: 10.1038/416141a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SIMERAL JD, KIM SP, BLACK MJ, DONOGHUE JP, HOCHBERG LR. Neural control of cursor trajectory and click by a human with tetraplegia 1000 days after implant of an intracortical microelectrode array. J Neural Eng. 2011;8:025027. doi: 10.1088/1741-2560/8/2/025027. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SLUTZKY MW, JORDAN LR, LINDBERG EW, LINDSAY KE, MILLER LE. Decoding the rat forelimb movement direction from epidural and intracortical field potentials. Journal of neural engineering. 2011;8:036013. doi: 10.1088/1741-2560/8/3/036013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SMITH MA, JIA X, ZANDVAKILI A, KOHN A. Laminar dependence of neuronal correlations in visual cortex. J Neurophysiol. 2013;109:940–7. doi: 10.1152/jn.00846.2012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STARK E, ABELES M. Predicting movement from multiunit activity. The Journal of neuroscience : the official journal of the Society for Neuroscience. 2007;27:8387–94. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1321-07.2007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TAYLOR DM, TILLERY SIH, SCHWARTZ AB. Direct cortical control of 3D neuroprosthetic devices. Science (New York, N Y) 2002;296:1829–32. doi: 10.1126/science.1070291. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TRUCCOLO W, FRIEHS GM, DONOGHUE JP, HOCHBERG LR. Primary motor cortex tuning to intended movement kinematics in humans with tetraplegia. J Neurosci. 2008;28:1163–78. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4415-07.2008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WANIFUCHI H, SHIMIZU T, MARUYAMA T. Age-related changes in the proportion of intracranial cerebrospinal fluid space measured using volumetric computerized tomography scanning. Journal of neurosurgery. 2002;97:607–10. doi: 10.3171/jns.2002.97.3.0607. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WHITTINGSTALL K, LOGOTHETIS NK. Frequency-band coupling in surface EEG reflects spiking activity in monkey visual cortex. Neuron. 2009;64:281–9. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2009.08.016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WU W, GAO Y, BIENENSTOCK E, DONOGHUE JP, BLACK MJ. Bayesian population decoding of motor cortical activity using a Kalman filter. Neural computation. 2006;18:80–118. doi: 10.1162/089976606774841585. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ZHUANG J, TRUCCOLO W, VARGAS-IRWIN C, DONOGHUE JP. Decoding 3-D reach and grasp kinematics from high-frequency local field potentials in primate primary motor cortex. IEEE transactions on bio-medical engineering. 2010a;57:1774–84. doi: 10.1109/TBME.2010.2047015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ZHUANG J, TRUCCOLO W, VARGAS-IRWIN C, DONOGHUE JP. Reconstructing grasping motions from high-frequency local field potentials in primary motor cortex. Conference proceedings : Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society Conference; 2010; 2010b. pp. 4347–50. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Suppl. Fig. 1. Offline decoding of open-loop and closed-loop trials yield similar prediction of movement direction. Open-loop calibration data (light blue bars) refers to trials during which participants watched a computer generated sequence of linear cursor movements to four cardinal targets and imagined moving their own arm as if they were controlling the cursor. Spike-based closed-loop data (dark blue) refers to retrospective analysis of broadband recordings during which participants voluntarily controlled neural cursor velocity based on intracortical spiking activity. Compared to open-loop calibration, cursor movements during spike-based closed-loop control had more variance. However, the average direction of the neural cursor within the two second time window closely approximated the actual target direction. This allowed us to retrospectively analyze broadband data from the spike-based closed-loop trials the same way as we did with open-loop trials, i.e., using the same frequency bands and four cardinal targets. Data are from n=12[14] research sessions. Only two conditions in participant S3 (right panel) showed statistically significant difference between open and spike-based closed-loop offline decoding performance (asterisks, paired t-test, 0.3–5Hz: p=0.03, 50–65Hz: p=0.04). Error bars indicate 95% confidence intervals as determined by bootstrapping.
Suppl. Fig. 2. Removing noise correlations does not improve decoding performance. A. Data with common average referencing (Methods). B. Data without referencing. Non-shuffled data is identical to Fig. 4. Shuffling retained directional information, but removed interelectrode correlations. Error bars indicate 95% confidence intervals as determined by bootstrapping.