Abstract
The ability of Eikenella corrodens to cause endocarditis in catheterized rabbits was studied. E. corrodens 1073, the serum-resistant strain used in the study, was isolated from a human periodontitis lesion. Thirty-four rabbits, surgically catheterized across the aortic valve and injected intravenously 24 to 48 h later with 10(7) to 10(9) log-phase organisms, were studied. Only three rabbits developed positive blood cultures and only two rabbits died before the time of sacrifice at 14 days after infection. Autopsies showed that all rabbits developed aortic vegetations, 52% of which were culture positive for E. corrodens. The organisms were recovered from aortic vegetations in a mean concentration of 10(5.3) colony-forming units/g of tissue and from liver or kidney in 28% of the animals in concentrations from 10(2) to 10(4) colony-forming units/g. Indirect immunofluorescent staining of vegetations, with the use of specific rat antiserum to E. corrodens 1073 and fluorescein isothiocyanate-labeled goat antirat serum, revealed colonies of E. corrodens in culture-negative vegetations as well as in those which were culture positive. The results showed that E. corrodens was an effective pathogen in the rabbit model of endocarditis, in which the disease was infrequently bacteremic and rarely fatal.
Full text
PDF

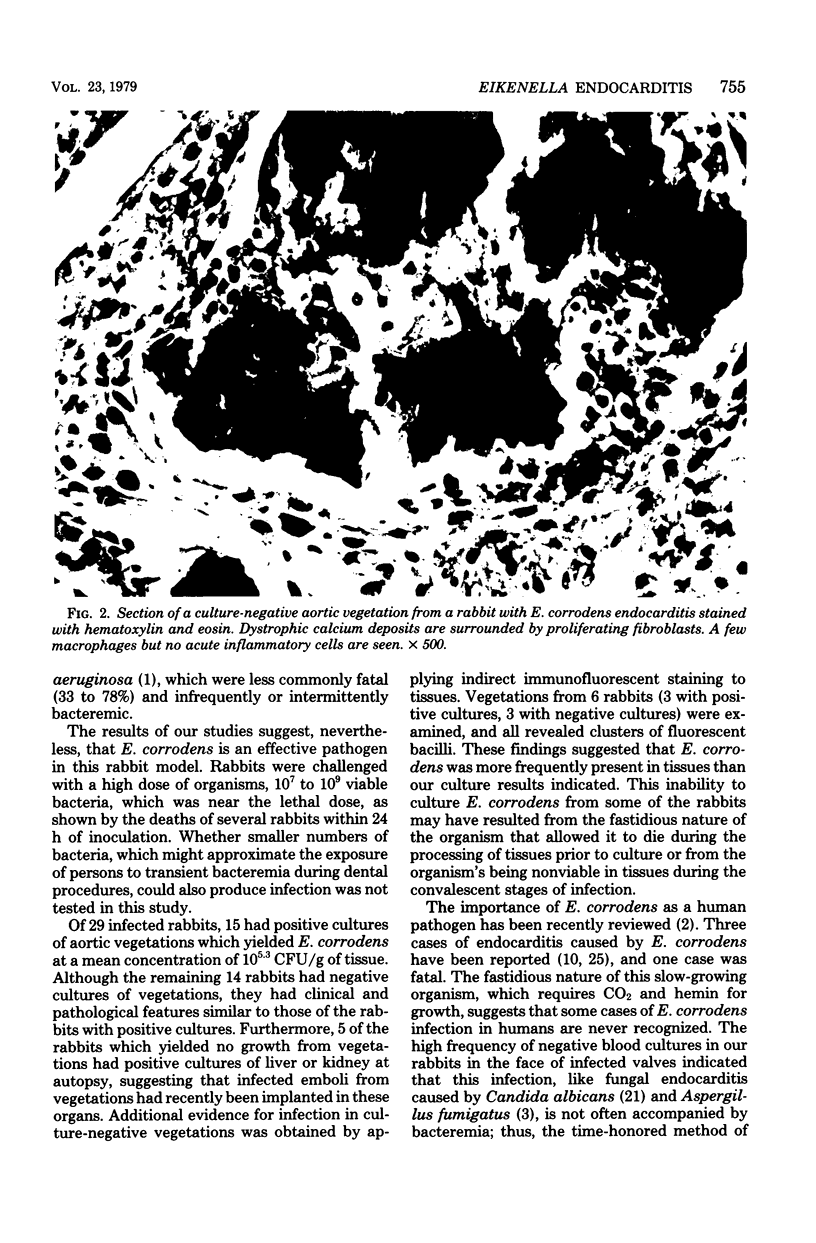


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Archer G., Fekety F. R., Jr Experimental endocarditis due to Pseudomonas aeruginosa. II. Therapy with carbenicillin and gentamicin. J Infect Dis. 1977 Sep;136(3):327–335. doi: 10.1093/infdis/136.3.327. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brooks G. F., O'Donoghue J. M., Rissing J. P., Soapes K., Smith J. W. Eikenella corrodens, a recently recognized pathogen: infections in medical-surgical patients and in association with methylphenidate abuse. Medicine (Baltimore) 1974 Sep;53(5):325–342. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carrizosa J., Kohn C., Levison M. E. Experimental aspergillus endocarditis in rabbits. J Lab Clin Med. 1975 Nov;86(5):746–753. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cherubin C. E., Neu H. C. Infective endocarditis at the Presbyterian Hospital in New York City from 1938-1967. Am J Med. 1971 Jul;51(1):83–96. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(71)90326-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorff G. J., Jackson L. J., Rytel M. W. Infections with Eikenella corrodens. A newly recognized human pathogen. Ann Intern Med. 1974 Mar;80(3):305–309. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-80-3-305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Durack D. T., Beeson P. B. Experimental bacterial endocarditis. I. Colonization of a sterile vegetation. Br J Exp Pathol. 1972 Feb;53(1):44–49. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Durack D. T., Beeson P. B. Protective role of complement in experimental Escherichia coli endocarditis. Infect Immun. 1977 Apr;16(1):213–217. doi: 10.1128/iai.16.1.213-217.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EIKEN M. Studies on an anaerobic, rodshaped, gram-negative microorganism: Bacteroides corrodens n. sp. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand. 1958;43(4):404–416. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garrison P. K., Freedman L. R. Experimental endocarditis I. Staphylococcal endocarditis in rabbits resulting from placement of a polyethylene catheter in the right side of the heart. Yale J Biol Med. 1970 Jun;42(6):394–410. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geraci J. E., Hermans P. E., Washington J. A., 2nd Eikenella corrodens endocarditis: report of cure in two cases. Mayo Clin Proc. 1974 Dec;49(12):950–953. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson F. L., Goodman Y. E., Bel F. R., Wong P. C., Whitehouse R. L. Taxonomic status of facultative and strictly anaerobic "corroding bacilli" that have been classified as Bacteroides corrodens. J Med Microbiol. 1971 May;4(2):171–184. doi: 10.1099/00222615-4-2-171. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson D. A., Behling U. H., Lai C. H., Listgarten M., Socransky S., Nowotny A. Role of bacterial products in periodontitis: immune response in gnotobiotic rats monoinfected with Eikenella corrodens. Infect Immun. 1978 Jan;19(1):246–253. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.1.246-253.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaspar R. L., Drutz D. J. Perihepatitis and hepatitis as complications of experimental endocarditis due to Neisseria gonorrhoeae in the rabbit. J Infect Dis. 1977 Jul;136(1):37–42. doi: 10.1093/infdis/136.1.37. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khairat O. Bacteroides corrodens isolated from bacteriaemias. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1967 Jul;94(1):29–40. doi: 10.1002/path.1700940106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labbé M., Hansen W., Schoutens E., Yourassowsky E. Isolation of Bacteroides corrodens and Eikenella corrodens from human clinical specimens. Comparative study of incidence and methods of identification. Infection. 1977;5(3):159–162. doi: 10.1007/BF01639752. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
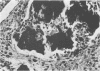
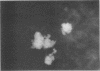
- Listgarten M. A., Johnson D., Nowotny A., Tanner A. C., Socransky S. S. Histopathology of periodontal disease in gnotobiotic rats monoinfected with Eikenella corrodens. J Periodontal Res. 1978 Mar;13(2):134–148. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0765.1978.tb00162.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newman M. G., Socransky S. S., Savitt E. D., Propas D. A., Crawford A. Studies of the microbiology of periodontosis. J Periodontol. 1976 Jul;47(7):373–379. doi: 10.1902/jop.1976.47.7.373. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sande M. A., Bowman C. R., Calderone R. A. Experimental Candida albicans endocarditis: characterization of the disease and response to therapy. Infect Immun. 1977 Jul;17(1):140–147. doi: 10.1128/iai.17.1.140-147.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sande M. A., Irvin R. G. Penicillin-aminoglycoside synergy in experimental Streptococcus viridans endocarditis. J Infect Dis. 1974 May;129(5):572–576. doi: 10.1093/infdis/129.5.572. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sande M. A., Johnson M. L. Antimicrobial therapy of experimental endocarditis caused by Staphylococcus aureus. J Infect Dis. 1975 Apr;131(4):367–375. doi: 10.1093/infdis/131.4.367. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Socransky S. S. Microbiology of periodontal disease -- present status and future considerations. J Periodontol. 1977 Sep;48(9):497–504. doi: 10.1902/jop.1977.48.9.497. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watsky D. Microbiology problem. Am J Med Technol. 1977 Aug;43(8):781–781. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]