Abstract
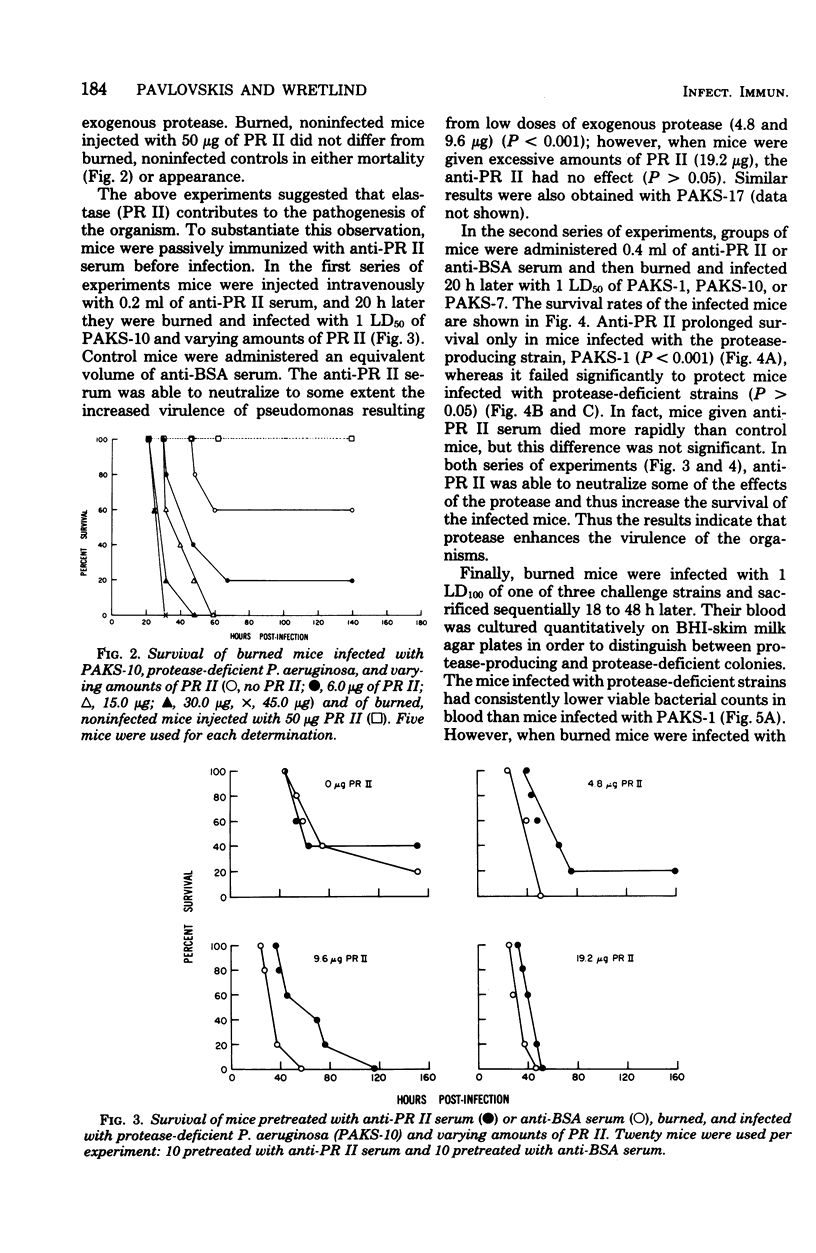
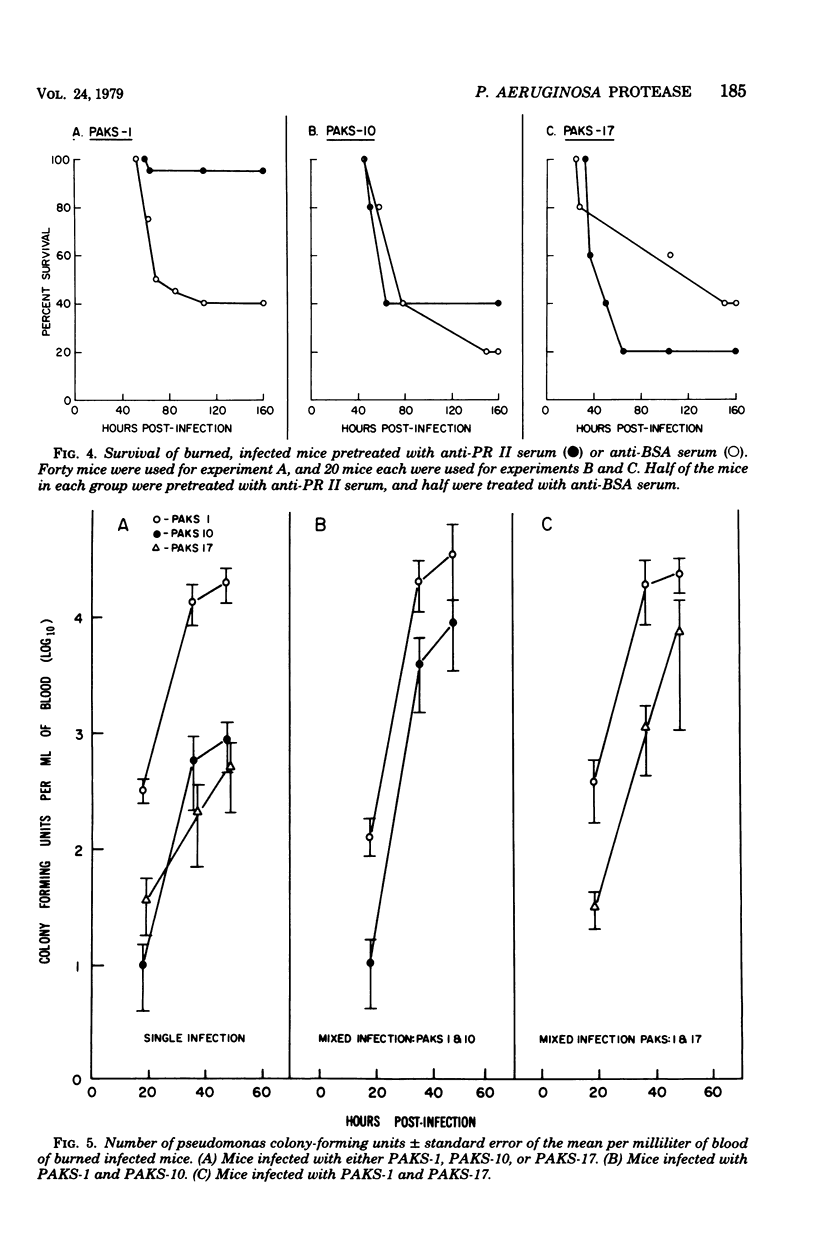
The data presented indicate that in experimental Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection of mice, protease enhances the virulence of the organism. Anesthetized CBA/Lü mice were subjected to a 15-s flame burn and infected with a wild-type protease-producing strain and two of its protease-deficient mutants. The average bacterial cell mean lethal dose (LD50) of 3.8 +/- 0.3 standard deviation (log10) for mice infected with the protease-producing P. aeruginosa was at least 1 log lower than the LD50 of the protease-deficient mutants (0.02 greater than P greater than 0.01). The addition of purified protease to the infecting inoculum of protease-deficient strains reduced the LD50. Although the generation time in vitro was the same for all three bacterial strains used, there were consistently fewer viable bacteria in the blood of mice infected with protease-deficient strains than in those infected with the protease-producing strain. When a protease-deficient strain was mixed with the protease-producing wild-type strain, the number of protease-producing pseudomonas found in the blood remained constant, whereas the number of protease-deficient organisms increased, suggesting that protease contributed to the invasiveness of the organisms. The survival of mice infected with protease-producing pseudomonas was enhanced by antiprotease serum. Antiprotease serum had no effect in mice infected with protease-deficient mutants.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Callahan L. T., 3rd Pseudomonas aeruginosa exotoxin: purification by preparative polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and the development of a highly specific antitoxin serum. Infect Immun. 1976 Jul;14(1):55–61. doi: 10.1128/iai.14.1.55-61.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Callahan L. T., 3rd Purification and characterization of Pseudomonas aeruginosa exotoxin. Infect Immun. 1974 Jan;9(1):113–118. doi: 10.1128/iai.9.1.113-118.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carney S. A., Dyster R. E., Jones R. J. The invasion of burned skin by Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Br J Dermatol. 1973 Jun;88(6):539–545. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2133.1973.tb08016.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eiche A. Effects of low dose X-irradiation on intra-uterine death in mice subjected to exposure when young or at foetal stage. Hereditas. 1977;85(1):63–66. doi: 10.1111/j.1601-5223.1977.tb00950.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FISHER E., Jr, ALLEN J. H. Mechanism of corneal destruction by pseudomonas proteases. Am J Ophthalmol. 1958 Nov;46(5 Pt 2):249–255. doi: 10.1016/0002-9394(58)90804-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forsgren A. Pathogenicity of Staphylococcus aureus mutants in general and local infections. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B Microbiol Immunol. 1972;80(4):564–570. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1972.tb00180.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray L. D., Kreger A. S. Rabbit corneal damage produced by Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection. Infect Immun. 1975 Aug;12(2):419–432. doi: 10.1128/iai.12.2.419-432.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holder I. A., Jogan M. Enhanced survival in burned mice treated with antiserum prepared against normal and burned skin. J Trauma. 1971 Dec;11(12):1041–1046. doi: 10.1097/00005373-197112000-00008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawaharajo K., Abe C., Homma J. Y., Kawano M., Goto E. Corneal ulcers caused by protease and elastase from Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Jpn J Exp Med. 1974 Oct;44(5):435–442. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawaharajo K., Homma J. Y., Aoyama Y., Morihara K. In vivo studies on protease and elastase from Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Jpn J Exp Med. 1975 Apr;45(2):89–100. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawaharajo K., Homma J. Y. Effects of elastase, protease and common antigen (OEP) from Pseudomonas aeruginosa on protection against burns in mice. Jpn J Exp Med. 1977 Dec;47(6):495–500. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawaharajo K., Homma J. Y. Pathogenesis of the mouse keratitis produced with Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Jpn J Exp Med. 1975 Dec;45(6):515–524. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreger A. S., Griffin O. K. Physicochemical fractionation of extracellular cornea-damaging proteases of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Infect Immun. 1974 May;9(5):828–834. doi: 10.1128/iai.9.5.828-834.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindberg A. A., Rosenberg L. T., Ljunggren A., Garegg P. J., Svensson S., Wallin N. H. Effect of synthetic disaccharide-protein conjugate as an immunogen in Salmonella infection in mice. Infect Immun. 1974 Sep;10(3):541–545. doi: 10.1128/iai.10.3.541-545.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu P. V. Extracellular toxins of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Infect Dis. 1974 Nov;130 (Suppl)(0):S94–S99. doi: 10.1093/infdis/130.supplement.s94. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu P. V., Hsieh H. C. Inhibition of protease production of various bacteria by ammonium salts: its effect on toxin production and virulence. J Bacteriol. 1969 Aug;99(2):406–413. doi: 10.1128/jb.99.2.406-413.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu P. V. The roles of various fractions of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in its pathogenesis. 3. Identity of the lethal toxins produced in vitro and in vivo. J Infect Dis. 1966 Oct;116(4):481–489. doi: 10.1093/infdis/116.4.481. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu P. V., Yoshii S., Hsieh H. Exotoxins of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. II. Concentration, purification, and characterization of exotoxin A. J Infect Dis. 1973 Oct;128(4):514–519. doi: 10.1093/infdis/128.4.514. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lynn M., Sensakovic J. W., Bartell P. F. In vivo distribution of Pseudomonas aeruginosa slime glycolipoprotein: association with leukocytes. Infect Immun. 1977 Jan;15(1):109–114. doi: 10.1128/iai.15.1.109-114.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MORIHARA K. PRODUCTION OF ELASTASE AND PROTEINASE BY PSEUDOMONAS AERUGINOSA. J Bacteriol. 1964 Sep;88:745–757. doi: 10.1128/jb.88.3.745-757.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MORIHARA K., TSUZUKI H., OKA T., INOUE H., EBATA M. PSEUDOMONAS AERUGINOSA ELASTASE. ISOLATION, CRYSTALLIZATION, AND PRELIMINARY CHARACTERIZATION. J Biol Chem. 1965 Aug;240:3295–3304. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meinke G., Barum J., Rosenberg B., Berk R. In Vivo Studies with the Partially Purified Protease (Elastase) from Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Infect Immun. 1970 Nov;2(5):583–589. doi: 10.1128/iai.2.5.583-589.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morihara K., Tsuzuki H. Production of protease and elastase by Pseudomonas aeruginosa strains isolated from patients. Infect Immun. 1977 Mar;15(3):679–685. doi: 10.1128/iai.15.3.679-685.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mull J. D., Callahan W. S. The role of the elastase of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in experimental infection. Exp Mol Pathol. 1965 Dec;4(6):567–575. doi: 10.1016/0014-4800(65)90037-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muszyński Z. Enzymatic and toxinogenic activity of culture filtrates of high and low virulent strains of Pseudomonas aeruginosa on mice. Pathol Microbiol (Basel) 1973;39(2):135–147. doi: 10.1159/000162641. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pavlovskis O. R., Iglewski B. H., Pollack M. Mechanism of action of Pseudomonas aeruginosa exotoxin A in experimental mouse infections: adenosine diphosphate ribosylation of elongation factor 2. Infect Immun. 1978 Jan;19(1):29–33. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.1.29-33.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pavlovskis O. R., Pollack M., Callahan L. T., 3rd, Iglewski B. H. Passive protection by antitoxin in experimental Pseudomonas aeruginosa burn infections. Infect Immun. 1977 Dec;18(3):596–602. doi: 10.1128/iai.18.3.596-602.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pavlovskis O. R., Voelker F. A., Shackelford A. H. Pseudomonas aeruginosa exotoxin in mice: histopathology and serum enzyme changes. J Infect Dis. 1976 Mar;133(3):253–259. doi: 10.1093/infdis/133.3.253. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SACHAR L. A., WINTER K. K., SICHER N., FRANKEL S. Photometric method for estimation of elastase activity. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1955 Nov;90(2):323–326. doi: 10.3181/00379727-90-22022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saelinger C. B., Snell K., Holder I. A. Experimental studies on the pathogenesis of infections due to Pseudomonas aeruginosa: direct evidence for toxin production during Pseudomonas infection of burned skin tissues. J Infect Dis. 1977 Oct;136(4):555–561. doi: 10.1093/infdis/136.4.555. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snell K., Holder I. A., Leppla S. A., Saelinger C. B. Role of exotoxin and protease as possible virulence factors in experimental infections with Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Infect Immun. 1978 Mar;19(3):839–845. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.3.839-845.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stieritz D. D., Holder I. A. Experimental studies of the pathogenesis of infections due to Pseudomonas aeruginosa: description of a burned mouse model. J Infect Dis. 1975 Jun;131(6):688–691. doi: 10.1093/infdis/131.6.688. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wretlind B., Hedén L., Sjöberg L., Wadström T. Production of enzymes and toxins by hospital strains of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in relation to serotype and phage-typing pattern. J Med Microbiol. 1973 Feb;6(1):91–100. doi: 10.1099/00222615-6-1-91. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wretlind B., Kronevi T. Experimental infections with protease-deficient mutants of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in mice. J Med Microbiol. 1978 May;11(2):145–154. doi: 10.1099/00222615-11-2-145. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wretlind B., Sjöberg L., Wadström T. Protease-deficient mutants of Pseudomonas aeruginosa: pleiotropic changes in activity of other extracellular enzymes. J Gen Microbiol. 1977 Dec;103(2):329–336. doi: 10.1099/00221287-103-2-329. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wretlind B., Wadström T. Purification and properties of a protease with elastase activity from Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Gen Microbiol. 1977 Dec;103(2):319–327. doi: 10.1099/00221287-103-2-319. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young L. S., Armstrong D. Pseudomonas aeruginosa infections. CRC Crit Rev Clin Lab Sci. 1972 Sep;3(3):291–347. doi: 10.3109/10408367209151698. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



