Abstract
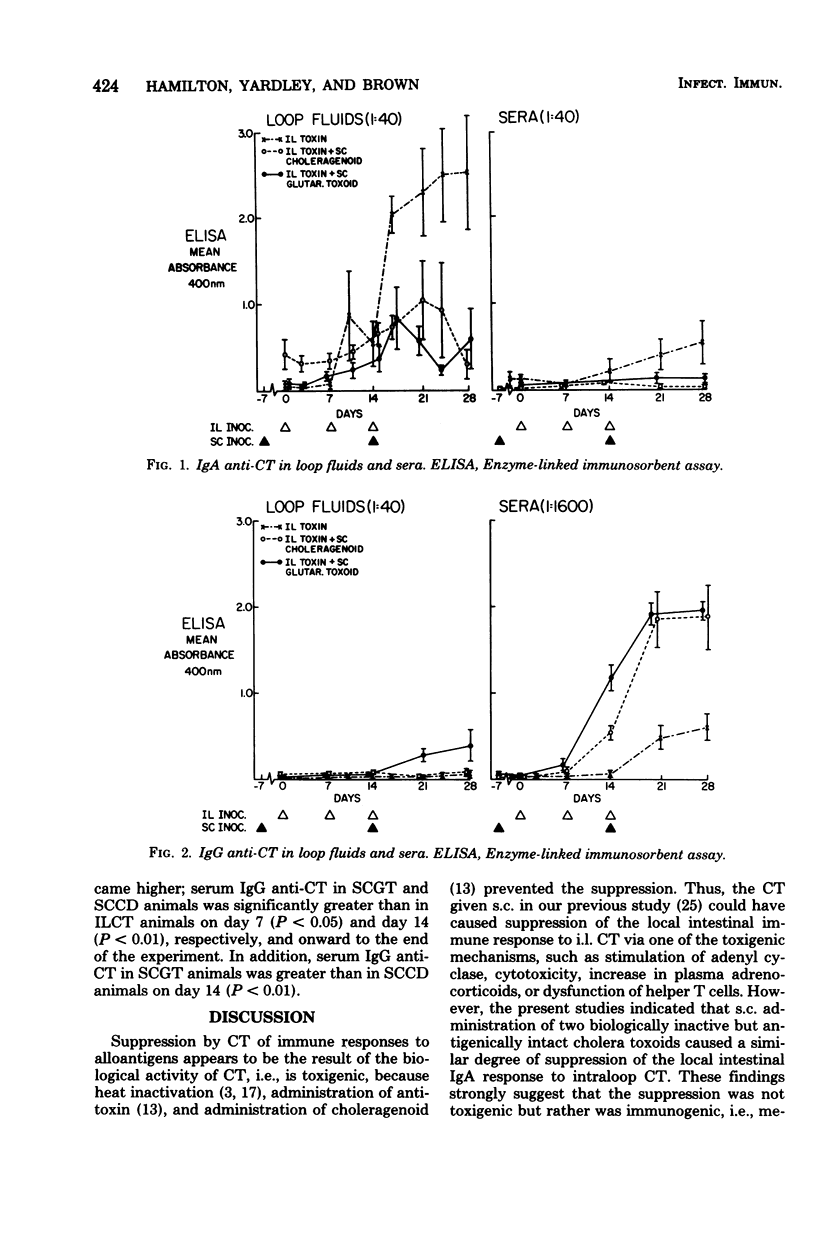
Cholera toxin has been shown to modulate immune responses, generally producing enhancement when administered simultaneously with antigen and suppression when administered a day or more earlier. In a previous study using chronically isolated ileal loops in rabbits, we found that two subcutaneous (s.c.) "priming" and "boosting" doses of biologically active cholera toxin suppressed the local intestinal immunoglobulin A response to intraloop doses of cholera toxin. In the study reported here, two different biologically inactive but antigenically intact cholera toxoids, glutaraldehyde toxoid and choleragenoid, where administered s.c. by the same immunization schedule as for toxin in the earlier experiment. Suppression of local immune response to intraloop cholera toxin as compared with animals receiving no s.c. inoculations was again found. The results suggest that in this model suppression was immunological (mediated by an immunological mechanism) rather than toxigenic (mediated by biological activity of cholera toxin). In addition, the occurrence of suppression of local intestinal immune response after systemic immunization suggests that suboptimal protection against enteric infections could occur after s.c. vaccination.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bourne H. R., Lichtenstein L. M., Melmon K. L., Henney C. S., Weinstein Y., Shearer G. M. Modulation of inflammation and immunity by cyclic AMP. Science. 1974 Apr 5;184(4132):19–28. doi: 10.1126/science.184.4132.19. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chisari F. V., Northrup R. S., Chen L. C. The modulating effect of cholera enterotoxin on the immune response. J Immunol. 1974 Sep;113(3):729–739. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook R. G., Stavitsky A. B., Schoenberg M. D. Regulation of the in vitro early anamnestic antibody response by exogenous cholera enterotoxin and cyclic AMP. J Immunol. 1975 Jan;114(1 Pt 2):426–434. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finkelstein R. A., Fujita K., LoSpalluto J. J. Procholeragenoid: an aggregated intermediate in the formation of choleragenoid. J Immunol. 1971 Oct;107(4):1043–1051. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henney C. S., Lichtenstein L. M., Gillespie E., Rolley R. T. In vivo suppression of the immune response to alloantigen by cholera enterotoxin. J Clin Invest. 1973 Nov;52(11):2853–2857. doi: 10.1172/JCI107481. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kateley J. R., Friedman H. Stimulation of cAMP levels and modulation of antibody formation in mice immunized with cholera toxin. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1975 Feb 28;249:413–423. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1975.tb29090.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kateley J. R., Kasarov L., Friedman H. Modulation of in vivo antibody responses by cholera toxin. J Immunol. 1975 Jan;114(1 Pt 1):81–84. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keren D. F., Elliott H. L., Brown G. D., Yardley J. H. Atrophy of villi with hypertrophy and hyperplasia of Paneth cells in isolated (thiry-Vella) ileal loops in rabbits. Light-microscopic studies. Gastroenterology. 1975 Jan;68(1):83–93. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lichtenstein L. M., Henney C. S., Bourne H. R., Greenough W. B., 3rd Effects of cholera toxin on in vitro models of immediate and delayed hypersensitivity. Further evidence for the role of cyclic adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate. J Clin Invest. 1973 Mar;52(3):691–697. doi: 10.1172/JCI107230. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindholm L., Holmgren J., Lange S., Lönnroth I. Interaction of cholera toxin and toxin derivatives with lymphocytes. II. Modulating effects of cholera toxin on in vivo humoral and cellular immune responses. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1976;50(5):555–573. doi: 10.1159/000231560. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lyons S. F., Friedman H. Cellular mechanisms of cholera toxin-mediated modulation of in vitro hemolysin formation by mouse immunocytes. J Immunol. 1978 Feb;120(2):452–458. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morse S. I., Stearns C. D., Goldsmith S. R. Lymphocyte depletion induced by cholera toxin; relationship to adrenal cortical function. J Immunol. 1975 Feb;114(2 Pt 1):665–670. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Northrup R. S., Fauci A. S. Adjuvant effect of cholera enterotoxin on the immune response of the mouse to sheep red blood cells. J Infect Dis. 1972 Jun;125(6):672–673. doi: 10.1093/infdis/125.6.672. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierce C. W., Kapp J. A. Regulation of immune responses by suppressor T cells. Tohoku J Exp Med. 1976;5:91–143. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierce N. F., Gowans J. L. Cellular kinetics of the intestinal immune response to cholera toxoid in rats. J Exp Med. 1975 Dec 1;142(6):1550–1563. doi: 10.1084/jem.142.6.1550. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierce N. F., Sack R. B., Sircar B. K. Immunity to experimental cholera. III. Enhanced duration of protection after sequential parenteral-oral administration of toxoid to dogs. J Infect Dis. 1977 Jun;135(6):888–896. doi: 10.1093/infdis/135.6.888. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierce N. F. The role of antigen form and function in the primary and secondary intestinal immune responses to cholera toxin and toxoid in rats. J Exp Med. 1978 Jul 1;148(1):195–206. doi: 10.1084/jem.148.1.195. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rappaport R. S., Pierzchala W. A., Bonde G., McCann T., Rubin B. A. Development of a purified cholera toxoid. III. Refinements in purification of toxin and methods for the determination of residual somatic antigen. Infect Immun. 1976 Sep;14(3):687–693. doi: 10.1128/iai.14.3.687-693.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waldmann T. A., Durm M., Broder S., Blackman M., Blaese R. M., Strober W. Role of suppressor T cells in pathogenesis of common variable hypogammaglobulinaemia. Lancet. 1974 Sep 14;2(7881):609–613. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(74)91940-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warren K. S., Mahmoud A. A., Boros D. L., Rall T. W., Mandel M. A., Carpenter C. C., Jr In vivo suppression by cholera toxin of cell-mediated and foreign body inflammatory responses. J Immunol. 1974 Mar;112(3):996–1007. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yardley J. H., Keren D. F., Hamilton S. R., Brown G. D. Local (immunoglobulin A) immune response by the intestine to cholera toxin and its partial suppression with combined systemic and intra-intestinal immunization. Infect Immun. 1978 Feb;19(2):589–597. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.2.589-597.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


