Abstract
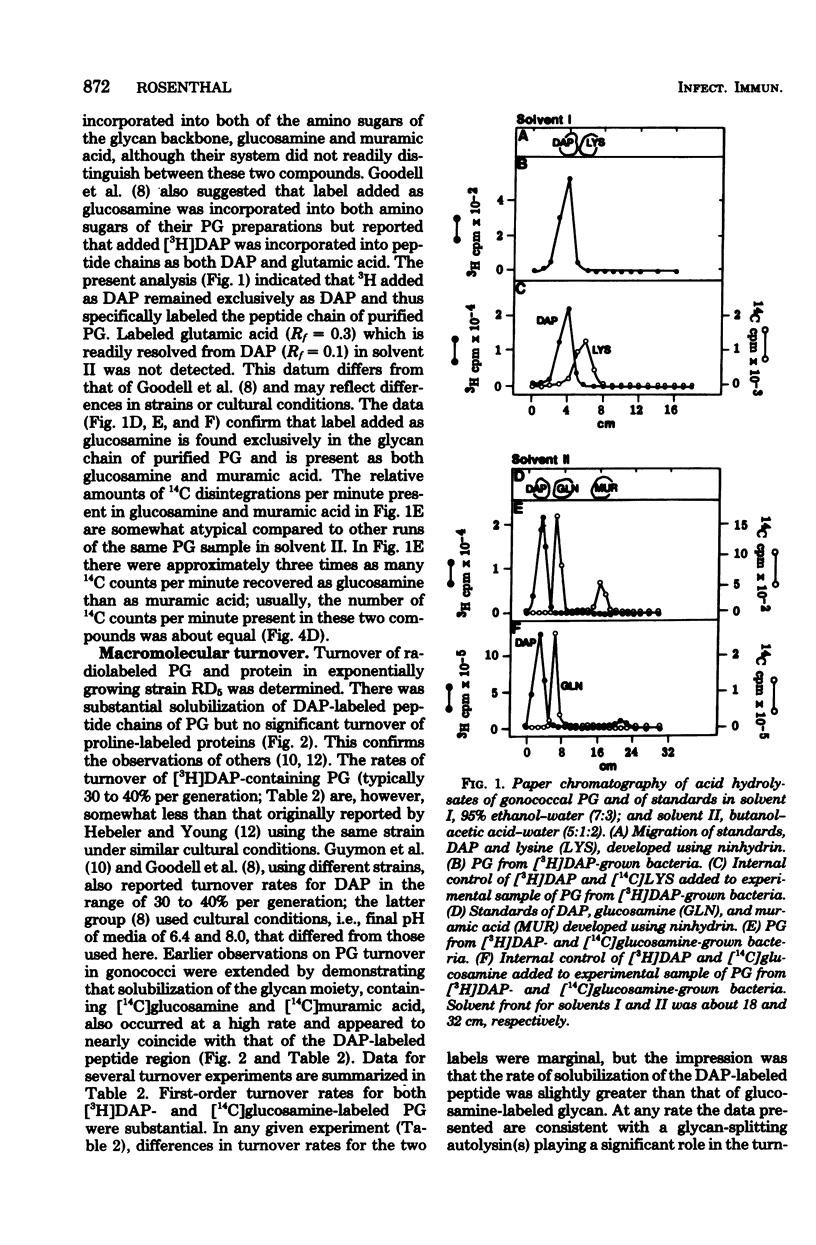
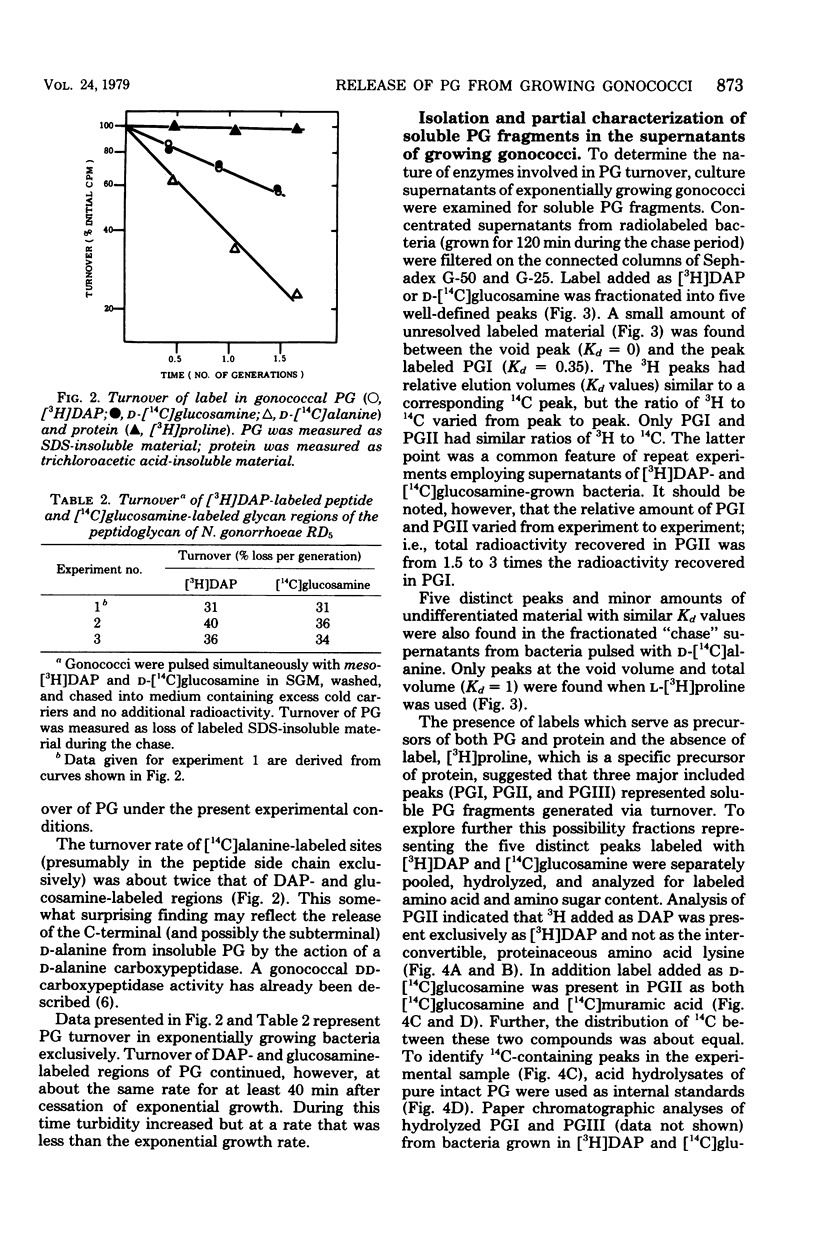
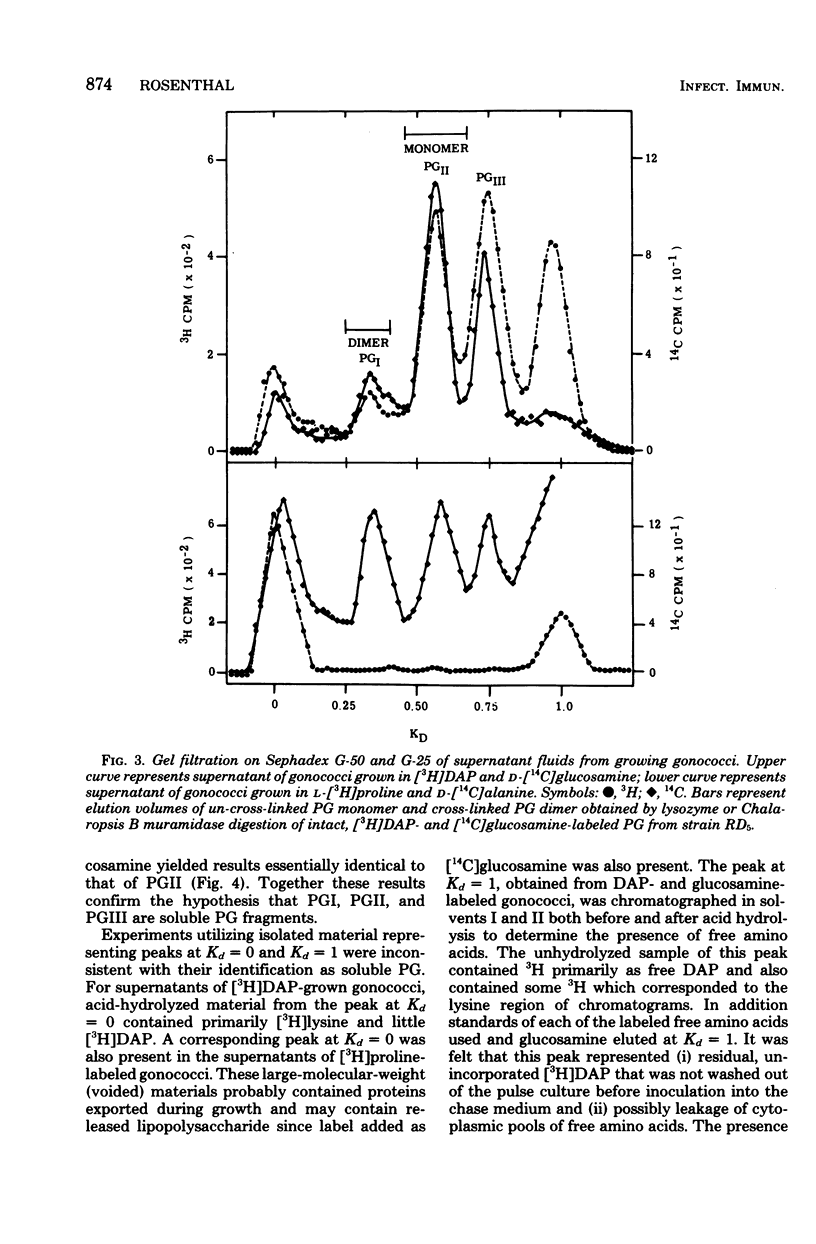
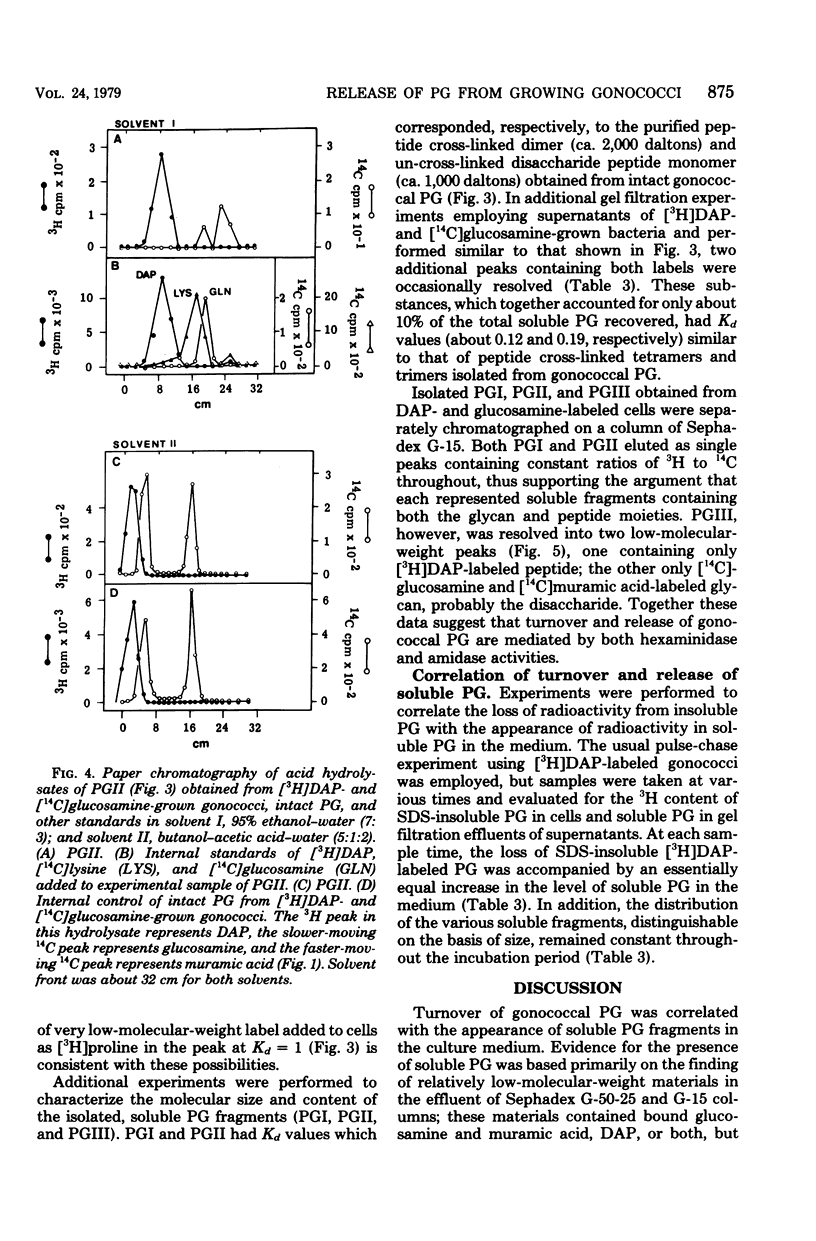
Peptidoglycan (PG) turnover in exponentially growing Neisseria gonorrhoeae RD5 type 4 was accompanied by release of soluble PG fragments into the medium. Turnover of the D-[14C]glucosamine-labeled glycan moiety and of the meso-[3H]diaminopimelic acid (DAP)-labeled peptide region occurred at similar rates (ca. 35% per generation). Turnover of D-[14C]alanine-labeled sites within the peptide side chain of PG occurred at roughly twice this rate; no turnover of L-[3H]proline-labeled protein was detected. Gel filtration of supernatants of cultures grown in the presence of labeled DAP, glucosamine, and D-alanine as described above and paper chromatography of hydrolyzed peak fractions revealed four major types of soluble PG. Two of these contained both peptide and glycan moieties and appeared to represent forms of disaccharide peptide monomers and dimers. The other two were (i) a 3H-labeled product lacking 14C and (ii) a 14C-containing product lacking 3H, which were similar in size to that expected for free tetrapeptides and free disaccharides, respectively. Together the appearance of these PG fragments and the concurrent turnover of glycan and peptide regions indicate that both glycan splitting and amidase PG hydrolase activities are involved in the turnover of PG in growing gonococci. If released during gonococcal infections, similar soluble PG fragments might influence the consequences of host-gonococcus interactions.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adam A., Ciorbaru R., Ellouz F., Petit J. F., Lederer E. Adjuvant activity of monomeric bacterial cell wall peptidoglycans. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1974 Feb 4;56(3):561–567. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(74)90640-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Audibert F., Chedid L., Lefrancier P., Choay J., Lederer E. Relationship between chemical structure and adjuvant activity of some synthetic analogues of N-acetyl-muramyl-L-alanyl-D-isoglutamine (MDP). Ann Immunol (Paris) 1977 Apr-Jun;128C(3):653–661. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blake M. S., Swanson J. Studies on gonococcus infection. XVI. Purification of Neisseria gonorrhoeae immunoglobulin A1 protease. Infect Immun. 1978 Nov;22(2):350–358. doi: 10.1128/iai.22.2.350-358.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bültmann B., Heymer B., Schleifer K. H., Seidl H. P., Haferkamp O. Migration inhibition of peritoneal macrophages by peptidoglycan. Z Immunitatsforsch Exp Klin Immunol. 1975 Jul;149(2-4):289–294. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chedid L., Parant M., Parant F., Lefrancher P., Choay J., Lederer E. Enhancement of nonspecific immunity to Klebsiella pneumoniae infection by a synthetic immunoadjuvant (N-acetylmuramyl-L-alanyl-D-isoglutamine) and several analogs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 May;74(5):2089–2093. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.5.2089. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis R. H., Salton M. R. Some properties of a D-alanine carboxypeptidase in envelope fractions of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Infect Immun. 1975 Nov;12(5):1065–1069. doi: 10.1128/iai.12.5.1065-1069.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodell E. W., Fazio M., Tomasz A. Effect of benzylpenicillin on the synthesis and structure of the cell envelope of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1978 Mar;13(3):514–526. doi: 10.1128/aac.13.3.514. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenblatt J., Boackle R. J., Schwab J. H. Activation of the alternate complement pathway by peptidoglycan from streptococcal cell wall. Infect Immun. 1978 Jan;19(1):296–303. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.1.296-303.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guymon L. F., Walstad D. L., Sparling P. F. Cell envelope alterations in antibiotic-sensitive and-resistant strains of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. J Bacteriol. 1978 Oct;136(1):391–401. doi: 10.1128/jb.136.1.391-401.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hebeler B. H., Young F. E. Autolysis of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. J Bacteriol. 1975 May;122(2):385–392. doi: 10.1128/jb.122.2.385-392.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hebeler B. H., Young F. E. Chemical composition and turnover of peptidoglycan in Neisseria gonorrhoeae. J Bacteriol. 1976 Jun;126(3):1180–1185. doi: 10.1128/jb.126.3.1180-1185.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hebeler B. H., Young F. E. Mechanism of autolysis of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. J Bacteriol. 1976 Jun;126(3):1186–1193. doi: 10.1128/jb.126.3.1186-1193.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Juy D., Chedid L. Comparison between macrophage activation and enhancement of nonspecific resistance to tumors by mycobacterial immunoadjuvants. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Oct;72(10):4105–4109. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.10.4105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KELLOGG D. S., Jr, PEACOCK W. L., Jr, DEACON W. E., BROWN L., PIRKLE D. I. NEISSERIA GONORRHOEAE. I. VIRULENCE GENETICALLY LINKED TO CLONAL VARIATION. J Bacteriol. 1963 Jun;85:1274–1279. doi: 10.1128/jb.85.6.1274-1279.1963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohashi O., Pearson C. M., Watanabe Y., Kotani S. Preparation of arthritogenic hydrosoluble peptidoglycans from both arthritogenic and non-arthritogenic bacterial cell walls. Infect Immun. 1977 Jun;16(3):861–866. doi: 10.1128/iai.16.3.861-866.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin J. P., Fleck J., Mock M., Ghuysen J. M. The wall peptidoglycans of Neisseria perflava, Moraxella glucidolytica, Pseudomonas alcaligenes and Proteus vulgaris strain P18. Eur J Biochem. 1973 Oct 5;38(2):301–306. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1973.tb03062.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenthal R. S., Fulbright R. S., Eads M. E., Sawyer W. D. Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid-sensitive antiphagocytic activity of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Infect Immun. 1977 Mar;15(3):817–827. doi: 10.1128/iai.15.3.817-827.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenthal R. S., Jungkind D., Daneo-Moore L., Shockman G. D. Evidence for the synthesis of soluble peptidoglycan fragments by protoplasts of Streptococcus faecalis. J Bacteriol. 1975 Oct;124(1):398–409. doi: 10.1128/jb.124.1.398-409.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Specter S., Friedman H., Chedid L. Dissociation between the adjuvant vs mitogenic activity of a synthetic muramyl dipeptide for murine splenocytes. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1977 Jul;155(3):349–352. doi: 10.3181/00379727-155-39804. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swanson J. Studies on gonococcus infection. XII. Colony color and opacity varienats of gonococci. Infect Immun. 1978 Jan;19(1):320–331. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.1.320-331.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka A., Nagao S., Saito R., Kotani S., Kusumoto S., Shiba T. Correlation of stereochemically specific structure in muramyl dipeptide between macrophage activation and adjuvant activity. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Jul 25;77(2):621–627. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(77)80024-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thongthai C., Sawyer W. D. Studies on the virulence of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. I. Relation of colonial morphology and resistance to phagocytosis by polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Infect Immun. 1973 Mar;7(3):373–379. doi: 10.1128/iai.7.3.373-379.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker T. S., Haak R. A., Wegener W. S. Plasmid DNA in virulent and avirulent gonococci. Can J Microbiol. 1975 Nov;21(11):1705–1710. doi: 10.1139/m75-250. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wegener W. S., Hebeler B. H., Morse S. A. Cell envelope of Neisseria gonorrhoeae: penicillin enhancement of peptidoglycan hydrolysis. Infect Immun. 1977 Dec;18(3):717–725. doi: 10.1128/iai.18.3.717-725.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wegener W. S., Hebeler B. H., Morse S. A. Cell envelope of Neisseria gonorrhoeae: relationship between autolysis in buffer and the hydrolysis of peptidoglycan. Infect Immun. 1977 Oct;18(1):210–219. doi: 10.1128/iai.18.1.210-219.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolf-Watz H., Elmros T., Normark S., Bloom G. D. Cell envelope of Neisseria gonorrhoeae: outer membrane and peptidoglycan composition of penicillin-sensitive and-resistant strains. Infect Immun. 1975 Jun;11(6):1332–1341. doi: 10.1128/iai.11.6.1332-1341.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



