Abstract
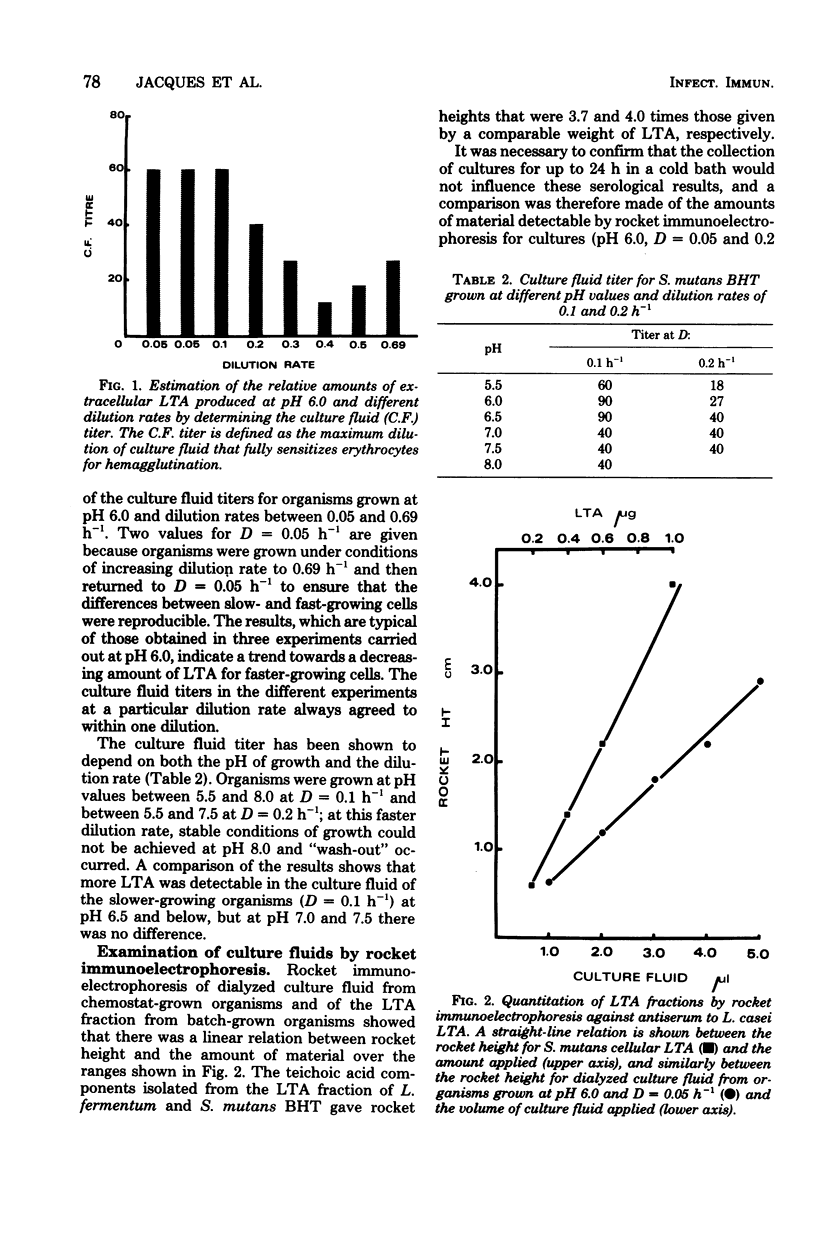
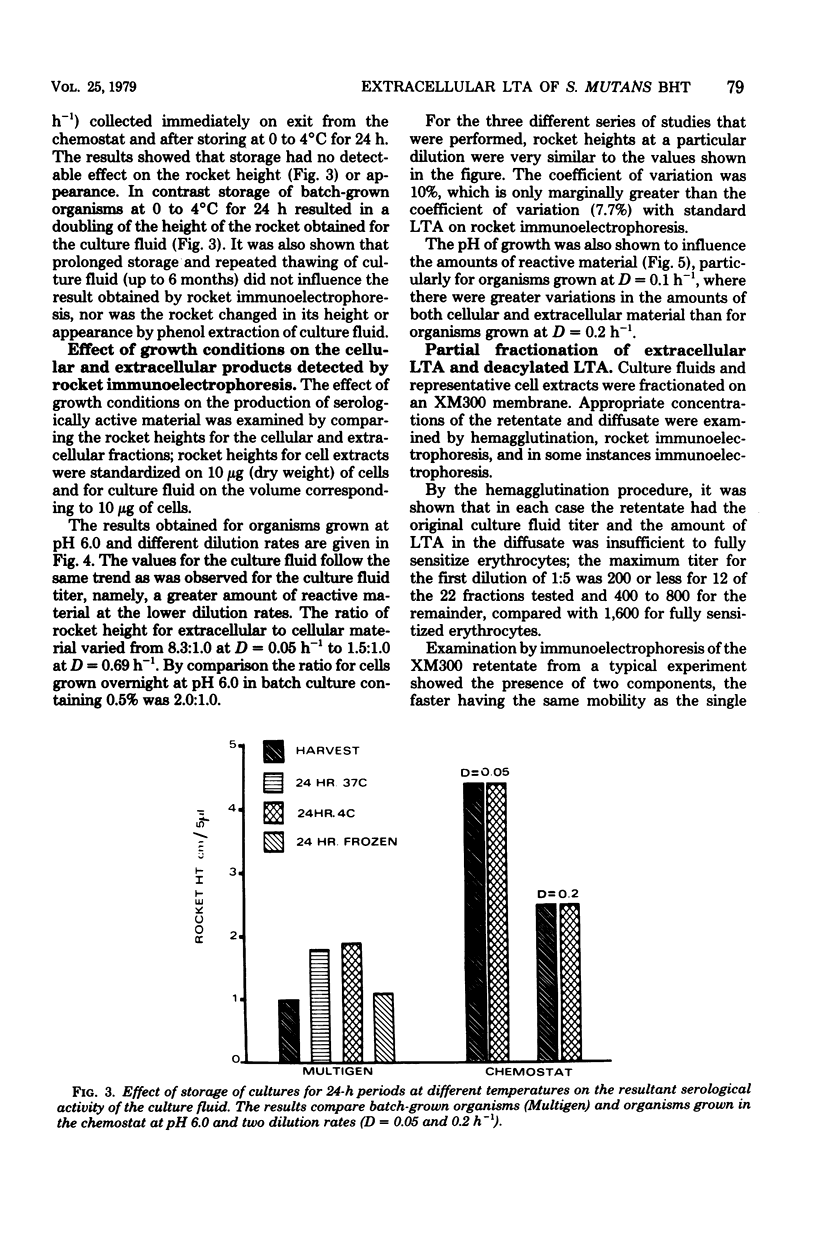
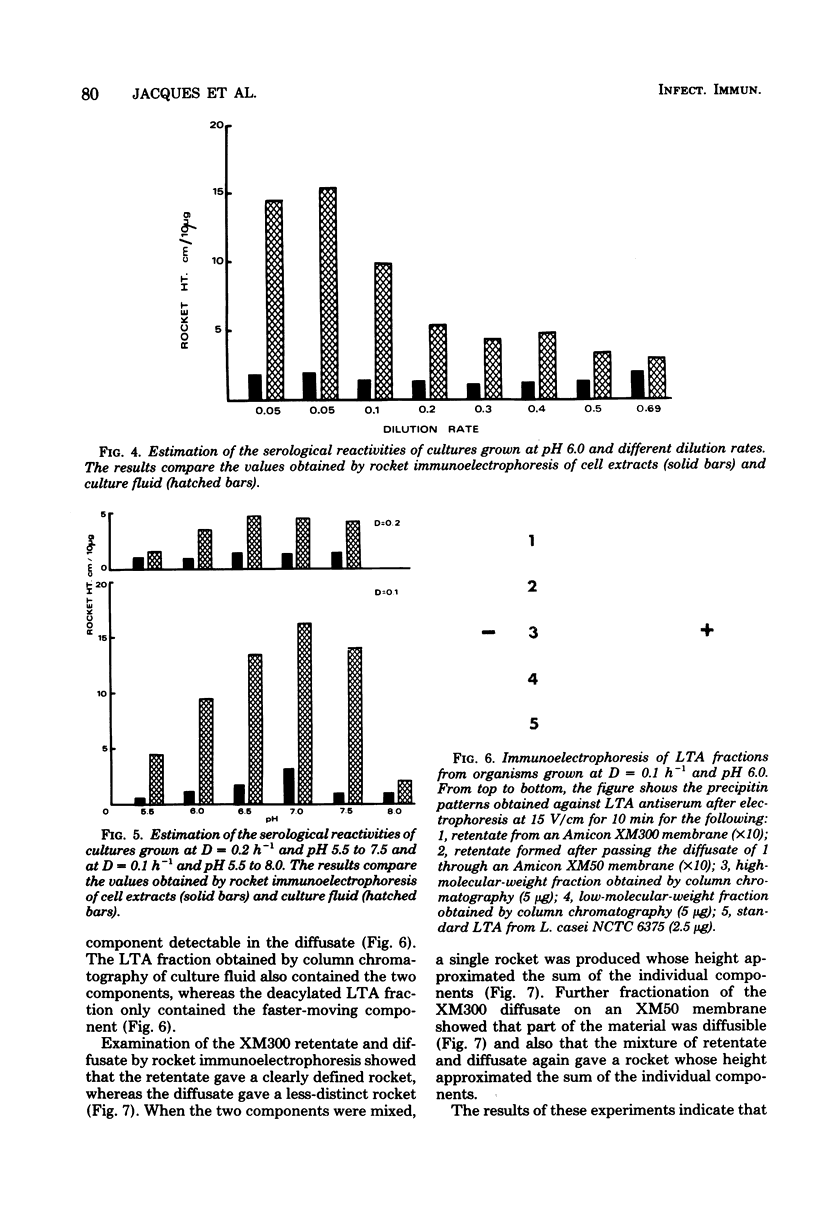
Streptococcus mutans BHT was grown in a chemostat with glucose limitation and at defined dilution rates and pH values. Lipoteichoic acid was estimated by determining the ability of dilutions of culture fluid to sensitize erythrocytes. The greatest amounts of extracellular lipoteichoic acid were produced by organisms growing at a low dilution rate and at pH 6.0 or 6.5. To enable a more accurate estimation of the total amount of extracellular material, rocket immunoelectrophoresis was employed. These results confirmed that the greatest amounts of reactive material were produced by slow-growing organisms, although there were discrepancies between these results and those obtained by hemagglutination. The extracellular material was fractionated by column chromatography and membrane ultrafiltration to yield a lipoteichoic acid-containing fraction and a presumptive deacylated lipoteichoic acid fraction. The relative proportions detected by rocket immunoelectrophoresis differed with the growth conditions, particularly the dilution rate. Analysis of the phenol-extracted cellular material also indicated the presence of deacylated lipoteichoic acid, although less than in the culture fluid.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beachey E. H., Chiang T. M., Ofek I., Kang A. H. Interaction of lipoteichoic acid of group A streptococci with human platelets. Infect Immun. 1977 May;16(2):649–654. doi: 10.1128/iai.16.2.649-654.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beachey E. H., Ofek I. Epithelial cell binding of group A streptococci by lipoteichoic acid on fimbriae denuded of M protein. J Exp Med. 1976 Apr 1;143(4):759–771. doi: 10.1084/jem.143.4.759. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleveland R. F., Daneo-Moore L., Wicken A. J., Shockman G. D. Effect of lipoteichoic acid and lipids on lysis of intact cells of Streptococcus faecalis. J Bacteriol. 1976 Sep;127(3):1582–1584. doi: 10.1128/jb.127.3.1582-1584.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleveland R. F., Holtje J. V., Wicken A. J., Tomasz A., Daneo-Moore L., Shockman G. D. Inhibition of bacterial wall lysins by lipoteichoic acids and related compounds. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1975 Dec 1;67(3):1128–1135. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(75)90791-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleveland R. F., Wicken A. J., Daneo-Moore L., Shockman G. D. Inhibition of wall autolysis in Streptococcus faecalis by lipoteichoic acid and lipids. J Bacteriol. 1976 Apr;126(1):192–197. doi: 10.1128/jb.126.1.192-197.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAHLQVIST A. Determination of maltase and isomaltase activities with a glucose-oxidase reagent. Biochem J. 1961 Sep;80:547–551. doi: 10.1042/bj0800547. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fiedel B. A., Jackson R. W. Activation of the alternative complement pathway by a streptococcal lipoteichoic acid. Infect Immun. 1978 Oct;22(1):286–287. doi: 10.1128/iai.22.1.286-287.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GIBBONS R. J. BACTERIOLOGY OF DENTAL CARIES. J Dent Res. 1964 Nov-Dec;43:SUPPL–SUPPL:1028. doi: 10.1177/00220345640430060301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUGGETT A. S., NIXON D. A. Use of glucose oxidase, peroxidase, and O-dianisidine in determination of blood and urinary glucose. Lancet. 1957 Aug 24;273(6991):368–370. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(57)92595-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamada S., Torii M. Effect of sucrose in culture media on the location of glucosyltransferase of Streptococcus mutans and cell adherence to glass surfaces. Infect Immun. 1978 Jun;20(3):592–599. doi: 10.1128/iai.20.3.592-599.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hausmann E., Lüderitz O., Knox K., Weinfeld N. Structural requirements for bone resorption by endotoxin and lipoteichoic acid. J Dent Res. 1975 Jun;54(SPEC):B94–B99. doi: 10.1177/00220345750540023401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hewett M. J., Knox K. W., Wicken A. J. Studies on the group F antigen of lactobacilli: detection of antibodies by haemagglutination. J Gen Microbiol. 1970 Mar;60(3):315–322. doi: 10.1099/00221287-60-3-315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joseph R., Shockman G. D. Synthesis and excretion of glycerol teichoic acid during growth of two streptococcal species. Infect Immun. 1975 Aug;12(2):333–338. doi: 10.1128/iai.12.2.333-338.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kessler R. E., Shockman G. D. Precursor-product relationship of intracellular and extracellular lipoteichoic acids of Streptococcus faecium. J Bacteriol. 1979 Feb;137(2):869–877. doi: 10.1128/jb.137.2.869-877.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knox K. W., Hewett M. J., Wicken A. J. Studies on the group F antigen of lactobacilli: antigenicity and serological specificity of teichoic acid preparations. J Gen Microbiol. 1970 Mar;60(3):303–313. doi: 10.1099/00221287-60-3-303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knox K. W., Markham J. L., Wicken A. J. Formation of cross-reacting antibodies against cellular and extracellular lipoteichoic acid of Streptococcus mutans BHT. Infect Immun. 1976 Mar;13(3):647–652. doi: 10.1128/iai.13.3.647-652.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knox K. W., Wicken A. J. Serological properties of the wall and membrane teichoic acids from Lactobacillus helveticus NCIB 8025. J Gen Microbiol. 1970 Oct;63(2):237–248. doi: 10.1099/00221287-63-2-237. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knox K. W., Wicken A. J. Serological studies on the teichoic acids of Lactobacillus plantarum. Infect Immun. 1972 Jul;6(1):43–49. doi: 10.1128/iai.6.1.43-49.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markham J. L., Knox K. W., Wicken A. J., Hewett M. J. Formation of extracellular lipoteichoic acid by oral streptococci and lactobacilli. Infect Immun. 1975 Aug;12(2):378–386. doi: 10.1128/iai.12.2.378-386.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owen P., Oppenheim J. D., Nachbar M. S., Kessler R. E. The use of lectins in the quantitation and analysis of macromolecules by affinoelectrophoresis. Anal Biochem. 1977 Jun;80(2):446–457. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(77)90667-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owen P., Salton M. R. Submicrogram quantitation of an acidic polysaccharide by rocket immunoelectrophoresis and rocket affinoelectrophoresis. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 21;73(1):20–26. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90137-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rölla G. Formation of dental integuments--some basic chemical considerations. Swed Dent J. 1977;1(6):241–251. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silvestri L. J., Craig R. A., Ingram L. O., Hoffmann E. M., Bleiweis A. S. Purification of lipoteichoic acids by using phosphatidyl choline vesicles. Infect Immun. 1978 Oct;22(1):107–118. doi: 10.1128/iai.22.1.107-118.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Driel D., Wicken A. J., Dickson M. R., Knox K. W. Cellular location of the lipoteichoic acids of Lactobacillus fermenti NCTC 6991 and Lactobacillus casei NCTC 6375. J Ultrastruct Res. 1973 Jun;43(5):483–497. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(73)90025-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaught R. M., Bleiweis A. S. Antigens of Streptococcus mutans. II. Characterization of an antigen resembling a glycerol teichoic acid in walls of strain BHT. Infect Immun. 1974 Jan;9(1):60–67. doi: 10.1128/iai.9.1.60-67.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wicken A. J., Knox K. W. A serological comparison of the membrane teichoic acids from lactobacilli of different serological groups. J Gen Microbiol. 1971 Aug;67(2):251–254. doi: 10.1099/00221287-67-2-251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wicken A. J., Knox K. W. Lipoteichoic acids: a new class of bacterial antigen. Science. 1975 Mar 28;187(4182):1161–1167. doi: 10.1126/science.46620. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wicken A. J., Knox K. W. Studies on the group F antigen of lactobacilli: isolation of a teichoic acid-lipid complex from Lactobacillus fermenti NCTC 6991. J Gen Microbiol. 1970 Mar;60(3):293–301. doi: 10.1099/00221287-60-3-293. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson S. G. Glycosyl diglycerides from Pseudomonas rubescens. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Oct 22;164(2):148–156. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(68)90141-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Houte J., Saxton C. A. Cell wall thickening and intracellular polysaccharide in microorganisms of the dental plaque. Caries Res. 1971;5(1):30–43. doi: 10.1159/000259730. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]