Abstract
Granzyme B serine protease is found in the granules of activated cytotoxic T cells and in natural and lymphokine-activated killer cells. This protease plays a critical role in the rapid induction of target cell DNA fragmentation. The DNA regulatory elements that are responsible for the specificity of granzyme B gene transcription in activated T-cells reside between nt -148 and +60 (relative to the transcription start point at +1) of the human granzyme B gene promoter. This region contains binding sites for the transcription factors Ikaros, CBF, Ets, and AP-1. Mutational analysis of the human granzyme B promoter reveals that the Ikaros binding site (-143 to -114) and the AP-1/CBF binding site (-103 to -77) are essential for the activation of transcription in phytohemagglutinin-activated peripheral blood lymphocytes, whereas mutation of the Ets binding site does not affect promoter activity in these cells.
Full text
PDF

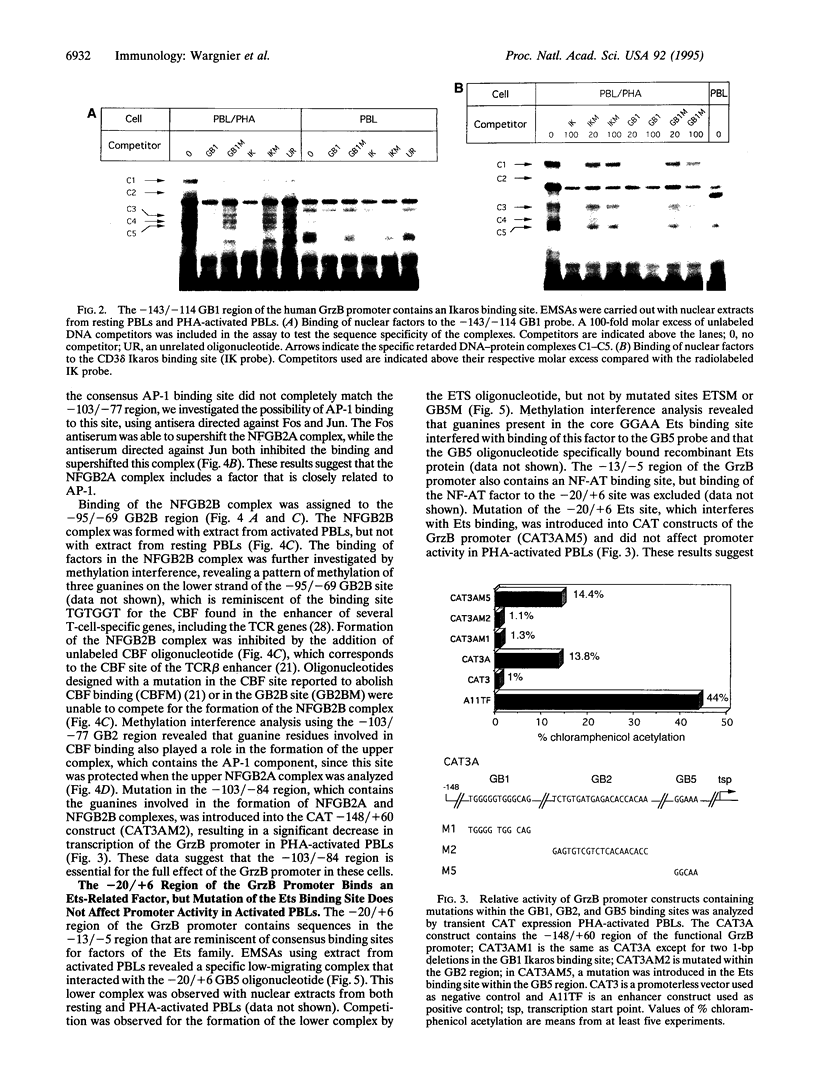
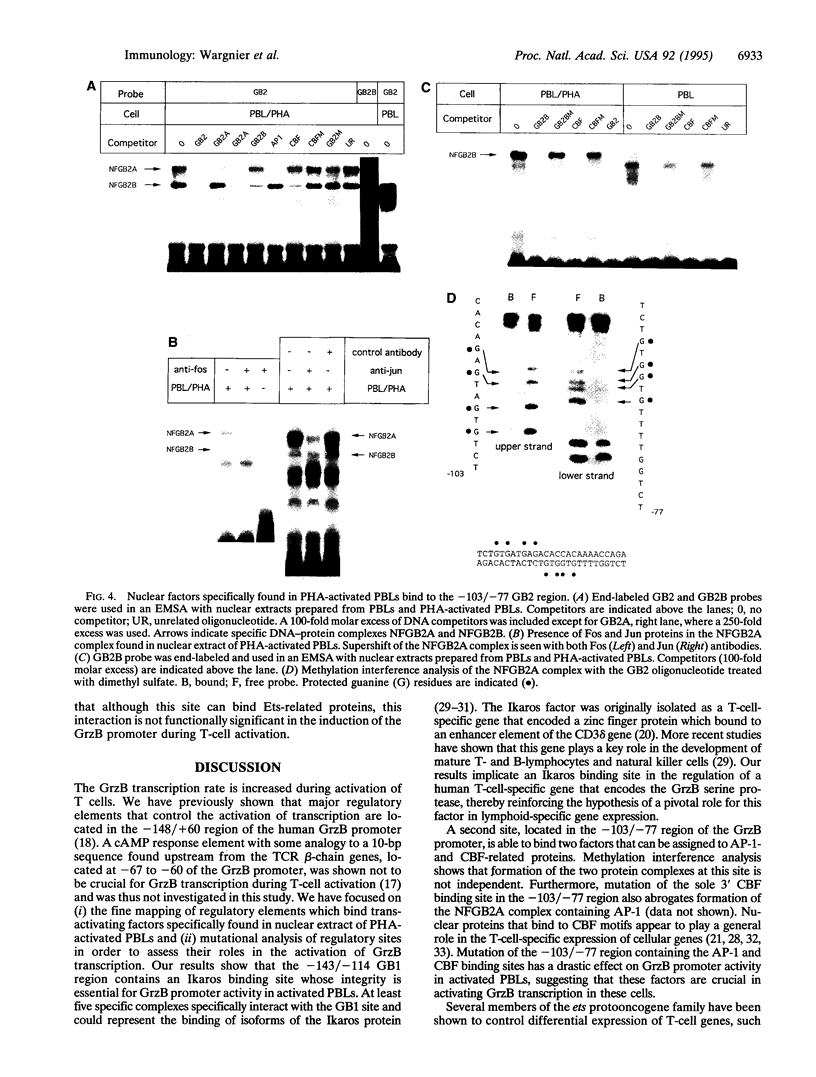

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Angel P., Imagawa M., Chiu R., Stein B., Imbra R. J., Rahmsdorf H. J., Jonat C., Herrlich P., Karin M. Phorbol ester-inducible genes contain a common cis element recognized by a TPA-modulated trans-acting factor. Cell. 1987 Jun 19;49(6):729–739. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90611-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Binétruy B., Smeal T., Karin M. Ha-Ras augments c-Jun activity and stimulates phosphorylation of its activation domain. Nature. 1991 May 9;351(6322):122–127. doi: 10.1038/351122a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blanchet O., Bourge J. F., Zinszner H., Israel A., Kourilsky P., Dausset J., Degos L., Paul P. Altered binding of regulatory factors to HLA class I enhancer sequence in human tumor cell lines lacking class I antigen expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Apr 15;89(8):3488–3492. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.8.3488. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caputo A., Fahey D., Lloyd C., Vozab R., McCairns E., Rowe P. B. Structure and differential mechanisms of regulation of expression of a serine esterase gene in activated human T lymphocytes. J Biol Chem. 1988 May 5;263(13):6363–6369. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duke R. C., Persechini P. M., Chang S., Liu C. C., Cohen J. J., Young J. D. Purified perforin induces target cell lysis but not DNA fragmentation. J Exp Med. 1989 Oct 1;170(4):1451–1456. doi: 10.1084/jem.170.4.1451. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Georgopoulos K., Bigby M., Wang J. H., Molnar A., Wu P., Winandy S., Sharpe A. The Ikaros gene is required for the development of all lymphoid lineages. Cell. 1994 Oct 7;79(1):143–156. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90407-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Georgopoulos K., Moore D. D., Derfler B. Ikaros, an early lymphoid-specific transcription factor and a putative mediator for T cell commitment. Science. 1992 Oct 30;258(5083):808–812. doi: 10.1126/science.1439790. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottschalk L. R., Giannola D. M., Emerson S. G. Molecular regulation of the human IL-3 gene: inducible T cell-restricted expression requires intact AP-1 and Elf-1 nuclear protein binding sites. J Exp Med. 1993 Nov 1;178(5):1681–1692. doi: 10.1084/jem.178.5.1681. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haddad P., Wargnier A., Bourge J. F., Sasportes M., Paul P. A promoter element of the human serine esterase granzyme B gene controls specific transcription in activated T cells. Eur J Immunol. 1993 Mar;23(3):625–629. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830230307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hahm K., Ernst P., Lo K., Kim G. S., Turck C., Smale S. T. The lymphoid transcription factor LyF-1 is encoded by specific, alternatively spliced mRNAs derived from the Ikaros gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Nov;14(11):7111–7123. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.11.7111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanson R. D., Grisolano J. L., Ley T. J. Consensus AP-1 and CRE motifs upstream from the human cytotoxic serine protease B (CSP-B/CGL-1) gene synergize to activate transcription. Blood. 1993 Nov 1;82(9):2749–2757. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanson R. D., Ley T. J. Transcriptional activation of the human cytotoxic serine protease gene CSP-B in T lymphocytes. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Nov;10(11):5655–5662. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.11.5655. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanson R. D., Sclar G. M., Kanagawa O., Ley T. J. The 5'-flanking region of the human CGL-1/granzyme B gene targets expression of a reporter gene to activated T-lymphocytes in transgenic mice. J Biol Chem. 1991 Dec 25;266(36):24433–24438. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henkart P. A., Millard P. J., Reynolds C. W., Henkart M. P. Cytolytic activity of purified cytoplasmic granules from cytotoxic rat large granular lymphocyte tumors. J Exp Med. 1984 Jul 1;160(1):75–93. doi: 10.1084/jem.160.1.75. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hernandez-Munain C., Krangel M. S. Regulation of the T-cell receptor delta enhancer by functional cooperation between c-Myb and core-binding factors. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Jan;14(1):473–483. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.1.473. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heusel J. W., Hanson R. D., Silverman G. A., Ley T. J. Structure and expression of a cluster of human hematopoietic serine protease genes found on chromosome 14q11.2. J Biol Chem. 1991 Apr 5;266(10):6152–6158. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heusel J. W., Wesselschmidt R. L., Shresta S., Russell J. H., Ley T. J. Cytotoxic lymphocytes require granzyme B for the rapid induction of DNA fragmentation and apoptosis in allogeneic target cells. Cell. 1994 Mar 25;76(6):977–987. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90376-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsiang Y. H., Spencer D., Wang S., Speck N. A., Raulet D. H. The role of viral enhancer "core" motif-related sequences in regulating T cell receptor-gamma and -delta gene expression. J Immunol. 1993 May 1;150(9):3905–3916. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hudig D., Ewoldt G. R., Woodard S. L. Proteases and lymphocyte cytotoxic killing mechanisms. Curr Opin Immunol. 1993 Feb;5(1):90–96. doi: 10.1016/0952-7915(93)90086-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koizumi H., Horta M. F., Youn B. S., Fu K. C., Kwon B. S., Young J. D., Liu C. C. Identification of a killer cell-specific regulatory element of the mouse perforin gene: an Ets-binding site-homologous motif that interacts with Ets-related proteins. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Nov;13(11):6690–6701. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.11.6690. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leiden J. M., Thompson C. B. Transcriptional regulation of T-cell genes during T-cell development. Curr Opin Immunol. 1994 Apr;6(2):231–237. doi: 10.1016/0952-7915(94)90096-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leung S., McCracken S., Ghysdael J., Miyamoto N. G. Requirement of an ETS-binding element for transcription of the human lck type I promoter. Oncogene. 1993 Apr;8(4):989–997. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luckow B., Schütz G. CAT constructions with multiple unique restriction sites for the functional analysis of eukaryotic promoters and regulatory elements. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Jul 10;15(13):5490–5490. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.13.5490. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masson D., Tschopp J. A family of serine esterases in lytic granules of cytolytic T lymphocytes. Cell. 1987 Jun 5;49(5):679–685. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90544-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Molnár A., Georgopoulos K. The Ikaros gene encodes a family of functionally diverse zinc finger DNA-binding proteins. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Dec;14(12):8292–8303. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.12.8292. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters P. J., Geuze H. J., Van der Donk H. A., Slot J. W., Griffith J. M., Stam N. J., Clevers H. C., Borst J. Molecules relevant for T cell-target cell interaction are present in cytolytic granules of human T lymphocytes. Eur J Immunol. 1989 Aug;19(8):1469–1475. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830190819. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Podack E. R., Hengartner H., Lichtenheld M. G. A central role of perforin in cytolysis? Annu Rev Immunol. 1991;9:129–157. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.09.040191.001021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prosser H. M., Wotton D., Gegonne A., Ghysdael J., Wang S., Speck N. A., Owen M. J. A phorbol ester response element within the human T-cell receptor beta-chain enhancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Oct 15;89(20):9934–9938. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.20.9934. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Redondo J. M., Pfohl J. L., Krangel M. S. Identification of an essential site for transcriptional activation within the human T-cell receptor delta enhancer. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Nov;11(11):5671–5680. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.11.5671. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salmon P., Giovane A., Wasylyk B., Klatzmann D. Characterization of the human CD4 gene promoter: transcription from the CD4 gene core promoter is tissue-specific and is activated by Ets proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Aug 15;90(16):7739–7743. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.16.7739. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw J. P., Utz P. J., Durand D. B., Toole J. J., Emmel E. A., Crabtree G. R. Identification of a putative regulator of early T cell activation genes. Science. 1988 Jul 8;241(4862):202–205. doi: 10.1126/science.3260404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shi L., Kam C. M., Powers J. C., Aebersold R., Greenberg A. H. Purification of three cytotoxic lymphocyte granule serine proteases that induce apoptosis through distinct substrate and target cell interactions. J Exp Med. 1992 Dec 1;176(6):1521–1529. doi: 10.1084/jem.176.6.1521. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shi L., Kraut R. P., Aebersold R., Greenberg A. H. A natural killer cell granule protein that induces DNA fragmentation and apoptosis. J Exp Med. 1992 Feb 1;175(2):553–566. doi: 10.1084/jem.175.2.553. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tschopp J., Schäfer S., Masson D., Peitsch M. C., Heusser C. Phosphorylcholine acts as a Ca2+-dependent receptor molecule for lymphocyte perforin. Nature. 1989 Jan 19;337(6204):272–274. doi: 10.1038/337272a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woods D. B., Ghysdael J., Owen M. J. Identification of nucleotide preferences in DNA sequences recognised specifically by c-Ets-1 protein. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Feb 25;20(4):699–704. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.4.699. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wotton D., Ghysdael J., Wang S., Speck N. A., Owen M. J. Cooperative binding of Ets-1 and core binding factor to DNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Jan;14(1):840–850. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.1.840. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young J. D., Cohn Z. A., Podack E. R. The ninth component of complement and the pore-forming protein (perforin 1) from cytotoxic T cells: structural, immunological, and functional similarities. Science. 1986 Jul 11;233(4760):184–190. doi: 10.1126/science.2425429. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]