Abstract
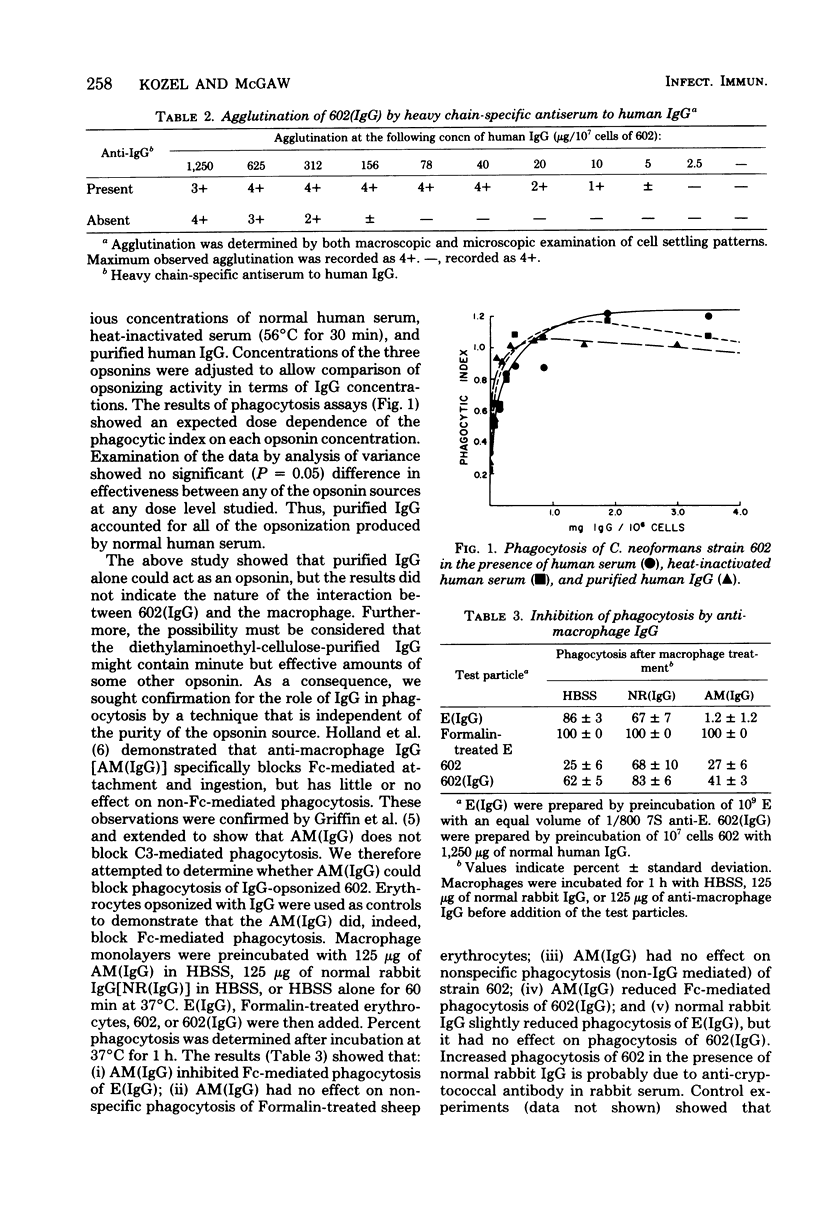
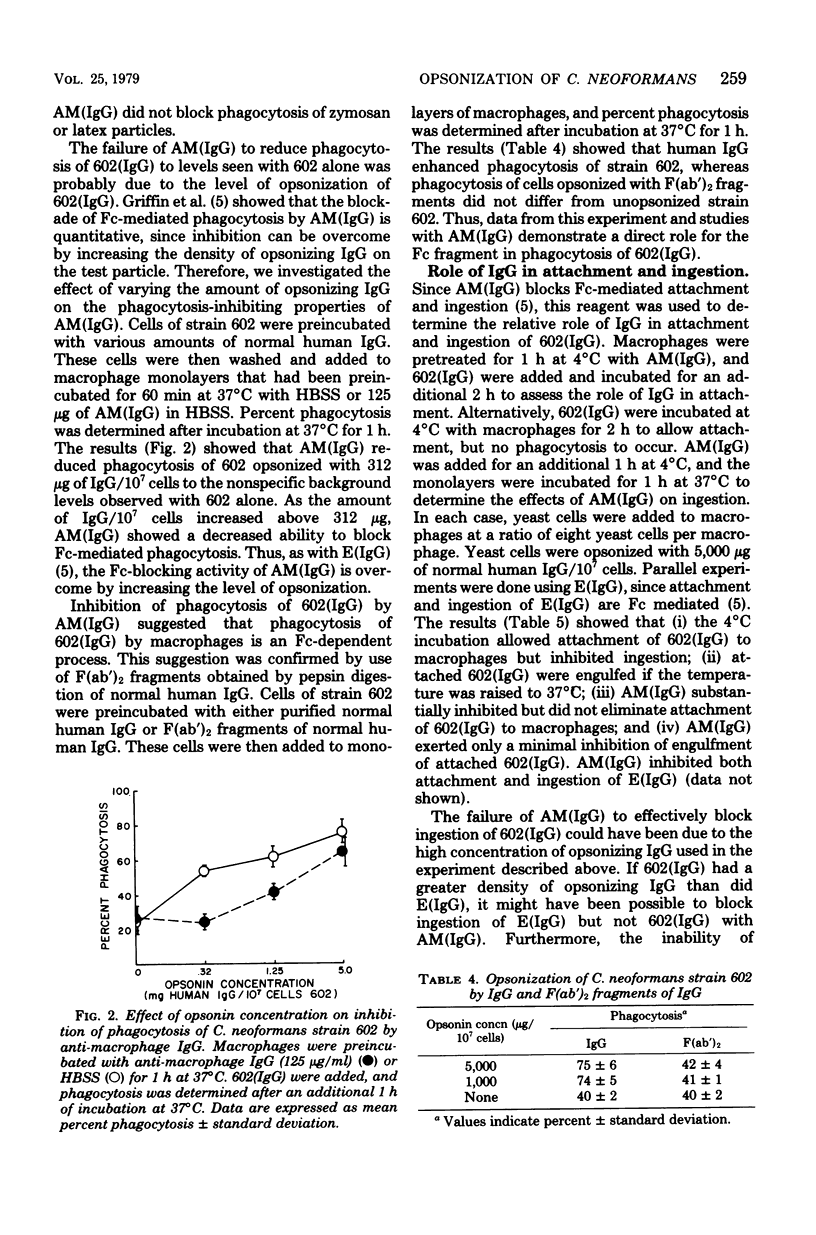
The role of immunoglobulin G (IgG) as an opsonin in phagocytosis of Cryptococcus neoformans by macrophages was investigated. Labeling with 125I showed that IgG isolated from normal human serum bound to non-encapsulated C. neoformans. Furthermore, IgG-opsonized cryptococci were agglutinated by anti-serum to IgG heavy chains, indicating that normal human serum contains antibody that will bind to the yeast surface. The IgG isolated from normal serum accounted for all opsonizing activity found in normal human serum, since differences were not noted between the opsonizing activities of whole serum, heat-inactivated serum and purified IgG when these opsonins were compared at equivalent concentrations of IgG. Phagocytosis of IgG-opsonized cryptococci was inhibited by anti-macrophage IgG, a reagent known to block Fc-mediated attachment and ingestion, and by pepsin digestion of opsonizing IgG. Thus, IgG opsonization is an Fc-dependent process. Opsonizing IgG appears to play its major role during the attachment phase of phagocytosis, since antimacrophage IgG blocked attachment of cryptococci to macrophages but could not block ingestion of IgG-opsonized cryptococci that had been allowed to attach to macrophages. Ingestion of opsonized cryptococci was not blocked by 2-deoxy-D-glucose, a reagent known to block Fc-mediated ingestion, thus confirming that IgG has a primary role in attachment and suggesting that ingestion is mediated by a process that is not Fc dependent.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Czop J. K., Fearon D. T., Austen K. F. Opsonin-independent phagocytosis of activators of the alternative complement pathway by human monocytes. J Immunol. 1978 Apr;120(4):1132–1138. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamond R. D., May J. E., Kane M. A., Frank M. M., Bennett J. E. The role of the classical and alternate complement pathways in host defenses against Cryptococcus neoformans infection. J Immunol. 1974 Jun;112(6):2260–2270. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamond R. D., Root R. K., Bennett J. E. Factors influencing killing of Cryptococcus neoformans by human leukocytes in vitro. J Infect Dis. 1972 Apr;125(4):367–376. doi: 10.1093/infdis/125.4.367. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffin F. M., Jr, Griffin J. A., Leider J. E., Silverstein S. C. Studies on the mechanism of phagocytosis. I. Requirements for circumferential attachment of particle-bound ligands to specific receptors on the macrophage plasma membrane. J Exp Med. 1975 Nov 1;142(5):1263–1282. doi: 10.1084/jem.142.5.1263. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holland P., Holland N. H., Cohn Z. A. The selective inhibition of macrophage phagocytic receptors by anti-membrane antibodies. J Exp Med. 1972 Mar 1;135(3):458–475. doi: 10.1084/jem.135.3.458. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan G. Differences in the mode of phagocytosis with Fc and C3 receptors in macrophages. Scand J Immunol. 1977;6(8):797–807. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1977.tb02153.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozel T. R., Cazin J. Nonencapsulated Variant of Cryptococcus neoformans I. Virulence Studies and Characterization of Soluble Polysaccharide. Infect Immun. 1971 Feb;3(2):287–294. doi: 10.1128/iai.3.2.287-294.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozel T. R., Mastroianni R. P. Inhibition of phagocytosis by cryptococcal polysaccharide: dissociation of the attachment and ingestion phases of phagocytosis. Infect Immun. 1976 Jul;14(1):62–67. doi: 10.1128/iai.14.1.62-67.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozel T. R. Non-encapsulated variant of Cryptococcus neoformans. II. Surface receptors for cryptococcal polysaccharide and their role in inhibition of phagocytosis by polysaccharide. Infect Immun. 1977 Apr;16(1):99–106. doi: 10.1128/iai.16.1.99-106.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marchalonis J. J. An enzymic method for the trace iodination of immunoglobulins and other proteins. Biochem J. 1969 Jun;113(2):299–305. doi: 10.1042/bj1130299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michl J., Ohlbaum D. J., Silverstein S. C. 2-Deoxyglucose selectively inhibits Fc and complement receptor-mediated phagocytosis in mouse peritoneal macrophages. I. Description of the inhibitory effect. J Exp Med. 1976 Dec 1;144(6):1465–1483. doi: 10.1084/jem.144.6.1465. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell T. G., Friedman L. In vitro phagocytosis and intracellular fate of variously encapsulated strains of Cryptococcus neoformans. Infect Immun. 1972 Apr;5(4):491–498. doi: 10.1128/iai.5.4.491-498.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nir S., Andersen M. Van der Waals interactions between cell surfaces. J Membr Biol. 1977 Feb 24;31(1-2):1–18. doi: 10.1007/BF01869396. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SPIEGELBERG H. L., WEIGLE W. O. THE CATABOLISM OF HOMOLOGOUS AND HETEROLOGOUS 7S GAMMA GLOBULIN FRAGMENTS. J Exp Med. 1965 Mar 1;121:323–338. doi: 10.1084/jem.121.3.323. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shahar A., Kletter Y., Aronson M. Granuloma formation in cryptococcosis. Isr J Med Sci. 1969 Nov-Dec;5(6):1164–1172. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swenson F. J., Kozel T. R. Phagocytosis of Cryptococcus neoformans by normal and thioglycolate-activated macrophages. Infect Immun. 1978 Sep;21(3):714–720. doi: 10.1128/iai.21.3.714-720.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thorell J. I., Johansson B. G. Enzymatic iodination of polypeptides with 125I to high specific activity. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Dec 28;251(3):363–369. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(71)90123-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weir D. M., Ogmundsdóttir H. M. Non-specific recognition mechanisms by mononuclear phagocytes. Clin Exp Immunol. 1977 Nov;30(2):323–329. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



