Abstract
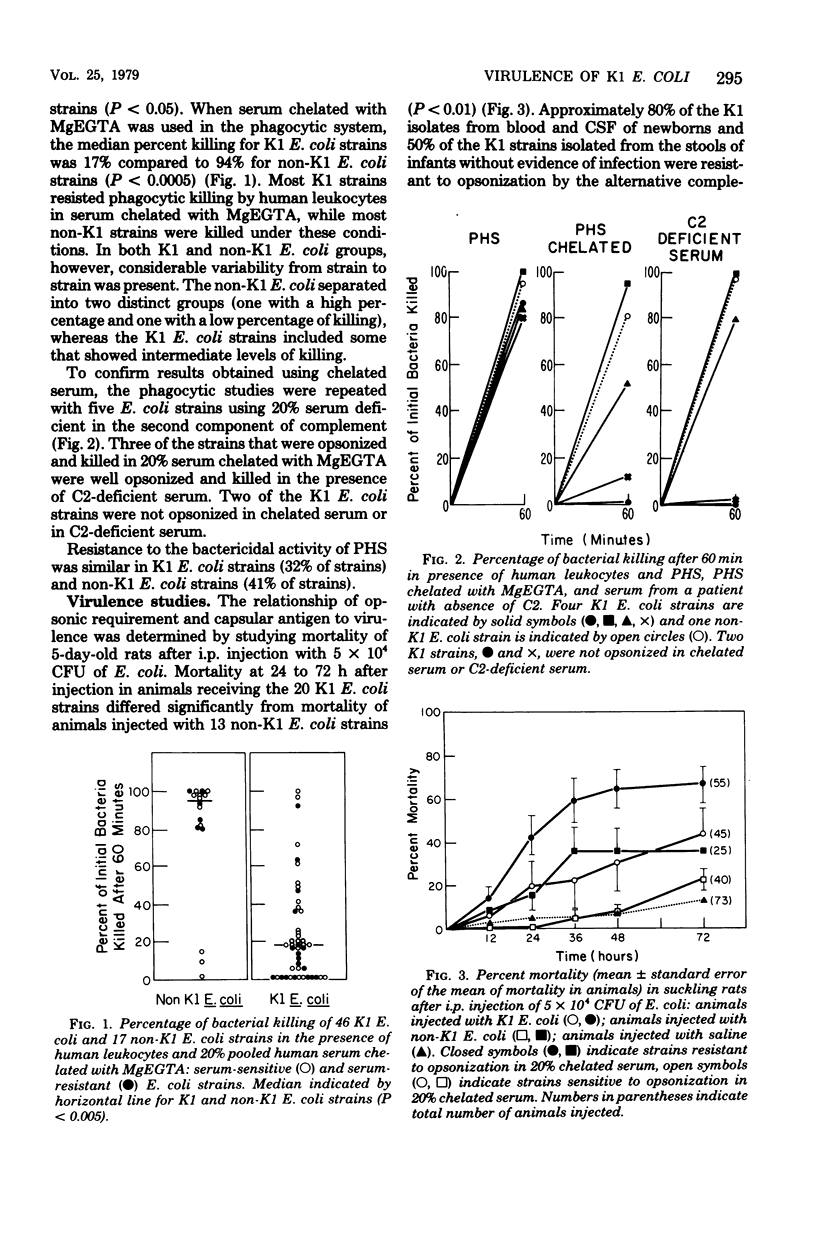
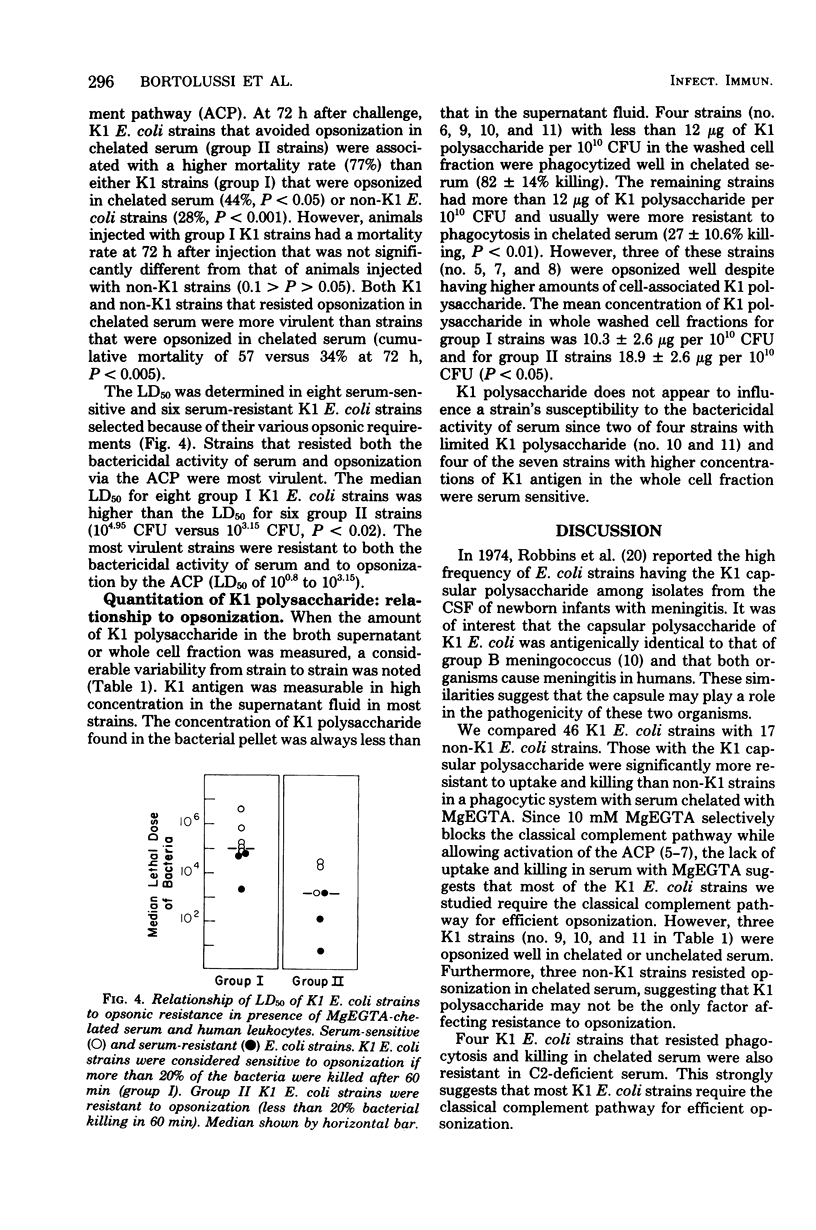
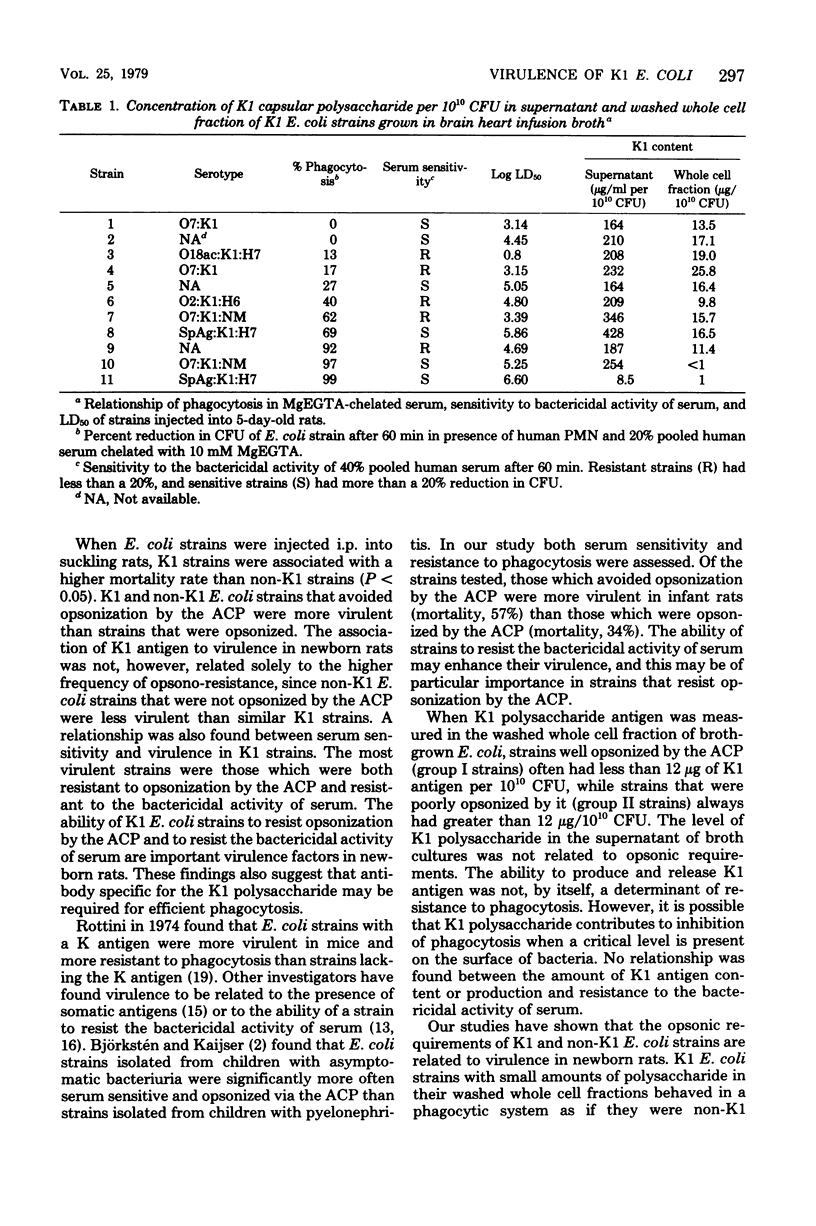
The virulence of Escherichia coli strains for newborn rats was related to opsonic requirements of the strains, sensitivity to the bactericidal activity of serum, and K1 capsular polysaccharide content. K1 E. coli strains were more virulent than non-K1 strains after intraperitoneal injection in newborn rats (P less than 0.05) and were more resistant to phagocytosis than non-K1 strains when the classical complement pathway was blocked with Mg-ethyleneglycoltetraacetic acid (P less than 0.0005). Sensitivity to the bactericidal activity of serum was similar among K1 and non-K1 E. coli strains. Two groups of K1 E. coli strains were defined on the basis of opsonic requirements. Group I strains were efficiently opsonized by the alternative complement pathway, while group II strains required the classical complement pathway for opsonization. Group I strains had less detectable K1 polysaccharide in the washed whole cell fraction than group II strains (10.3 versus 18.9 microgram of K1 polysaccharide per 10(10) colony-forming units) and were less virulent than group II strains (mortality, 44 versus 77%, P less than 0.05). The K1 capsular polysaccharide appears to play an important role in determining virulence in newborn rats and opsonic requirements of these strains, but does not contribute to the sensitivity of strains to the bactericidal activity of serum.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Björkstén B., Bortolussi R., Gothefors L., Quie P. G. Interaction of E. coli strains with human serum: lack of relationship to K1 antigen. J Pediatr. 1976 Dec;89(6):892–897. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(76)80592-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Björkstén B., Kaijser B. Interaction of human serum and neutrophils with Escherichia coli strains: differences between strains isolated from urine of patients with pyelonephritis or asymptomatic bacteriuria. Infect Immun. 1978 Nov;22(2):308–311. doi: 10.1128/iai.22.2.308-311.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bortolussi R., Ferrieri P., Wannamaker L. W. Dynamics of Escherichia coli infection and meningitis in infant rats. Infect Immun. 1978 Nov;22(2):480–485. doi: 10.1128/iai.22.2.480-485.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bortolussi R., Krishnan C., Armstrong D., Tovichayathamrong P. Prognosis for survival in neonatal meningitis: clinical and pathologic review of 52 cases. Can Med Assoc J. 1978 Jan 21;118(2):165–168. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forsgren A., Mclean R. H., Michael A. F., Quie P. G. Studies of the alternate pathway in chelated serum. J Lab Clin Med. 1975 Jun;85(6):904–912. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forsgren A., Quie P. G. Influence of the alternate complement pathway in opsonization of several bacterial species. Infect Immun. 1974 Aug;10(2):402–404. doi: 10.1128/iai.10.2.402-404.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forsgren A., Quie P. G. Opsonic activity in human serum chelated with ethylene glycoltetra-acetic acid. Immunology. 1974 Jun;26(6):1251–1256. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldacre M. J. Acute bacterial meningitis in childhood. Incidence and mortality in a defined population. Lancet. 1976 Jan 3;1(7949):28–31. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(76)92921-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard C. J., Glynn A. A. The virulence for mice of strains of Escherichia coli related to the effects of K antigens on their resistance to phagocytosis and killing by complement. Immunology. 1971 May;20(5):767–777. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasper D. L., Winkelhake J. L., Zollinger W. D., Brandt B. L., Artenstein M. S. Immunochemical similarity between polysaccharide antigens of Escherichia coli 07: K1(L):NM and group B Neisseria meningitidis. J Immunol. 1973 Jan;110(1):262–268. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim Y., Friend P. S., Dresner I. G., Yunis E. J., Michael A. F. Inherited deficiency of the second component of complement (C2) with membranoproliferative glomerulonephritis. Am J Med. 1977 May;62(5):765–771. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(77)90881-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCabe W. R., Carling P. C., Bruins S., Greely A. The relation of K-antigen to virulence of Escherichia coli. J Infect Dis. 1975 Jan;131(1):6–10. doi: 10.1093/infdis/131.1.6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCabe W. R., Kaijser B., Olling S., Uwaydah M., Hanson L. A. Escherichia coli in bacteremia: K and O antigens and serum sensitivity of strains from adults and neonates. J Infect Dis. 1978 Jul;138(1):33–41. doi: 10.1093/infdis/138.1.33. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCracken G. H., Jr, Sarff L. D., Glode M. P., Mize S. G., Schiffer M. S., Robbins J. B., Gotschlich E. C., Orskov I., Orskov F. Relation between Escherichia coli K1 capsular polysaccharide antigen and clinical outcome in neonatal meningitis. Lancet. 1974 Aug 3;2(7875):246–250. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(74)91413-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Medearis D. N., Jr, Camitta B. M., Heath E. C. Cell wall composition and virulence in Escherichia coli. J Exp Med. 1968 Sep 1;128(3):399–414. doi: 10.1084/jem.128.3.399. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olling S., Hanson L. A., Holmgren J., Jodal U., Lincoln K., Lindberg U. The bactericidal effect of normal human serum on E. coli strains from normals and from patients with urinary tract infections. Infection. 1973;1(1):24–28. doi: 10.1007/BF01638251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quie P. G., White J. G., Holmes B., Good R. A. In vitro bactericidal capacity of human polymorphonuclear leukocytes: diminished activity in chronic granulomatous disease of childhood. J Clin Invest. 1967 Apr;46(4):668–679. doi: 10.1172/JCI105568. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robbins J. B., McCracken G. H., Jr, Gotschlich E. C., Orskov F., Orskov I., Hanson L. A. Escherichia coli K1 capsular polysaccharide associated with neonatal meningitis. N Engl J Med. 1974 May 30;290(22):1216–1220. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197405302902202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rottini G., Dri P., Soranzo M. R., Patriarca P. Correlation between phagocytic activity and metabolic response of polymorphonuclear leukocytes toward different strains of Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1975 Mar;11(3):417–423. doi: 10.1128/iai.11.3.417-423.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarff L. D., McCracken G. H., Schiffer M. S., Glode M. P., Robbins J. B., Orskov I., Orskov F. Epidemiology of Escherichia coli K1 in healthy and diseased newborns. Lancet. 1975 May 17;1(7916):1099–1104. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(75)92496-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weeke B. Rocket immunoelectrophoresis. Scand J Immunol Suppl. 1973;1:37–46. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1973.tb03777.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



