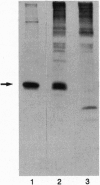
Abstract
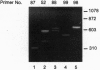
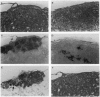
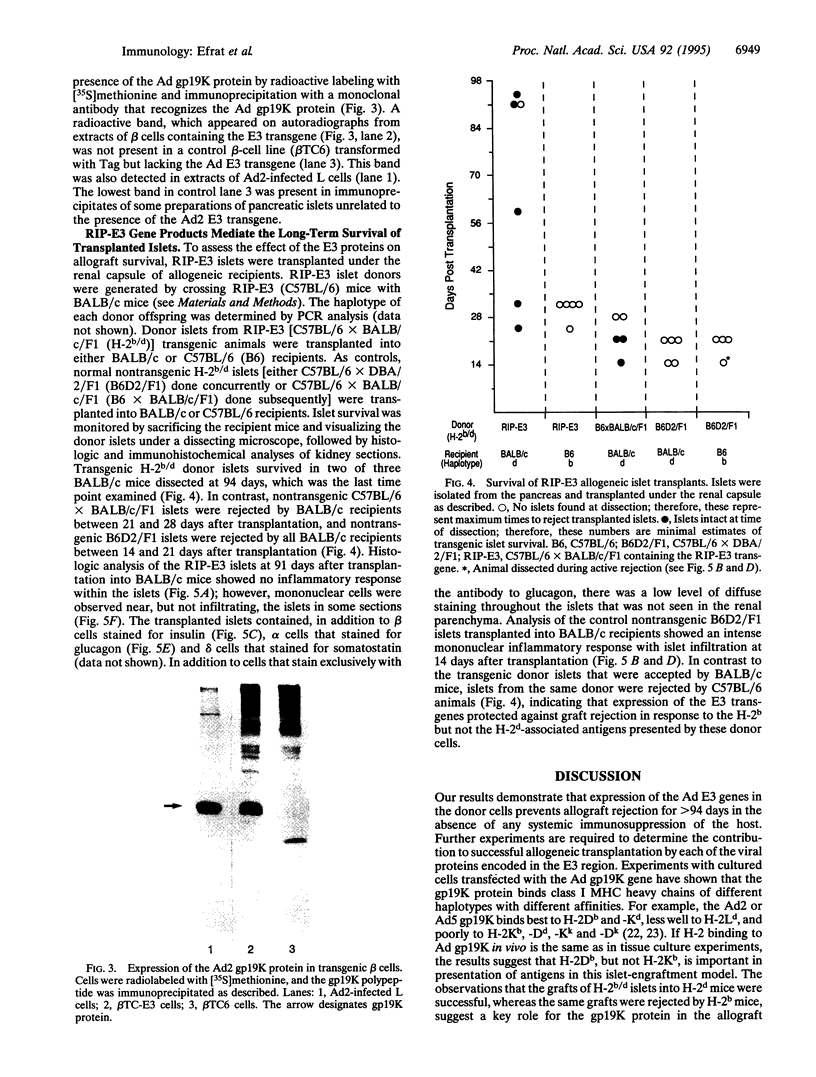
The adenovirus (Ad) early region 3 (E3) genes code for at least four proteins that inhibit the host immune responses mediated by cytotoxic T lymphocytes and tumor necrosis factor alpha. To evaluate the potential use of these immunoregulatory viral functions in facilitating allogeneic cell transplantation, the Ad E3 genes were expressed in pancreatic beta cells in transgenic mice under control of the rat insulin II promoter. Transgenic H-2b/d (C57BL/6 x BALB/c) islets, expressing the Ad E3 genes, remained viable for at least 94 days after transplantation under the kidney capsule of BALB/c (H-2d) recipients. Nontransgenic H-2b/d control islets were rejected as anticipated between 14 and 28 days. Histological analysis of the transplanted transgenic islets revealed normal architecture. Immunohistochemical studies with antisera to islet hormones revealed the presence of both beta and non-beta islet cells, suggesting a propagation of the immunosuppressive effect of Ad proteins from beta cells to other islet cells. The use of viral genes, which have evolved to regulate virus-host interactions, to immunosupress the anti-genicity of donor transplant tissue suggests additional ways for prolonging allograft survival. In addition, these findings have implications for designing Ad vectors for gene therapy.
Full text
PDF

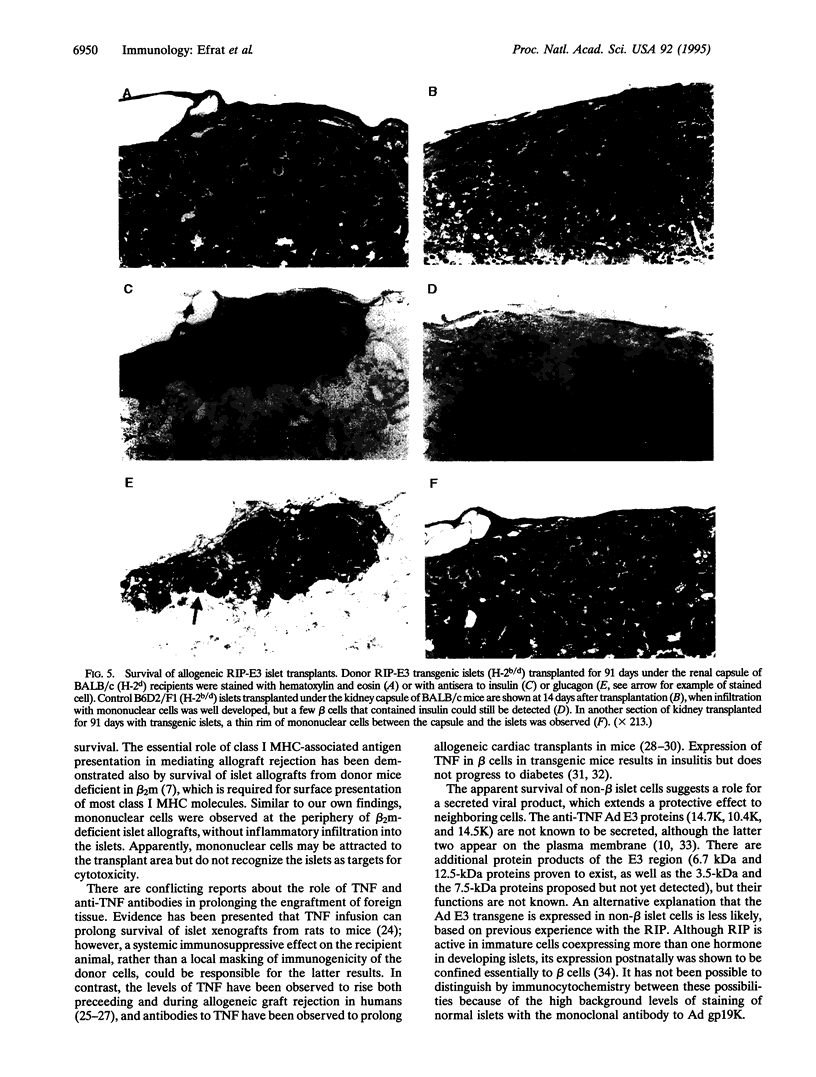

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alpert S., Hanahan D., Teitelman G. Hybrid insulin genes reveal a developmental lineage for pancreatic endocrine cells and imply a relationship with neurons. Cell. 1988 Apr 22;53(2):295–308. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90391-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beier D. C., Cox J. H., Vining D. R., Cresswell P., Engelhard V. H. Association of human class I MHC alleles with the adenovirus E3/19K protein. J Immunol. 1994 Apr 15;152(8):3862–3872. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolling S. F., Kunkel S. L., Lin H. Prolongation of cardiac allograft survival in rats by anti-TNF and cyclosporine combination therapy. Transplantation. 1992 Feb;53(2):283–286. doi: 10.1097/00007890-199202010-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgert H. G., Kvist S. An adenovirus type 2 glycoprotein blocks cell surface expression of human histocompatibility class I antigens. Cell. 1985 Jul;41(3):987–997. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80079-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlin C. R., Tollefson A. E., Brady H. A., Hoffman B. L., Wold W. S. Epidermal growth factor receptor is down-regulated by a 10,400 MW protein encoded by the E3 region of adenovirus. Cell. 1989 Apr 7;57(1):135–144. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90179-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chengalvala M. V., Bhat B. M., Bhat R., Lubeck M. D., Mizutani S., Davis A. R., Hung P. P. Immunogenicity of high expression adenovirus-hepatitis B virus recombinant vaccines in dogs. J Gen Virol. 1994 Jan;75(Pt 1):125–131. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-75-1-125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cladaras C., Bhat B., Wold W. S. Mapping the 5' ends, 3' ends, and splice sites of mRNAs from the early E3 transcription unit of adenovirus 5. Virology. 1985 Jan 15;140(1):44–54. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(85)90444-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox J. H., Bennink J. R., Yewdell J. W. Retention of adenovirus E19 glycoprotein in the endoplasmic reticulum is essential to its ability to block antigen presentation. J Exp Med. 1991 Dec 1;174(6):1629–1637. doi: 10.1084/jem.174.6.1629. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox J. H., Yewdell J. W., Eisenlohr L. C., Johnson P. R., Bennink J. R. Antigen presentation requires transport of MHC class I molecules from the endoplasmic reticulum. Science. 1990 Feb 9;247(4943):715–718. doi: 10.1126/science.2137259. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duerksen-Hughes P. J., Hermiston T. W., Wold W. S., Gooding L. R. The amino-terminal portion of CD1 of the adenovirus E1A proteins is required to induce susceptibility to tumor necrosis factor cytolysis in adenovirus-infected mouse cells. J Virol. 1991 Mar;65(3):1236–1244. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.3.1236-1244.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Efrat S., Hanahan D. Bidirectional activity of the rat insulin II 5'-flanking region in transgenic mice. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jan;7(1):192–198. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.1.192. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Efrat S., Linde S., Kofod H., Spector D., Delannoy M., Grant S., Hanahan D., Baekkeskov S. Beta-cell lines derived from transgenic mice expressing a hybrid insulin gene-oncogene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(23):9037–9041. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.23.9037. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Efrat S. Sexual dimorphism of pancreatic beta-cell degeneration in transgenic mice expressing an insulin-ras hybrid gene. Endocrinology. 1991 Feb;128(2):897–901. doi: 10.1210/endo-128-2-897. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engelhardt J. F., Ye X., Doranz B., Wilson J. M. Ablation of E2A in recombinant adenoviruses improves transgene persistence and decreases inflammatory response in mouse liver. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Jun 21;91(13):6196–6200. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.13.6196. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faustman D., Coe C. Prevention of xenograft rejection by masking donor HLA class I antigens. Science. 1991 Jun 21;252(5013):1700–1702. doi: 10.1126/science.1710828. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fejer G., Gyory I., Tufariello J., Horwitz M. S. Characterization of transgenic mice containing adenovirus early region 3 genomic DNA. J Virol. 1994 Sep;68(9):5871–5881. doi: 10.1128/jvi.68.9.5871-5881.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerasimidi A., Sheehan K. C., Schreiber R. D., Lacy P. E. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha prevents rejection of islet xenografts (rat to mouse). Diabetes. 1993 May;42(5):651–657. doi: 10.2337/diab.42.5.651. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Germain R. N. MHC-dependent antigen processing and peptide presentation: providing ligands for T lymphocyte activation. Cell. 1994 Jan 28;76(2):287–299. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90336-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gooding L. R., Wold W. S. Molecular mechanisms by which adenoviruses counteract antiviral immune defenses. Crit Rev Immunol. 1990;10(1):53–71. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grewal H. P., Kotb M., Salem A., el Din A. B., Novak K., Martin J., Gaber L. W., Gaber A. O. Elevated tumor necrosis factor levels are predictive for pancreas allograft transplant rejection. Transplant Proc. 1993 Feb;25(1 Pt 1):132–135. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton G., Prettenhofer M., Zommer A., Hofbauer S., Götzinger P., Gnant F. X., Függer R. Intraoperative course and prognostic significance of endotoxin, tumor necrosis factor-alpha and interleukin-6 in liver transplant recipients. Immunobiology. 1991 Aug;182(5):425–439. doi: 10.1016/s0171-2985(11)80207-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanahan D. Heritable formation of pancreatic beta-cell tumours in transgenic mice expressing recombinant insulin/simian virus 40 oncogenes. Nature. 1985 May 9;315(6015):115–122. doi: 10.1038/315115a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higuchi Y., Herrera P., Muniesa P., Huarte J., Belin D., Ohashi P., Aichele P., Orci L., Vassalli J. D., Vassalli P. Expression of a tumor necrosis factor alpha transgene in murine pancreatic beta cells results in severe and permanent insulitis without evolution towards diabetes. J Exp Med. 1992 Dec 1;176(6):1719–1731. doi: 10.1084/jem.176.6.1719. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imagawa D. K., Millis J. M., Seu P., Olthoff K. M., Hart J., Wasef E., Dempsey R. A., Stephens S., Busuttil R. W. The role of tumor necrosis factor in allograft rejection. III. Evidence that anti-TNF antibody therapy prolongs allograft survival in rats with acute rejection. Transplantation. 1991 Jan;51(1):57–62. doi: 10.1097/00007890-199101000-00008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knaack D., Fiore D. M., Surana M., Leiser M., Laurance M., Fusco-DeMane D., Hegre O. D., Fleischer N., Efrat S. Clonal insulinoma cell line that stably maintains correct glucose responsiveness. Diabetes. 1994 Dec;43(12):1413–1417. doi: 10.2337/diab.43.12.1413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koller B. H., Smithies O. Inactivating the beta 2-microglobulin locus in mouse embryonic stem cells by homologous recombination. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Nov;86(22):8932–8935. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.22.8932. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krajcsi P., Tollefson A. E., Anderson C. W., Wold W. S. The adenovirus E3 14.5-kilodalton protein, which is required for down-regulation of the epidermal growth factor receptor and prevention of tumor necrosis factor cytolysis, is an integral membrane protein oriented with its C terminus in the cytoplasm. J Virol. 1992 Mar;66(3):1665–1673. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.3.1665-1673.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuivinen E., Hoffman B. L., Hoffman P. A., Carlin C. R. Structurally related class I and class II receptor protein tyrosine kinases are down-regulated by the same E3 protein coded for by human group C adenoviruses. J Cell Biol. 1993 Mar;120(5):1271–1279. doi: 10.1083/jcb.120.5.1271. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Körner H., Fritzsche U., Burgert H. G. Tumor necrosis factor alpha stimulates expression of adenovirus early region 3 proteins: implications for viral persistence. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Dec 15;89(24):11857–11861. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.24.11857. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin H., Chensue S. W., Strieter R. M., Remick D. G., Gallagher K. P., Bolling S. F., Kunkel S. L. Antibodies against tumor necrosis factor prolong cardiac allograft survival in the rat. J Heart Lung Transplant. 1992 Mar-Apr;11(2 Pt 1):330–335. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markmann J. F., Bassiri H., Desai N. M., Odorico J. S., Kim J. I., Koller B. H., Smithies O., Barker C. F. Indefinite survival of MHC class I-deficient murine pancreatic islet allografts. Transplantation. 1992 Dec;54(6):1085–1089. doi: 10.1097/00007890-199212000-00025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noronha I. L., Eberlein-Gonska M., Hartley B., Stephens S., Cameron J. S., Waldherr R. In situ expression of tumor necrosis factor-alpha, interferon-gamma, and interleukin-2 receptors in renal allograft biopsies. Transplantation. 1992 Dec;54(6):1017–1024. doi: 10.1097/00007890-199212000-00015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osorio R. W., Ascher N. L., Jaenisch R., Freise C. E., Roberts J. P., Stock P. G. Major histocompatibility complex class I deficiency prolongs islet allograft survival. Diabetes. 1993 Oct;42(10):1520–1527. doi: 10.2337/diab.42.10.1520. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Picarella D. E., Kratz A., Li C. B., Ruddle N. H., Flavell R. A. Transgenic tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-alpha production in pancreatic islets leads to insulitis, not diabetes. Distinct patterns of inflammation in TNF-alpha and TNF-beta transgenic mice. J Immunol. 1993 May 1;150(9):4136–4150. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prince G. A., Porter D. D., Jenson A. B., Horswood R. L., Chanock R. M., Ginsberg H. S. Pathogenesis of adenovirus type 5 pneumonia in cotton rats (Sigmodon hispidus). J Virol. 1993 Jan;67(1):101–111. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.1.101-111.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenfeld M. A., Yoshimura K., Trapnell B. C., Yoneyama K., Rosenthal E. R., Dalemans W., Fukayama M., Bargon J., Stier L. E., Stratford-Perricaudet L. In vivo transfer of the human cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator gene to the airway epithelium. Cell. 1992 Jan 10;68(1):143–155. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90213-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Routes J. M., Metz B. A., Cook J. L. Endogenous expression of E1A in human cells enhances the effect of adenovirus E3 on class I major histocompatibility complex antigen expression. J Virol. 1993 Jun;67(6):3176–3181. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.6.3176-3181.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tollefson A. E., Stewart A. R., Yei S. P., Saha S. K., Wold W. S. The 10,400- and 14,500-dalton proteins encoded by region E3 of adenovirus form a complex and function together to down-regulate the epidermal growth factor receptor. J Virol. 1991 Jun;65(6):3095–3105. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.6.3095-3105.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tufariello J., Cho S., Horwitz M. S. The adenovirus E3 14.7-kilodalton protein which inhibits cytolysis by tumor necrosis factor increases the virulence of vaccinia virus in a murine pneumonia model. J Virol. 1994 Jan;68(1):453–462. doi: 10.1128/jvi.68.1.453-462.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss E., Golden L., Zakut R., Mellor A., Fahrner K., Kvist S., Flavell R. A. The DNA sequence of the H-2kb gene: evidence for gene conversion as a mechanism for the generation of polymorphism in histocompatibilty antigens. EMBO J. 1983;2(3):453–462. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01444.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wold W. S. Adenovirus genes that modulate the sensitivity of virus-infected cells to lysis by TNF. J Cell Biochem. 1993 Dec;53(4):329–335. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240530410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wold W. S., Gooding L. R. Region E3 of adenovirus: a cassette of genes involved in host immunosurveillance and virus-cell interactions. Virology. 1991 Sep;184(1):1–8. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90815-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zijlstra M., Li E., Sajjadi F., Subramani S., Jaenisch R. Germ-line transmission of a disrupted beta 2-microglobulin gene produced by homologous recombination in embryonic stem cells. Nature. 1989 Nov 23;342(6248):435–438. doi: 10.1038/342435a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zilli D., Voelkel-Johnson C., Skinner T., Laster S. M. The adenovirus E3 region 14.7 kDa protein, heat and sodium arsenite inhibit the TNF-induced release of arachidonic acid. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1992 Oct 15;188(1):177–183. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(92)92366-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]