Abstract
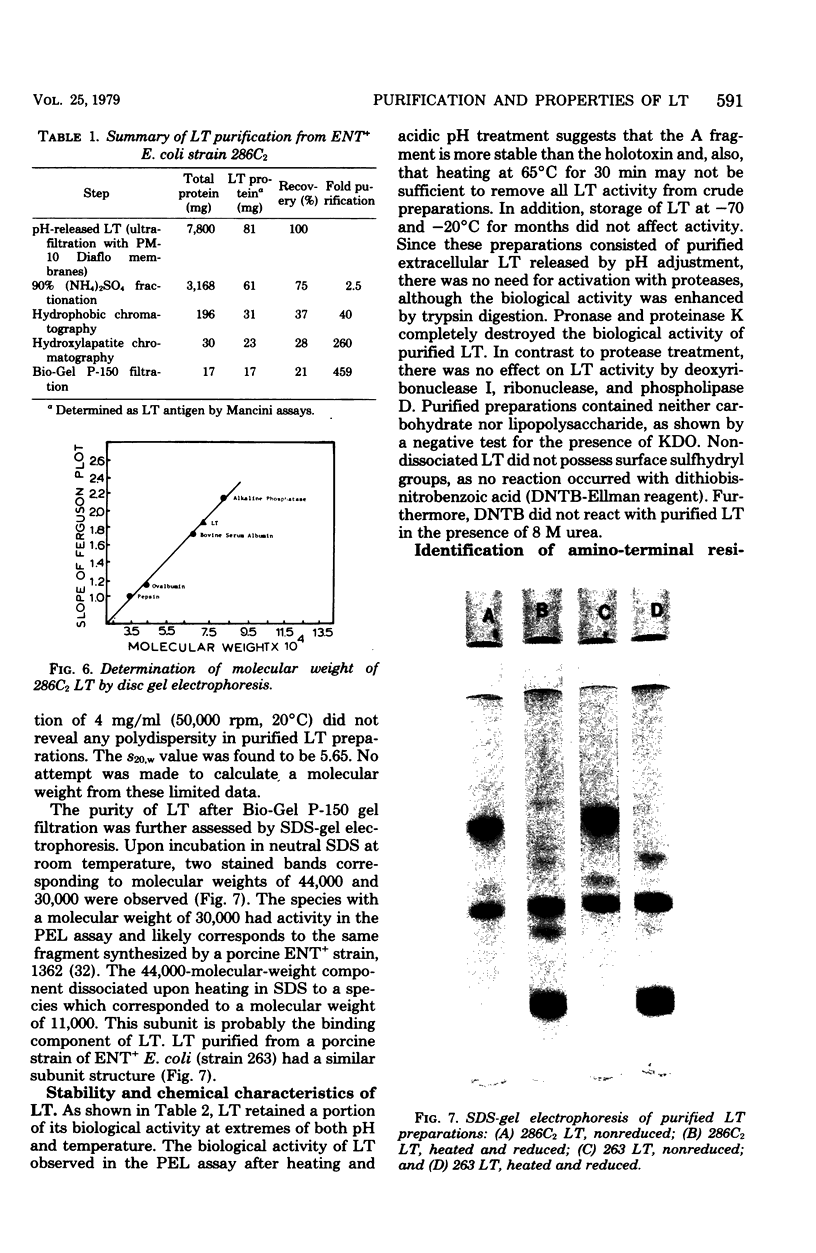
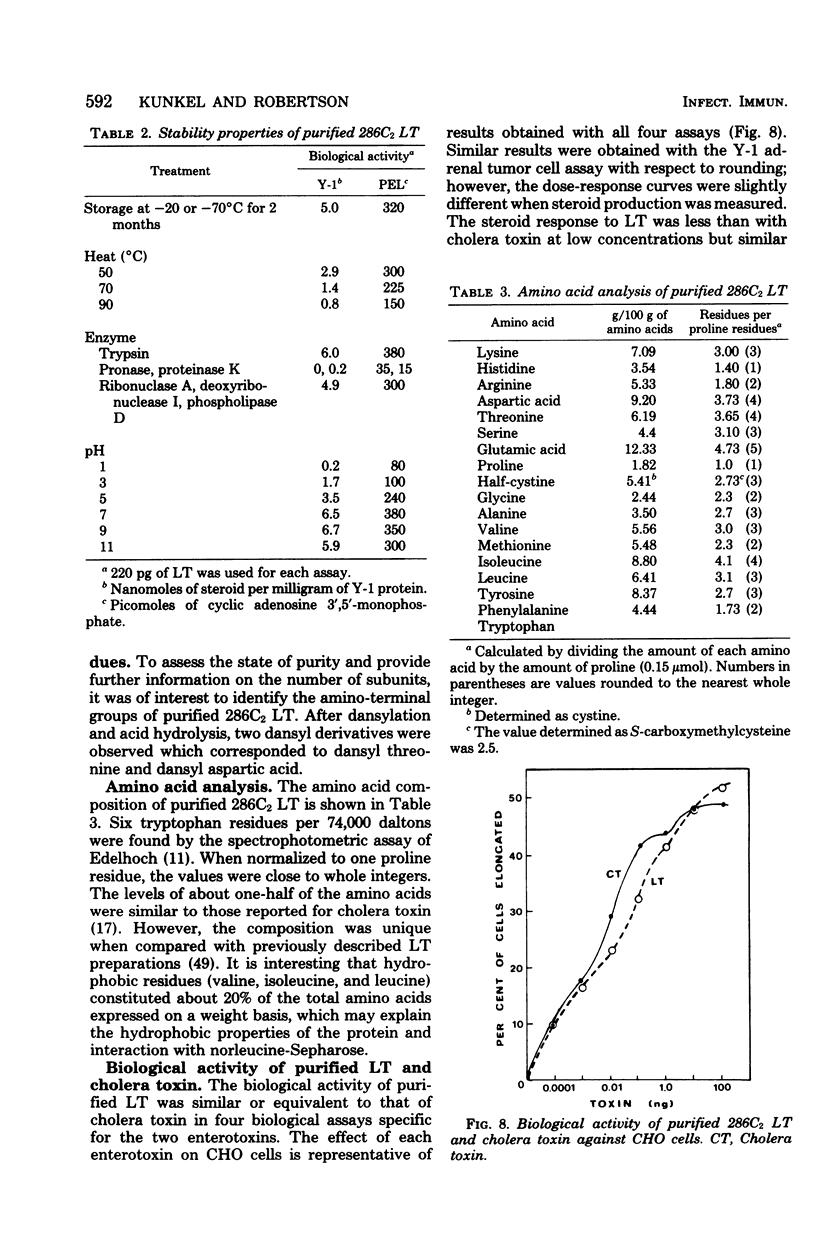
Heat-labile enterotoxin (LT) produced by a human strain of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli (286C2) was purified to homogeneity from pH extracts of fermentor-grown cells by ultrafiltration, (NH4)2SO4 fractionation, hydrophobic chromatography on norleucine-Sepharose 4B, hydroxylapatite chromatography, and Bio-Gel P-150 filtration. Purified LT preparations exhibited biological activity comparable to that of cholera toxin in four bioassays specific for the two enterotoxins (Y-1 adrenal tumor cells, Chinese hamster ovary cells, pigeon erythrocyte lysates, and skin permeability test). The overall yield of LT protein was 20%, which represented a 500-fold purification over pH extracts. A native molecular weight of 73,000 was determined by gel electrophoresis. The toxin dissociated upon treatment with sodium dodecyl sulfate, pH 7.0, into two components with molecular weights of 44,000 and 30,000. Purified LT preparations were remarkably stable over a wide range of storage conditions, temperatures, and pH's. The biological activity was increased by incubation with trypsin and completely destroyed by pronase and proteinase K, whereas deoxyribonuclease I, ribonuclease, and phospholipase D had no effect. The amino acid composition of purified LT was quite different from that of cholera toxin. Neither carbohydrate nor lipopolysaccharide was present in purified preparations. The purification scheme appeared applicable to LT produced by other human and porcine enterotoxigenic strains, but reflected the amount of LT produced by each strain. These data show that LT and cholera toxin share many common chemical and physical properties, but must be purified by different techniques.
Full text
PDF






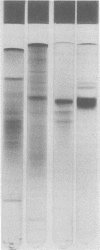
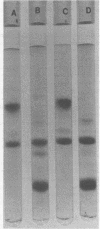
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alderete J. F., Robertson D. C. Purification and chemical characterization of the heat-stable enterotoxin produced by porcine strains of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1978 Mar;19(3):1021–1030. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.3.1021-1030.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ames G. F. Resolution of bacterial proteins by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis on slabs. Membrane, soluble, and periplasmic fractions. J Biol Chem. 1974 Jan 25;249(2):634–644. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bramucci M. G., Holmes R. K. Radial passive immune hemolysis assay for detection of heat-labile enterotoxin produced by individual colonies of Escherichia coli or Vibrio cholerae. J Clin Microbiol. 1978 Aug;8(2):252–255. doi: 10.1128/jcm.8.2.252-255.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CRESTFIELD A. M., MOORE S., STEIN W. H. The preparation and enzymatic hydrolysis of reduced and S-carboxymethylated proteins. J Biol Chem. 1963 Feb;238:622–627. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuatrecasas P. Protein purification by affinity chromatography. Derivatizations of agarose and polyacrylamide beads. J Biol Chem. 1970 Jun;245(12):3059–3065. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dafni Z., Sack R. B., Craig J. P. Purification of heat-labile enterotoxin from four Escherichia coli strains by affinity immunoadsorbent: evidence for similar subunit structure. Infect Immun. 1978 Dec;22(3):852–860. doi: 10.1128/iai.22.3.852-860.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donta S. T., Moon H. W., Whipp S. C. Detection of heat-labile Escherichia coli enterotoxin with the use of adrenal cells in tissue culture. Science. 1974 Jan 25;183(4122):334–336. doi: 10.1126/science.183.4122.334. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorner F. Escherichia coli enterotoxin. Purification and partial characterization. J Biol Chem. 1975 Nov 25;250(22):8712–8719. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ELLMAN G. L. Tissue sulfhydryl groups. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1959 May;82(1):70–77. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(59)90090-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebeling W., Hennrich N., Klockow M., Metz H., Orth H. D., Lang H. Proteinase K from Tritirachium album Limber. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Aug 15;47(1):91–97. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03671.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edelhoch H. Spectroscopic determination of tryptophan and tyrosine in proteins. Biochemistry. 1967 Jul;6(7):1948–1954. doi: 10.1021/bi00859a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans D. J., Jr, Evans D. G., Gorbach S. L. Production of vascular permeability factor by enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli isolated from man. Infect Immun. 1973 Nov;8(5):725–730. doi: 10.1128/iai.8.5.725-730.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Field M., Graf L. H., Jr, Laird W. J., Smith P. L. Heat-stable enterotoxin of Escherichia coli: in vitro effects on guanylate cyclase activity, cyclic GMP concentration, and ion transport in small intestine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jun;75(6):2800–2804. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.6.2800. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geren C. R., Magee S. C., Ebner K. E. Hydrophobic chromatography of galactosyltransferase. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1976 Jan;172(1):149–155. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(76)90060-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gill D. M., King C. A. The mechanism of action of cholera toxin in pigeon erythrocyte lysates. J Biol Chem. 1975 Aug 25;250(16):6424–6432. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilligan P. H., Robertson D. C. Nutritional requirements for synthesis of heat-labile enterotoxin by enterotoxigenic strains of Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1979 Jan;23(1):99–107. doi: 10.1128/iai.23.1.99-107.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guerrant R. L., Brunton L. L., Schnaitman T. C., Rebhun L. I., Gilman A. G. Cyclic adenosine monophosphate and alteration of Chinese hamster ovary cell morphology: a rapid, sensitive in vitro assay for the enterotoxins of Vibrio cholerae and Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1974 Aug;10(2):320–327. doi: 10.1128/iai.10.2.320-327.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedrick J. L., Smith A. J. Size and charge isomer separation and estimation of molecular weights of proteins by disc gel electrophoresis. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1968 Jul;126(1):155–164. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(68)90569-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoekstra D., van der Laan J. W., de Leij L., Witholt B. Release of outer membrane fragments from normally growing Escherichia coli. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Dec 14;455(3):889–899. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(76)90058-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofstee B. H. Hydrophobic affinity chromatography of proteins. Anal Biochem. 1973 Apr;52(2):430–448. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(73)90046-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohler E. M. Enterotoxic activity of filtrates of escherichia coli in young pigs. Am J Vet Res. 1968 Dec;29(12):2263–2274. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konowalchuk J., Dickie N., Stavric S., Speirs J. I. Comparative studies of five heat-labile toxic products of Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1978 Dec;22(3):644–648. doi: 10.1128/iai.22.3.644-648.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel S. L., Robertson D. C. Factors affecting release of heat-labile enterotoxin by enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1979 Mar;23(3):652–659. doi: 10.1128/iai.23.3.652-659.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laas T. Agarderivatives for chromatography, electrophoresis and gel-bound enzymes. IV. Benzylated dibromopropanol cross-linked sepharose as an amphophilic gel for hydrophobic salting-out chromatography of enzymes with special emphasis on denaturing risks. J Chromatogr. 1975 Sep 3;111(2):373–387. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9673(00)99287-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lariviére S., Gyles C. L., Barnum D. A. Preliminary characterization of the heat-labile enterotoxin of Escherichia coli F11(P155). J Infect Dis. 1973 Sep;128(3):312–320. doi: 10.1093/infdis/128.3.312. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lugtenberg B., Meijers J., Peters R., van der Hoek P., van Alphen L. Electrophoretic resolution of the "major outer membrane protein" of Escherichia coli K12 into four bands. FEBS Lett. 1975 Oct 15;58(1):254–258. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(75)80272-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mancini G., Carbonara A. O., Heremans J. F. Immunochemical quantitation of antigens by single radial immunodiffusion. Immunochemistry. 1965 Sep;2(3):235–254. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(65)90004-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Memoli V. A., Doellgast G. J. Hemoglobin & serum albumin: salt-mediated hydrophobic chromatography. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1975 Oct 6;66(3):1011–1016. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(75)90740-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris G. K., Merson M. H., Sack D. A., Wells J. G., Martin W. T., Dewitt W. E., Feeley J. C., Sack R. B., Bessudo D. M. Laboratory investigation of diarrhea in travelers to Mexico: evaluation of methods for detecting enterotoxigenic Echerichia coli. J Clin Microbiol. 1976 May;3(5):486–495. doi: 10.1128/jcm.3.5.486-495.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Möhler H., Decker K., Wood W. A. Structure of 2-keto-3-deoxy-6-phosphogluconate aldolase. IV. Structural features revealed by treatment with urea and Ellman's reagent. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1972 Jul;151(1):251–260. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(72)90495-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Möllby R., Hjalmarsson S. G., Wadström T. Separation of E. coli heat-labile enterotoxin by preparative isotachophoresis. FEBS Lett. 1975 Aug 1;56(1):30–33. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(75)80104-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierce N. F. Differential inhibitory effects of cholera toxoids and ganglioside on the enterotoxins of Vibrio cholerae and Escherichia coli. J Exp Med. 1973 Apr 1;137(4):1009–1023. doi: 10.1084/jem.137.4.1009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raibaud O., Högberg-Raibaud A., Goldberg M. E. Purification of E. coli enzymes by chromatography on amphiphilic gels. FEBS Lett. 1975 Feb 1;50(2):130–134. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(75)80472-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryder R. W., Wachsmuth I. K., Buxton A. E., Evans D. G., DuPont H. L., Mason E., Barrett F. F. Infantile diarrhea produced by heat-stable enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. N Engl J Med. 1976 Oct 14;295(16):849–853. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197610142951601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sack D. A., Merson M. H., Wells J. G., Sack R. B., Morris G. K. Diarrhoea associated with heat-stable enterotoxin-producing strains of Escherichia coli. Lancet. 1975 Aug 9;2(7928):239–241. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(75)90958-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sack R. B., Gorbach S. L., Banwell J. G., Jacobs B., Chatterjee B. D., Mitra R. C. Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli isolated from patients with severe cholera-like disease. J Infect Dis. 1971 Apr;123(4):378–385. doi: 10.1093/infdis/123.4.378. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sack R. B. Human diarrheal disease caused by enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1975;29:333–353. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.29.100175.002001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schenkein I., Green R. F., Santos D. S., Maas W. K. Partial purification and characterization of a heat-labile enterotoxin of Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1976 Jun;13(6):1710–1720. doi: 10.1128/iai.13.6.1710-1720.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaltiel S., Er-El Z. Hydrophobic chromatography: use for purification of glycogen synthetase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Mar;70(3):778–781. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.3.778. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith H. W., Halls S. Studies on Escherichia coli enterotoxin. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1967 Apr;93(2):531–543. doi: 10.1002/path.1700930212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Söderlind O., Möllby R., Wadström T. Purification and some properties of a heat-labile enterotoxin from escherichia coli. Zentralbl Bakteriol Orig A. 1974;229(2):190–204. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Heyningen W. E., Carpenter C. C., Pierce N. F., Greenough W. B., 3rd Deactivation of cholera toxin by ganglioside. J Infect Dis. 1971 Oct;124(4):415–418. doi: 10.1093/infdis/124.4.415. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wadström T., Möllby R., Söderlind O. Heat-labile enterotoxins of Escherichia coli. Toxicon. 1977;15(6):511–519. doi: 10.1016/0041-0101(77)90102-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Osborn M. The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4406–4412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woods K. R., Wang K. T. Separation of dansyl-amino acids by polyamide layer chromatography. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1967 Feb 21;133(2):369–370. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(67)90078-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yon R. J., Simmonds R. J. Protein chromatography on adsorbents with hydrophobic and ionic groups. Some properties of N-(3-carboxypropionyl)aminodecyl-sepharose and its interaction with wheat-germ aspartate transcarbamoylase. Biochem J. 1975 Nov;151(2):281–290. doi: 10.1042/bj1510281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]