Abstract
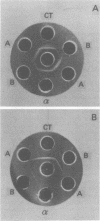
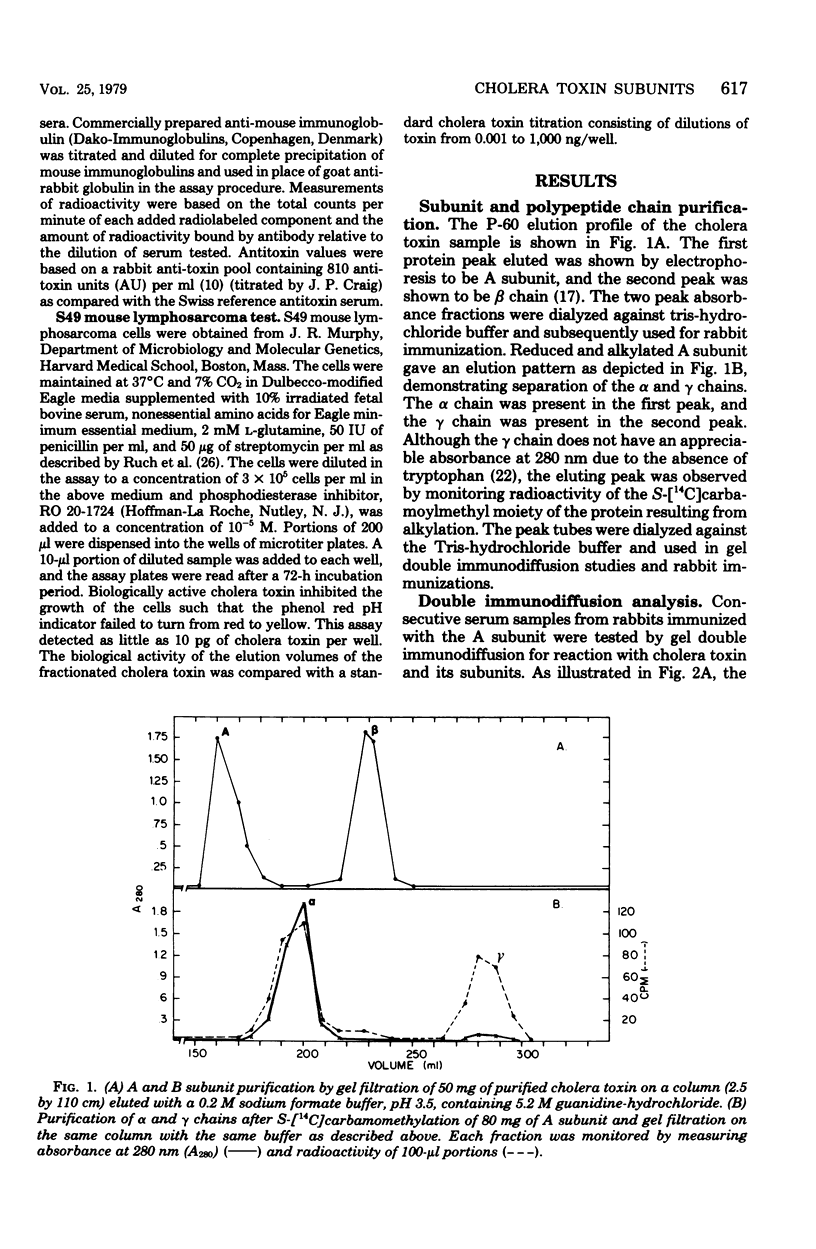
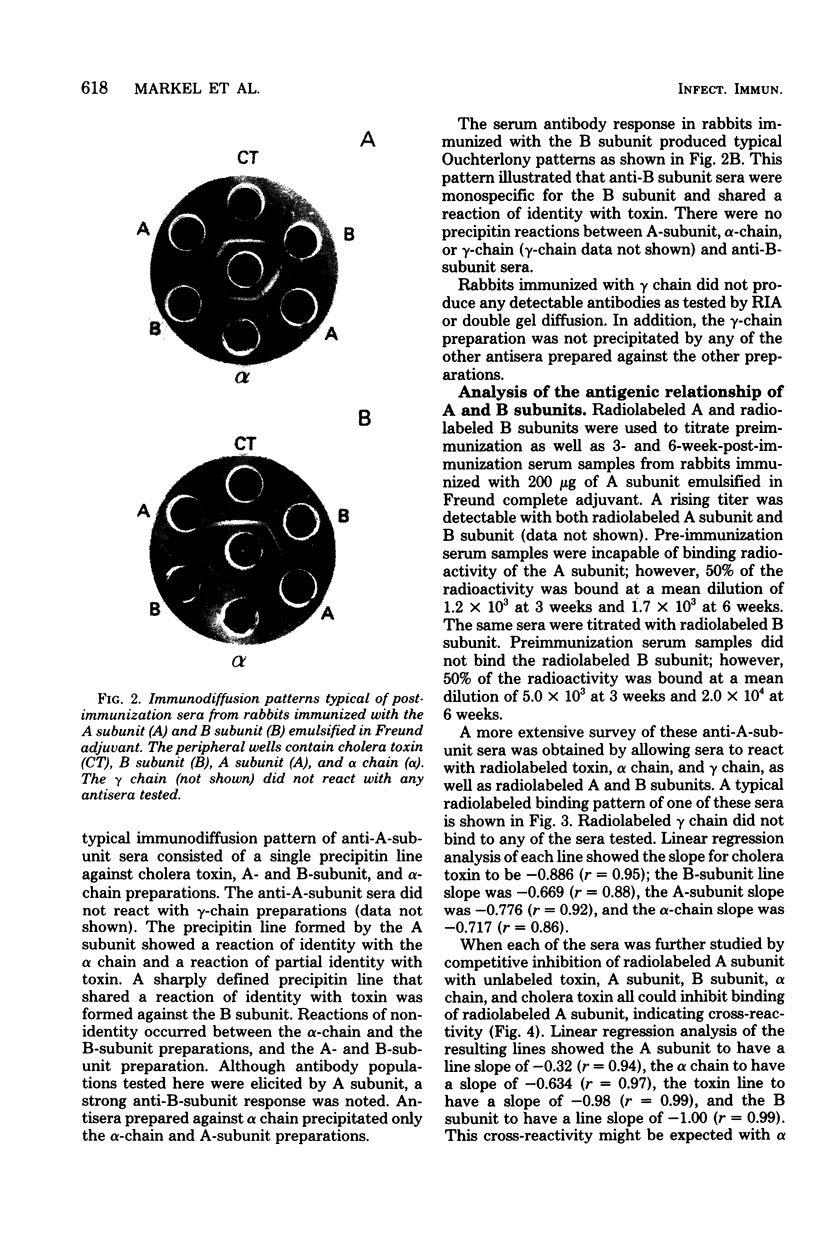
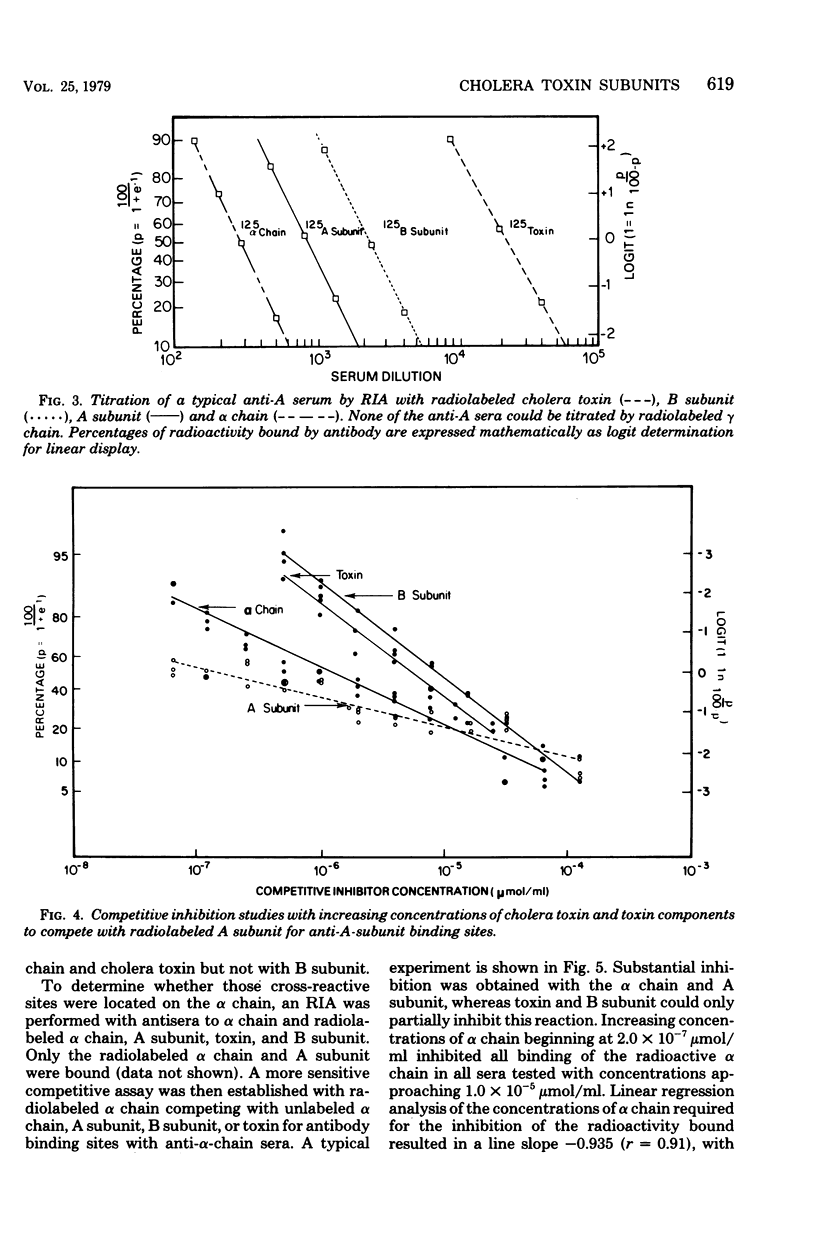
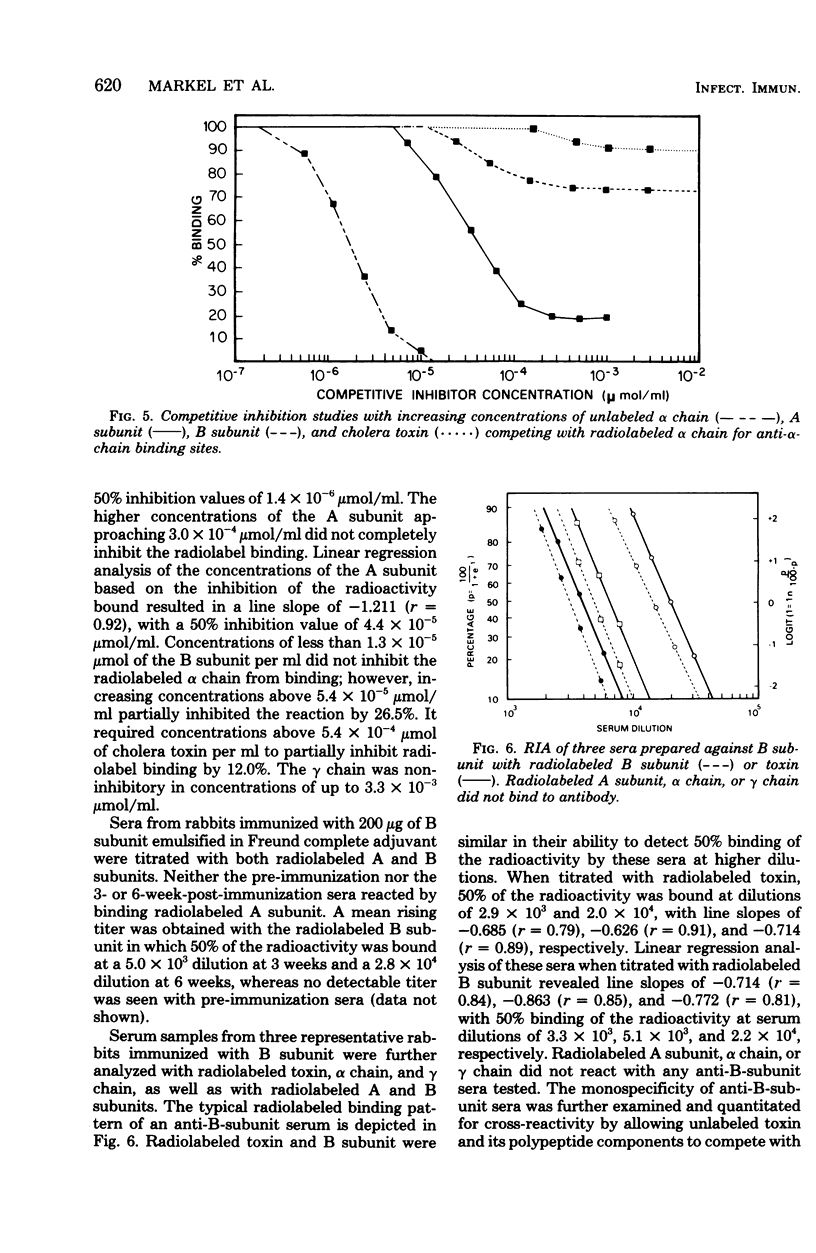
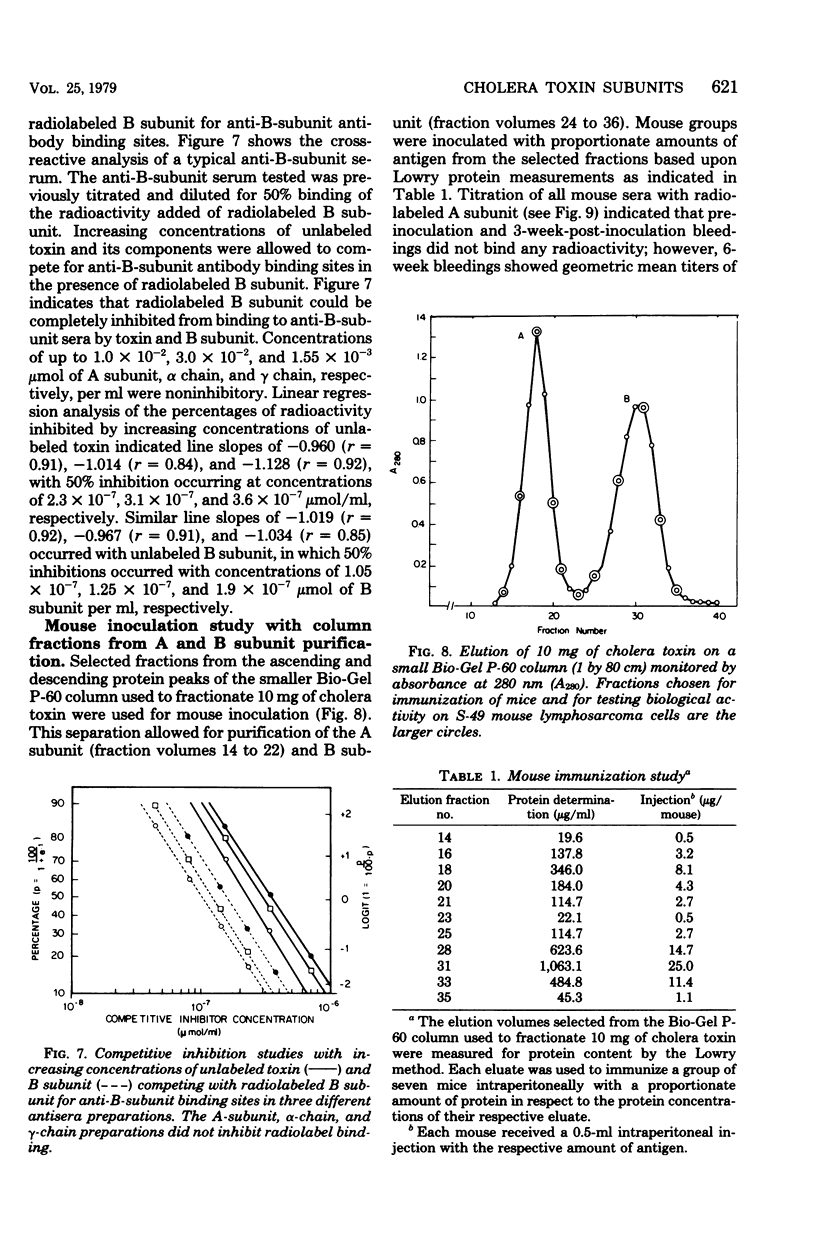
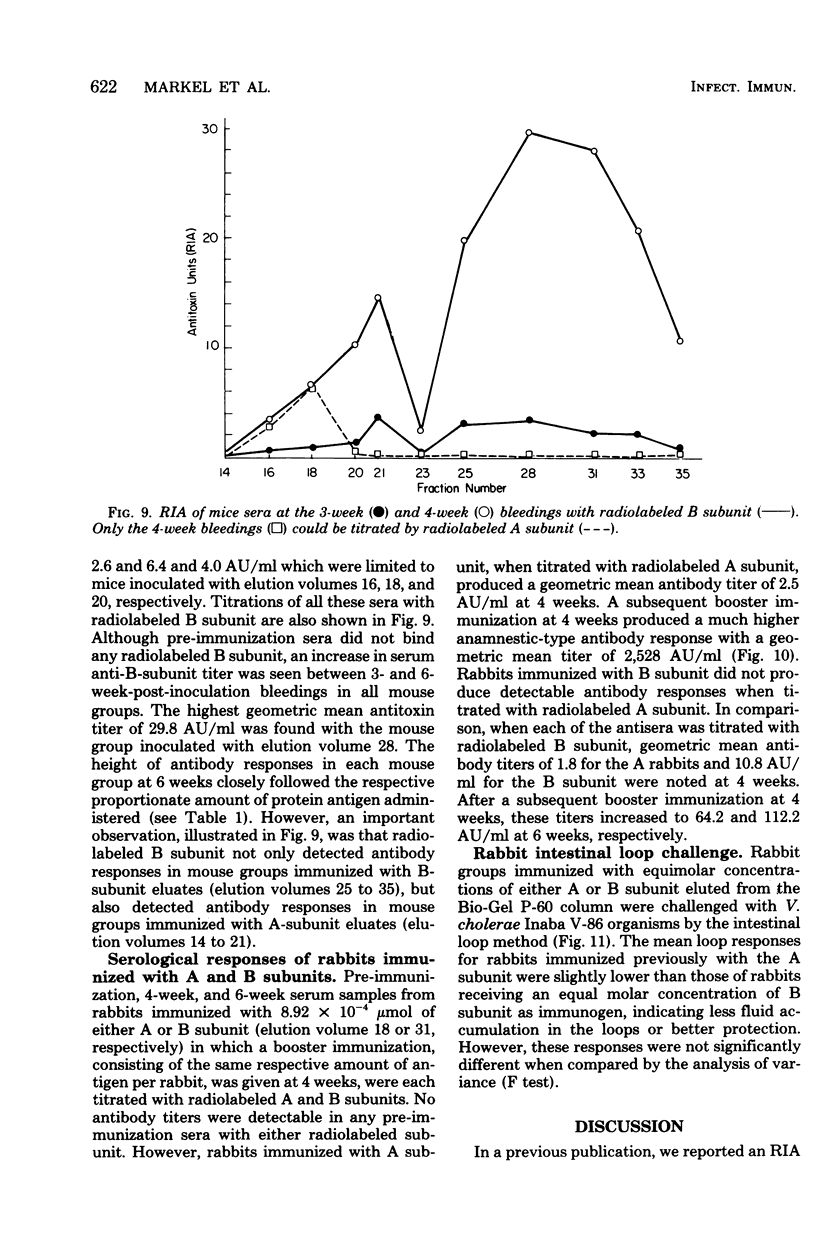
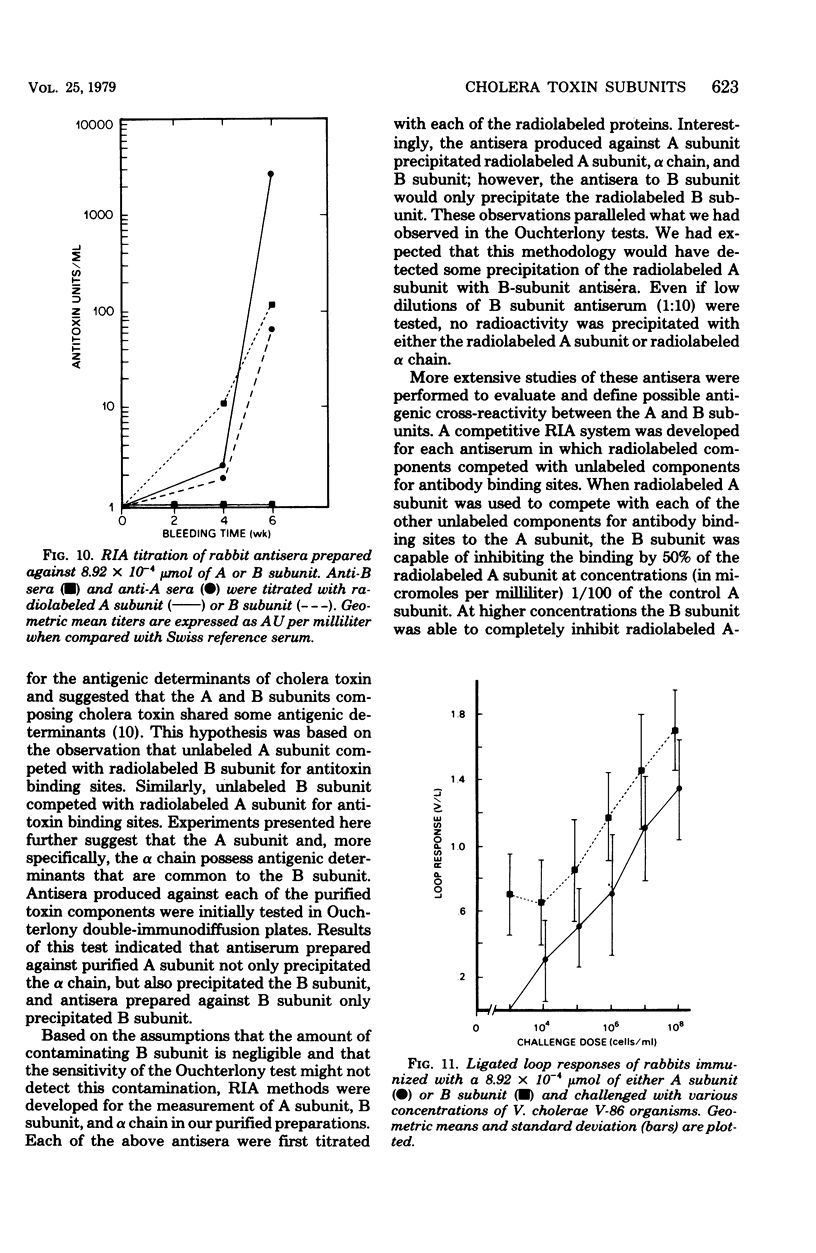
The antigenic specificity of purified preparations of A subunit, B subunit, α chain, and γ chain of cholera toxin was studied by double immunodiffusion and radioimmunoassay with antisera produced in rabbits and mice. Rabbits immunized with A subunit produced serum antibodies which were capable of binding radiolabeled A subunit, α chain, and B subunit. Rabbits immunized with α chain produced serum antibodies that would bind radiolabeled α chain and A subunit. Rabbits immunized with the B subunit produced serum antibodies monospecific for the B subunit. The γ chain did not elicit measurable antibodies in rabbits or mice as evidenced by radioimmunoassay or double immunodiffusion. A sensitive competitive radioimmunoassay was developed in which the B subunit could inhibit binding of radiolabeled A subunit and α chain with either antisera prepared against A subunit or α chain. Neither the A subunit nor the α chain could inhibit binding of B subunit with the antiserum prepared against B subunit. In addition, selected elution fractions obtained during A- and B-subunit purification were used to immunize groups of mice. Mice responded to immunization with the elution fractions of A subunit by producing anti-A-subunit and anti-B-subunit serum antibody responses, whereas mice immunized with elution fractions of B subunit produced only antibodies specific for the B subunit. An equimolar amount of the two resulting protein peaks was used to immunize two groups of rabbits. Rabbits immunized with A subunit, produced a serum anti-B subunit response equal to that of rabbits immunized with the B subunit. Rabbits immunized with equimolar concentrations of A and B subunits were observed to be equally protected against intestinal loop challenge with Vibrio cholerae Inaba V86. The A subunit, not the B subunit, was biologically active when tested by the S49 mouse lymphosarcoma cell test. These studies provide additional evidence supporting the hypothesis that the A subunit, specifically of α chain, of cholera toxin contains antigenic determinants in common with the B subunit.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cassel D., Pfeuffer T. Mechanism of cholera toxin action: covalent modification of the guanyl nucleotide-binding protein of the adenylate cyclase system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jun;75(6):2669–2673. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.6.2669. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DE S. N., CHATTERJE D. N. An experimental study of the mechanism of action of Vibriod cholerae on the intestinal mucous membrane. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1953 Oct;66(2):559–562. doi: 10.1002/path.1700660228. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finkelstein R. A., Boesman M., Neoh S. H., LaRue M. K., Delaney R. Dissociation and recombination of the subunits of the cholera enterotoxin (choleragen). J Immunol. 1974 Jul;113(1):145–150. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finkelstein R. A., Peterson J. W. In vitro detection of antibody to cholera enterotoxin in cholera patients and laboratory animals. Infect Immun. 1970 Jan;1(1):21–29. doi: 10.1128/iai.1.1.21-29.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gill D. M., King C. A. The mechanism of action of cholera toxin in pigeon erythrocyte lysates. J Biol Chem. 1975 Aug 25;250(16):6424–6432. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gill D. M. Multiple roles of erythrocyte supernatant in the activation of adenylate cyclase by Vibrio cholerae toxin in vitro. J Infect Dis. 1976 Mar;133 (Suppl):55–63. doi: 10.1093/infdis/133.supplement_1.s55. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hejtmancik K. E., Peterson J. W., Markel D. E., Kurosky A. Radioimmunoassay for the antigenic determinants of cholera toxin and its components. Infect Immun. 1977 Sep;17(3):621–628. doi: 10.1128/iai.17.3.621-628.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heyningen S Van Cholera toxin: interaction of subunits with ganglioside GM1. Science. 1974 Feb 15;183(4125):656–657. doi: 10.1126/science.183.4125.656. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmgren J., Lindholm L., Lönnroth I. Interaction of cholera toxin and toxin derivatives with lymphocytes. I. Binding properties and interference with lectin-induced cellular stimulation. J Exp Med. 1974 Apr 1;139(4):801–819. doi: 10.1084/jem.139.4.801. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klapper D. G., Finkelstein R. A., Capra J. D. Subunit structure and N-terminal amino acid sequence of the three chains of cholera enterotoxin. Immunochemistry. 1976 Jul;13(7):605–611. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(76)90173-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurosky A., Markel D. E., Peterson J. W. Covalent structure of the beta chain of cholera enterotoxin. J Biol Chem. 1977 Oct 25;252(20):7257–7264. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai C. Y. Determination of the primary structure of cholera toxin B subunit. J Biol Chem. 1977 Oct 25;252(20):7249–7256. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lospalluto J. J., Finkelstein R. A. Chemical and physical properties of cholera exo-enterotoxin (choleragen) and its spontaneously formed toxoid (choleragenoid). Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Jan 26;257(1):158–166. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(72)90265-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markel D. E., Hejtmancik K. E., Peterson J. W., Kurosky A. Structure, function, and antigenicity of cholera toxin. J Supramol Struct. 1979;10(2):137–149. doi: 10.1002/jss.400100204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rifkind D., Frey J. A., Petersen E. A., Dinowitz M. Delayed hypersensitivity to fungal antigens in mice. II. Molecular classes in immunogenic RNA extracts that transfer delayed hypersensitivity. J Infect Dis. 1976 May;133(5):523–532. doi: 10.1093/infdis/133.5.523. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Heyningen S., King C. A. Short communications. Subunit A from cholera toxin is an activator of adenylate cyclase in pigeon erythrocytes. Biochem J. 1975 Jan;146(1):269–271. doi: 10.1042/bj1460269. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wodnar-Filipowicz A., Lai C. Y. Stimulation of adenylate cyclase in washed pigeon erythrocyte membrane with cholera toxin and its subunits. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1976 Oct;176(2):465–471. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(76)90189-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]