Abstract
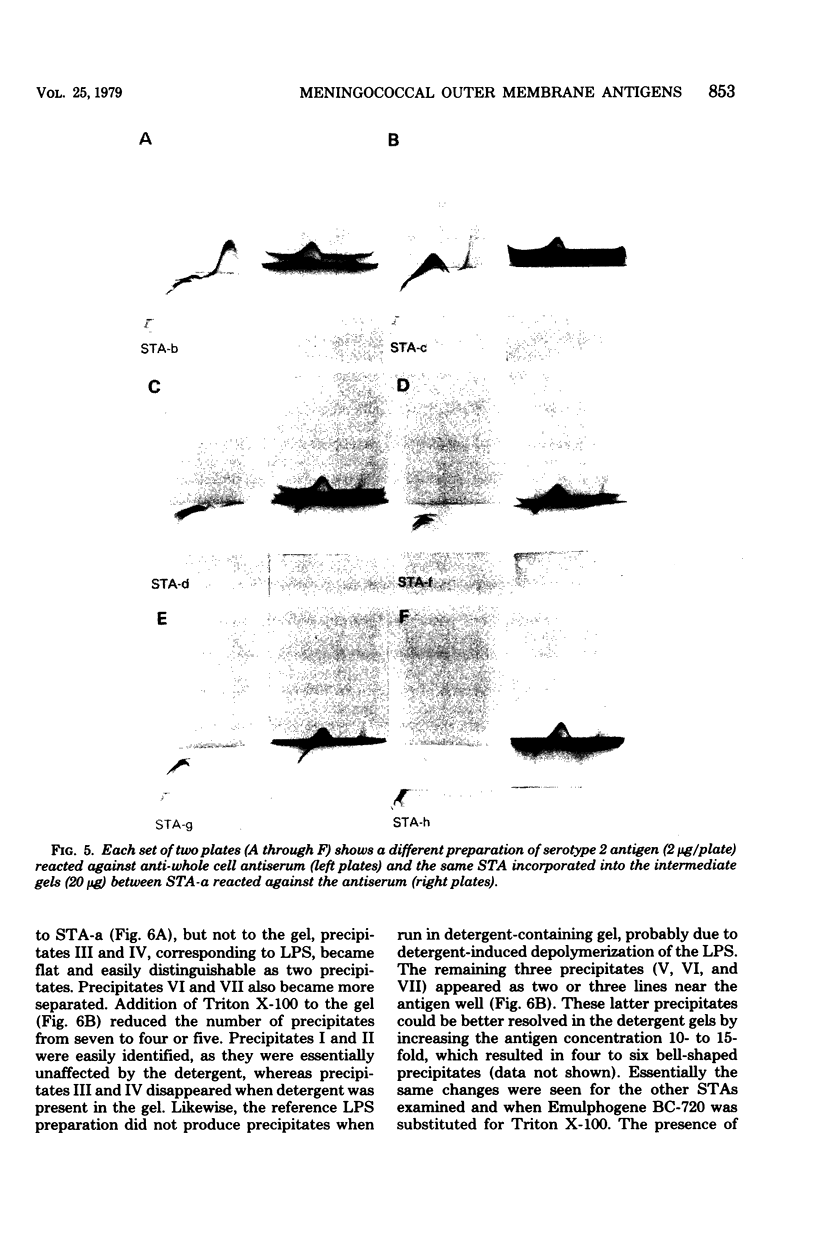
This study shows that the capsular polysaccharide, protein, and lipopolysaccharide antigens from the outer membrane of Neisseria meningitidis group B serotype 2 may be identified by crossed immunoelectrophoresis. By using this technique, seven precipitates were resolved when outer membrane preparations were reacted against goat anti-whole cell group B type 2 antiserum. Most of these precipitates were identified by comparison with purified reference preparations. Different outer membrane preparations, reflecting different growth conditions, varied in their compositions of lipopolysaccharide, protein, and polysaccharide. Detergent treatment altered the protein and lipopolysaccharide precipitation patterns. In the presence of detergent, the lipopolysaccharide did not precipitate, and the electrophoretic migration of the protein antigens decreased. Crossed immunoelectrophoresis is a useful qualitative method for analysis of the antigenic components of the meningococcal outer membrane. The crossed immunoelectrophoresis with intermediate gel technique is presently being used to measure the human immune response to the different cell surface components.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Apicella M. A. Identification of a subgroup antigen on the Neisseria meningitidis group C capsular polysaccharide. J Infect Dis. 1974 Feb;129(2):147–153. doi: 10.1093/infdis/129.2.147. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devoe I. W., Gilchrist J. E. Release of endotoxin in the form of cell wall blebs during in vitro growth of Neisseria meningitidis. J Exp Med. 1973 Nov 1;138(5):1156–1167. doi: 10.1084/jem.138.5.1156. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frasch C. E., Chapman S. S. Classification of Neisseria meningitidis group B into distinct serotypes. 3. Application of a new bactericidal-inhibition technique to distribution of serotypes among cases and carriers. J Infect Dis. 1973 Feb;127(2):149–154. doi: 10.1093/infdis/127.2.149. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frasch C. E., Gotschlich E. C. An outer membrane protein of Neisseria meningitidis group B responsible for serotype specificity. J Exp Med. 1974 Jul 1;140(1):87–104. doi: 10.1084/jem.140.1.87. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frasch C. E., McNelis R. M., Gotschlich E. C. Strain-specific variation in the protein and lipopolysaccharide composition of the group B meningococcal outer membrane. J Bacteriol. 1976 Aug;127(2):973–981. doi: 10.1128/jb.127.2.973-981.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frasch C. E., Robbins J. D. Protection against group B meningococcal disease. III. Immunogenicity of serotype 2 vaccines and specificity of protection in a guinea pig model. J Exp Med. 1978 Mar 1;147(3):629–644. doi: 10.1084/jem.147.3.629. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frasch C. E. Role of protein serotype antigens in protection against disease due to Neisseria meningitidis. J Infect Dis. 1977 Aug;136 (Suppl):S84–S90. doi: 10.1093/infdis/136.supplement.s84. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gold R., Lepow M. L., Goldschneider I., Gotschlich E. C. Immune Response of human infants of polysaccharide vaccines of group A and C Neisseria meningitidis. J Infect Dis. 1977 Aug;136 (Suppl):S31–S35. doi: 10.1093/infdis/136.supplement.s31. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gold R., Winklehake J. L., Mars R. S., Artenstein M. S. Identification of an epidemic strain of group C Neisseria meningitidis by bactericidal serotyping. J Infect Dis. 1971 Dec;124(6):593–597. doi: 10.1093/infdis/124.6.593. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldschneider I., Gotschlich E. C., Artenstein M. S. Human immunity to the meningococcus. II. Development of natural immunity. J Exp Med. 1969 Jun 1;129(6):1327–1348. doi: 10.1084/jem.129.6.1327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gotschlich E. C. Development of polysaccharide vaccines for the prevention of meningococcal diseases. Monogr Allergy. 1975;9:245–258. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoff G. E., Høiby N. Crossed immunoelectrophoretic analysis of Neisseria meningitidis antigens and of corresponding antibodies in patients with meningococcal disease. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand C. 1978 Feb;86(1):1–9. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1978.tb02549.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasper D. L., Winkelhake J. L., Zollinger W. D., Brandt B. L., Artenstein M. S. Immunochemical similarity between polysaccharide antigens of Escherichia coli 07: K1(L):NM and group B Neisseria meningitidis. J Immunol. 1973 Jan;110(1):262–268. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kroll J. Crossed-line immunoelectrophoresis (73, 76). Scand J Immunol Suppl. 1973;1:79–81. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandrell R. E., Zollinger W. D. Lipopolysaccharide serotyping of Neisseria meningitidis by hemagglutination inhibition. Infect Immun. 1977 May;16(2):471–475. doi: 10.1128/iai.16.2.471-475.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munford R. S., Patton C. M., Gorman G. W. Epidemiologic studies of serotype antigens common to groups B and C Neisseria meningitidis. J Infect Dis. 1975 Mar;131(3):286–290. doi: 10.1093/infdis/131.3.286. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orskov F., Orskov I., Sutton A., Schneerson R., Lin W., Egan W., Hoff G. E., Robbins J. B. Form variation in Escherichia coli K1: determined by O-acetylation of the capsular polysaccharide. J Exp Med. 1979 Mar 1;149(3):669–685. doi: 10.1084/jem.149.3.669. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tettmar R. E., Abbott J. D., Jones D. M. Meningococcal meningitis in Royal Air Force recruits. Public Health. 1977 Sep;91(5):253–257. doi: 10.1016/s0033-3506(77)80054-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tramont E. C., Sadoff J. C., Artenstein M. S. Cross-reactivity of Neisseria gonorrhoeae and Neisseria meningitidis and the nature of antigens involved in the bactericidal reaction. J Infect Dis. 1974 Sep;130(3):240–247. doi: 10.1093/infdis/130.3.240. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weeke B. Crossed immunoelectrophoresis. Scand J Immunol Suppl. 1973;1:47–56. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1973.tb03778.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyle F. A., Artenstein M. S., Brandt B. L., Tramont E. C., Kasper D. L., Altieri P. L., Berman S. L., Lowenthal J. P. Immunologic response of man to group B meningococcal polysaccharide vaccines. J Infect Dis. 1972 Nov;126(5):514–521. doi: 10.1093/infdis/126.5.514. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zollinger W. D., Mandrell R. E., Altieri P., Berman S., Lowenthal J., Artenstein M. S. Safety and immunogenicity of a Neisseria meningitidis type 2 protein vaccine in animals and humans. J Infect Dis. 1978 Jun;137(6):728–739. doi: 10.1093/infdis/137.6.728. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zollinger W. D., Mandrell R. E. Outer-membrane protein and lipopolysaccharide serotyping of Neisseria meningitidis by inhibition of a solid-phase radioimmunoassay. Infect Immun. 1977 Nov;18(2):424–433. doi: 10.1128/iai.18.2.424-433.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zollinger W. D., Pennington C. L., Artenstein M. S. Human antibody response to three meningococcal outer membrane antigens: comparison by specific hemagglutination assays. Infect Immun. 1974 Nov;10(5):975–984. doi: 10.1128/iai.10.5.975-984.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]