Abstract
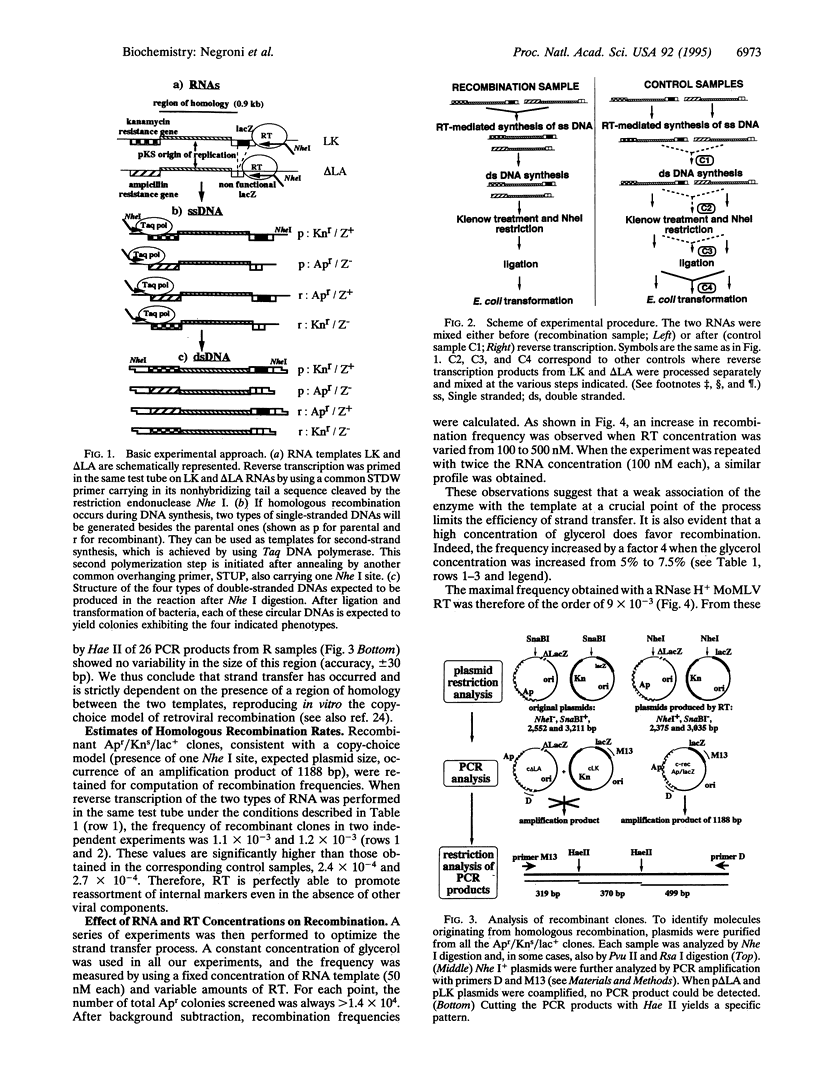
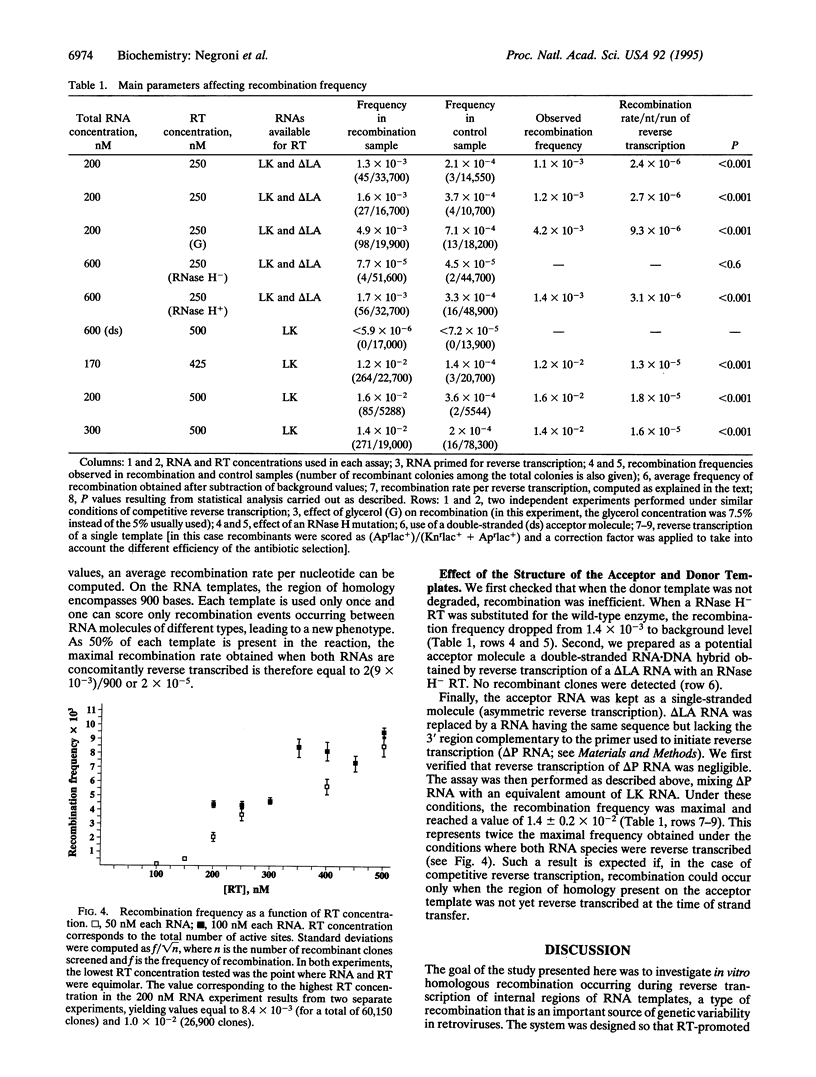
Retroviruses are known to mutate at high rates. An important source of genetic variability is recombination taking place during reverse transcription of internal regions of the two genomic RNAs. We have designed an in vitro model system, involving genetic markers carried on two RNA templates, to allow a search for individual recombination events and to score their frequency of occurrence. We show that Moloney murine leukemia virus reverse transcriptase alone promotes homologous recombination efficiently. While RNA concentration has little effect on recombination frequency, there is a clear correlation between the amount of reverse transcriptase used in the assay and the extent of recombination observed. Under conditions mimicking the in vivo situation, a rate compatible with ex vivo estimates has been obtained.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allain B., Lapadat-Tapolsky M., Berlioz C., Darlix J. L. Transactivation of the minus-strand DNA transfer by nucleocapsid protein during reverse transcription of the retroviral genome. EMBO J. 1994 Feb 15;13(4):973–981. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06342.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boosalis M. S., Petruska J., Goodman M. F. DNA polymerase insertion fidelity. Gel assay for site-specific kinetics. J Biol Chem. 1987 Oct 25;262(30):14689–14696. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clavel F., Hoggan M. D., Willey R. L., Strebel K., Martin M. A., Repaske R. Genetic recombination of human immunodeficiency virus. J Virol. 1989 Mar;63(3):1455–1459. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.3.1455-1459.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coffin J. M. Structure, replication, and recombination of retrovirus genomes: some unifying hypotheses. J Gen Virol. 1979 Jan;42(1):1–26. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-42-1-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeStefano J. J., Mallaber L. M., Rodriguez-Rodriguez L., Fay P. J., Bambara R. A. Requirements for strand transfer between internal regions of heteropolymer templates by human immunodeficiency virus reverse transcriptase. J Virol. 1992 Nov;66(11):6370–6378. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.11.6370-6378.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fu T. B., Taylor J. When retroviral reverse transcriptases reach the end of their RNA templates. J Virol. 1992 Jul;66(7):4271–4278. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.7.4271-4278.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Golovkina T. V., Jaffe A. B., Ross S. R. Coexpression of exogenous and endogenous mouse mammary tumor virus RNA in vivo results in viral recombination and broadens the virus host range. J Virol. 1994 Aug;68(8):5019–5026. doi: 10.1128/jvi.68.8.5019-5026.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodrich D. W., Duesberg P. H. Retroviral recombination during reverse transcription. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Mar;87(6):2052–2056. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.6.2052. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C., Padmanabhan R., Howard B. H. High efficiency DNA-mediated transformation of primate cells. Science. 1983 Aug 5;221(4610):551–553. doi: 10.1126/science.6306768. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu W. S., Temin H. M. Effect of gamma radiation on retroviral recombination. J Virol. 1992 Jul;66(7):4457–4463. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.7.4457-4463.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu W. S., Temin H. M. Retroviral recombination and reverse transcription. Science. 1990 Nov 30;250(4985):1227–1233. doi: 10.1126/science.1700865. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lobel L. I., Goff S. P. Reverse transcription of retroviral genomes: mutations in the terminal repeat sequences. J Virol. 1985 Feb;53(2):447–455. doi: 10.1128/jvi.53.2.447-455.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luo G. X., Taylor J. Template switching by reverse transcriptase during DNA synthesis. J Virol. 1990 Sep;64(9):4321–4328. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.9.4321-4328.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pandey R., Ghosh A. K., Kumar D. V., Bachman B. A., Shibata D., Roy-Burman P. Recombination between feline leukemia virus subgroup B or C and endogenous env elements alters the in vitro biological activities of the viruses. J Virol. 1991 Dec;65(12):6495–6508. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.12.6495-6508.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panganiban A. T., Fiore D. Ordered interstrand and intrastrand DNA transfer during reverse transcription. Science. 1988 Aug 26;241(4869):1064–1069. doi: 10.1126/science.2457948. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pathak V. K., Temin H. M. Broad spectrum of in vivo forward mutations, hypermutations, and mutational hotspots in a retroviral shuttle vector after a single replication cycle: deletions and deletions with insertions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Aug;87(16):6024–6028. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.16.6024. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pathak V. K., Temin H. M. Broad spectrum of in vivo forward mutations, hypermutations, and mutational hotspots in a retroviral shuttle vector after a single replication cycle: substitutions, frameshifts, and hypermutations. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Aug;87(16):6019–6023. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.16.6019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peliska J. A., Balasubramanian S., Giedroc D. P., Benkovic S. J. Recombinant HIV-1 nucleocapsid protein accelerates HIV-1 reverse transcriptase catalyzed DNA strand transfer reactions and modulates RNase H activity. Biochemistry. 1994 Nov 22;33(46):13817–13823. doi: 10.1021/bi00250a036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peliska J. A., Benkovic S. J. Fidelity of in vitro DNA strand transfer reactions catalyzed by HIV-1 reverse transcriptase. Biochemistry. 1994 Apr 5;33(13):3890–3895. doi: 10.1021/bi00179a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peliska J. A., Benkovic S. J. Mechanism of DNA strand transfer reactions catalyzed by HIV-1 reverse transcriptase. Science. 1992 Nov 13;258(5085):1112–1118. doi: 10.1126/science.1279806. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoye J. P., Moroni C., Coffin J. M. Virological events leading to spontaneous AKR thymomas. J Virol. 1991 Mar;65(3):1273–1285. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.3.1273-1285.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stuhlmann H., Berg P. Homologous recombination of copackaged retrovirus RNAs during reverse transcription. J Virol. 1992 Apr;66(4):2378–2388. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.4.2378-2388.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsuchihashi Z., Brown P. O. DNA strand exchange and selective DNA annealing promoted by the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 nucleocapsid protein. J Virol. 1994 Sep;68(9):5863–5870. doi: 10.1128/jvi.68.9.5863-5870.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



