Abstract
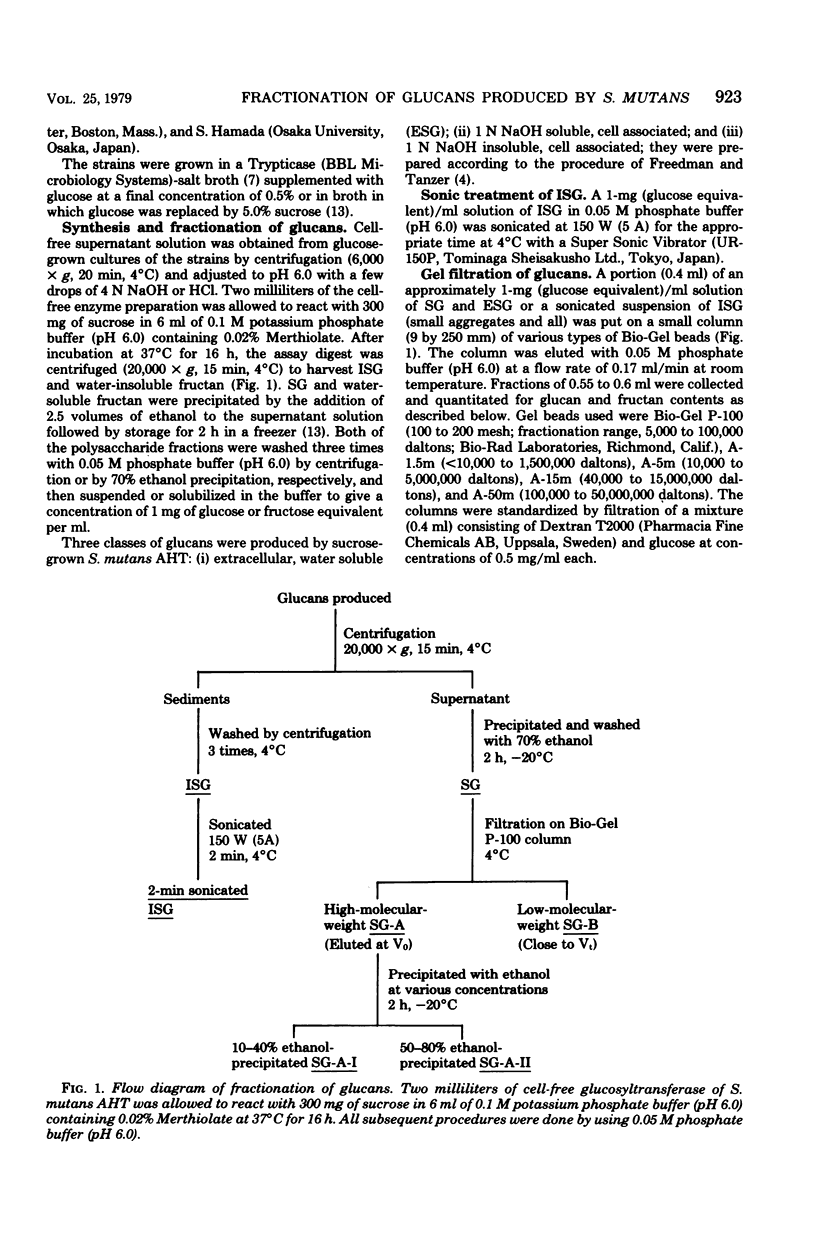
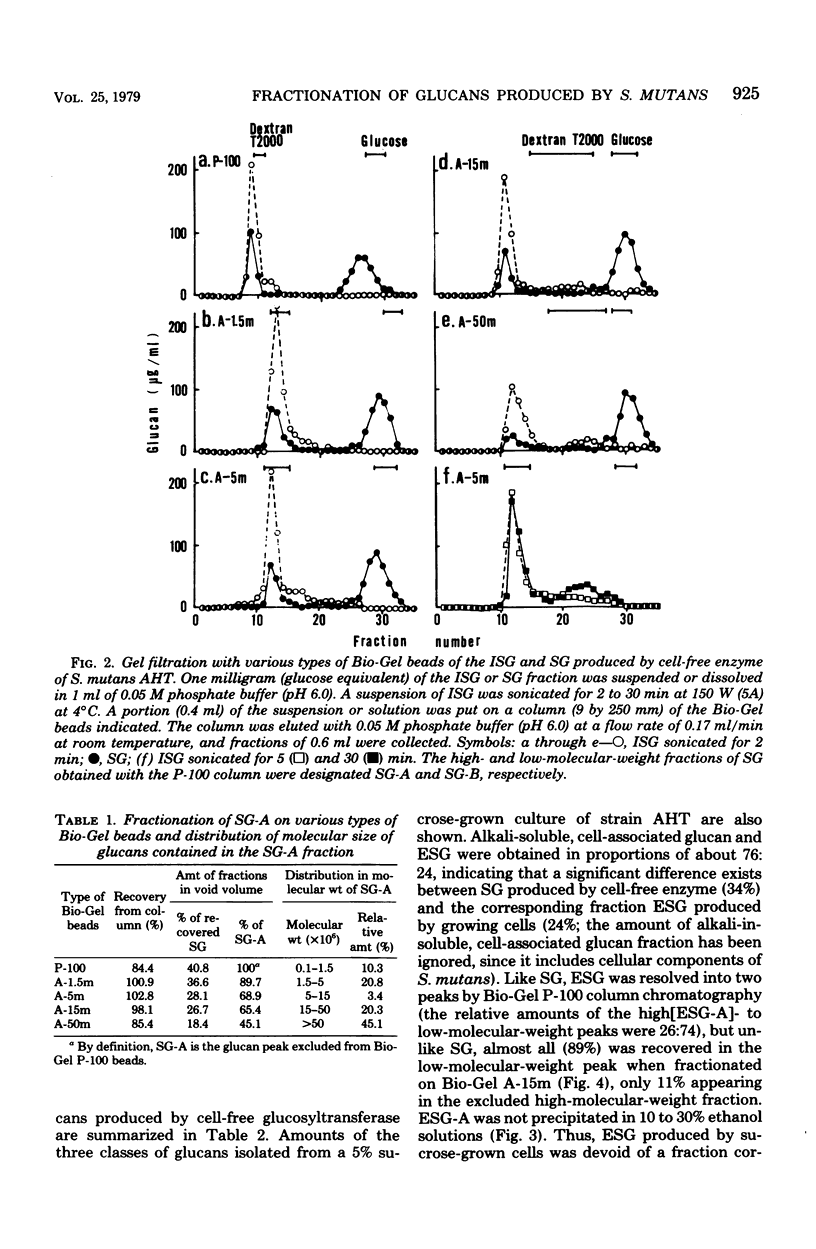
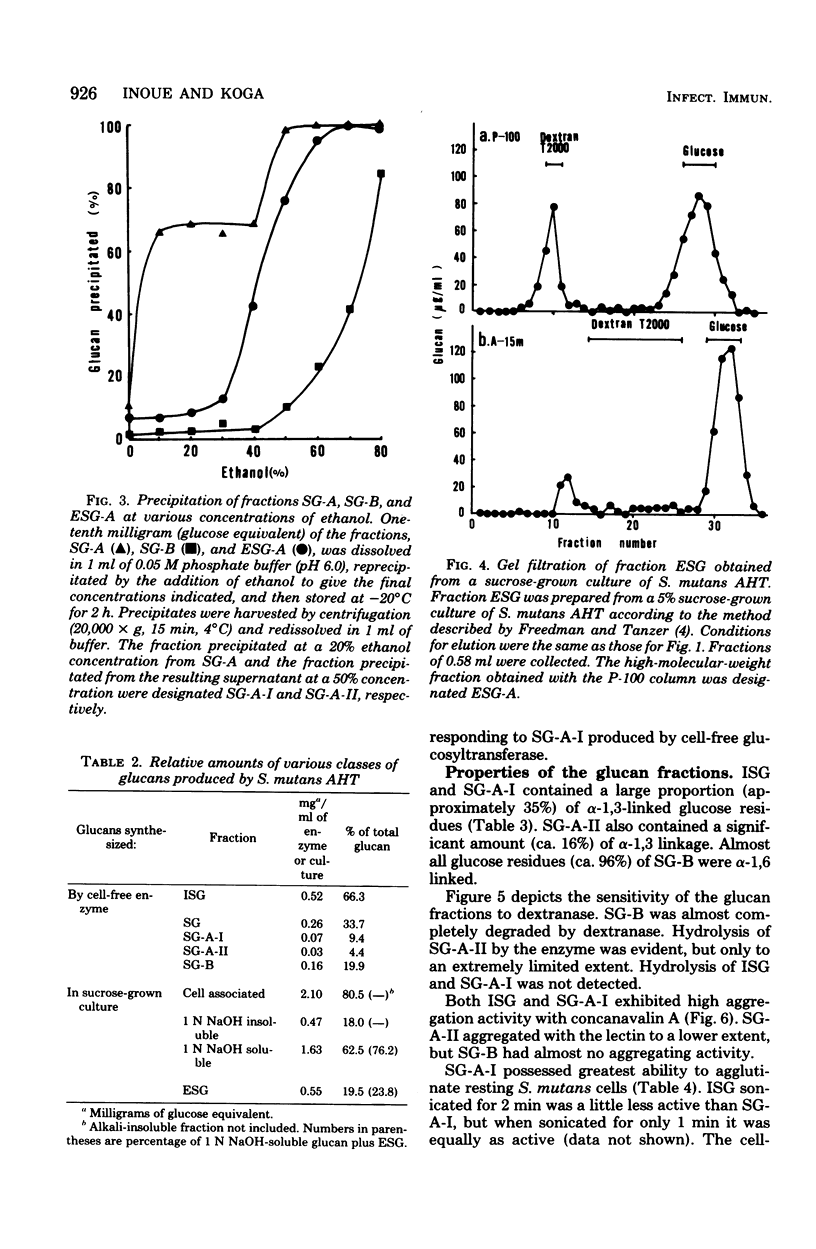
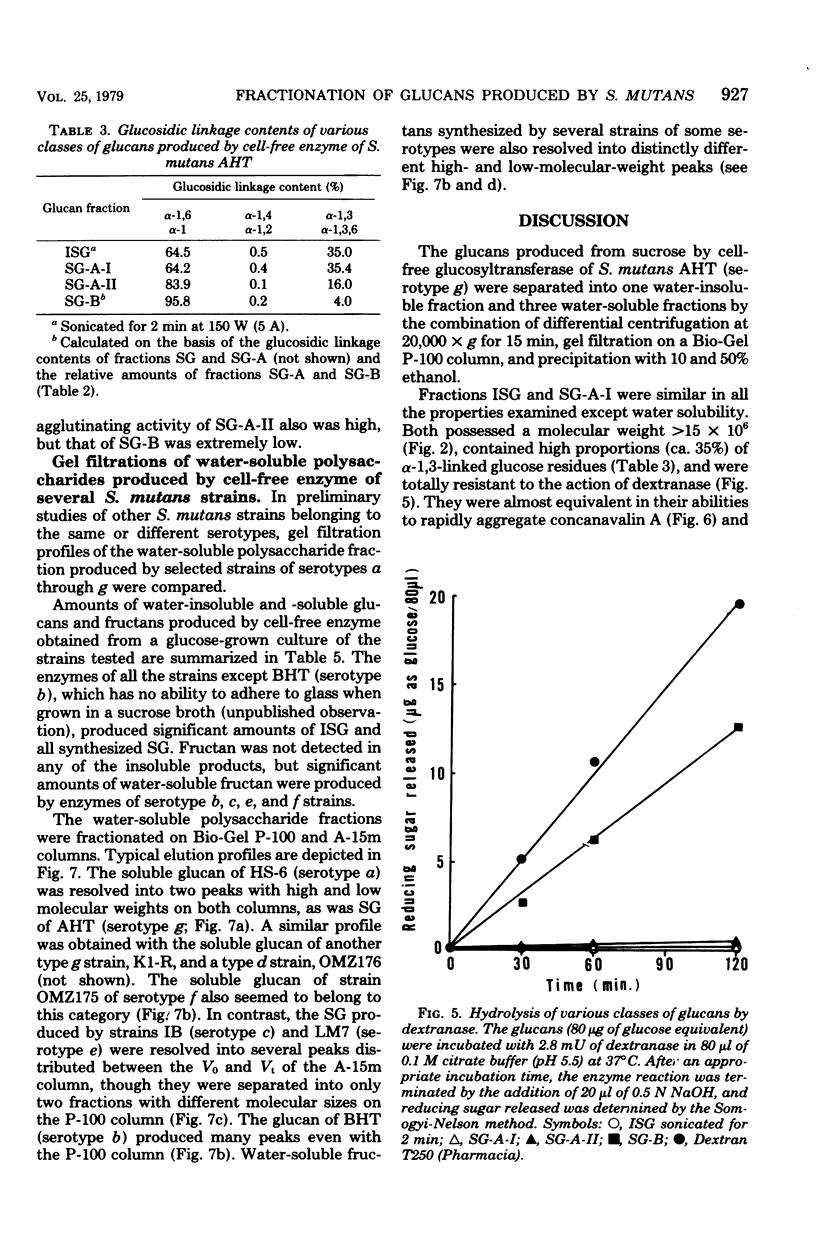
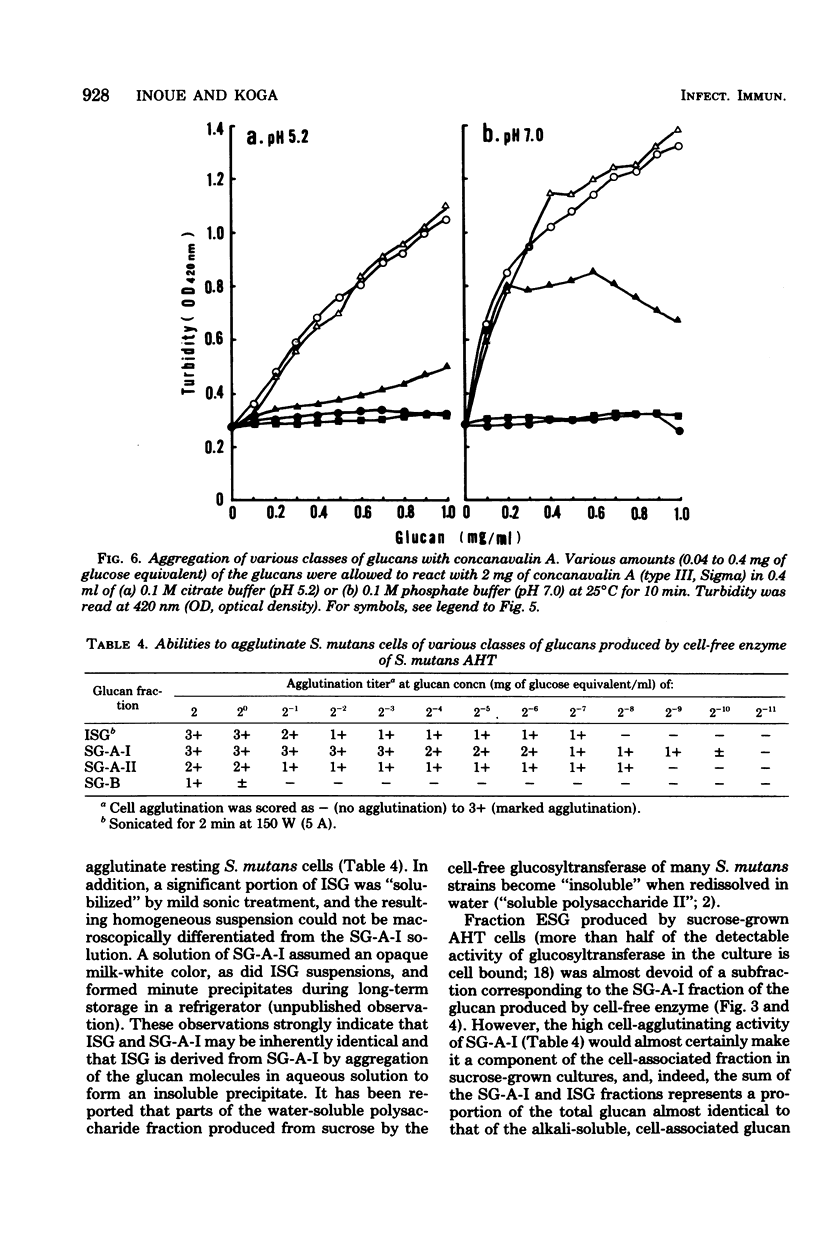
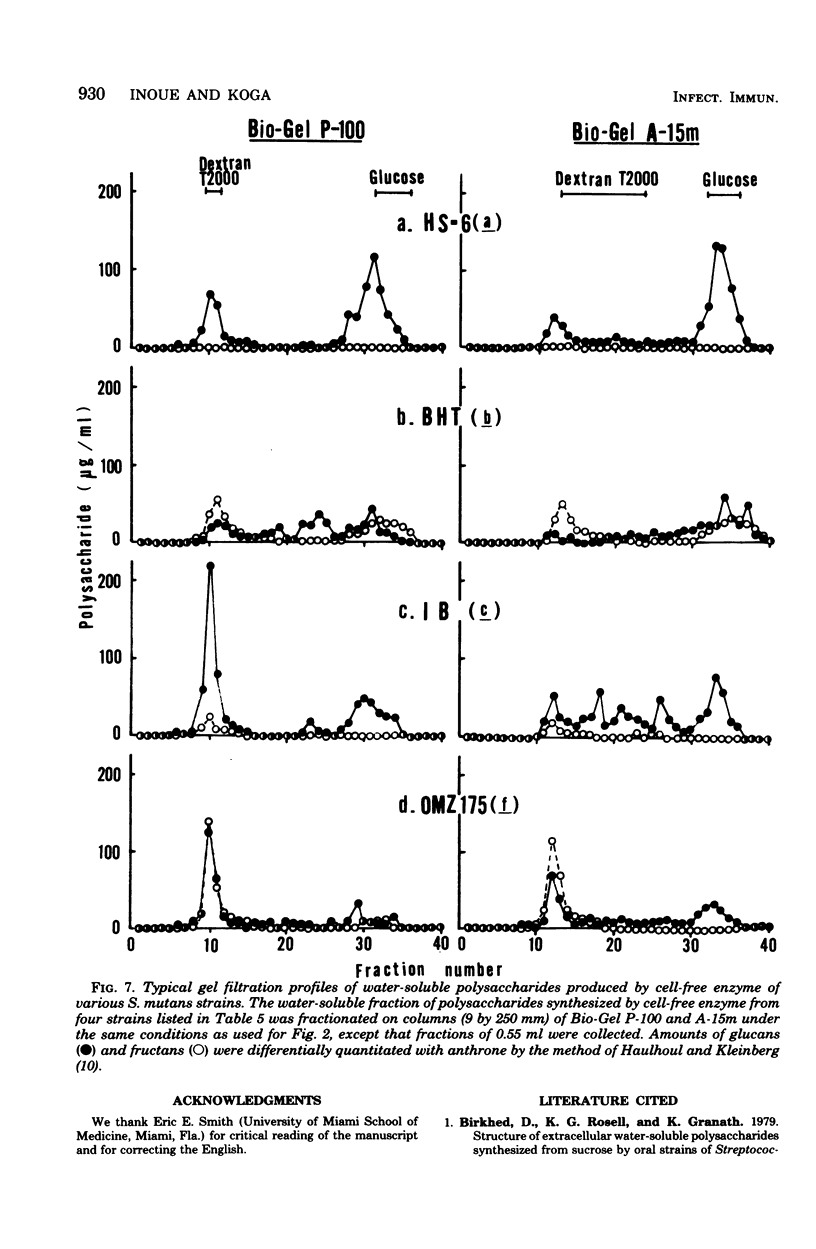
Water-insoluble (ISG) and water-soluble (SG) fractions of glucans produced by cell-free glucosyltransferase of Streptococcus mutans AHT (serotype g) were isolated by centrifugation at 20,000 × g for 15 min. No further resolution of slightly sonicated ISG was observed with gel filtrations on any Bio-Gel beads, including A-50m. Bio-Gel P-100 filtration subdivided SG into two fractions with higher and lower molecular weights (designated SG-A and SG-B, respectively). SG-A was further resolved into two subfractions, SG-A-I and SG-A-II, by 10 to 40% and 50 to 80% ethanol precipitation, respectively. Relative amounts of ISG, SG-A-I, SG-A-II, and SG-B were 66.3:9.4:4.4:19.9. The molecular sizes of these fractions were >1.5 × 107, ≧1.5 × 107, ≦5 × 106 (>1 × 105), and ≦1 × 104 daltons, and their α-1,3 glucosidic linkage contents were approximately 35, 35, 16, and 4% for fractions ISG, SG-A-I, SG-A-II, and SG-B, respectively. Both ISG and SG-A-I were resistant to hydrolysis by dextranase and possessed the ability to aggregate with concanavalin A and to agglutinate S. mutans cells. SG-A-II had extremely low dextranase susceptibility and significant agglutinating activities, whereas SG-B showed high dextranase sensitivity and neither aggregating nor agglutinating activity. These results indicate that SG of S. mutans AHT consists of three types of glucans with distinctly different molecular sizes and chemical structures and strongly suggest that the ISG and SG-A-I fractions are different physical states of an inherently identical glucan. Preliminary observations suggest that the glucans produced by other S. mutans strains of several serotypes may be similarly classified.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ebisu S., Kato K., Kotani S., Misaki A. Isolation and purification of Flavobacterium alpha-1,3-glucanase-hydrolyzing, insoluble, sticky glucan of Streptococcus mutans. J Bacteriol. 1975 Dec;124(3):1489–1501. doi: 10.1128/jb.124.3.1489-1501.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freedman M., Birked D., Granath K. Analyses of glucans from cariogenic and mutant Streptococcus mutans. Infect Immun. 1978 Jul;21(1):17–27. doi: 10.1128/iai.21.1.17-27.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOLDSTEIN I. J., HOLLERMAN C. E., MERRICK J. M. PROTEIN-CARBOHYDRATE INTERACTION. I. THE INTERACTION OF POLYSACCHARIDES WITH CONCANAVALIN A. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1965 Jan 4;97:68–76. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(65)90270-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbons R. J., Fitzgerald R. J. Dextran-induced agglutination of Streptococcus mutans, and its potential role in the formation of microbial dental plaques. J Bacteriol. 1969 May;98(2):341–346. doi: 10.1128/jb.98.2.341-346.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbons R. J. Formation and significance of bacterial polysaccharides in caries etiology. Caries Res. 1968;2(2):164–171. doi: 10.1159/000259554. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbons R. J., Nygaard M. Synthesis of insoluble dextran and its significance in the formation of gelatinous deposits by plaque-forming streptococci. Arch Oral Biol. 1968 Oct;13(10):1249–1262. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(68)90081-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guggenheim B. Extracellular polysaccharides and microbial plaque. Int Dent J. 1970 Dec;20(4):657–678. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halhoul M. N., Kleinberg I. Differential determination of glucose and fructose, and glucose- and fructose-yielding substances with anthrone. Anal Biochem. 1972 Dec;50(2):337–343. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(72)90042-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamada S., Masuda N., Kotani S. Demonstration of serotype d and g specificities of Streptococcus mutans by immunodiffusion. Arch Oral Biol. 1978;23(6):495–499. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(78)90083-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koga T., Inoue M. Cellular adherence, glucosyltransferase adsorption, and glucan synthesis of Streptococcus mutans AHT mutants. Infect Immun. 1978 Feb;19(2):402–410. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.2.402-410.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koga T., Inoue M. Effects of dextranases on cell adherence, glucan-film formation and glucan synthesis by Streptococcus mutans glucosyltransferase. Arch Oral Biol. 1979;24(3):191–198. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(79)90139-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melvaer K. L., Helgeland K., Rölla G. A charged component in purified polysaccharide preparations from Streptococcus mutans and Streptococcus sanguis. Arch Oral Biol. 1974 Jul;19(7):589–595. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(74)90077-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nisizawa T., Imai S., Akada H., Hinoide M., Araya S. Extracellular glucans produced by oral streptococci. Arch Oral Biol. 1976;21(3):207–213. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(76)90131-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TREVELYAN W. E., HARRISON J. S. Studies on yeast metabolism. 7. Yeast carbohydrate fractions. Separation from nucleic acid, analysis, and behaviour during anaerobic fermentation. Biochem J. 1956 May;63(1):23–33. doi: 10.1042/bj0630023. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanzer J. M., Freedman M. L., Fitzgerald R. J., Larson R. H. Diminished virulence of glucan synthesis-defective mutants of Streptococcus mutans. Infect Immun. 1974 Jul;10(1):197–203. doi: 10.1128/iai.10.1.197-203.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trautner K., Gehring F., Lohmann D. Extracellular glucans synthesized by strains of two types of Streptococcus mutans in vitro. Arch Oral Biol. 1978;23(3):175–181. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(78)90213-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



