Abstract
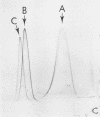
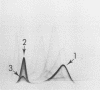
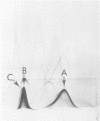
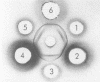
A complex antigenic preparation obtained from Listeria monocytogenes serovariant 4b by freeze-pressing, centrifugation, and gel filtration treatment was studied by crossed immunoelectrophoresis, with the aim of preparing an antigenic fraction that could be used to investigate the serological response to listeric infection. Of 17 immunoprecipitates revealed in the soluble extract, one of three major antigens (designated antigen 2) was shown to be a strong antigen in humans or rabbits infected with L. monocytogenes serovariant 4b. A monospecific antiantigen 2 serum was obtained and used to prepare a serologically homogeneous antigen by immunoadsorption. Antigen 2, most probably located on the bacterial surface, is common to all serovariants of L. monocytogenes and to Listeria grayi and is not shared by the main bacterial species known to have common antigens with L. monocytogenes.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Armstrong A. S., Sword C. P. Antibody responses in experimental infections with Listeria monocytogenes. J Immunol. 1967 Mar;98(3):510–520. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Axelsen N. H. Human precipitins against a micro-organism (Candida albicans) demonstrated by means of quantitative immunoelectrophoresis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1971 Dec;9(6):749–752. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Axelsen N. H. Quantitative immunoelectrophoretic methods as tools for a polyvalent approach to standardization in the immunochemistry of Candida albicans. Infect Immun. 1973 Jun;7(6):949–960. doi: 10.1128/iai.7.6.949-960.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Axén R., Porath J., Ernback S. Chemical coupling of peptides and proteins to polysaccharides by means of cyanogen halides. Nature. 1967 Jun 24;214(5095):1302–1304. doi: 10.1038/2141302a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capron A., Biguet J., Vernes A., Afchain D. Structure antigénique des helminthes. Aspects immunologiques des relations hote-parasite. Pathol Biol. 1968 Feb;16(3):121–138. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elsayed S., Bennich H. The primary structure of allergen M from cod. Scand J Immunol. 1975;4(2):203–208. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1975.tb02618.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray M. L., Killinger A. H. Listeria monocytogenes and listeric infections. Bacteriol Rev. 1966 Jun;30(2):309–382. doi: 10.1128/br.30.2.309-382.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmberg K., Nord C. E., Wadström T. Serological studies of actionomyces israelii by crossed immunoelectrophoresis: standard antigen-antibody system for A. israelii. Infect Immun. 1975 Aug;12(2):387–397. doi: 10.1128/iai.12.2.387-397.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LAURELL C. B. ANTIGEN-ANTIBODY CROSSED ELECTROPHORESIS. Anal Biochem. 1965 Feb;10:358–361. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(65)90278-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MURASCHI T. F., TOMPKINS V. N. SOMATIC PRECIPITINOGENS IN THE IDENTIFICATION AND TYPING OF LISTERIA MONOCYTOGENES. J Infect Dis. 1963 Nov-Dec;113:151–154. doi: 10.1093/infdis/113.3.151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin G. R., Warocquier R., Boulanger P. A. Quantitation of adenovirus soluble antigens by crossed immunoelectrophoresis: application to serological characterization of mutants. Intervirology. 1975;5(3-4):162–172. doi: 10.1159/000149893. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OUCHTERLONY O. Diffusion-in-gel methods for immunological analysis. Prog Allergy. 1958;5:1–78. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owen P., Salton M. R. Antigenic and enzymatic architecture of Micrococcus lysodeikticus membranes established by crossed immunoelectrophoresis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Sep;72(9):3711–3715. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.9.3711. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pease P. E., Nicholls L., Stuart M. R. Evidence that precipitin cross-reactions between Listeria, Erysipelothrix and Bacillus licheniformis are not due to the Rantz antigen. J Gen Microbiol. 1972 Dec;73(3):567–569. doi: 10.1099/00221287-73-3-567. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts D. B., Wright G. L., Jr, Affronti L. F., Reich M. Characterization and comparison of mycobacterial antigens by two-dimensional immunoelectrophoresis. Infect Immun. 1972 Oct;6(4):564–573. doi: 10.1128/iai.6.4.564-573.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHEIDEGGER J. J. Une micro-méthode de l'immuno-electrophorèse. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1955;7(2):103–110. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seeliger H. P. Serovariants of Listeria monocytogenes and other Listeria species. Acta Microbiol Acad Sci Hung. 1975;22(2):179–181. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shivers C. A., James J. M. Specific antibodies produced against antigens of agar-gel precipitates. Immunology. 1967 Dec;13(6):547–554. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smyth C. J., Siegel J., Salton M. R., Owen P. Immunochemical analysis of inner and outer membranes of Escherichia coli by crossed immunoelectrophoresis. J Bacteriol. 1978 Jan;133(1):306–319. doi: 10.1128/jb.133.1.306-319.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sweet G. H., Wilson D. E., Gerber J. D. Application of electroimmunodiffusion and crossed electroimmunodiffusion to the comparative serology of a microorganism (Histoplasma capsulatum). J Immunol. 1973 Aug;111(2):554–564. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thirkill C. E., Kenny G. E. Serological comparison of five arginine-utilizing Mycoplasma species by two-dimensional immunoelectrophoresis. Infect Immun. 1974 Sep;10(3):624–632. doi: 10.1128/iai.10.3.624-632.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vestergaard B. F. Crossed immunoelectrophoretic characterization of Herpesvirus hominis type 1 and 2 antigens. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B Microbiol Immunol. 1973 Dec;81(6):808–810. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1973.tb02282.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weeke B. Crossed immunoelectrophoresis. Scand J Immunol Suppl. 1973;1:47–56. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1973.tb03778.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weeke B. Rocket immunoelectrophoresis. Scand J Immunol Suppl. 1973;1:37–46. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1973.tb03777.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]