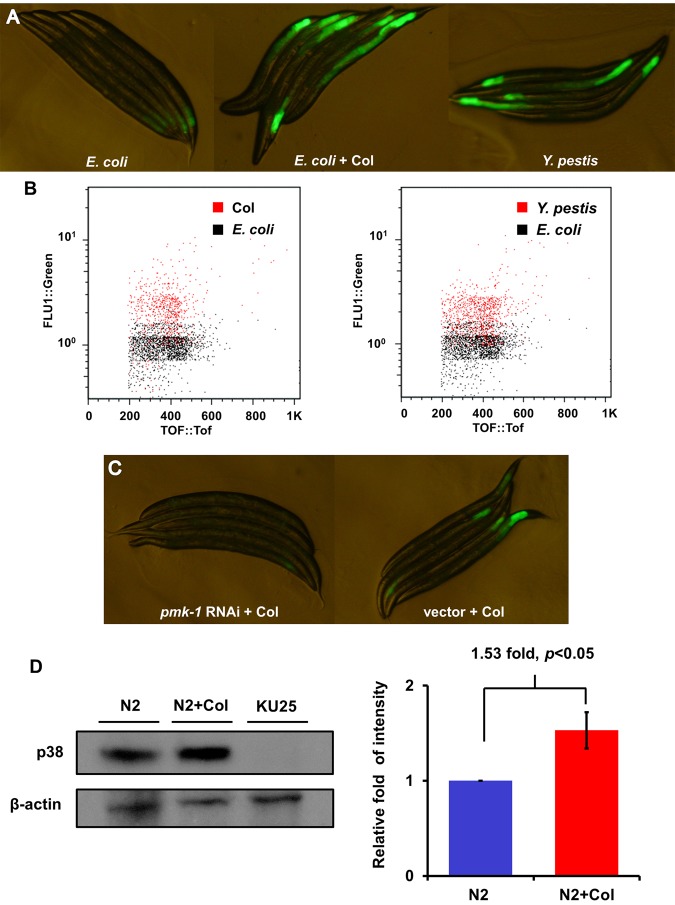
FIG 2 .
Colistin activates pF35E12.5::gfp through the p38/PMK-1 pathway. (A) AY101 acIs101[pDB09.1 (pF35E12.5::gfp), pRF4(rol-6(su1006))] animals carrying a transcriptional reporter for F35E12.5 were exposed to E. coli, E. coli plus colistin, or Y. pestis for 24 h and imaged using fluorescence microscopy. (B) GFP fluorescence intensity in AY101 animals was analyzed using the Copas Biosort instrument (Union Biometrica, Holliston, MA). The fluorescence of AY101 animals exposed to colistin or Y. pestis was compared to that of animals exposed to E. coli. GFP fluorescence intensity (FLU1) was plotted against adult animal size, measured as time of flight (TOF). Each dot represents an individual nematode. (C) AY101 animals were treated with a control vector or pmk-1-specific RNAi and exposed to colistin for 24 h. (D) Western blot analysis of active p38 expression level of N2 treated with (N2+Col) or without colistin for 24 h. Strain KU25, which carries a pmk-1 deletion allele, was used as a control. The level of active p38 in the “N2+Col” group is 1.53-fold higher than that of the N2 group (n = 3; P < 0.05). Image quantification was performed using the software program ImageJ.