Abstract
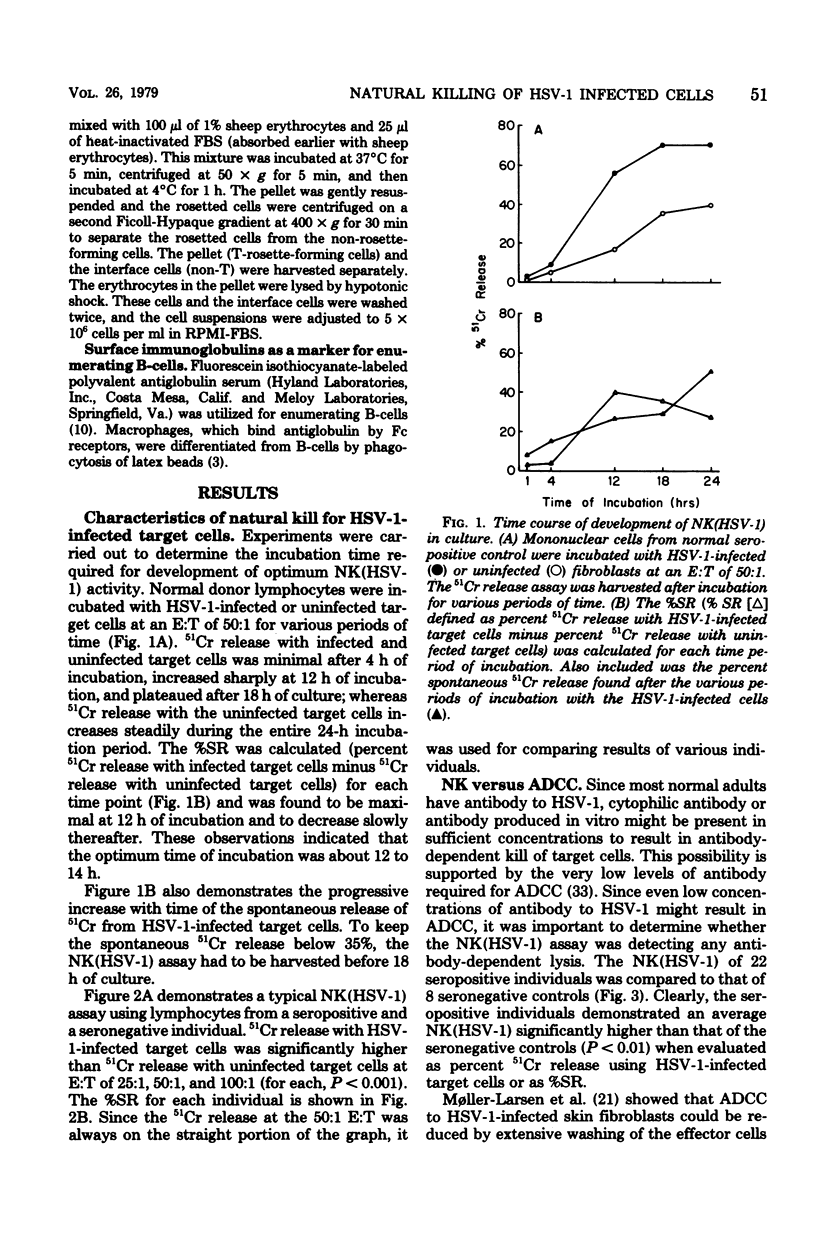
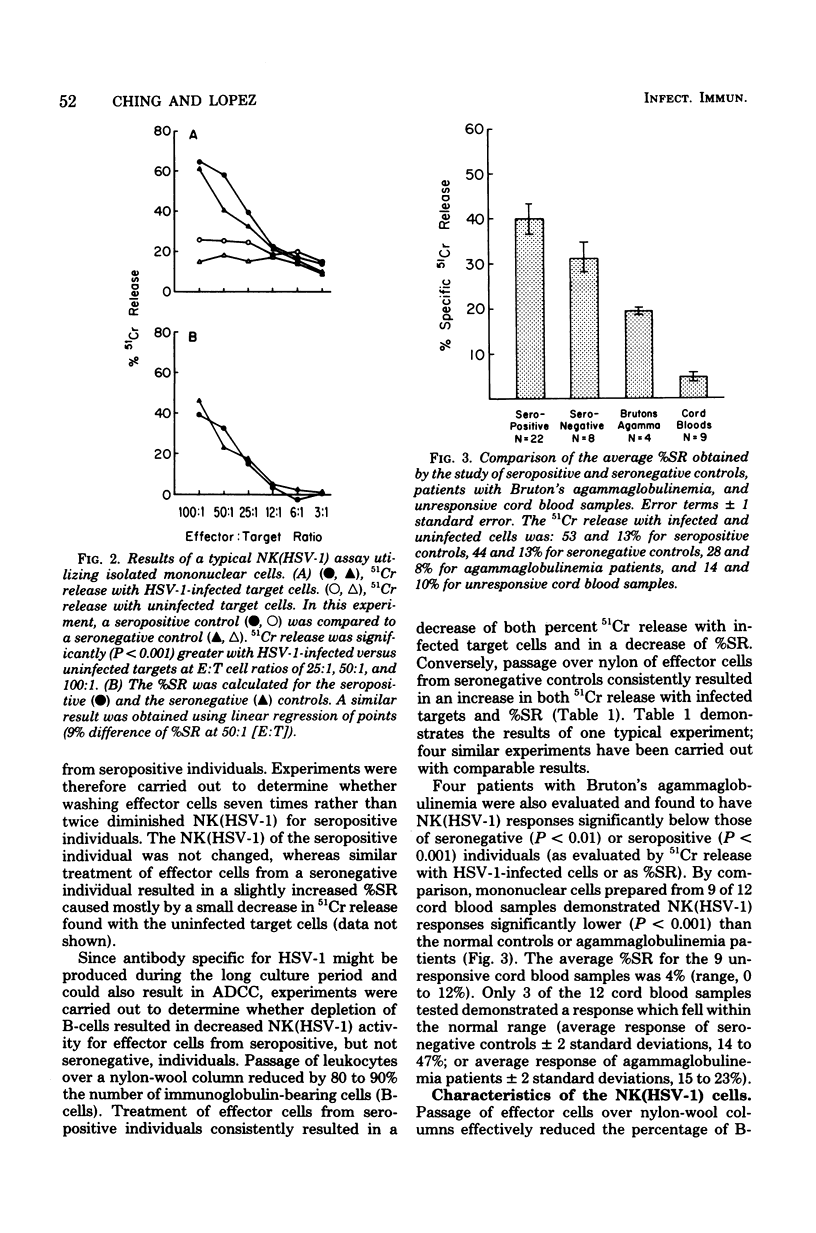
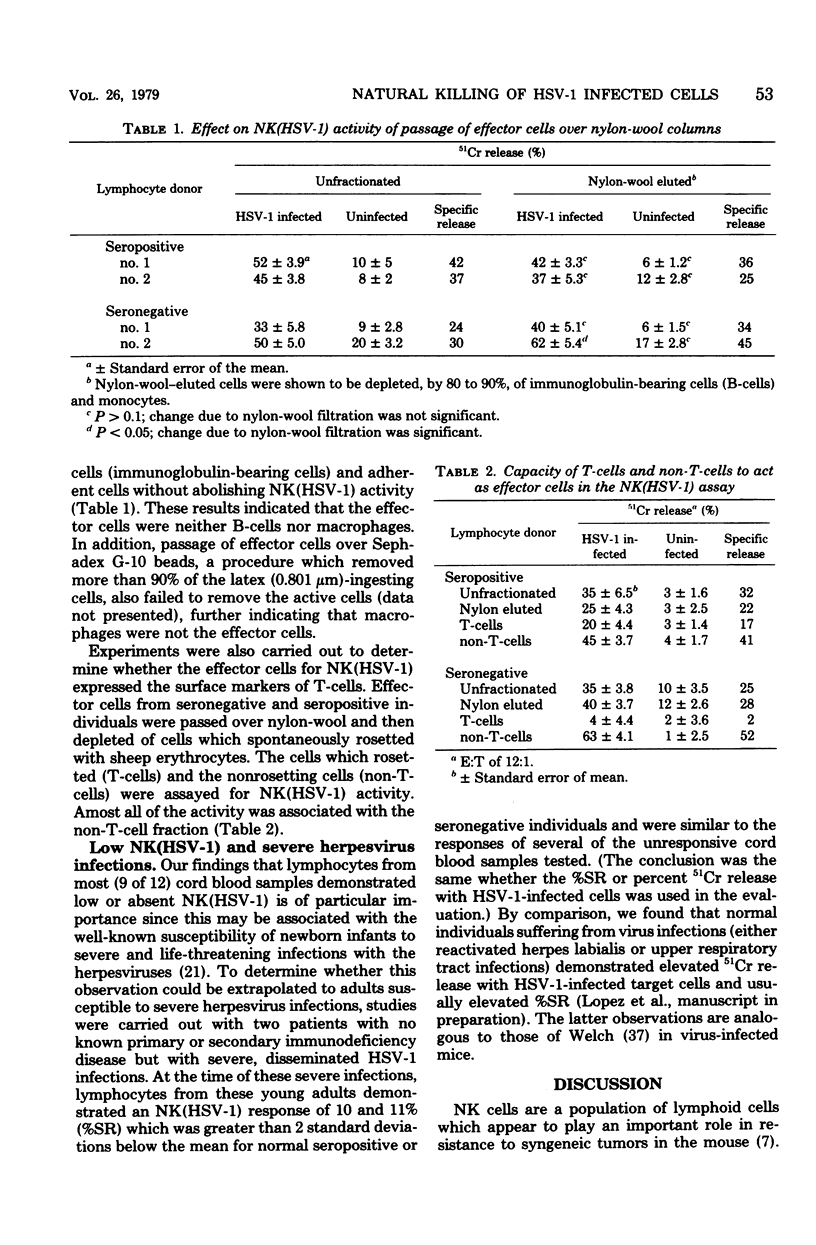
Studies of a mouse model of genetic resistance to herpes simplex virus type 1 (HSV-1) indicate that the marrow-dependent effector cell of allogeneic resistance plays an important role in natural resistance to this virus infection. Since the marrow-dependent effector cell appears to be closely related to the natural killer (NK) cells, an NK assay with HSV-1-infected fibroblasts [NK(HSV-1)] has been developed to study this resistance mechanism in humans. Incubation of effector and target cells for 12 to 14 h gave the greatest percent specific release (%SR) and kept spontaneous 51Cr release from infected target cells below 35%. Patients with Bruton's agammaglobulinemia demonstrated significant kill indicating antiviral antibody was not necessary. Seropositive individuals gave a 9% greater%SR than seronegative individuals. Depletion of B-cells consistently diminished NK (HSV-1) for seropositive individuals and augmented kill for seronegative individuals. Although antiviral antibody produced in culture may contribute to NK (HSV-1), depletion of B-cells allowed quantitation of NK (HSV-1) to the exclusion of most of the antibody-dependent kill. The NK cells detected by this assay showed many of the properties reported for NK cells with K562 targets. Two patients with severe herpesvirus infections demonstrated NK (HSV-1) responses greater than 2 standard deviations below the normal mean. Since normal individuals with virus infections have higher rather than lower natural kill, the low NK (HSV-1) may reflect their susceptibility to the virus infection.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Armstrong D., Young L. S., Meyer R. D., Blevins A. H. Infectious complications of neoplastic disease. Med Clin North Am. 1971 May;55(3):729–745. doi: 10.1016/s0025-7125(16)32514-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett M., Baker E. E., Eastcott J. W., Kumar V., Yonkosky D. Selective elimination of marrow precursors with the bone-seeking isotope 89Sr: implications for hemopoiesis, lymphopoiesis, viral leukemogenesis and infection. J Reticuloendothel Soc. 1976 Jul;20(1):71–87. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berlinger N. T., Lopez C., Lipkin M., Vogel J. E., Good R. A. Defective recognitive immunity in family aggregates of colon carcinoma. J Clin Invest. 1977 May;59(5):761–769. doi: 10.1172/JCI108697. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark E. A., Harmon R. C., Wicker L. S. Resistance of H-2 heterozygous mice to parental tumors. II. Characterization of Hh-1 controlled hybrid resistance to syngeneic fibrosarcomas and the EL-4 lymphoma. J Immunol. 1977 Aug;119(2):648–656. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cudkowicz G., Bennett M. Peculiar immunobiology of bone marrow allografts. I. Graft rejection by irradiated responder mice. J Exp Med. 1971 Jul 1;134(1):83–102. doi: 10.1084/jem.134.1.83. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haller O., Hansson M., Kiessling R., Wigzell H. Role of non-conventional natural killer cells in resistance against syngeneic tumour cells in vivo. Nature. 1977 Dec 15;270(5638):609–611. doi: 10.1038/270609a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haller O., Wigzell H. Suppression of natural killer cell activity with radioactive strontium: effector cells are marrow dependent. J Immunol. 1977 Apr;118(4):1503–1506. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herberman R. B., Holden H. T. Natural cell-mediated immunity. Adv Cancer Res. 1978;27:305–377. doi: 10.1016/s0065-230x(08)60936-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jondal M., Holm G., Wigzell H. Surface markers on human T and B lymphocytes. I. A large population of lymphocytes forming nonimmune rosettes with sheep red blood cells. J Exp Med. 1972 Aug 1;136(2):207–215. doi: 10.1084/jem.136.2.207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jondal M. Surface markers on human B and T lymphocytes. IV. Distribution of surface markers on resting and blast-transformed lymphocytes. Scand J Immunol. 1974;3(6):739–747. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1974.tb01309.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Julius M. H., Simpson E., Herzenberg L. A. A rapid method for the isolation of functional thymus-derived murine lymphocytes. Eur J Immunol. 1973 Oct;3(10):645–649. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830031011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiessling R., Klein E., Wigzell H. "Natural" killer cells in the mouse. I. Cytotoxic cells with specificity for mouse Moloney leukemia cells. Specificity and distribution according to genotype. Eur J Immunol. 1975 Feb;5(2):112–117. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830050208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lopez C. Genetics of natural resistance to herpesvirus infections in mice. Nature. 1975 Nov 13;258(5531):152–153. doi: 10.1038/258152a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lopez C. Immunological nature of genetic resistance of mice to herpes simplex virus type 1 infection. IARC Sci Publ. 1978;(24 Pt 2):775–781. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lopez C., O'Reilly R. J. Cell-mediated immune responses in recurrent herpesvirus infections. I. Lymphocyte proliferation assay. J Immunol. 1977 Mar;118(3):895–902. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lopez C., Simmons R. L., Park B. H., Najarian J. S., Good R. A. Cell-mediated and humoral immune responses or renal transplant recipients with cytomegalovirus infections. Clin Exp Immunol. 1974 Apr;16(4):565–573. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ly I. A., Mishell R. I. Separation of mouse spleen cells by passage through columns of sephadex G-10. J Immunol Methods. 1974 Aug;5(3):239–247. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(74)90108-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moller-Larsen A., Heron I., Haahr S. Cell-mediated cytotoxicity to herpes-infected cells in humans: dependence on antibodies. Infect Immun. 1977 Apr;16(1):43–47. doi: 10.1128/iai.16.1.43-47.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nahmias A. J., Roizman B. Infection with herpes-simplex viruses 1 and 2. 1. N Engl J Med. 1973 Sep 27;289(13):667–674. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197309272891305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neiman P. E., Thomas E. D., Reeves W. C., Ray C. G., Sale G., Lerner K. G., Buckner C. D., Clift R. A., Storb R., Weiden P. L. Opportunistic infection and interstitial pneumonia following marrow transplantation for aplastic anemia and hematologic malignancy. Transplant Proc. 1976 Dec;8(4):663–667. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rager-Zisman B., Bloom B. R. Immunological destruction of herpes simplex virus I infected cells. Nature. 1974 Oct 11;251(5475):542–543. doi: 10.1038/251542a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell A. S., Essery G. Cellular immunity to herpes simplex virus in man. VII. K-cell activity to HSV1 infected target cells in disease. Cancer. 1977 Jul;40(1):42–45. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(197707)40:1<42::aid-cncr2820400109>3.0.co;2-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santoli D., Trinchieri G., Koprowski H. Cell-mediated cytotoxicity against virus-infected target cells in humans. II. Interferon induction and activation of natural killer cells. J Immunol. 1978 Aug;121(2):532–538. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shore S. L., Black C. M., Melewicz F. M., Wood P. A., Nahmias A. J. Antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity to target cells infected with type 1 and type 2 herpes simplex virus. J Immunol. 1976 Jan;116(1):194–201. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shore S. L., Milgrom H., Wood P. A., Nahmias A. J. Antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity to target cells infected with herpes simplex viruses: functional adequacy in the neonate. Pediatrics. 1977 Jan;59(1):22–28. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shore S. L., Nahmias A. J., Starr S. E., Wood P. A., McFarlin D. E. Detection of cell-dependent cytotoxic antibody to cells infected with herpes simplex virus. Nature. 1974 Sep 27;251(5473):350–352. doi: 10.1038/251350a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spencer E. S., Andersen H. K. Clinically evident, non-terminal infections with herpesviruses and the wart virus in immunosuppressed renal allograft recipients. Br Med J. 1970 Aug 1;3(5717):251–254. doi: 10.1136/bmj.3.5717.251. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutton A. L., Smithwick E. M., Seligman S. J., Kim D. S. Fatal disseminated herpesvirus hominis type 2 infection in an adult with associated thymic dysplasia. Am J Med. 1974 Apr;56(4):545–553. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(74)90487-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welsh R. M., Jr Mouse natural killer cells: induction specificity, and function. J Immunol. 1978 Nov;121(5):1631–1635. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



