Abstract
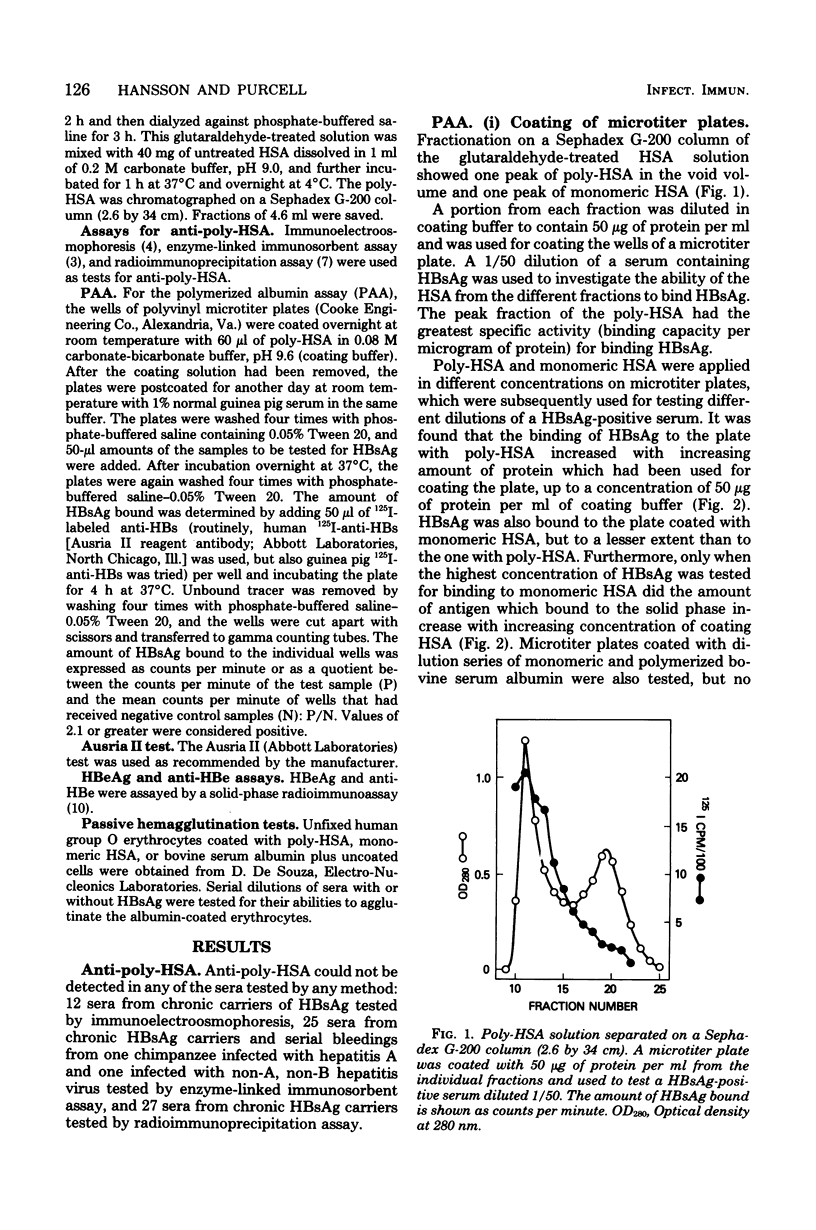
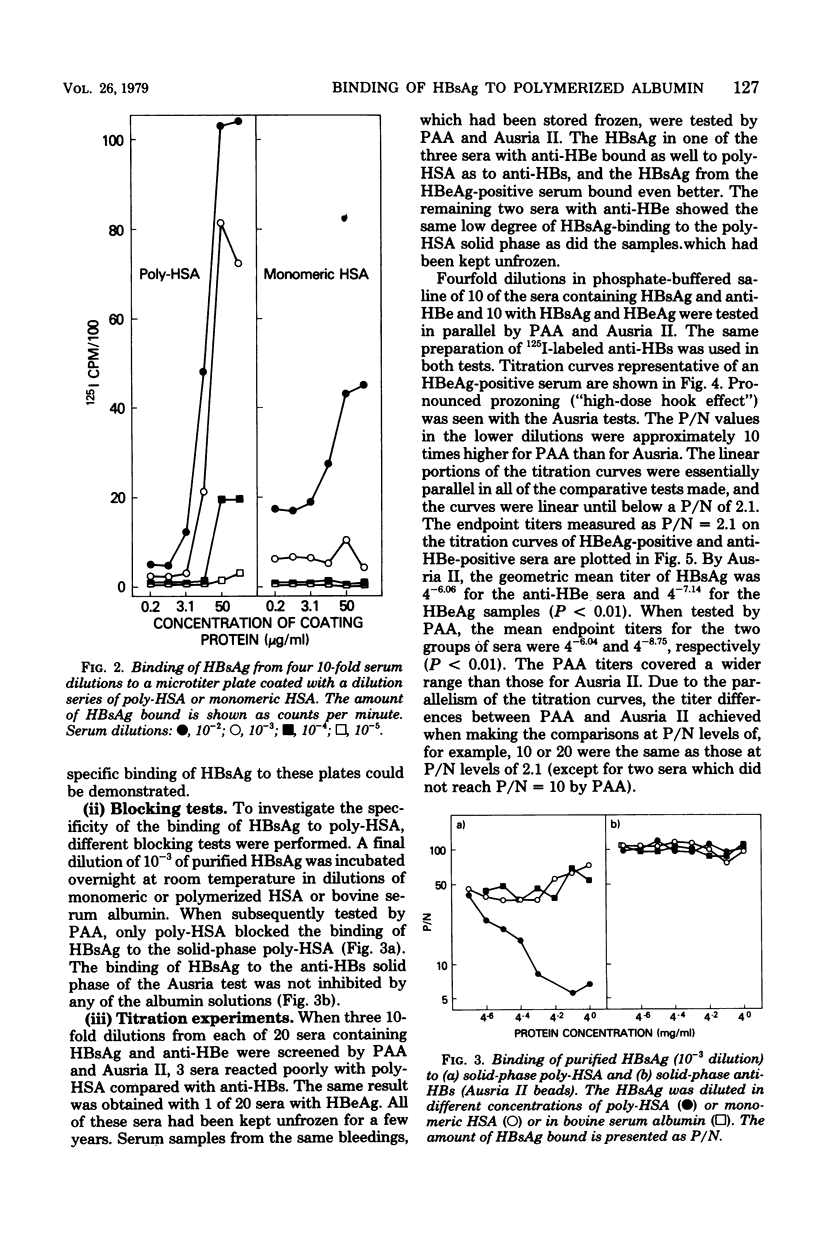
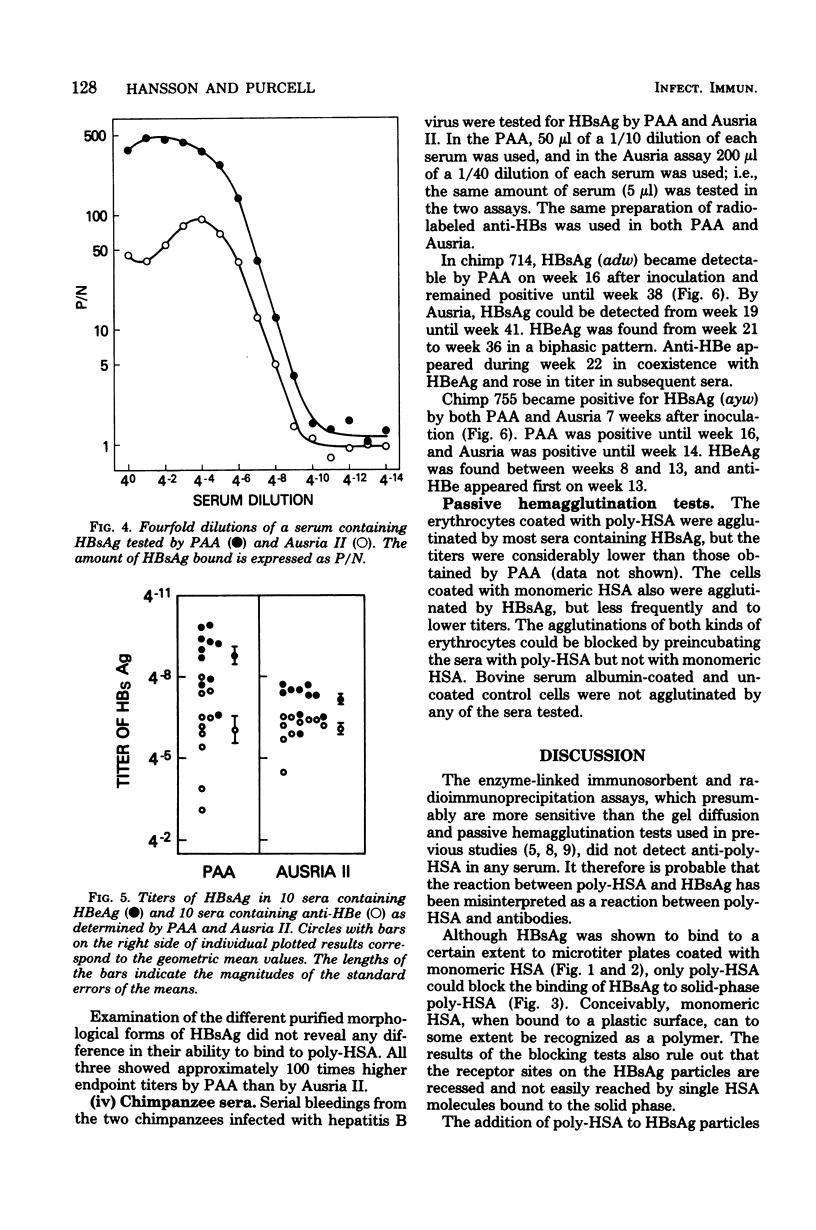
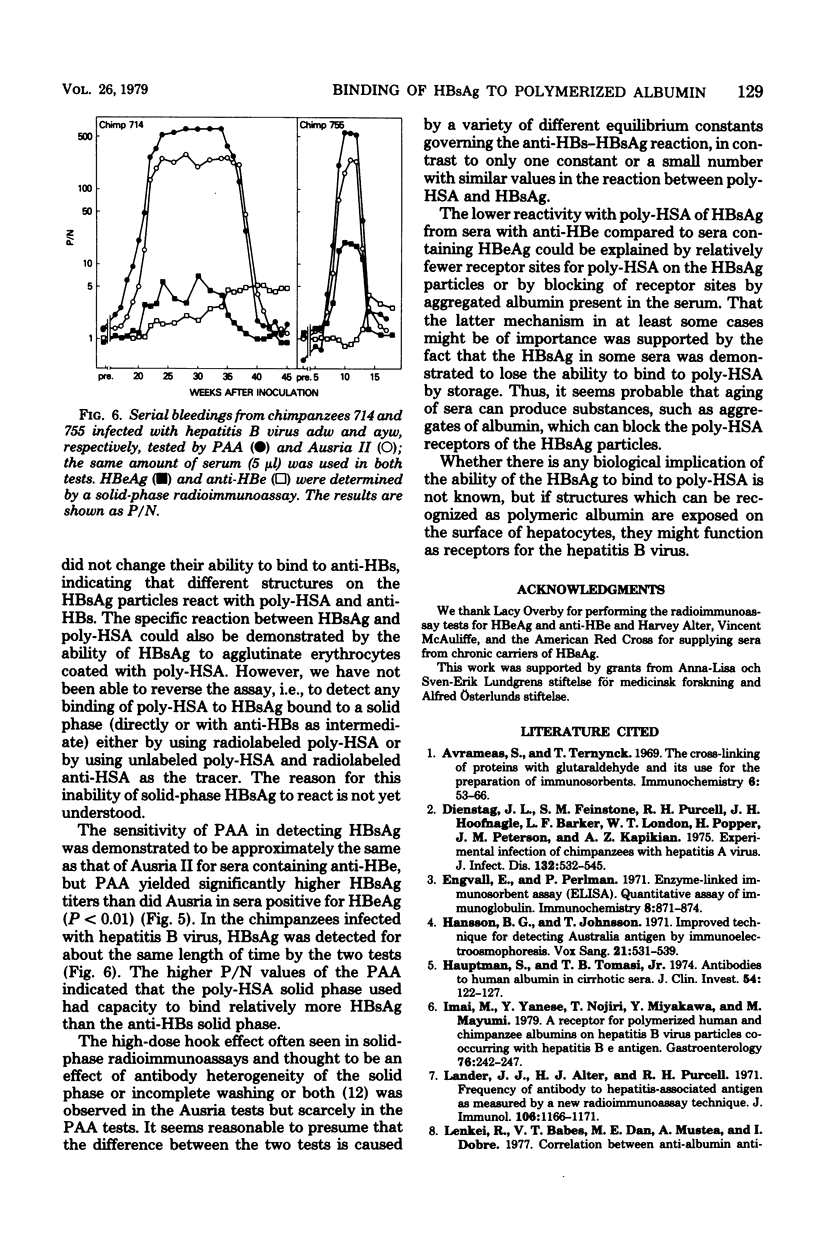
Antibodies to polymerized human albumin (poly-HSA) could not be detected by using sensitive methods (enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay and radioimmunoprecipitation) in sera from chronic carriers of hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg) or in serial bleedings from one chimpanzee infected with type A hepatitis virus and one infected with non-A, non-B hepatitis virus. By a solid-phase radioimmunoassay, receptor sites for poly-HSA could be detected on HBsAg particles from sera containing either hepatitis B "e" antigen (HBeAg) or anti-HBe. Blocking experiments showed that monomeric HSA did not bind to this receptor. In general, the HBsAg particles from sera with HBeAg had more poly-HSA receptor sites or relatively more particles carrying this receptor compared with HBsAg from sera with anti-HBe. Microtiter plates coated with poly-HSA bound HBsAg from sera containing HBeAg with greater efficiency than did anti-HBs coupled to a solid phase (Ausria II beads), whereas with sera positive for anti-HBe, the two assays were equally sensitive. Decreased ability of HBsAg to bind to poly-HSA was seen in some sera which had been stored for a few years at 4 degrees C, whereas the binding to anti-HBs was unaffected. It is possible that polymers of albumin on the surface of hepatocytes could function as receptors for hepatitis B virus.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Avrameas S., Ternynck T. The cross-linking of proteins with glutaraldehyde and its use for the preparation of immunoadsorbents. Immunochemistry. 1969 Jan;6(1):53–66. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(69)90178-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dienstag J. L., Feinstone S. M., Purcell R. H., Hoofnagle J. H., Barker L. F., London W. T., Popper H., Peterson J. M., Kapikian A. Z. Experimental infection of chimpanzees with hepatitis A virus. J Infect Dis. 1975 Nov;132(5):532–545. doi: 10.1093/infdis/132.5.532. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engvall E., Perlmann P. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). Quantitative assay of immunoglobulin G. Immunochemistry. 1971 Sep;8(9):871–874. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(71)90454-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansson B. G., Johnsson T. Improved technique for detecting Australia antigen by immunoelectroosmophoresis. Vox Sang. 1971 Dec;21(6):531–539. doi: 10.1111/j.1423-0410.1971.tb04812.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hauptman S., Tomasi T. B., Jr Antibodies to human albumin in cirrhotic sera. J Clin Invest. 1974 Jul;54(1):122–127. doi: 10.1172/JCI107733. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imai M., Yanase Y., Nojiri T., Miyakawa Y., Mayumi M. A receptor for polymerized human and chimpanzee albumins on hepatitis B virus particles co-occurring with HBeAg. Gastroenterology. 1979 Feb;76(2):242–247. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lander J. J., Alter H. J., Purcell R. H. Frequency of antibody to hepatitis-associated antigen as measured by a new radioimmunoassay technique. J Immunol. 1971 May;106(5):1166–1171. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lenkei R., Babes V. T., Dan M. E., Mustea A., Dobre I. Correlations between anti-albumin antibodies and HBsAG in hepatic patients. J Med Virol. 1977;1(1):29–34. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890010106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matuhasi T., Hosokawa Z. Reactants to human serum albumin-coated red cells found in Au(1)-positive sera. Jpn J Exp Med. 1972 Apr;42(2):183–185. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodbard D., Feldman Y., Jaffe M. L., Miles L. E. Kinetics of two-site immunoradiometric ('sandwich') assays-II. Studies on the nature of the 'high-dose hook effect'. Immunochemistry. 1978 Feb;15(2):77–82. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(78)90046-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



