Abstract
OBJECTIVE:
To evaluate the effectiveness and safety of filiform needle acupuncture for poststroke depression, and to compare acupuncture with the therapeutic efficacy of antidepressant drugs.
DATA RETRIEVAL:
We retrieved data from the Chinese National Knowledge Infrastructure (1979–2012), Wanfang (1980–2012), VIP (1989–2012), Chinese Biomedical Literature (1975–2012), PubMed (1966–2012), Ovid Lww (–2012), and Cochrane Library (–2012) Database using the internet.
SELECTION CRITERIA:
Randomized controlled trials on filiform needle acupuncture versus antidepressant drugs for treatment of poststroke depression were included. Moreover, the included articles scored at least 4 points on the Jadad scale. Exclusion criteria: other acupuncture therapies as treatment group, not stroke-induced depression patients, score < 4 points, non-randomized controlled trials, or animal trials.
MAIN OUTCOME MEASURES:
These were the Hamilton Depression Scale scores, clinical effective rate, Self-Rating Depression Scale scores, Side Effect Rating Scale scores, and incidence of adverse reaction and events.
RESULTS:
A total of 17 randomized controlled clinical trials were included. Meta-analysis results displayed that after 4 weeks of treatment, clinical effective rate was better in patients treated with filiform needle acupuncture than those treated with simple antidepressant drugs [relative risk = 1.11, 95% confidence interval (CI): 1.03–1.21, P = 0.01]. At 6 weeks, clinical effective rate was similar between filiform needle acupuncture and antidepressant drug groups. At 2 weeks after filiform needle acupuncture, Hamilton Depression Scale (17 items) scores were lower than in the antidepressant drug group (mean difference = −2.34, 95%CI: −3.46 to −1.22, P < 0.000,1). At 4 weeks, Hamilton Depression Scale (24 items) scores were similar between filiform needle acupuncture and antidepressant drug groups. Self-Rating Depression Scale scores were lower in filiform needle acupuncture group than in the antidepressant drug group. Side Effect Rating Scale was used in only two articles, and no meta-analysis was conducted. Safety evaluation of the 17 articles showed that gastrointestinal tract reactions such as nausea and vomiting were very common in the antidepressant drug group. Incidence of adverse reaction and events was very low in the filiform needle acupuncture group.
CONCLUSION:
Early filiform needle acupuncture for poststroke depression can perfectly control depression. Filiform needle acupuncture is safe and reliable. Therapeutic effects of filiform needle acupuncture were better than those of antidepressant drugs.
Keywords: nerve regeneration, poststroke depression, filiform needle acupuncture, antidepressant drugs, randomized controlled trials, clinical effective rate, safety, meta-analysis, the Guangdong Provincial “211 Engineering”, Stage-III Key Disciplines Construction Project, neural regeneration
Introduction
Poststroke depression is a complication of stroke and frequently presents with despair, anxiety, disordered sleep and poor responsiveness[1]. Pohjasvaara et al[2] found that the incidence of poststroke depression is between 30–60%. Poststroke depression causes a decrease in the effectiveness of functional rehabilitation in patients. A previous study confirmed that depression was an independent risk factor for rehabilitation of stroke patients[3], and mortality of depressed patients was three times that of patients without depression[3]. Therefore, how to improve the depressive state in patients with poststroke depression remains poorly understood. This paper sought to compare and analyze the therapeutic effects of poststroke depression-related therapies by systematically evaluating previous studies.
What are poststroke depression-related therapies? Which methods are dominant in the treatment of poststroke depression? At present, treatments for poststroke depression mainly include drug treatment, traditional Chinese medicine and psychotherapy[4]. The development of antidepressant drugs is rapid, and the continuous research and development of new antidepressant drugs greatly promote the treatment of poststroke depression. However, the adverse reactions to antidepressant drugs cannot be ignored. Apparent adverse reactions somewhat decrease the compliance of patients, and then affect therapeutic efficacy[5]. Acupuncture therapy is considered as a traditional Chinese method and the clinical therapeutic effects of acupuncture have been extensively affirmed[6]. Moreover, the adverse reactions of acupuncture therapy are less. Tian et al.[7] believed that obvious effective rate of acupuncture for poststroke depression was noticeably higher than that of taking fluoxetine at 4 weeks. Wu et al.[8] confirmed that therapeutic effects of acupuncture based on differentiation of symptoms and signs were better than that of fluoxetine in 150 patients with various types of poststroke depression. Chu et al.[9] verified that clinical therapeutic effects were identical between acupuncture therapy and fluoxetine treatment. This paper was designed to compare the differences between acupuncture therapy and antidepressant drugs for poststroke depression.
Evidence-based medicine, whose philosophical origins extend back to 1992, as proposed by Guyatt at McMaster University in Canada, is the conscientious, explicit and judicious use of current best evidence in making decisions about the care of individual patients[10]. Meta-analysis is a statistical method that focuses on contrasting and combining results from different studies, in the hope of identifying patterns among study results, sources of disagreement among those results, or other interesting relationships that may come to light in the context of multiple studies. Meta-analysis is widely used on a daily basis in systematic evaluation of evidence-based medicine[11]. Meta-analysis has compared the therapeutic effects of acupuncture and Western medicine for poststroke depression. However, current articles[3,12,13] only concluded that the dominance of acupuncture for poststroke depression remains unclear, because (1) the quality of included studies was low; (2) acupuncture treatments were different in the experimental groups; (3) the edition of the Hamilton Depression Scale was different; and (4) the course of treatment was not grouped.
This paper performed a meta-analysis on filiform needle acupuncture versus antidepressant drugs in high-quality randomized controlled trials so as to obtain well-defined therapeutic effects and safety evaluation of filiform needle acupuncture. Our methods are characterized by overall retrieval data, long retrieval time, and high quality of included articles which ensures homogeneity and objectivity of the meta-analysis. This paper described the difference in therapeutic effects between filiform needle acupuncture versus antidepressant drugs in different therapeutic stages, and meta-analysis results were tested by sensitivity analysis to increase the reliability of results.
The present study sought to objectively assess the effectiveness and safety of filiform needle acupuncture versus antidepressant drugs for poststroke depression, explore whether the therapeutic effects of filiform needle acupuncture are better than that of antidepressant drugs, and provide theoretical evidence for selecting optimal methods for the treatment of poststroke depression in the clinic.
Data Sources and Methodology
Data retrieval
Retrieval scope: We retrieved data from the VIP Database, Wanfang Database, China National Knowledge Infrastructure, Chinese Biomedical Literature Database, Ovid Lww, PubMed and Cochrane Library using the internet and a computer. The search spanned from database building to August 2012.
Search query: (stroke or shock or apoplexy) and (depression or depressive illness) or (post stroke depression or PSD) and (acupuncture or acupuncture point or needing or acupuncture therapy or acupuncture treatment) and (antidepressant or antidepressant drug or counterdepressant).
Inclusion and exclusion criteria
Diagnostic criteria: stroke was diagnosed in accordance with Diagnostic main points in all kinds of cerebrovascular diseases[14], and Chinese Disease Diagnosis and Efficacy Standards[15]. Depression was diagnosed in accordance with Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, the fourth edition[16], Chinese Classification of Mental Disorders and Diagnostic Criteria, the third edition[17], and The International Statistical Classification of Diseases and Related Health Problems 10th Revision[18].
Inclusion criteria: (1) articles of high-quality randomized controlled trials about filiform needle acupuncture versus antidepressant drugs for poststroke depression, no matter whether the patients had received conventional therapy or rehabilitative management for cerebrovascular disease; (2) experimental group used filiform needle acupuncture; different patients used different acupoints, different reinforcing and reducing method, different needle maintenance time, and different courses of treatment; no limitation was conducted (filiform needle acupuncture at ear acupoint was not included), but electroacupuncture and acupoint injection were not used. Acupuncture treatment in the experimental group was simple manual acupuncture. Control group received antidepressant drugs. The type of antidepressant drugs was not confined, and included tricyclic, norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors, and serotonin reuptake inhibitors.
Exclusion criteria: (1) repeatedly detected or repeatedly published articles (one article with highest quality was added for analysis); (2) reviews, animal experiments, experiences, comments, and evaluations; (3) subjects without cerebrovascular disease, but combined with poststroke depression; (4) intervention in the experimental group was combined with filiform needle acupuncture. Acupuncture therapy is in accordance with the Techniques of Acupuncture and Moxibustion[19]; and/or control group received non-antidepressant drugs; (5) non-randomized controlled trials or semi-randomized controlled trials; (6) randomized controlled trials with modified Jadad score < 4; (7) no full text (unpublished periodical thesis or dissertation, periodical thesis with wrong information in the database).
Data extraction
Articles were independently read by two evaluators. Articles were screened in accordance with inclusion and exclusion criteria. Included articles were cross checked. If evalutors could not agree, a third researcher (Jiping Zhang) decided whether the article was included.
Quality evaluation
Modified Jadad scale[20] was utilized to assess the quality of randomized controlled trials. The score contained four aspects: (1) random sequence generation; (2) allocation concealment; (3) blind methodology; and (4) follow-up and withdrawal. High-quality articles had 4–7 points. The included articles were separately assessed by the two evaluators, and then results were cross checked. If disagreements appeared, the third evaluator assisted to solve the problem.
Outcome measures
(1) Clinical effective rate: The reducing score rate of Hamilton Depression Scale = [(total score pretreatment – total score posttreatment)/total score pretreatment] × 100%. Clinical control > 75%; 75% ≥ marked effect > 50%; 50% ≥ improved > 25%; ineffective ≤ 25%. (2) Hamilton Depression Scale[21]: a high score indicated severe depression. (3) Self-Rating Depression Scale score[22]: a high score indicated severe depression. (4) Safety: Side Effect Rating Scale[23]: a high score showed severe side effects, as well as incidence of adverse reaction and events.
Statistical analysis
Meta-analysis was performed using RevMan 5.1 software provided by Cochrane Collaboration. Measurement data were expressed as mean difference (MD). Numeration data were expressed as relative risk (RR). All data were expressed as 95% confidence interval (CI). Heterogeneity tests were conducted among studies (P ≤ 0.1). The studies were considered homogenous if P > 0.1. Fixed effect model was used. The studies were considered heterogenous if P ≤ 0.1 and I2 ≥ 50%. A random effect model was employed if study combination was needed. If necessary, sensitivity analysis was applied to evaluate the stability of results. If a large amount heterogeneity existed among studies and sensitivity analysis verified that the results of meta-analysis were not stable, only descriptive analysis was conducted.
Results
Data retrieval
1,029 articles were primarily retrieved. After excluding were included[24,25,26,27,28,29,30,31,32,33,34,35,36,37,38,39,40]. The screening flow chart is shown in Figure 1.
Figure 1.
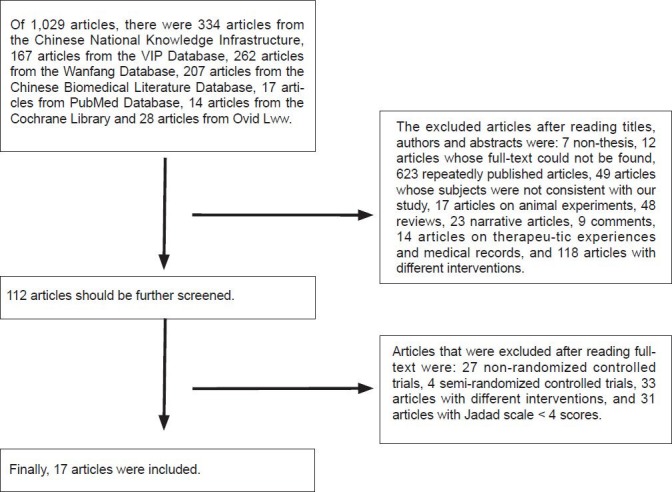
Flow diagram for article retrieval.
Basic characteristics of the included articles
Study design
The 17 included articles[24,25,26,27,28,29,30,31,32,33,34,35,36,37,38,39,40] were randomized parallel controlled trials.
Study subjects
1,132 poststroke depression patients from inpatient or out-patient clinics were included in this study. Stroke was diagnosed in accordance with the Diagnostic main points in all kinds of cerebrovascular diseases[24,25,26,27,28,29,30,31,32]. Some trials also used the Stroke diagnosis evaluation standard[33,34,35,36,37,38,39]. One trial did not describe the stroke diagnosis standard[40]. Depression was mainly diagnosed by the Chinese Classification of Mental Disorders and Diagnostic Criteria, the third edition[24,27,34,36]. Some trials combined diagnosis between the Chinese Disease Diagnosis and Efficacy Standards[31,33,35,37] or Chinese Classification of Mental Disorders and Diagnostic Criteria-2-Revised Version[29] or The International Statistical Classification of Diseases and Related Health Problems 10th Revision[28]. Some trials used the Chinese Classification of Mental Disorders and Diagnostic Criteria (2nd edition)[31] or the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders-3-Revised Version[30] or the Depression Diagnosis Criteria of Affective Disorder After Poststroke Depression[26]. Some trials only used the Hamilton Depression Scale ≥ 7[24]. Three test specifications described inclusion criteria, exclusion criteria, termination criteria, and rejection criteria[25,28,40].
Basic characteristics and quality evaluation of the included articles
Specific contents are shown in Tables 1 and 2.
Table 1.
Basic characteristics of the included articles
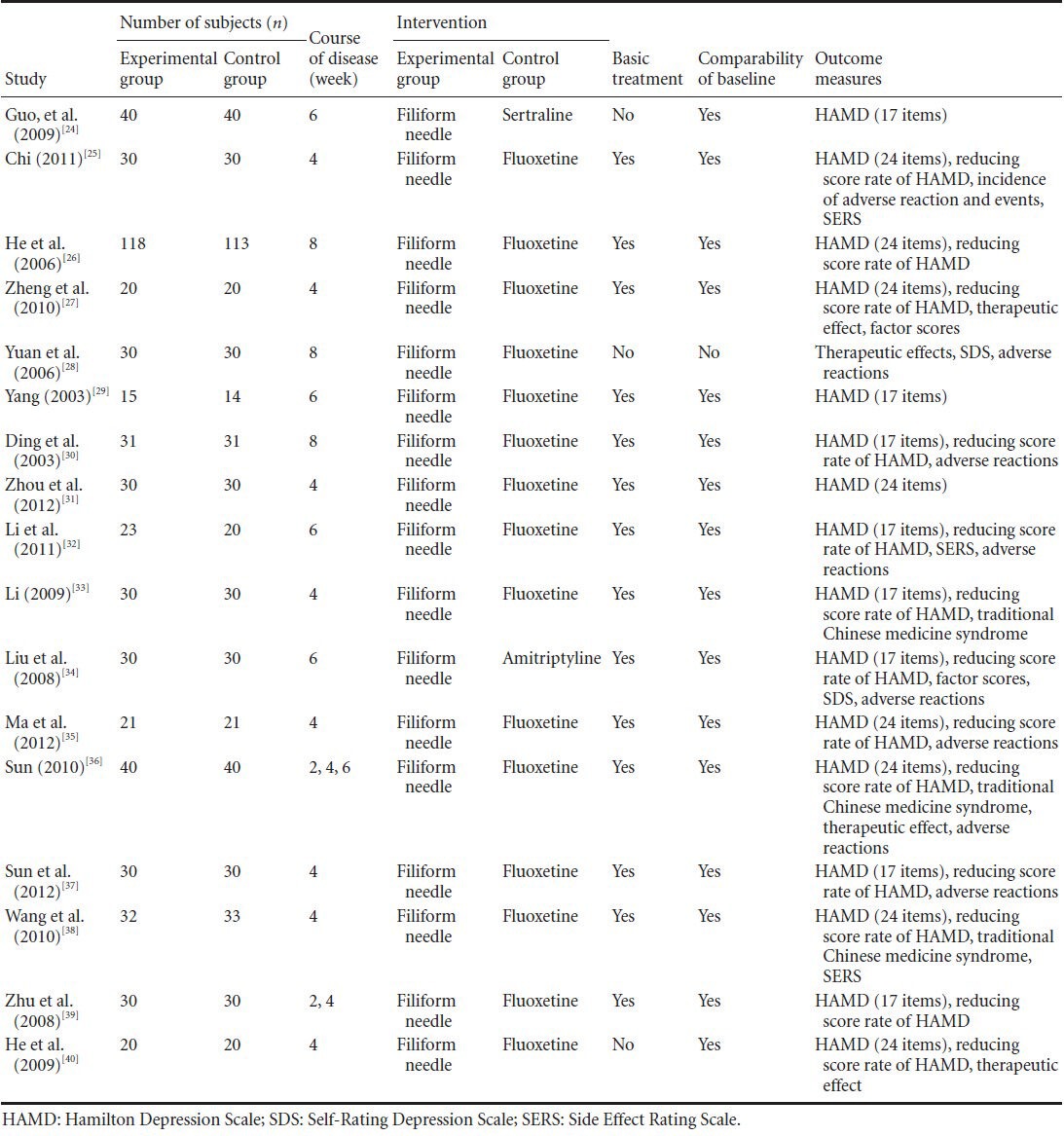
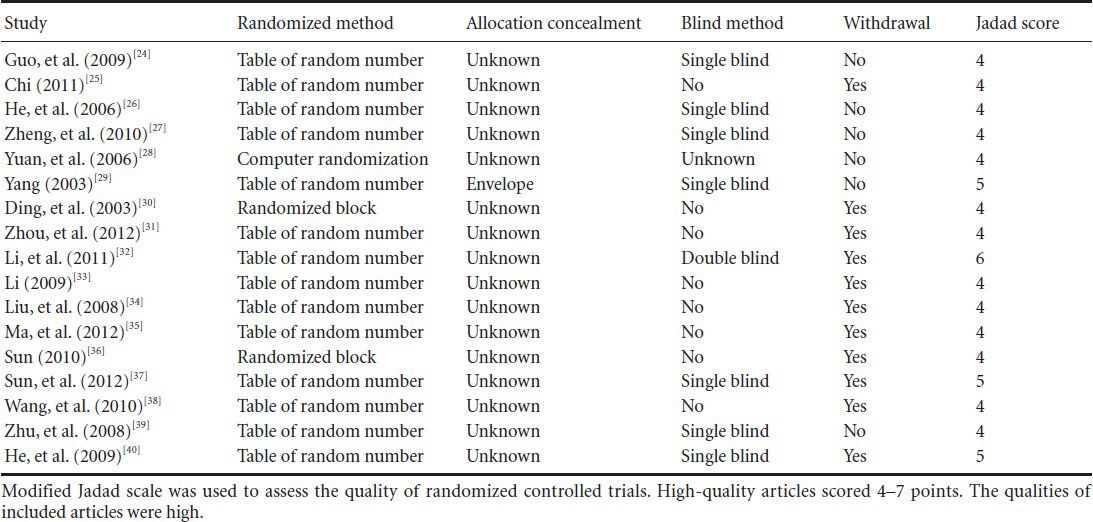
Table 2.
Methodology quality evaluation of the included articles addressing filiform needle acupuncture for poststroke depression
As shown in Table 1, sample size of the included articles was small. Three articles[24,28,40] did not describe the basic treatment of stroke in patients with poststroke depression. One article[28] described the comparability of basic numbers. Most articles[24,25,26,27,29,30,31,32,33,34,35,36,37,38,39,40] used the Hamilton Depression Scale and/or the reducing score rate of the Hamilton Depression Scale. One article[28] used the Self-Rating Depression Scale. Only nine articles[25,28,30,32,34,35,36,37,38] described adverse reactions.
As exhibited in Table 2, quality of methodology in each study was relatively high. All articles demonstrated random methods. Only one article[29] demonstrated allocation concealment method, and other articles[24,25,26,27,28,30,31,32,33,34,35,36,37,38,39,40] did not mention concealment measures. One article[32] used double-blind methodology. Seven articles[24,26,27,29,37,39,40] used single-blinded methods. Only one article[28] mentioned the allocation concealment. A total of 11 articles[25,30,31,32,33,34,35,36,37,38,40] presented the withdrawal of volunteers. Some deficiencies in study design possibly increased selective and measure bias.
Statistical methods
Three articles did not mention statistical methods. One article[28] used the chi-square test. Twelve articles[24,25,29,30,31,33,34,36,37,38,39] compared intragroup Hamilton Depression Scale score and Self-Rating Depression Scale score pretreatment and posttreatment using paired sample t-test. Intergroup difference posttreatment was compared using independent sample t-test. Clinical effective rate of five articles[30,33,37,38,39] was evaluated using Radit analysis. Clinical effective rate of one article[25] was evaluated using rank sum test. One article[35] did not describe statistical methods used to evaluate clinical efficacy.
Evaluation of total clinical effective rate
Of the 17 articles[24,25,26,27,28,29,30,31,32,33,34,35,36,37,38,39,40], 13 articles[25,26,27,30,31,32,33,34,35,36,37,38,40] evaluated total clinical effective rate using reducing score rate of the Hamilton Depression Scale. Meta-analysis was conducted in different groups according to different courses of treatment.
Comparison of reducing score rate of the Hamilton Depression Scale at 4 weeks after treatment
Of the 17 articles[24,25,26,27,28,29,30,31,32,33,34,35,36,37,38,39,40], 8 articles[25,27,31,33,35,36,38,40] compared the reducing score rate of the Hamilton Depression Scale between filiform needle acupuncture and fluoxetine groups 4 weeks later. Heterogeneity tests were undertaken (P = 0.50). Using a fixed effect model, meta-analysis demonstrated that total effective rate was higher in the filiform needle acupuncture group than that in the fluoxetine group (RR = 1.11, 95%CI: 1.03–1.21, P = 0.01; Figure 2).
Figure 2.
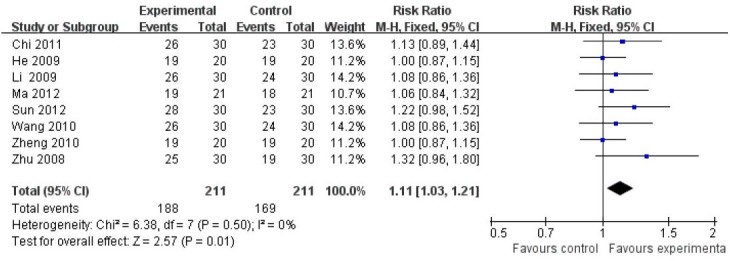
Comparison of reducing score rate of the Hamilton Depression Scale after 4-week treatment with filiform needle acupuncture and fluoxetine for poststroke depression (retative risk).
The total effective rate of filiform needle acupuncture was higher than that of fluoxetine. Reference sequence number of articles: Chi 2011[25], He 2009[40], Li 2009[33], Ma 2012[35], Sun 2012[37], Wang 2010[38], Zheng 2010[27], Zhu 2008[39]. CI: Confidence interval.
Sensitivity analysis of the above-mentioned results was conducted using risk difference (RD) as a summary statistic. As displayed in Figure 3, the clinical effects of filiform needle acupuncture were better than that of fluoxetine at 4 weeks after treatment (RD = 0.09, 95%CI: 0.02–0.16, P = 0.008). There was no essential change between the results as shown in Figures 2 and 3, indicating that the results of meta-analysis were stable. After 4 weeks of treatment, the therapeutic effects of filiform needle acupuncture against poststroke depression were better than that of fluoxetine.
Figure 3.
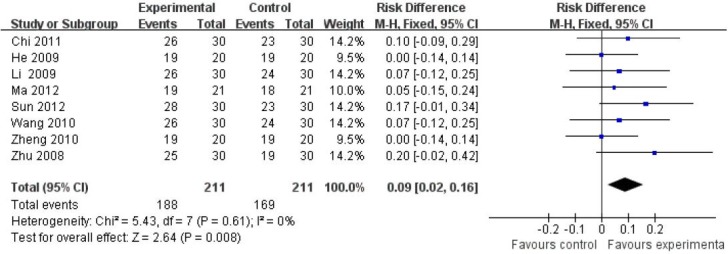
Comparison of reducing score rate of the Hamilton Depression Scale after 4-week treatment with filiform needle acupuncture and fluoxetine for poststroke depression (risk difference).
After 4 weeks of treatment, the therapeutic effects of filiform needle acupuncture against poststroke depression were better than that of fluox-etine. Reference sequence number of articles: Chi 2011[25], He 2009[40], Li 2009[33], Ma 2012[35], Sun 2012[37], Wang 2010[38], Zheng 2010[27], Zhu 2008[39]. CI: Confidence interval.
Comparison of reducing score rate of Hamilton Depression Scale at 6 weeks after treatment
Three articles[32,34,36] compared the reducing score rate of Hamilton Depression Scale at 6 weeks after treatment. Heterogeneity tests were undertaken (P = 0.19). Using a fixed effect model, meta-analysis demonstrated that the reducing score rates of the Hamilton Depression Scale were identical between filiform needle acupuncture and fluoxetine groups, showing no significant difference (RR = 1.10, 95%CI: 0.98–1.28, P = 0.24; Figure 4).
Figure 4.
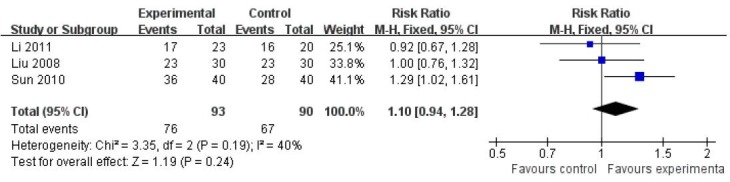
Comparison of reducing score rate of the Hamilton Depression Scale after 6-weeks treatment with filiform needle acupuncture and fluoxetine for poststroke depression (retative risk).
The reducing score rates of the Hamilton Depression Scale were identical between filiform needle acupuncture and fluoxetine groups. Reference sequence number of articles: Li 2011[32], Liu 2008[34], Sun 2010[36].
Sensitivity analysis of the above-mentioned results was conducted using RD as a summary statistic. As displayed in Figure 5, the reducing score rates of the Hamilton Depression Scale were identical between filiform needle acupuncture and fluoxetine groups at 6 weeks after treatment, showing no significant difference (RD = 0.07, 95%CI: −0.04–0.19, P = 0.22). There was no essential change between the results as shown in Figures 4 and 5, suggesting that the results of meta-analysis were stable. After 6 weeks of treatment, the therapeutic effects of filiform needle acupuncture were the same as that of fluoxetine.
Figure 5.
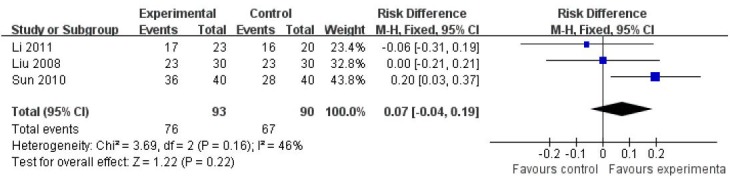
Comparison of reducing score rate of the Hamilton Depression Scale after 6-weeks treatment with filiform needle acupuncture and fluoxetine for poststroke depression (risk difference).
After 6 weeks of treatment, the therapeutic effects of filiform needle acupuncture were similar to that of fluoxetine. Reference sequence number of articles: Li 2011[32], Liu 2008[34], Sun 2010[36].
Comparison of reducing score rate of the Hamilton Depression Scale at 8 weeks after treatment
He et al.[26] and Ding et al.[30] compared the total effective rate (reducing score rate of Hamilton Depression Scale) at 8 weeks after filiform needle acupuncture. He et al.[26] found that total effective rates were respectively 92.38% and 72.80% in the filiform needle acupuncture and fluoxetine groups. The therapeutic effects were significantly better in the filiform needle acupuncture group compared with the fluoxetine group (χ2 = 9.763; P < 0.05). Ding et al.[30] confirmed that no significant difference in total effective rate was detected between the filiform needle acupuncture group (86.67%) and fluoxetine group (83.33%; P > 0.05).
Evaluation of Hamilton Depression Scale results
A total of 16 high-quality articles[24,25,26,27,29,30,31,32,33,34,35,36,37,38,39,40] compared the results of Hamilton Depression Scale. Patients were grouped according to the Hamilton Depression Scale with 17 items and the Hamilton Depression Scale with 24 items as well as different courses of treatment, and their Hamilton Depression Scale scores were analyzed.
Comparison of Hamilton Depression Scale (17 items) scores at 2 weeks after treatment
Five articles[29,32,33,34,39] evaluated the Hamilton Depression Scale (17 items) scores at 2 weeks after treatment. The control group in Liu's study[34] used amitriptyline. After combining studies, heterogeneity was significant. Thus, Liu's study was deleted during meta-analysis. Results demonstrated that therapeutic effects were better in the filiform needle acupuncture group compared with the fluoxetine group (MD = −2.34, 95%CI: −3.46 to −1.22, P < 0.001; Figure 6).
Figure 6.
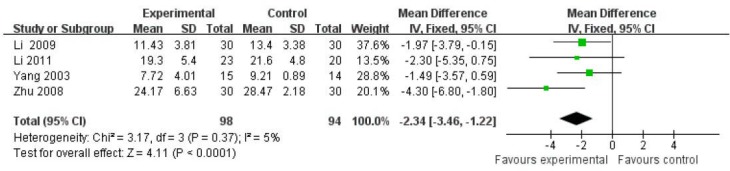
Comparison of the Hamilton Depression Scale (17 items) between filiform needle acupuncture and fluoxetine groups at 2 weeks after treatment (fixed effect model).
The Hamilton Depression Scale score was better in the filiform needle acupuncture group compared with the fluoxetine group. Reference sequence number of articles: Li 2009[33], Li 2011[32], Yang 2003[29], Zhu 2008[39].
Sensitivity analysis of the above-mentioned results was conducted using a random effect model. As displayed in Figure 7, the Hamilton Depression Scale scores were significantly lower in the filiform needle acupuncture group than those in the fluoxetine group (MD = −2.35, 95%CI: −3.51 to −1.20, P < 0.001). There was no essential change between the results shown in Figures 6 and 7, suggesting that effects on decreasing Hamilton Depression Scale (17 items) scores were better in the filiform needle acupuncture group than in the fluoxetine group at 2 weeks after treatment.
Figure 7.
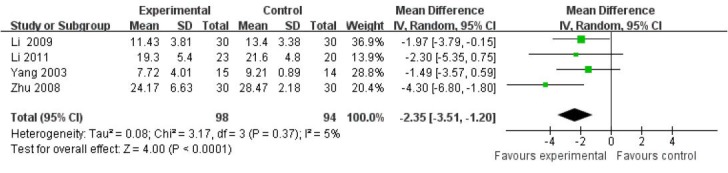
Comparison of the Hamilton Depression Scale (17 items) between filiform needle acupuncture and fluoxetine groups at 2 weeks after treatment (random effect model).
The Hamilton Depression Scale scores were significantly lower in the filiform needle acupuncture group than that in the fluoxetine group. Refer-ence sequence number of articles: Li 2009[33], Li 2011[32], Yang 2003[29], Zhu 2008[39].
Comparison of Hamilton Depression Scale (17 items) scores at 4 weeks after treatment
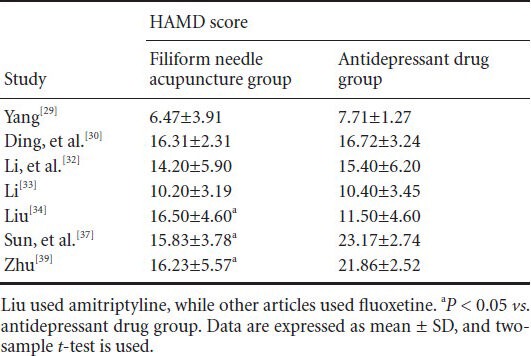
Seven articles[29,30,32,33,34,37,39] evaluated the Hamilton Depression Scale (17 items) scores at 4 weeks after treatment. Heterogeneity among trials was great, and meta-analysis and sensitivity analysis verified that results were not stable. Thus, only descriptive analysis is listed in Table 3.
Table 3.
Comparison of the Hamilton Depression Scale (HAMD; 17 items) scores between filiform needle acupuncture and fluoxetine groups at 4 weeks after treatment
Comparison of Hamilton Depression Scale (17 items) scores at 6 weeks after treatment
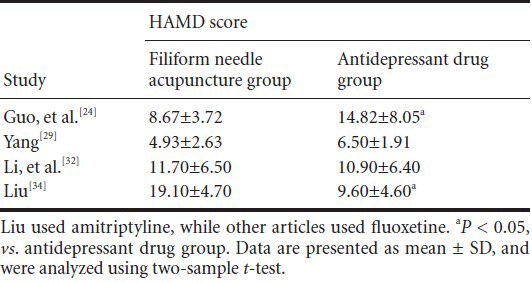
Four articles[24,29,32,34] evaluated the Hamilton Depression Scale (17 items) scores at 6 weeks after treatment. Heterogeneity was great among different articles. No meta-analysis was performed (Table 4).
Table 4.
Comparison of Hamilton Depression Scale (HAMD; 17 items) scores between filiform needle acupuncture and fluoxetine groups at 6 weeks after treatment
Comparison of Hamilton Depression Scale (24 items) scores at 2 weeks after treatment
Three articles[35,36,38] evaluated the Hamilton Depression Scale (24 items) scores at 2 weeks after treatment. Heterogeneity was great among different articles, so meta-analysis was not performed. No significant difference in Hamilton Depression Scale scores was detectable between the filiform needle acupuncture and fluoxetine groups (P > 0.05).
Comparison of Hamilton Depression Scale (24 items) scores at 4 weeks after treatment
Seven articles[25,27,31,35,36,38,40] evaluated Hamilton Depression Scale (24 items) scores at 4 weeks after treatment. After combining all trials, heterogeneity tests were undertaken (P = 0.05). No significant difference in therapeutic methods was observed in different articles. A random effect model of meta-analysis was used. Results displayed that therapeutic effects of filiform needle acupuncture and fluoxetine were identical, showing no significant difference (MD = −0.49, 95%CI: −1.72 to 0.74, P = 0.43; Figure 8).
Figure 8.
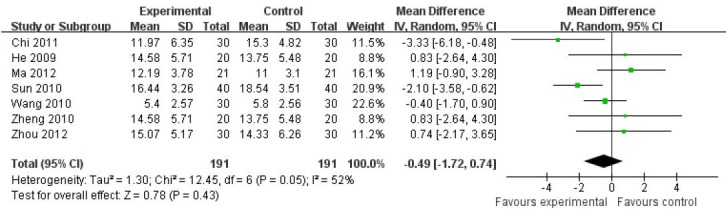
Comparison of the Hamilton Depression Scale (24 items) between filiform needle acupuncture and fluoxetine groups at 4 weeks after treatment (random effect model).
The therapeutic effects of filiform needle acupuncture and fluoxetine were identical. Reference sequence number of articles: Chi 2011[25], He 2009[40], Ma 2012[35], Sun 2010[36], Wang 2010[38], Zheng 2010[27], Zhou 2012[31].
Sensitivity analysis of the above-mentioned results was conducted using a fixed effect model. As displayed in Figure 9, no significant difference in Hamilton Depression Scale score was detectable between the filiform needle acupuncture group and fluoxetine group at 4 weeks after treatment (MD = −0.65, 95%CI: −1.43 to 0.12, P = 0.10), which showed a consistency with meta-analysis results. These findings indicated that filiform needle acupuncture had a similar effect on Hamilton Depression Scale score to fluoxetine at 4 weeks.
Figure 9.
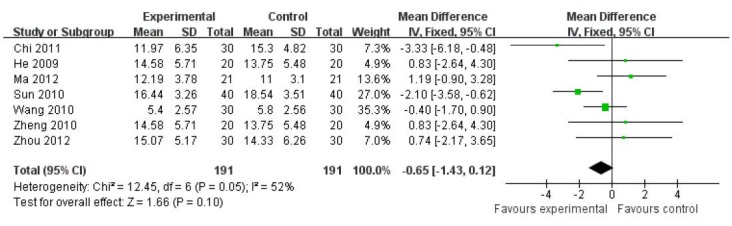
Comparison of the Hamilton Depression Scale (24 items) between filiform needle acupuncture and fluoxetine groups at 4 weeks after treatment (fixed effect model).
The therapeutic effects of filiform needle acupuncture and fluoxetine were identical. Reference sequence number of articles: Chi 2011[25], He 2009[40], Ma 2012[35], Sun 2010[37], Wang 2010[38], Zheng 2010[27], Zhou 2012[31].
Comparison of Hamilton Depression Scale (24 items) scores at 6 or 8 weeks after treatment
Sun et al.[36] found that the decreased degree of Hamilton Depression Scale (24 items) score was higher in the filiform needle acupuncture group than that in the fluoxetine group at 6 weeks (P < 0.05). He et al.[26] verified that improvement in Hamilton Depression Scale (24 items) score was better in the filiform needle acupuncture group than in the fluoxetine group at 8 weeks (P < 0.01). Ding et al.[30] confirmed that the decreased degree of Hamilton Depression Scale (17 items) score was identical between filiform needle acupuncture and fluoxetine groups at 8 weeks (P > 0.05).
Evaluation of Self-Rating Depression Scale
Two high-quality articles[28,34] used the Self-Rating Depression Scale. The number of high-quality articles was less than 3, so meta-analysis was not performed. Liu[34] found that improved effects of amitriptyline on Self-Rating Depression Scale score were smaller than that of filiform needle acupuncture at 6 weeks after treatment (P = 0.000). Yuan et al.[28] demonstrated that Self-Rating Depression Scale score was significantly lower in the filiform needle acupuncture group than in the fluoxetine group at 4 and 8 weeks (P < 0.05).
Safety evaluation
Nine high-quality articles[25,28,30,32,34,35,36,37,38] observed adverse reactions. Li et al.[32] and Wang et al.[38] assessed adverse reactions using a Side Effect Rating Scale, and confirmed that Side Effect Rating Scale score was lower in the filiform needle acupuncture group than that in the fluoxetine group. Chi[25] found that the incidence of adverse reactions was significantly lower in the filiform needle acupuncture group than in the fluoxetine group (P < 0.05). Yuan et al.[28] observed the adverse reactions of fluoxetine in a few patients, including nausea, dry mouth and insomnia, but these symptoms gradually disappeared. Ding et al.[30] reported that one patient withdrew from the trial because of intolerance to acupuncture-induced pain in the filiform needle acupuncture group. Simultaneously, in the fluoxetine group, one patient withdrew because of rash, three patients suffered from abdominal pain within 1 week of commencing medication, and two patients experienced mild nausea and vomiting. Sun et al.[38] demonstrated that the patients undergoing filiform needle acupuncture did not experience adverse reactions, but three patients taking fluoxetine had a gastrointestinal reaction within 1 week of commencing the medication; one patient suffered from anxiety, weakness and spontaneous perspiration at 4 days after treatment, and one patient experienced insomnia at 2 weeks. Liu[34] reported that the incidence of adverse reactions was lower in the filiform needle acupuncture group than that in the amitriptyline group. Sun et al.[37] showed that adverse reactions did not appear in the acupuncture group, but appeared in the control group after taking fluoxetine, with the presence of dry mouth and palpitation in four cases, nausea and anorexia in two cases, dizziness and headache in one case, and abdominal pain and diarrhea in two cases. Ma et al.[35] did not show obvious adverse reactions in the filiform needle acupuncture group. By contrast, in the fluoxetine group, three patients experienced a gastrointestinal reaction and one patient suffered from lethargy within 1 week of the medication, one patient experienced dizziness and headache within 2 weeks after medication.
Evaluation of publication bias
Funnel plots were created taking standard error as the Y axis and MD as the X axis[24,25,26,27,28,29,30,31,32,33,34,35,36,37,38,39,40] (Figure 10).
Figure 10.
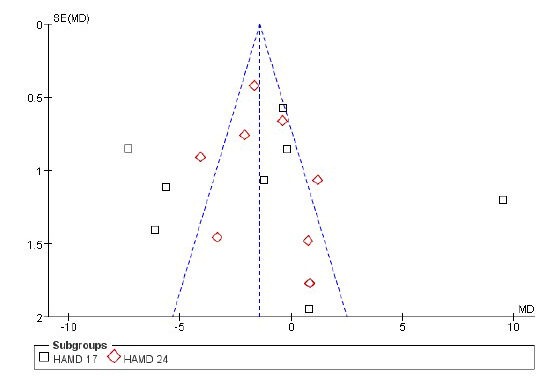
Funnel plot of meta-analysis of filiform needle acupuncture and antidepressant drugs for poststroke depression.
Partial graph was not symmetrical, indicating that the included articles showed publication bias.
Results of the funnel plots illustrated that the 17 articles[24,25,26,27,28,29,30,31,32,33,34,35,36,37,38,39,40] had publication bias. Possible reasons include: (1) large studies with positive results are easily published, but those with negative results are difficult to publish. Some master's or doctorial theses dissertations were not published because the contents were confidential. (2) Some study results did not obey the benefits of sponsors, so the study was stopped. (3) Methodological quality had some shortcomings, such as small size, incomplete randomization, deficiency in blind methodology, and neglect of self-evaluation of poststroke depression patients. Moreover, some trials did not record adverse reactions, follow-up, withdrawal and termination. The above-described problems can increase the occurrence of bias and finally affect the accuracy of study results.
Discussion
Meta-analysis results demonstrated that clinical effective rate was remarkably higher in the filiform needle acupuncture group than that in the antidepressant drug group at 4 weeks after treatment. The clinical effective rate was identical between the filiform needle acupuncture and antidepressant drug groups at 6 weeks. Filiform needle acupuncture could rapidly increase endopioid peptide release in the body. The endopioid peptide could relieve anxiety and gastrointestinal discomfort[41]. Thus, acupuncture would have therapeutic effects on depression within one week. Fluoxetine used in the control group is a selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor, and can suppress serotonin reuptake, thus increasing serotonin concentration in the synaptic cleft. Serotonin receptor in postsynaptic membrane is supersensitive and nerve impulses from serotonergic neurons decrease following this increased presence in the synapse. Two to four weeks later, serotonin receptor expression is appropriate for serotonin concentration, and nerve impulses increase again[41]. Therefore, clinical effects were better in the filiform needle acupuncture group than that in the antidepressant drug group at 4 weeks. Clinical effective rates were similar between the two groups at 6 weeks.
Experimental results demonstrated that the Hamilton Depression Scale (17 items) score was significantly lower in the filiform needle acupuncture group than that in the fluoxetine group at 2 weeks, but the Hamilton Depression Scale (24 items) score was identical between the two groups at 4 weeks. This is probably the result of: (1) acupuncture lessened depression by increasing endopioid peptide content in a short time, but fluoxetine had slow inhibitory effects against serotonin reuptake. Thus, the results were different between 2 and 4 weeks. (2) The Hamilton Depression Scales (17 items and 24 items) are different in involved areas and total score. Hamilton Depression Scale (24 items) also includes circadian variations, depersonalization, paranoid symptoms, obsessive-compulsive behavior, feeling of decreased ability, feeling of despair and feelings of inferiority. The different total scores of the two scales also cause different score results.
The total effective rate of filiform needle acupuncture for 4 weeks against poststroke depression is higher than that of antidepressant drugs. However, no significant difference in Hamilton Depression Scale score was detectable 4 weeks later. Total effective rate is based on the reducing score rate of the Hamilton Depression Scale, and is a manifestation of grading Hamilton Depression Scale score. Hamilton Depression Scale score is a precise numerical value. Their effect sizes are different, so the results are not consistent.
The number of articles (total effective rate of 8-week acupuncture, Hamilton Depression Scale score, and Self-Rating Depression Scale score at each time point) was less than three, so meta-analysis was not performed. Only descriptive analysis was conducted. Results of each study are varied, so the differences in Hamilton Depression Scale score and Self-Rating Depression Scale score at 8 weeks were not clear between filiform needle acupuncture and antidepressant drugs. Only two studies used Side Effect Rating Scale to describe adverse reactions, so meta-analysis was not performed. Results demonstrated that adverse reactions of antidepressant drugs such as nausea, vomiting and abdominal pain were more compared with the filiform needle acupuncture group. The subjects in the filiform needle acupuncture group only affected pain. Thus, it is concluded that filiform needle acupuncture had better safety compared with antidepressant drugs. Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors act on serotonin receptors, which have various subtypes. Activated serotonin-1 receptor resisted depression[40]. Activated serotonin-2 receptor induced anxiety, insomnia and hyposexuality[42]. Activated serotonin-3 receptor caused nausea, vomiting and anorexia[42]. Thus, we presumed that filiform needle acupuncture could better control depressive state in early clinical treatment of poststroke depression.
The present study has some limitations. Our included articles mainly used fluoxetine, but citalopram is the latest selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor, and has few adverse reactions. The basic treatment of stroke in the included articles is many, and rehabilitation efficacy of stroke directly affects patients’ depression. Publication bias in the articles affects the validity of meta-analysis results. Taken together, leading high-quality randomized trials with large size and multiple centers are needed to confirm the validity of filiform needle acupuncture.
Acknowledgments:
We are very grateful to teachers from the Department of Statistics of Southern Medical University in China for providing technical support in meta analysis.
Footnotes
Funding: This study was supported by the Guangdong Provincial “211 Engineering” Stage-III Key Disciplines Construction Project in China, No. Yue 2009431.
Conflicts of interest: None declared.
Copyedited by Aprico K, Stow A, Xu SF, Wang XM, Wang J, Qiu Y, Li CH, Song LP, Zhao M
References
- [1].Han Y, Min F, Liu XY. Role of microRNA in stroke and stroke drepession. ScientificWorldJournal. 2013;12(2):1–6. [Google Scholar]
- [2].Pohjasvaara T, Vataja R, Leppavuori A, et al. Depression is an independent predictor of poor long-term functional outcome post-stroke. Eur J Neurol. 2001;8(4):315–319. doi: 10.1046/j.1468-1331.2001.00182.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [3].Nie RZ, Fu WB. Acupuncture versus western medicine for post stroke depression: a systematic review. Shijie Zhongyiyao. 2012;7(2):147–151. [Google Scholar]
- [4].Chen FZ, Yan Q, Zhao YZ, et al. Integrative medicine research progress in the treatment of post-stroke depression. Zhongguo Laonianxue Zazhi. 2011;11(31):2145–2147. [Google Scholar]
- [5].Zhang ZJ, Chen HY, Yip KC, et al. The effectiveness and safety of acupuncture therapy in depressive disorders: systematic review and meta-analysis. J Affect Disord. 2010;124(1-2):9–21. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2009.07.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [6].Yang JW, Li QQ, Li F. The holistic effects of acupuncture treatment. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2014;2014:1–10. doi: 10.1155/2014/739708. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [7].Tian XW, Zhang QM. Assessment of the clinical efficacy of acupuncture with intelligent three needles as main treatment for post-stroke depression. Shanghai Zhenjiu Zazhi. 2011;10(10):663–665. [Google Scholar]
- [8].Wu JP. Clinical observation on acupuncture treatment of 150 cases of post-stroke depression according to syndrom differentiation. Zhen Ci Yan Jiu. 2010;35(4):303–306. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [9].Chu YJ, Wang CY, Zhang H. 72 Cases of clinical observation of acupuncture treatment for post-stroke depression. Zhongguo Laonianxue Zazhi. 2007;17(27):1720–1721. [Google Scholar]
- [10].Pronovost PJ, Berenholtz SM, Dorman T, et al. Evidence-based medicine in anesthesiology. Anesth Analg. 2001;92(3):787–794. doi: 10.1097/00000539-200103000-00045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [11].Shi XQ. Wuhan: Huazhong University of Science and Technology, China; 2009. Application of Meta-analysis and biostatistical models for the risk assessment of population health hazard exposed to PAHs . [Google Scholar]
- [12].Li XH, Chen JQ, Wang HT, et al. Comparison between effects of electroacupuncture and antidepressants for post stroke depression: a systematic review. Zhongguo Quanke Yixue. 2012;15(3A):802–806. [Google Scholar]
- [13].Xiong J, Du YH, Liu JL, et al. Acupuncture versus western medicine for depression neurosis: a systematic review. Xunzheng Yixue. 2010;10(3):179–185. 190. [Google Scholar]
- [14].Journal of neuroscience, China association of neurological surgeons. Diagnostic main points in all kinds of cerebrovascular diseases. Zhong Hua Shen Jing Ke Za Zhi. 1996;29(6):379–380. [Google Scholar]
- [15].Nanjing: Nanjing University Press, China; 1994. State Administration of Traditional. Chinese Disease Diagnosis and Efficacy Standards. [Google Scholar]
- [16].4th ed. Washington DC: American Psychiatric Association, USA; 1994. American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-IV) [Google Scholar]
- [17].3rd ed. Jinan: Shandong Science and Technology Press, China; 2001. Psychiatry Branch of the Chinese Medical Association. Chinese Classification of Mental Disorders and Diagnostic Criteria. [Google Scholar]
- [18].Shen YC. 5th ed. Beijing: People's Medicine Publishing House; 2009. Psychiatry. [Google Scholar]
- [19].Lu SK. 2nd ed. Beijing: Chinese Medicine Press, China; 2007. Techniques of Acupuncture and Moxibustion. [Google Scholar]
- [20].Moher D, Pham B, Jones A, et al. Does quality of reports of randomised trials affect estimates of intervention efficacy reported in meta-analyses? Lancet. 1998;352(9128):609–613. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(98)01085-X. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [21].Hamilton M. A rating scale for depression. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1960;23:56–62. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.23.1.56. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [22].Zung WWK. Zung Self-Rating Depression Scale and Depression Status Inventory. Assessment of Depression. 1986 [Google Scholar]
- [23].Svanborg P, Asberg M. A comparison between the Beck Depression Inventory (BDI) and the self-rating version of the Montgomery Asberg Depression Rating Scale (MADRS) J Affect Disord. 2001;64(2-3):203–216. doi: 10.1016/s0165-0327(00)00242-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [24].Guo RY, Su L, Liu LA, et al. Effects of Linggui Bafa on the therapeutic effect and quality of life in patients of post-stroke depression. Zhongguo Zhen Jiu. 2009;29(10):785–790. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [25].Chi H. Haerbin: Helongjiang University of Chinese Medicine, China; 2011. Clinical observation on post-stroke depression treated by “Tiao Qi Tong Du” acupuncture therapy. [Google Scholar]
- [26].He XJ, Lai XS, Tan JL, et al. Clinical study on acupuncture in the treatment of post-stroke depression on with the method of activating the Du meridian and clearing the mind. Shijie Zhenjiu Zazhi. 2006;16(3):8–12. 27. [Google Scholar]
- [27].Zheng MF, Zhang YS, Yuan CL, et al. Effect of “regulating Du channel and Ren channel” acupuncture method on initial post-stroke depression. Fu Jian Zhong Yi Xue Yuan Xue Bao. 2010;1(1):16–18. [Google Scholar]
- [28].Yuan P, Zhang YJ, Dong GR. The clinical study for the treatment of post-stroke depression with scalp penetration acupuncture. Zhen Jiu Lin Chuang Za Zhi. 2006;22(11):3–4. [Google Scholar]
- [29].Yang M. Chengdu: Chengdu University of Chinese Medicine, China; 2003. Chendu: The clinical study of acupoint application on the treatment of post-stroke depression. [Google Scholar]
- [30].Ding Z, Yu XG. Clinical study on treatment of post-stroke depression with acupuncture of du meridian as main therapy. Bei Jing Zhong Yi Yao Da Xue Xue Bao. 2003;10(3):31–32. [Google Scholar]
- [31].Zhou CX, Cui X, Hu YS, et al. Effect of combined use of acupuncture and medicine on the activities of daily living in the treatment of post-stroke depression. Shanghai Zhenjiu Zazhi. 2012;31(4):228–230. [Google Scholar]
- [32].Li HJ, Zhong BL, Fan YP, et al. Acupuncture for post-stroke depression: a randomized controlled trial. Zhongguo Zhen Jiu. 2011;31(1):3–6. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [33].Li CP. Haerbin: Heilongjiang University of Chinese Medicine, China; 2009. The clinical study on acupuncture of “Shu Gan Li Qi” in treatment of the post-stroke depression. [Google Scholar]
- [34].Liu YR. Guangzhou: Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, China; 2008. Qantizational observation on acupuncture and point-injection treatment of baihui acupoint for post cerebral infarction depression. [Google Scholar]
- [35].Ma LY, Gong SF, Huo J. Clinical observation of Yu's scalp acupuncture on poststroke depression. Zhen Jiu Lin Chuang Za Zhi. 2012;28(5):66–68. [Google Scholar]
- [36].Sun XW, Zou W, Li HT, et al. The Clinical study of ‘Tiao Shen Jie Yu’ acupuncture treatment on post-stroke depression. The elderly medical academic conference in conjunction with the world in the third session of Chinese medicine, traditional Chinese and Western Medicine. 2010 [Google Scholar]
- [37].Sun YZ, Jia SY. Clinical study on Yu's cluster needling at scalp acupoints for post-stroke depression. Shang Hai Zhen Jiu Za Zhi. 2012;31(8):564–556. [Google Scholar]
- [38].Wang LJ. Shenyang: Liaoning Zhongyiyao Daxue; 2010. Clinical research of treatment of the “Gan Qi Yu Jie” post-stroke depression by acupuncture. [Google Scholar]
- [39].Zhu SS. Nanjing: Nanjing University of Chinese Medicine, China; 2008. The impact of brain-reinforcing and mind-regulating acupuncture on the life of post-stroke depression patient. [Google Scholar]
- [40].He FR. Xiamen: Fujian University of Traditional Chinese Medicine; 2009. Effect on acupuncture therapy of “Tong Tiao Du Ren” in initial post-stroke depression. [Google Scholar]
- [41].Wang XJ, Wang LL. A mechanism of endogenous opioid peptides for rapid onset of acupuncture effect in treatment of depression. Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Xue Bao. 2010;8(11):1014–1017. doi: 10.3736/jcim20101102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [42].Zhang Y, Cui XL, Yang P, et al. Adverse drug reaction induced by antidepressants of SSRI and SNRI. Zhongguo Yaowu Jingjie. 2010;7(9):554–556. [Google Scholar]


