Abstract
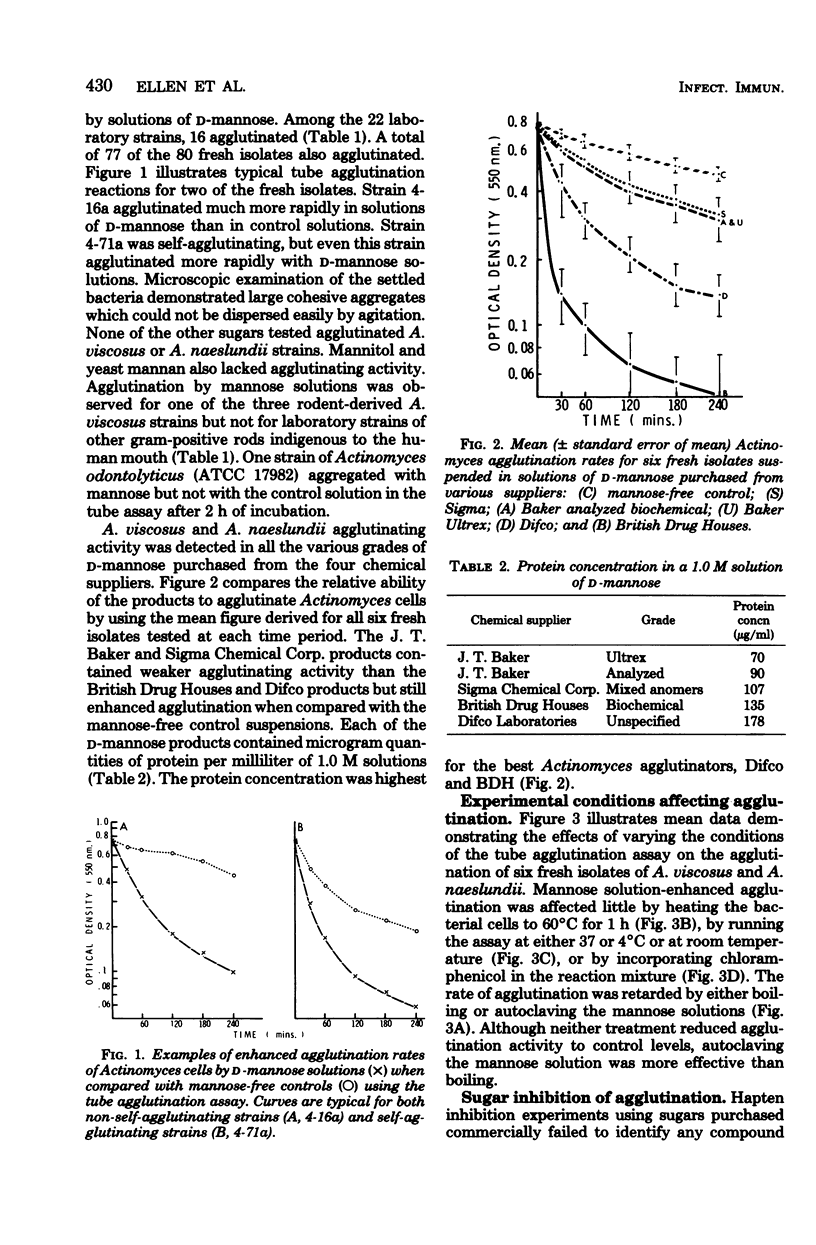
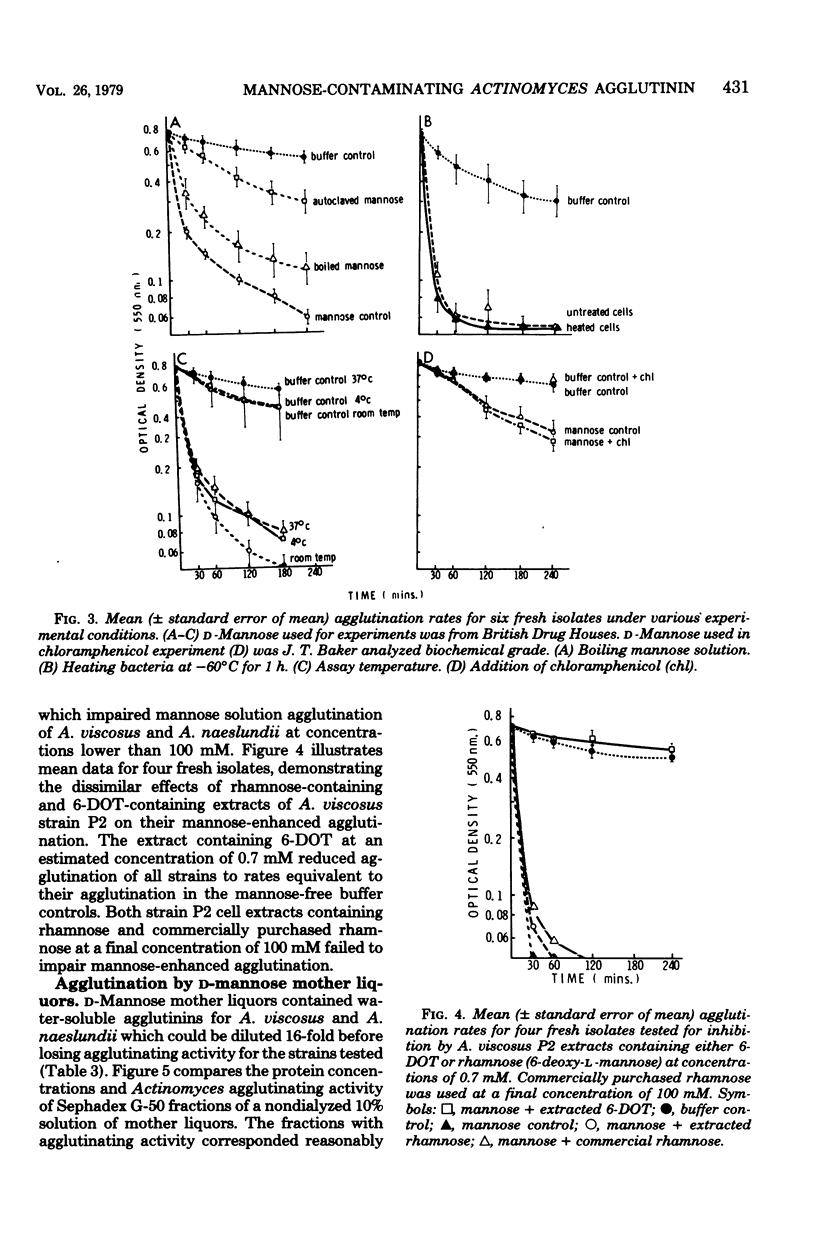
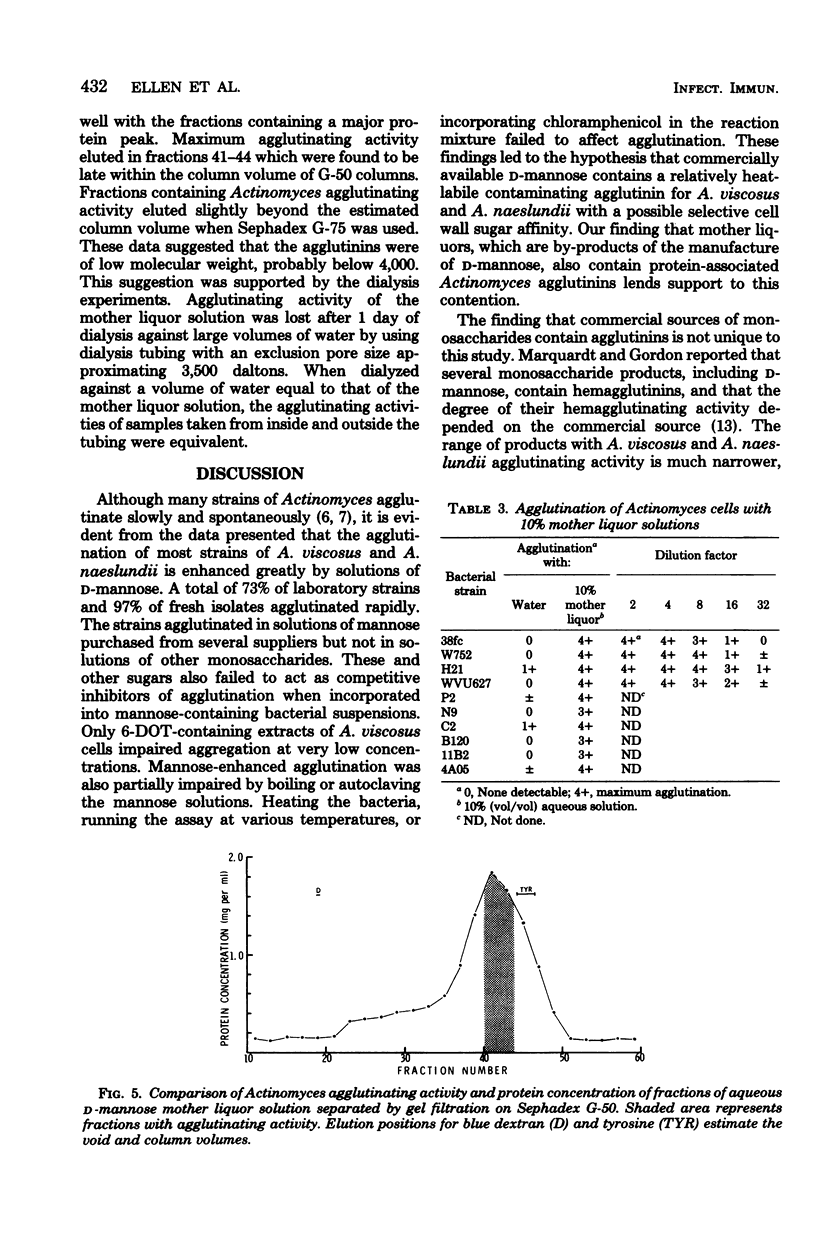
Rapid agglutination of Actinomyces viscosus and Actinomyces naeslundii cells by D-mannose solutions was observed during studies of their attachment to mammalian cells in vitro. The specificity of the agglutination reaction was studied by slide agglutination tests and by measuring the rate of decrease in optical density of bacterial phosphate buffer suspensions caused by the setting of bacterial aggregates. Actinomyces cells were agglutinated by protein-containing mannose solutions of several chemical suppliers. Solutions of sugars other than D-mannose and solutions of mannitol and mannan all failed to agglutinate A. viscsus and A. naeslundii. "Mannose-enhanced" agglutination was impaired by boiling or autoclaving the mannose but was not affected by heating the bacteria, the presence of chloramphenicol, running the assay in the cold, or incorporating any of several commercially purchased sugars in the reaction mixture. During these hapten inhibition experiments, only 6-deoxy-L-talcose-containing extracts of an A. viscosus strain retarded the rate of mannose-enhanced agglutination. Protein-containing fractions of D-mannose mother liquors also agglutinated cells of A. viscosus and A. naeslundii. Other species of oral gram-positive rods were not agglutinated by mannose solutions. Together the data indicate that plant seed-derived D-mannose contains a protein-associated agglutinin for A. viscosus and A. naeslundii which may function via a "lectin-like" selective affinity for the unique cell wall sugar 6-deoxy-L-talose.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brecher S. M., van Houte J., Hammond B. F. Role of colonization in the virulence of Actinomyces viscosus strains T14-Vi and T14-Av. Infect Immun. 1978 Nov;22(2):603–614. doi: 10.1128/iai.22.2.603-614.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellen R. P., Balcerzak-Raczkowski I. B. Interbacterial aggregation of Actinomyces naeslundii and dental plaque streptococci. J Periodontal Res. 1977 Jan;12(1):11–20. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0765.1977.tb00104.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellen R. P. Establishment and distribution of Actinomyces viscosus and Actinomyces naeslundii in the human oral cavity. Infect Immun. 1976 Nov;14(5):1119–1124. doi: 10.1128/iai.14.5.1119-1124.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellen R. P., Walker D. L., Chan K. H. Association of long surface appendages with adherence-related functions of the gram-positive species Actinomyces naeslundii. J Bacteriol. 1978 Jun;134(3):1171–1175. doi: 10.1128/jb.134.3.1171-1175.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fillery E. D., Bowden G. H., Hardie J. M. A comparison of strains of bacteria designated Actinomyces viscosus and Actinomyces naeslundii. Caries Res. 1978;12(6):299–312. doi: 10.1159/000260349. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammond B. F., Steel C. F., Peindl K. S. Antigens and surface components associated with virulence of Actinomyces viscosus. J Dent Res. 1976 Jan;55:A19–A25. doi: 10.1177/002203457605500111011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jordan H. V., Sumney D. L. Root surface caries: review of the literature and significance of the problem. J Periodontol. 1973 Mar;44(3):158–163. doi: 10.1902/jop.1973.44.3.158. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loesche W. J., Syed S. A. Bacteriology of human experimental gingivitis: effect of plaque and gingivitis score. Infect Immun. 1978 Sep;21(3):830–839. doi: 10.1128/iai.21.3.830-839.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marquardt M. D., Gordon J. A. Haemagglutinins in commercial preparations of monosaccharides. Nature. 1974 Nov 8;252(5479):175–176. doi: 10.1038/252175a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McIntire F. C., Vatter A. E., Baros J., Arnold J. Mechanism of coaggregation between Actinomyces viscosus T14V and Streptococcus sanguis 34. Infect Immun. 1978 Sep;21(3):978–988. doi: 10.1128/iai.21.3.978-988.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ofek I., Beachey E. H. Mannose binding and epithelial cell adherence of Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1978 Oct;22(1):247–254. doi: 10.1128/iai.22.1.247-254.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ofek I., Mirelman D., Sharon N. Adherence of Escherichia coli to human mucosal cells mediated by mannose receptors. Nature. 1977 Feb 17;265(5595):623–625. doi: 10.1038/265623a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Old D. C. Inhibition of the interaction between fimbrial haemagglutinins and erythrocytes by D-mannose and other carbohydrates. J Gen Microbiol. 1972 Jun;71(1):149–157. doi: 10.1099/00221287-71-1-149. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salit I. E., Gotschlich E. C. Type I Escherichia coli pili: characterization of binding to monkey kidney cells. J Exp Med. 1977 Nov 1;146(5):1182–1194. doi: 10.1084/jem.146.5.1182. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharon N., Lis H. Lectins: cell-agglutinating and sugar-specific proteins. Science. 1972 Sep 15;177(4053):949–959. doi: 10.1126/science.177.4053.949. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Socransky S. S. Microbiology of periodontal disease -- present status and future considerations. J Periodontol. 1977 Sep;48(9):497–504. doi: 10.1902/jop.1977.48.9.497. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tylenda C. A., Charon D., Lombardi F. P., Jr, Gabriel O. Model studies on dental plaque formation: deoxyhexoses in Actinomyces viscosus. Infect Immun. 1979 Feb;23(2):312–319. doi: 10.1128/iai.23.2.312-319.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


