Abstract
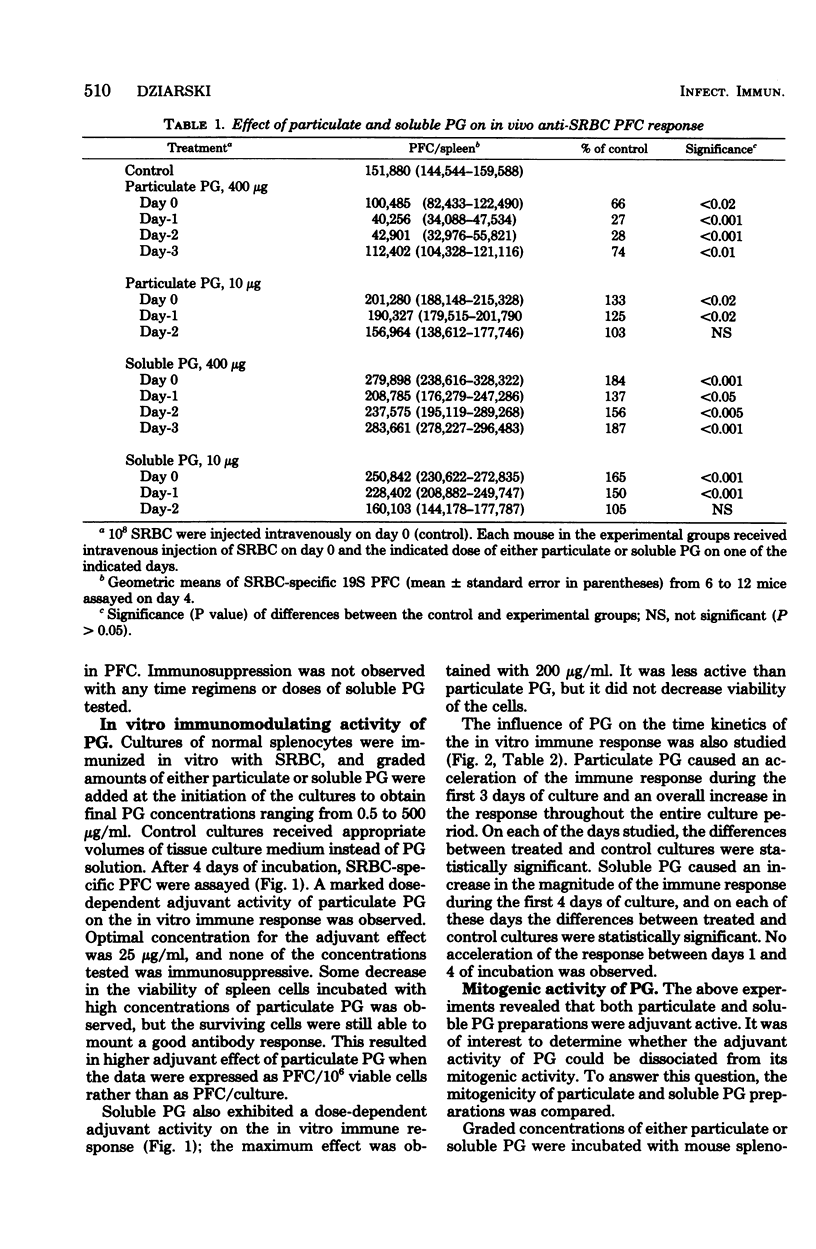
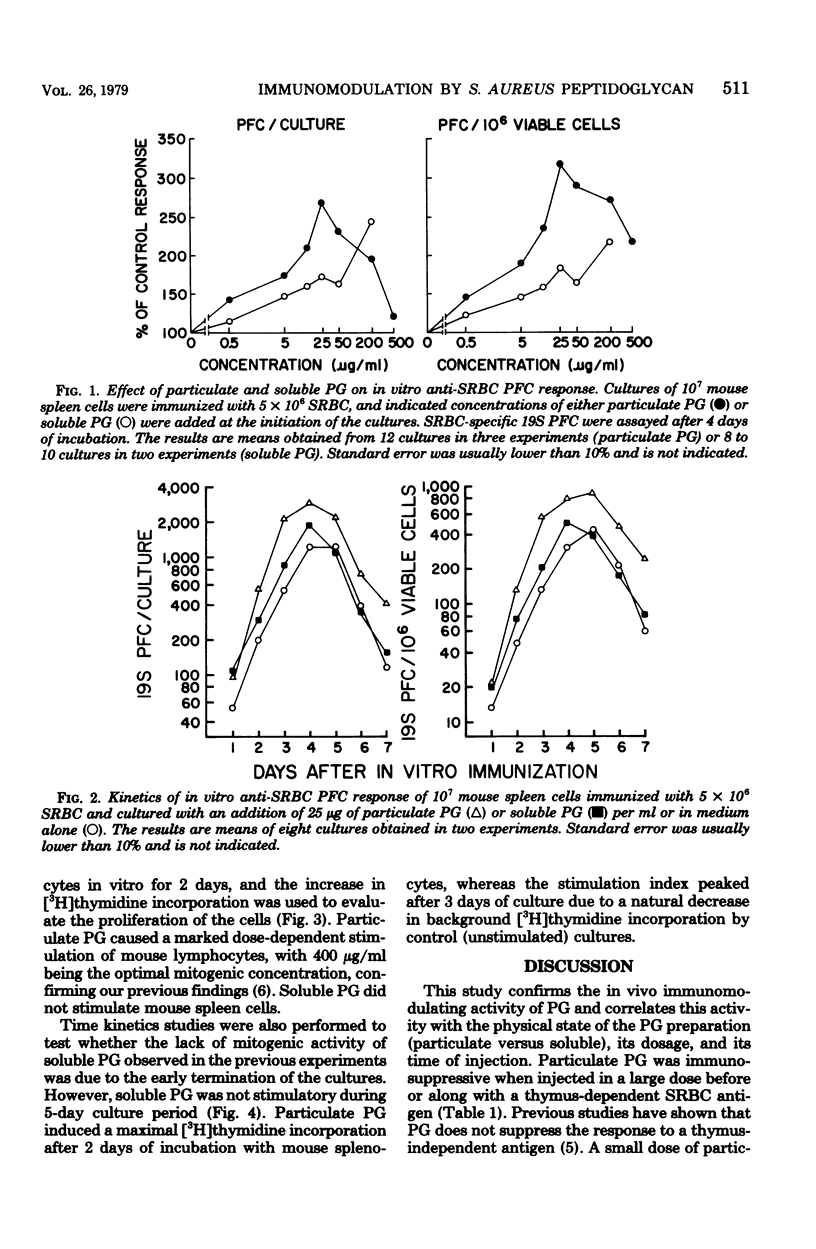
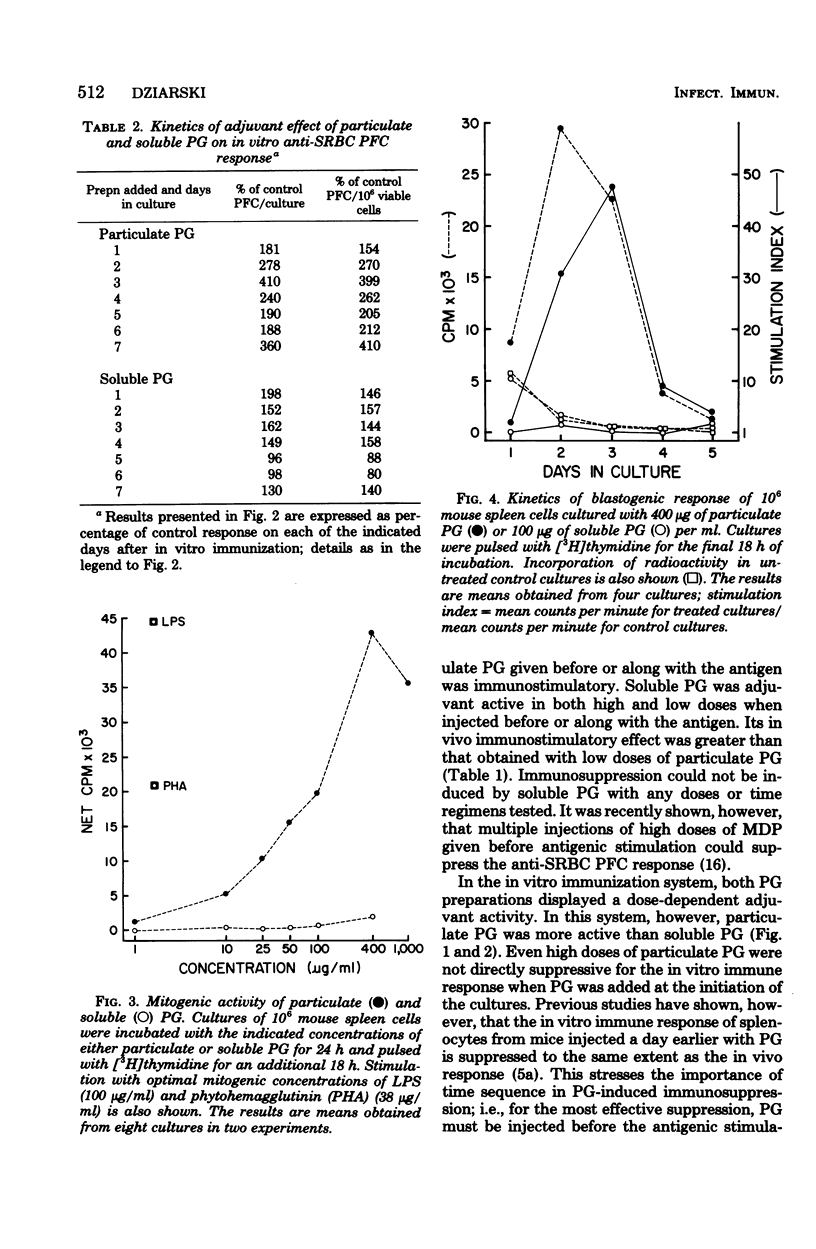
Staphylococcal peptidoglycan (PG) possesses in vivo immunodulating activity and is a B-cell mitogen in mice. The effect of PG on in vitro immune response of mouse splenocytes to sheep erythrocytes (SRBC) was studied, as well as the relationships between in vivo and in vitro adjuvant, immunosuppressive, and mitogenic activities of PG in terms of dose response, time kinetics, and physical state. Particulate PG suppressed in vivo anti-SRBC response when injected in a large dose before or simultaneously with SRBC. A small dose of particulate PG given before or along with the antigen was immunostimulatory. Soluble PG was adjuvant active in both high and low doses when injected before or along with the antigen. Both PG preparations were adjuvant active for mouse splenocytes in vitro immunized with SRBC, but particulate PG was more active. Even high doses of particulate PG were not directly suppressive for the in vitro immune response. Particulate PG was also mitogenic for mouse splenocytes, and the maximum increase in [3H]thymidine incorporation was observed after 2 days of culture. Soluble PG was not mitogenic during the 5-day incubation period. These results indicate that the physical state of PG, its dose, and its time of application are important factors determining its immunomodulating and mitogenic activities, and that by changing them it is possible to dissociate the adjuvant, immunosuppressive, and mitogenic properties of PG.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adam A., Ciorbaru R., Ellouz F., Petit J. F., Lederer E. Adjuvant activity of monomeric bacterial cell wall peptidoglycans. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1974 Feb 4;56(3):561–567. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(74)90640-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adam A., Ellouz F., Ciorbaru R., Petit J. F., Lederer E. Peptidoglycan adjuvants: minimal structure required for activity. Z Immunitatsforsch Exp Klin Immunol. 1975 Jul;149(2-4):341–348. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cunningham A. J., Szenberg A. Further improvements in the plaque technique for detecting single antibody-forming cells. Immunology. 1968 Apr;14(4):599–600. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Damais C., Bona C., Chedid L., Fleck J., Nauciel C., Martin J. P. Mitogenic effect of bacterial peptidoglycans possessing adjuvant activity. J Immunol. 1975 Jul;115(1):268–271. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dziarski R., Dziarski A. Mitogenic activity of staphylococcal peptidoglycan. Infect Immun. 1979 Mar;23(3):706–710. doi: 10.1128/iai.23.3.706-710.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dziarski R. Immunosuppressive effect of Staphylococcus aureus peptidoglycan on antibody response in mice. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1978;57(4):304–311. doi: 10.1159/000232119. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dziarski R. Splenic macrophages: mediators of immunosuppressive activity of staphylococcal peptidoglycan. J Reticuloendothel Soc. 1979 Sep;26(3):239–247. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fevrier M., Birrien J. L., Leclerc C., Chedid L., Liacopoulos P. The macrophage, target cell of the synthetic adjuvant muramyl dipeptide. Eur J Immunol. 1978 Aug;8(8):558–562. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830080804. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frank S., Specter S., Nowotny A., Friedman H. Immunocycte stimulation in vitro by nontoxic bacterial lipopolysaccharide derivatives. J Immunol. 1977 Sep;119(3):855–860. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffmann M. K., Galanos C., Koenig S., Oettgen H. F. B-cell activation by lipopolysaccharide. Distinct pathways for induction of mitosis and antibody production. J Exp Med. 1977 Dec 1;146(6):1640–1647. doi: 10.1084/jem.146.6.1640. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holton J. B., Schwab J. H. Adjuvant properties of bacterial cell wall mucopeptides. J Immunol. 1966 Jan;96(1):134–138. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jollès P., Migliore-Samour D., Maral R., Floc'h F., Werner G. H. Low molecular weight water-soluble peptidoglycans as adjuvants and immunostimulants. Z Immunitatsforsch Exp Klin Immunol. 1975 Jul;149(2-4):331–340. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamo I., Pan S. H., Friedman H. A simplified procedure for in vitro immunization of dispersed spleen cell cultures. J Immunol Methods. 1976;11(1):55–62. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(76)90018-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kotani S., Watanabe Y., Shimono T., Narita T., Kato K. Immunoadjuvant activities of cell walls, their water-soluble fractions and peptidoglycan subunits, prepared from various gram-positive bacteria, and of synthetic n-acetylmuramyl peptides. Z Immunitatsforsch Exp Klin Immunol. 1975 Jul;149(2-4):302–319. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leclerc C., Juy D., Bourgeois E., Chedid L. In vivo regulation of humoral and cellular immune responses of mice by a synthetic adjuvant, N-acetyl-muramyl-L-alanyl-D-isoglutamine, muramyl dipeptide for MDP. Cell Immunol. 1979 Jun;45(1):199–206. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(79)90377-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leclerc C., Juy D., Chedid L. Inhibitory and stimulatory effects of a synthetic glycopeptide (MDP) on the in vitro PFC response: factors affecting the response. Cell Immunol. 1979 Feb;42(2):336–343. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(79)90199-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Löwy I., Bona C., Chedid L. Target cells for the activity of a synthetic adjuvant: muramyl dipeptide. Cell Immunol. 1977 Mar 1;29(1):195–199. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(77)90288-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merser C., Sinay P., Adam A. Total synthesis and adjuvant activity of bacterial peptidoglycan derivatives. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1975 Oct 27;66(4):1316–1322. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(75)90503-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Möller G. One non-specific signal triggers b lymphocytes. Transplant Rev. 1975;23:126–137. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nauciel C., Fleck J. Adjuvant activity of bacterial peptidoglycans. Z Immunitatsforsch Exp Klin Immunol. 1975 Jul;149(2-4):349–353. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwab J. H. Suppression of the immune response by microorganisms. Bacteriol Rev. 1975 Jun;39(2):121–143. doi: 10.1128/br.39.2.121-143.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Specter S., Cimprich R., Friedman H., Chedid L. Stimulation of an enhanced in vitro immune response by a synthetic adjuvant, muramyl dipeptide. J Immunol. 1978 Feb;120(2):487–491. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugimoto M., Germain R. N., Chedid L., Benacerraf B. Enhancement of carrier-specific helper T cell function by the synthetic adjuvant, N-acetyl muramyl-L-alanyl-D-isoglutamine (MDP). J Immunol. 1978 Mar;120(3):980–982. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takada H., Kotani S., Kusumoto S., Tarumi Y., Ikenaka K. Mitogenic activity of adjuvant-active N-acetylmuramyl-L-alanyl-D-isoglutamine and its analogues. Biken J. 1977 Jun;20(2):81–85. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White R. G. The adjuvant effect of microbial products on the immune response. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1976;30:579–600. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.30.100176.003051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



