Figure 1.
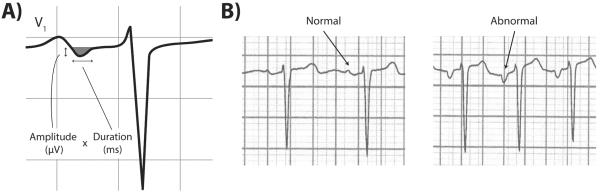
A. Illustration of components of P-wave terminal force (PTFV1), defined as the duration (ms) of the downward deflection (shaded grey area) of the P-wave in lead V1 multiplied by the absolute value of its amplitude (μV).7
B. Representative examples of ECGs with normal and abnormal P-wave terminal force in lead V1 (PTFV1). Note the deep downward deflection of the terminal portion of the P-wave in the ECG on the right, compared with the absence of a deep downward deflection in the normal ECG on the left.
