Abstract
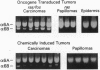
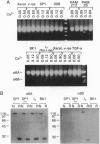
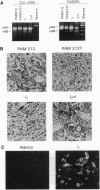
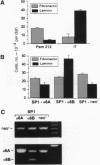
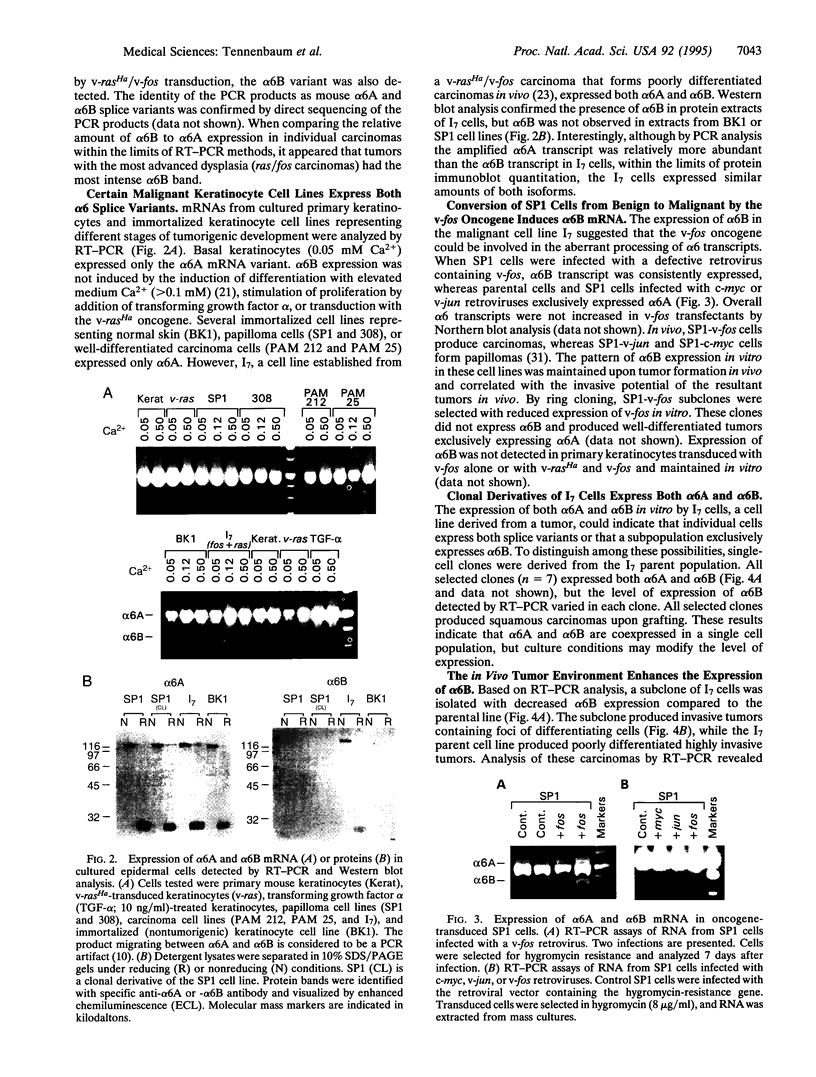
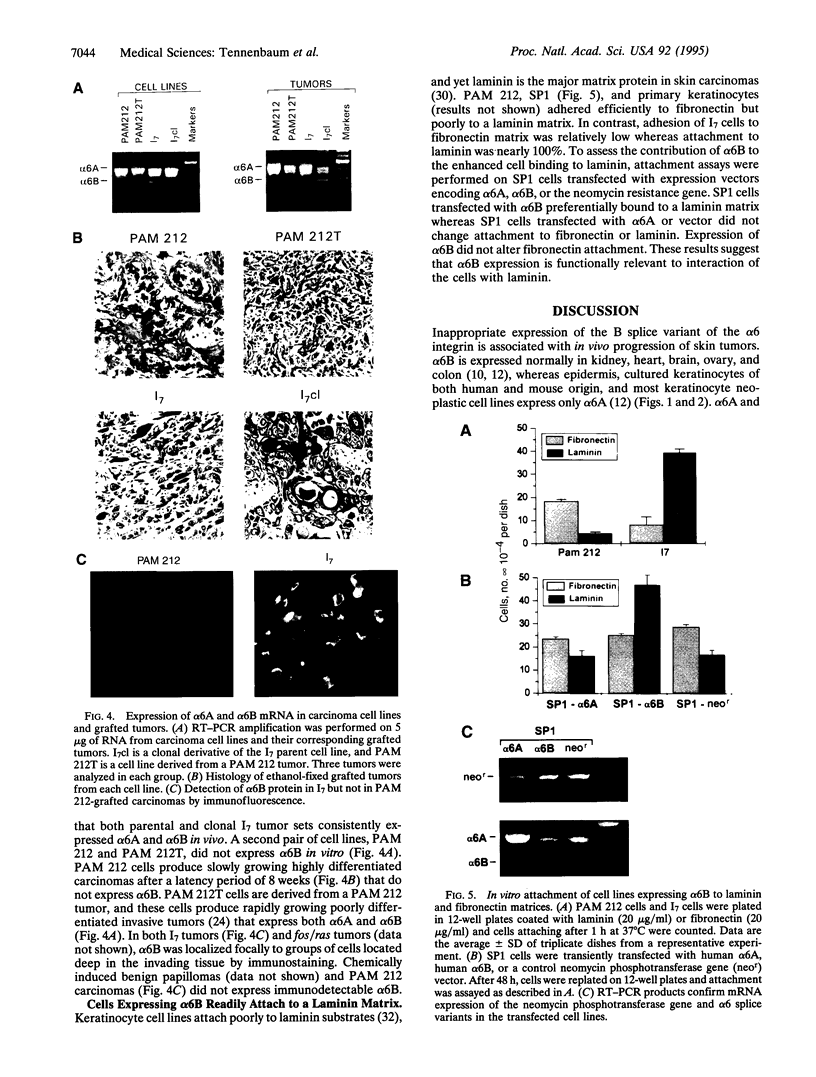
The epithelial-specific integrin alpha 6 beta 4 is suprabasally expressed in benign skin tumors (papillomas) and is diffusely expressed in carcinomas associated with an increase in the proliferating compartment. Analysis of RNA samples by reverse transcriptase-PCR and DNA sequencing revealed that chemically or oncogenically induced papillomas (n = 8) expressed a single transcript of the alpha 6 subunit, identified as the alpha 6 A splice variant. In contrast, carcinomas (n = 13) expressed both alpha 6A and an alternatively spliced form, alpha 6B. Primary keratinocytes and a number of keratinocyte cell lines that vary in biological potential from normal skin, to benign papillomas, to well-differentiated slowly growing carcinomas exclusively expressed alpha 6A. However, I7, an oncogene-induced cell line that produces highly invasive carcinomas, expressed both alpha 6A and alpha 6B transcript and protein. The expression of alpha 6B in I7 cells was associated with increased attachment to a laminin matrix compared to cell lines exclusively expressing alpha 6A. Furthermore, introduction of an alpha 6B expression vector into a papilloma cell line expressing alpha 6A increased laminin attachment. When a papilloma cell line was converted to an invasive carcinoma by introduction of the v-fos oncogene, the malignant cells expressed both alpha 6A and alpha 6B, while the parent cell line and cells transduced with v-jun or c-myc, which retained the papilloma phenotype, expressed only alpha 6A. Comparative analysis of alpha 6B expression in cell lines and their derived tumors indicate that alpha 6B transcripts are more abundant in tumors than cell lines, and alpha 6B is expressed to a greater extent in poorly differentiated tumors. These results establish a link between malignant conversion and invasion of squamous tumor cells and the regulation of transcript processing of the alpha 6 beta 4 integrin.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Carter W. G., Kaur P., Gil S. G., Gahr P. J., Wayner E. A. Distinct functions for integrins alpha 3 beta 1 in focal adhesions and alpha 6 beta 4/bullous pemphigoid antigen in a new stable anchoring contact (SAC) of keratinocytes: relation to hemidesmosomes. J Cell Biol. 1990 Dec;111(6 Pt 2):3141–3154. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.6.3141. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collo G., Starr L., Quaranta V. A new isoform of the laminin receptor integrin alpha 7 beta 1 is developmentally regulated in skeletal muscle. J Biol Chem. 1993 Sep 5;268(25):19019–19024. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper H. M., Tamura R. N., Quaranta V. The major laminin receptor of mouse embryonic stem cells is a novel isoform of the alpha 6 beta 1 integrin. J Cell Biol. 1991 Nov;115(3):843–850. doi: 10.1083/jcb.115.3.843. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dedhar S. Integrins and tumor invasion. Bioessays. 1990 Dec;12(12):583–590. doi: 10.1002/bies.950121205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delwel G. O., Hogervorst F., Kuikman I., Paulsson M., Timpl R., Sonnenberg A. Expression and function of the cytoplasmic variants of the integrin alpha 6 subunit in transfected K562 cells. Activation-dependent adhesion and interaction with isoforms of laminin. J Biol Chem. 1993 Dec 5;268(34):25865–25875. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Domann F. E., Jr, Levy J. P., Finch J. S., Bowden G. T. Constitutive AP-1 DNA binding and transactivating ability of malignant but not benign mouse epidermal cells. Mol Carcinog. 1994 Feb;9(2):61–66. doi: 10.1002/mc.2940090202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dong Z., Birrer M. J., Watts R. G., Matrisian L. M., Colburn N. H. Blocking of tumor promoter-induced AP-1 activity inhibits induced transformation in JB6 mouse epidermal cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Jan 18;91(2):609–613. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.2.609. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glick A. B., Lee M. M., Darwiche N., Kulkarni A. B., Karlsson S., Yuspa S. H. Targeted deletion of the TGF-beta 1 gene causes rapid progression to squamous cell carcinoma. Genes Dev. 1994 Oct 15;8(20):2429–2440. doi: 10.1101/gad.8.20.2429. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenhalgh D. A., Welty D. J., Player A., Yuspa S. H. Two oncogenes, v-fos and v-ras, cooperate to convert normal keratinocytes to squamous cell carcinoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jan;87(2):643–647. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.2.643. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenhalgh D. A., Yuspa S. H. Malignant conversion of murine squamous papilloma cell lines by transfection with the fos oncogene. Mol Carcinog. 1988;1(2):134–143. doi: 10.1002/mc.2940010209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Günthert U., Hofmann M., Rudy W., Reber S., Zöller M., Haussmann I., Matzku S., Wenzel A., Ponta H., Herrlich P. A new variant of glycoprotein CD44 confers metastatic potential to rat carcinoma cells. Cell. 1991 Apr 5;65(1):13–24. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90403-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hemler M. E. VLA proteins in the integrin family: structures, functions, and their role on leukocytes. Annu Rev Immunol. 1990;8:365–400. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.08.040190.002053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hennings H., Michael D., Cheng C., Steinert P., Holbrook K., Yuspa S. H. Calcium regulation of growth and differentiation of mouse epidermal cells in culture. Cell. 1980 Jan;19(1):245–254. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90406-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hierck B. P., Thorsteinsdóttir S., Niessen C. M., Freund E., Iperen L. V., Feyen A., Hogervorst F., Poelmann R. E., Mummery C. L., Sonnenberg A. Variants of the alpha 6 beta 1 laminin receptor in early murine development: distribution, molecular cloning and chromosomal localization of the mouse integrin alpha 6 subunit. Cell Adhes Commun. 1993 May;1(1):33–53. doi: 10.3109/15419069309095680. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hogervorst F., Admiraal L. G., Niessen C., Kuikman I., Janssen H., Daams H., Sonnenberg A. Biochemical characterization and tissue distribution of the A and B variants of the integrin alpha 6 subunit. J Cell Biol. 1993 Apr;121(1):179–191. doi: 10.1083/jcb.121.1.179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hogervorst F., Kuikman I., Noteboom E., Sonnenberg A. The role of phosphorylation in activation of the alpha 6A beta 1 laminin receptor. J Biol Chem. 1993 Sep 5;268(25):18427–18430. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hynes R. O. Integrins: a family of cell surface receptors. Cell. 1987 Feb 27;48(4):549–554. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90233-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hynes R. O. Integrins: versatility, modulation, and signaling in cell adhesion. Cell. 1992 Apr 3;69(1):11–25. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90115-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones J. C., Kurpakus M. A., Cooper H. M., Quaranta V. A function for the integrin alpha 6 beta 4 in the hemidesmosome. Cell Regul. 1991 Jun;2(6):427–438. doi: 10.1091/mbc.2.6.427. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin A. Y., Devaux B., Green A., Sagerström C., Elliott J. F., Davis M. M. Expression of T cell antigen receptor heterodimers in a lipid-linked form. Science. 1990 Aug 10;249(4969):677–679. doi: 10.1126/science.1696397. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Toole T. E., Katagiri Y., Faull R. J., Peter K., Tamura R., Quaranta V., Loftus J. C., Shattil S. J., Ginsberg M. H. Integrin cytoplasmic domains mediate inside-out signal transduction. J Cell Biol. 1994 Mar;124(6):1047–1059. doi: 10.1083/jcb.124.6.1047. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rousselle P., Aumailley M. Kalinin is more efficient than laminin in promoting adhesion of primary keratinocytes and some other epithelial cells and has a different requirement for integrin receptors. J Cell Biol. 1994 Apr;125(1):205–214. doi: 10.1083/jcb.125.1.205. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salmi M., Grön-Virta K., Sointu P., Grenman R., Kalimo H., Jalkanen S. Regulated expression of exon v6 containing isoforms of CD44 in man: downregulation during malignant transformation of tumors of squamocellular origin. J Cell Biol. 1993 Jul;122(2):431–442. doi: 10.1083/jcb.122.2.431. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw L. M., Lotz M. M., Mercurio A. M. Inside-out integrin signaling in macrophages. Analysis of the role of the alpha 6A beta 1 and alpha 6B beta 1 integrin variants in laminin adhesion by cDNA expression in an alpha 6 integrin-deficient macrophage cell line. J Biol Chem. 1993 May 25;268(15):11401–11408. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sonnenberg A., Calafat J., Janssen H., Daams H., van der Raaij-Helmer L. M., Falcioni R., Kennel S. J., Aplin J. D., Baker J., Loizidou M. Integrin alpha 6/beta 4 complex is located in hemidesmosomes, suggesting a major role in epidermal cell-basement membrane adhesion. J Cell Biol. 1991 May;113(4):907–917. doi: 10.1083/jcb.113.4.907. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strickland J. E., Greenhalgh D. A., Koceva-Chyla A., Hennings H., Restrepo C., Balaschak M., Yuspa S. H. Development of murine epidermal cell lines which contain an activated rasHa oncogene and form papillomas in skin grafts on athymic nude mouse hosts. Cancer Res. 1988 Jan 1;48(1):165–169. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strickland J. E., Ueda M., Hennings H., Yuspa S. H. A model for initiated mouse skin: suppression of papilloma but not carcinoma formation by normal epidermal cells in grafts on athymic nude mice. Cancer Res. 1992 Mar 15;52(6):1439–1444. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamura R. N., Cooper H. M., Collo G., Quaranta V. Cell type-specific integrin variants with alternative alpha chain cytoplasmic domains. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Nov 15;88(22):10183–10187. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.22.10183. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamura R. N., Rozzo C., Starr L., Chambers J., Reichardt L. F., Cooper H. M., Quaranta V. Epithelial integrin alpha 6 beta 4: complete primary structure of alpha 6 and variant forms of beta 4. J Cell Biol. 1990 Oct;111(4):1593–1604. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.4.1593. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tennenbaum T., Weiner A. K., Belanger A. J., Glick A. B., Hennings H., Yuspa S. H. The suprabasal expression of alpha 6 beta 4 integrin is associated with a high risk for malignant progression in mouse skin carcinogenesis. Cancer Res. 1993 Oct 15;53(20):4803–4810. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tennenbaum T., Yuspa S. H., Grover A., Castronovo V., Sobel M. E., Yamada Y., De Luca L. M. Extracellular matrix receptors and mouse skin carcinogenesis: altered expression linked to appearance of early markers of tumor progression. Cancer Res. 1992 May 15;52(10):2966–2976. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ylänne J., Chen Y., O'Toole T. E., Loftus J. C., Takada Y., Ginsberg M. H. Distinct functions of integrin alpha and beta subunit cytoplasmic domains in cell spreading and formation of focal adhesions. J Cell Biol. 1993 Jul;122(1):223–233. doi: 10.1083/jcb.122.1.223. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yuspa S. H., Hawley-Nelson P., Koehler B., Stanley J. R. A survey of transformation markers in differentiating epidermal cell lines in culture. Cancer Res. 1980 Dec;40(12):4694–4703. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yuspa S. H., Koehler B., Kulesz-Martin M., Hennings H. Clonal growth of mouse epidermal cells in medium with reduced calcium concentration. J Invest Dermatol. 1981 Feb;76(2):144–146. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12525490. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ziober B. L., Vu M. P., Waleh N., Crawford J., Lin C. S., Kramer R. H. Alternative extracellular and cytoplasmic domains of the integrin alpha 7 subunit are differentially expressed during development. J Biol Chem. 1993 Dec 15;268(35):26773–26783. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Kuppevelt T. H., Languino L. R., Gailit J. O., Suzuki S., Ruoslahti E. An alternative cytoplasmic domain of the integrin beta 3 subunit. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(14):5415–5418. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.14.5415. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]