Abstract
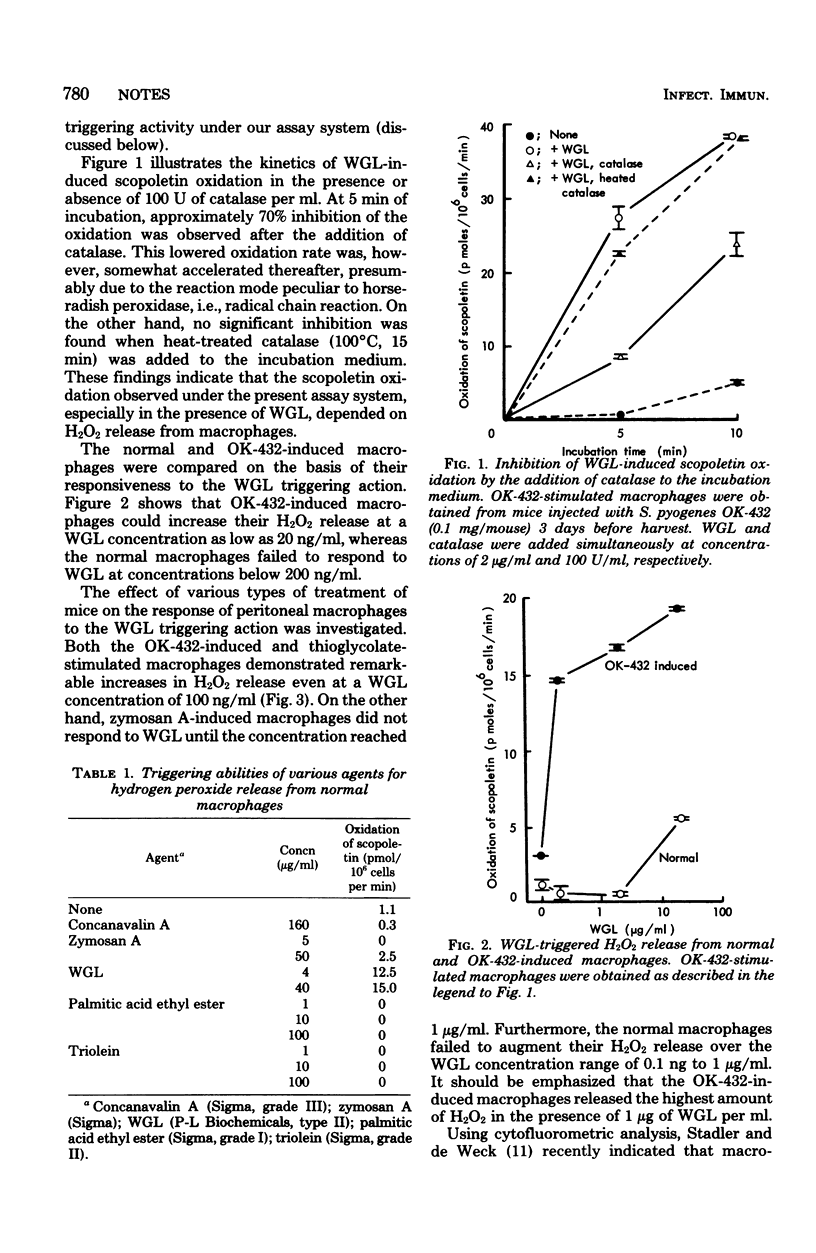
Wheat germ lectin was found to be a potent triggering agent for hydrogen peroxide release from mouse peritoneal macrophages. Macrophages stimulated by intraperitoneal injection of OK-432, a lyophilized attenuated streptococcal preparation, were highly responsive to wheat germ lectin.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bennett W. E., Cohn Z. A. The isolation and selected properties of blood monocytes. J Exp Med. 1966 Jan 1;123(1):145–160. doi: 10.1084/jem.123.1.145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COHN Z. A., BENSON B. THE DIFFERENTIATION OF MONONUCLEAR PHAGOCYTES. MORPHOLOGY, CYTOCHEMISTRY, AND BIOCHEMISTRY. J Exp Med. 1965 Jan 1;121:153–170. doi: 10.1084/jem.121.1.153. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fowles R. E., Fajardo I. M., Leibowitch J. L., David J. R. The enhancement of macrophage bacteriostasis by products of activated lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 1973 Oct 1;138(4):952–964. doi: 10.1084/jem.138.4.952. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keller R. Mechanisms by which activated normal macrophages destroy syngeneic rat tumour cells in vitro. Cytokinetics, non-involvement of T lymphocytes, and effect of metabolic inhibitors. Immunology. 1974 Aug;27(2):285–298. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meltzer M. S., Oppenheim J. J. Bidirectional amplification of macrophage-lymphocyte interactions: enhanced lymphocyte activation factor production by activated adherent mouse peritoneal cells. J Immunol. 1977 Jan;118(1):77–82. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nathan C. F., Remold H. G., David J. R. Characterization of a lymphocyte factor which alters macrophage functions. J Exp Med. 1973 Feb 1;137(2):275–290. doi: 10.1084/jem.137.2.275. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nathan C. F., Root R. K. Hydrogen peroxide release from mouse peritoneal macrophages: dependence on sequential activation and triggering. J Exp Med. 1977 Dec 1;146(6):1648–1662. doi: 10.1084/jem.146.6.1648. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okamoto H., Minami M., Shoin S., Koshimura S., Shimizu R. Experimental anticancer studies. XXXI. On the streptococcal preparation having potent anticancer activity. Jpn J Exp Med. 1966 Apr;36(2):175–186. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Root R. K., Metcalf J., Oshino N., Chance B. H2O2 release from human granulocytes during phagocytosis. I. Documentation, quantitation, and some regulating factors. J Clin Invest. 1975 May;55(5):945–955. doi: 10.1172/JCI108024. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon H. B., Sheagren J. N. Cellular immunity in vitro. I. Immunologically mediated enhancement of macrophage bactericidal capacity. J Exp Med. 1971 Jun 1;133(6):1377–1389. doi: 10.1084/jem.133.6.1377. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stadler B. M., de Weck A. L. Cytofluorometric analysis of macrophages activated in vivo or in vitro. Eur J Immunol. 1978 Apr;8(4):243–246. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830080405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



