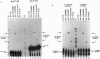Abstract
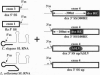
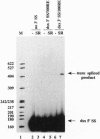
Splice-site selection and alternative splicing of nuclear pre-mRNAs can be controlled by splicing enhancers that act by promoting the activity of upstream splice sites. Here we show that RNA molecules containing a 3' splice site and enhancer sequence are efficiently spliced in trans to RNA molecules containing normally cis-spliced 5' splice sites or to normally trans-spliced spliced leader RNAs from lower eukaryotes. In addition, we show that this reaction is stimulated by (Ser + Arg)-rich splicing factors that are known to promote protein-protein interactions in the cis-splicing reaction. Thus, splicing enhancers facilitate the assembly of protein complexes on RNAs containing a 3' splice site, and this complex is sufficiently stable to functionally interact with 5' splice sites located on separate RNAs. This trans-splicing is mediated by interactions between (Ser + Arg)-rich splicing factors bound to the enhancer and general splicing factors bound to the 5' and 3' splice sites. These same interactions are likely to play a crucial role in alternative splicing and splice-site selection in cis.
Full text
PDF
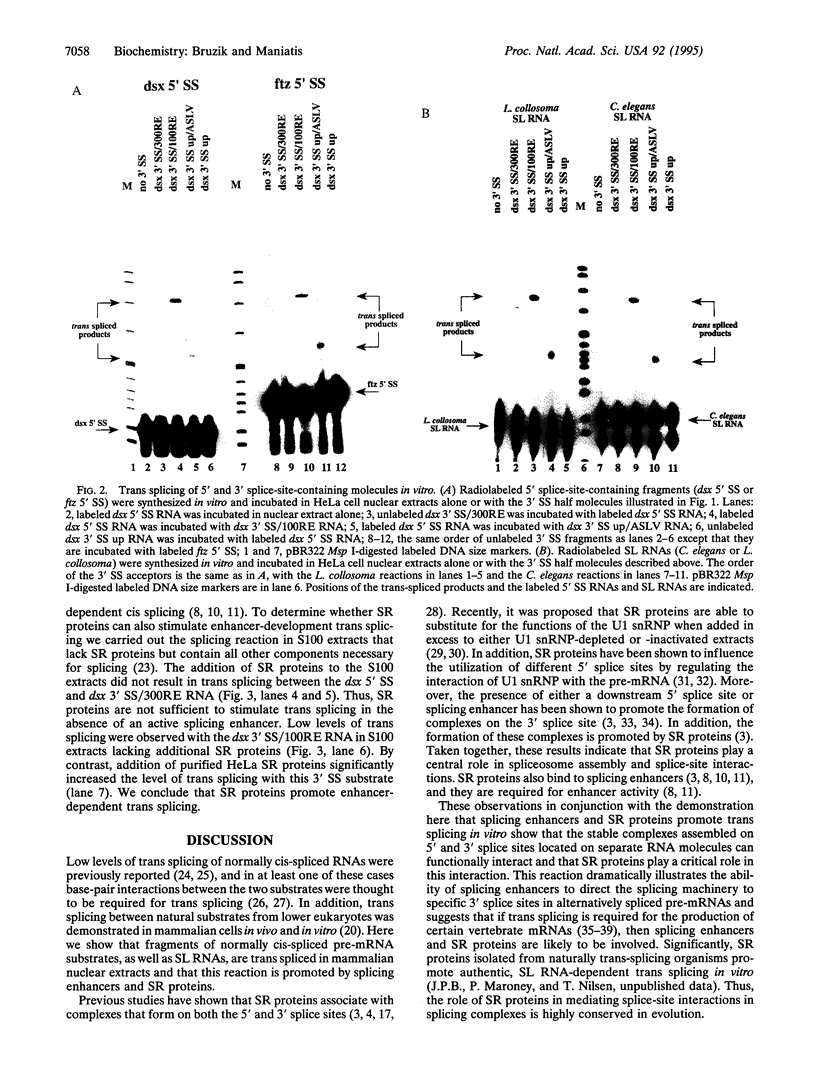
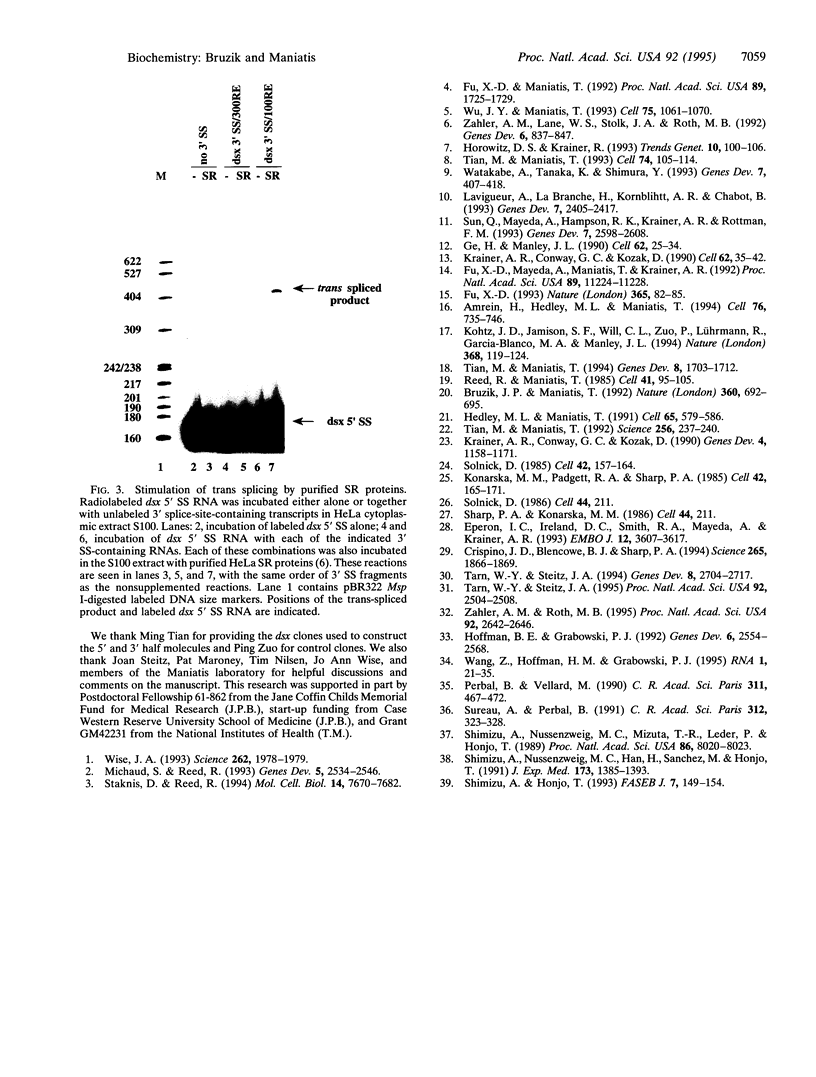
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amrein H., Hedley M. L., Maniatis T. The role of specific protein-RNA and protein-protein interactions in positive and negative control of pre-mRNA splicing by Transformer 2. Cell. 1994 Feb 25;76(4):735–746. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90512-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruzik J. P., Maniatis T. Spliced leader RNAs from lower eukaryotes are trans-spliced in mammalian cells. Nature. 1992 Dec 17;360(6405):692–695. doi: 10.1038/360692a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crispino J. D., Blencowe B. J., Sharp P. A. Complementation by SR proteins of pre-mRNA splicing reactions depleted of U1 snRNP. Science. 1994 Sep 23;265(5180):1866–1869. doi: 10.1126/science.8091213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eperon I. C., Ireland D. C., Smith R. A., Mayeda A., Krainer A. R. Pathways for selection of 5' splice sites by U1 snRNPs and SF2/ASF. EMBO J. 1993 Sep;12(9):3607–3617. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb06034.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fu X. D., Maniatis T. The 35-kDa mammalian splicing factor SC35 mediates specific interactions between U1 and U2 small nuclear ribonucleoprotein particles at the 3' splice site. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Mar 1;89(5):1725–1729. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.5.1725. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fu X. D., Mayeda A., Maniatis T., Krainer A. R. General splicing factors SF2 and SC35 have equivalent activities in vitro, and both affect alternative 5' and 3' splice site selection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Dec 1;89(23):11224–11228. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.23.11224. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fu X. D. Specific commitment of different pre-mRNAs to splicing by single SR proteins. Nature. 1993 Sep 2;365(6441):82–85. doi: 10.1038/365082a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ge H., Manley J. L. A protein factor, ASF, controls cell-specific alternative splicing of SV40 early pre-mRNA in vitro. Cell. 1990 Jul 13;62(1):25–34. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90236-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedley M. L., Maniatis T. Sex-specific splicing and polyadenylation of dsx pre-mRNA requires a sequence that binds specifically to tra-2 protein in vitro. Cell. 1991 May 17;65(4):579–586. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90090-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman B. E., Grabowski P. J. U1 snRNP targets an essential splicing factor, U2AF65, to the 3' splice site by a network of interactions spanning the exon. Genes Dev. 1992 Dec;6(12B):2554–2568. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.12b.2554. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horowitz D. S., Krainer A. R. Mechanisms for selecting 5' splice sites in mammalian pre-mRNA splicing. Trends Genet. 1994 Mar;10(3):100–106. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(94)90233-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohtz J. D., Jamison S. F., Will C. L., Zuo P., Lührmann R., Garcia-Blanco M. A., Manley J. L. Protein-protein interactions and 5'-splice-site recognition in mammalian mRNA precursors. Nature. 1994 Mar 10;368(6467):119–124. doi: 10.1038/368119a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konarska M. M., Padgett R. A., Sharp P. A. Trans splicing of mRNA precursors in vitro. Cell. 1985 Aug;42(1):165–171. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80112-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krainer A. R., Conway G. C., Kozak D. Purification and characterization of pre-mRNA splicing factor SF2 from HeLa cells. Genes Dev. 1990 Jul;4(7):1158–1171. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.7.1158. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krainer A. R., Conway G. C., Kozak D. The essential pre-mRNA splicing factor SF2 influences 5' splice site selection by activating proximal sites. Cell. 1990 Jul 13;62(1):35–42. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90237-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lavigueur A., La Branche H., Kornblihtt A. R., Chabot B. A splicing enhancer in the human fibronectin alternate ED1 exon interacts with SR proteins and stimulates U2 snRNP binding. Genes Dev. 1993 Dec;7(12A):2405–2417. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.12a.2405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michaud S., Reed R. An ATP-independent complex commits pre-mRNA to the mammalian spliceosome assembly pathway. Genes Dev. 1991 Dec;5(12B):2534–2546. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.12b.2534. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perbal B., Vellard M. Intermolecular recombination of the c-myb proto-oncogene coding sequences in chicken: clues for a mechanism. C R Acad Sci III. 1990;311(13):467–472. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed R., Maniatis T. Intron sequences involved in lariat formation during pre-mRNA splicing. Cell. 1985 May;41(1):95–105. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90064-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimizu A., Honjo T. Synthesis and regulation of trans-mRNA encoding the immunoglobulin epsilon heavy chain. FASEB J. 1993 Jan;7(1):149–154. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.7.1.7916698. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimizu A., Nussenzweig M. C., Han H., Sanchez M., Honjo T. Trans-splicing as a possible molecular mechanism for the multiple isotype expression of the immunoglobulin gene. J Exp Med. 1991 Jun 1;173(6):1385–1393. doi: 10.1084/jem.173.6.1385. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimizu A., Nussenzweig M. C., Mizuta T. R., Leder P., Honjo T. Immunoglobulin double-isotype expression by trans-mRNA in a human immunoglobulin transgenic mouse. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Oct;86(20):8020–8023. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.20.8020. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solnick D. Does trans splicing in vitro require base pairing between RNAs? Cell. 1986 Jan 31;44(2):211–211. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90752-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solnick D. Does trans splicing in vitro require base pairing between RNAs? Cell. 1986 Jan 31;44(2):211–211. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90752-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solnick D. Trans splicing of mRNA precursors. Cell. 1985 Aug;42(1):157–164. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80111-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staknis D., Reed R. SR proteins promote the first specific recognition of Pre-mRNA and are present together with the U1 small nuclear ribonucleoprotein particle in a general splicing enhancer complex. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Nov;14(11):7670–7682. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.11.7670. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun Q., Mayeda A., Hampson R. K., Krainer A. R., Rottman F. M. General splicing factor SF2/ASF promotes alternative splicing by binding to an exonic splicing enhancer. Genes Dev. 1993 Dec;7(12B):2598–2608. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.12b.2598. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sureau A., Perbal B. Intermolecular recombination of human c-myb proto-oncogene coding sequences. C R Acad Sci III. 1991;312(7):323–328. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tarn W. Y., Steitz J. A. Modulation of 5' splice site choice in pre-messenger RNA by two distinct steps. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Mar 28;92(7):2504–2508. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.7.2504. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tarn W. Y., Steitz J. A. SR proteins can compensate for the loss of U1 snRNP functions in vitro. Genes Dev. 1994 Nov 15;8(22):2704–2717. doi: 10.1101/gad.8.22.2704. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tian M., Maniatis T. A splicing enhancer complex controls alternative splicing of doublesex pre-mRNA. Cell. 1993 Jul 16;74(1):105–114. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90298-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tian M., Maniatis T. A splicing enhancer exhibits both constitutive and regulated activities. Genes Dev. 1994 Jul 15;8(14):1703–1712. doi: 10.1101/gad.8.14.1703. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tian M., Maniatis T. Positive control of pre-mRNA splicing in vitro. Science. 1992 Apr 10;256(5054):237–240. doi: 10.1126/science.1566072. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang Z., Hoffmann H. M., Grabowski P. J. Intrinsic U2AF binding is modulated by exon enhancer signals in parallel with changes in splicing activity. RNA. 1995 Mar;1(1):21–35. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watakabe A., Tanaka K., Shimura Y. The role of exon sequences in splice site selection. Genes Dev. 1993 Mar;7(3):407–418. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.3.407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wise J. A. Guides to the heart of the spliceosome. Science. 1993 Dec 24;262(5142):1978–1979. doi: 10.1126/science.8266091. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu J. Y., Maniatis T. Specific interactions between proteins implicated in splice site selection and regulated alternative splicing. Cell. 1993 Dec 17;75(6):1061–1070. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90316-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zahler A. M., Lane W. S., Stolk J. A., Roth M. B. SR proteins: a conserved family of pre-mRNA splicing factors. Genes Dev. 1992 May;6(5):837–847. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.5.837. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zahler A. M., Roth M. B. Distinct functions of SR proteins in recruitment of U1 small nuclear ribonucleoprotein to alternative 5' splice sites. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Mar 28;92(7):2642–2646. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.7.2642. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]